Increased blood cholesterol is a problem that can lead to the development of atherosclerosis. That is why experts recommend minimizing products containing this lipoprotein compound. However, you shouldn’t completely abandon them - after all, they include both meat and eggs - irreplaceable sources of animal protein. But do not forget that you need to monitor your LDL levels. It should not be either too low or too high. We will talk about what foods contain cholesterol and how to avoid health problems associated with exceeding the norm in this article.
Our additional services: Bioimpedance | Marutaka Massage | Pressotherapy | Ion-Detox
General rules
Cholesterol is a fat-like substance belonging to the group of sterols of animal origin.
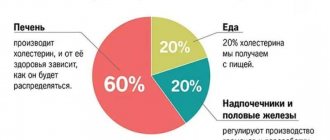
Therefore, it cannot be found in plant products. In the human body it is produced by almost all organs, but most of it is produced by the liver. Many body systems cannot function without the participation of cholesterol. It is an indispensable building material for cell membranes (provides strength, protects intracellular structures from the effects of free radicals), and is necessary for the formation of adrenal hormones, female and male sex hormones. The important thing is that cholesterol forms complexes with acids, proteins, and salts. Being in the blood, it creates lipoproteins with protein. Low-density lipoproteins transport cholesterol from the liver to all organs. LDL becomes harmful when it carries more cholesterol into cells than is required for their functioning. If the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is higher than normal, then this is a sure risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
High-density lipoproteins transport cholesterol from tissues back to the liver, where it is broken down and excreted in bile. Thus, HDL or HDL prevents the development of heart and vascular diseases.
Why do cholesterol levels increase?
- Poor nutrition. Its level is affected by saturated fats contained in fatty red meat, sausage, lard, cheeses, and confectionery products.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Excess weight is a risk factor for elevated LDL cholesterol.
- Smoking.
- Alcohol abuse.
Its level is considered normal up to 5 mmol/l. A cause for concern and for increased attention to your diet and health is already a cholesterol level from 5 to 6.4 mmol/l. Since cholesterol levels depend on diet, a cholesterol diet will help reduce its levels by 10-15%. It is called differently: anticholesterol, hypocholesterol or cholesterol-free, but the meaning is the same - limiting animal fats and foods containing cholesterol.
Depending on the degree of abnormalities in blood tests, diet may limit foods containing cholesterol or eliminate them completely. If you follow this diet for a short time, for example, for a week, then this will not affect your cholesterol levels, but it will help you lose weight (one or two kilograms per week). For therapeutic purposes, such nutrition must be adhered to for a long time or constantly. Proper nutrition helps eliminate lipid metabolism disorders and reduce weight. If after 3-5 months the cholesterol level does not normalize, they switch to drug treatment, but always while following a diet.
A low cholesterol diet involves:
- Reducing the total calorie content of food, which means weight loss due to low-calorie and low-carbohydrate nutrition, but balanced in essential substances. According to the latest data, it is not so much a “low-fat” diet that helps reduce “bad” cholesterol (LDL), but rather a low-carbohydrate diet. Do not eat sugar, any food containing refined carbohydrates, flour products, potatoes and baked goods.
- Reducing the consumption of animal fats and foods containing cholesterol.
- Increasing the consumption of vegetable fats and fiber. The danger is not so much the cholesterol found in foods, but the lack of fiber in food, which can remove excess cholesterol from the body.
- Limit salt to 8 g (dishes are prepared without adding salt, and ready-made food is added with salt).
Excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates, animal fats and alcohol increases the caloric content of the diet, which affects the state of lipid metabolism. An increase in calories is accompanied by an increase in cholesterol synthesis in the body and an increase in its level in the blood. To reduce the calorie content of the diet, fat and extractive substances are removed from meat products by boiling, after which the meat can be baked or stewed. When boiling meat and poultry, the fat goes into the broth, and they lose up to 40% of fat.
The degree of restriction of dietary cholesterol is 250-500 mg/day, which depends on the degree of hypercholesterolemia . For moderate cases, no more than 300 mg per day, and for severe cases, 200 mg. All animal products contain cholesterol, but a person cannot completely avoid them. The diet allows periodic consumption of foods, but with a low cholesterol content, and “cholesterol” foods are excluded. A table showing the cholesterol content in foods will help you navigate this.
| Food 100 g | Cholesterol in them (in descending order in mg) |
| Brain | 800-2300 |
| Kidneys | 300-800 |
| Quail eggs | 600 |
| Beef liver | 270-400 |
| Chicken liver | 492 |
| Pork loin | 380 |
| Pork knuckle | 360 |
| Mackerel | 360 |
| Stellate sturgeon | 300 |
| Butter (ghee) | 280 |
| Carp | 270 |
| Cuttlefish | 275 |
| Butter | 240 |
| Natotenia | 210 |
| Chicken heart | 170 |
| Oysters | 170 |
| Liverwurst | 169 |
| Acne | 160-190 |
| Beef tongue | 150 |
| Pate | 150 |
| Shrimps | 144 |
| Sardines (canned in oil) | 120-140 |
| Pork liver | 130 |
| Cheese "Gouda" | 114 |
| Smoked sausage | 112 |
| Pork | 110 |
| Roe deer meat | 110 |
| Pollock | 110 |
| Beef fat | 110 |
| Cream cheese 60% | 105 |
| Sausages, sausages | 100 |
| Pork fat | 100 |
| Goose fat | 100 |
| Chester cheese - 50% | 100 |
| Veal | 99 |
| Mutton | 98 |
| Herring | 97 |
| Beef I | 90 |
| Rabbit meat | 90 |
| Duck with skin | 90 |
| Chicken dark meat (no skin) | 89 |
| Medium fat fish | 88 |
| Crabs | 87 |
| Vienna sausages, salami, mortadella, cervelat | 85 |
| Mackerel | 85 |
| Cream 20% | 80 |
| White meat chicken (no skin) | 79 |
| Lamb | 70 |
| Processed cheese | 66 |
| Beef (lean) | 65 |
| Mussels | 64 |
| Cheese "Tilsit" - 45% | 60 |
| Broilers and chicken | 40-60 |
| Turkey | 40-60 |
| Duck | 60 |
| Cheese "Kostromskoy" | 57 |
| Trout | 56 |
| Tuna | 55 |
| Shellfish | 53 |
| Pig tongue | 50 |
| Sole tongue, pike | 50 |
| Low-fat boiled sausage | 40 |
| Horse mackerel | 40 |
| Sour cream 10% | 33 |
| Cod | 30 |
| Goat milk | 30 |
| Milk 3% | 15 |
| Kefir and milk 1% | 3,2 |
| Serum | 2 |
| Low-fat cottage cheese | 1 |
| Low fat yogurt | 1 |
| Homemade cheese - 0.6% | 1 |
| Vegetable oil | 0 |
| Margarines | 0 |
This table will allow you to correctly compose your diet. Of course, you need to give up “cholesterol” foods: brains, egg yolk, offal, fatty meats, ghee. A little butter is allowed.
Fats should account for 30% of the total calorie intake. No more than 10% should be saturated fatty acids (fatty meat, sausages, fish, dairy products). It is necessary to take into account that beef, pork, and chicken meat contain a large amount of, at first glance, invisible, intracellular fat.
As a source of protein, you should give preference to fish. Monounsaturated fatty acids should make up 15% of all fats, and polyunsaturated fatty acids should make up 6% (foods containing them will be discussed below). Vegetables and fruits should be consumed more than 400 g per day. Salt is allowed 5 g per day. Simple carbohydrates should be excluded.
Cholesterol-lowering foods
- A representative of MUFA is oleic acid . Olive oil is rich in it , which forms the basis of the “Mediterranean diet”. According to survey data, the population of these countries has a very low mortality rate from heart disease.
- Omega-6 PUFAs also help reduce hypercholesterolemia. Their sources are sunflower, corn, cottonseed, and vegetable oils.
- Omega-3 PUFAs are represented by fatty sea fish (sardine, mackerel, herring, salmon, halibut). A daily intake of 0.5-1.0 g of omega-3 from fish or fish oil (purified) reduces the risk of disease. Omega-3 PUFAs also contain vegetable oils (linseed, rapeseed, soybean, mustard, nut, sesame). It is necessary that vegetable oils be present in the diet and constitute the fat component, since in addition to beneficial unsaturated fatty acids, they also contain other anti-atherogenic components - phospholipids, phytosterols, squalene and phytostanols.
- Phytosterols and phytostanols are found in wheat germ, coconut, corn, rapeseed, soybean, fir, cedar oils, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, flax and sesame seeds, nuts (pistachios, pine, almonds), vegetables and fruits (especially avocado), rice bran . These substances are practically not absorbed in the intestine and have a local effect. According to studies, products with phytosterols can reduce cholesterol levels by 10% if consumed in a dose of 2-3 g per day, and in combination with a low-cholesterol diet by 24%. The longer you consume foods enriched with them, the more pronounced the lipid-lowering effect. In one article l. olive oil contains 22 mg of phytosterols.
- Plant products as a source of dietary fiber. A wide inclusion of vegetables, fruits and grains allows you to meet the need for dietary fiber (30-50 g per day is required). Thus, adding only 15 g of pectin to the diet reduces cholesterol levels by 15-20%. Additionally, when indicated in the diet, the amount of dietary fiber increases due to wheat bran, methylcellulose or pure pectin. It should be remembered that long-term consumption of more than 60 g leads to impaired absorption of essential vitamins and microelements.
- Cereals containing fiber and complex carbohydrates also help reduce cholesterol and triglycerides . Beans and soy products reduce cholesterol due to their high content of soluble fiber, and in terms of protein content they can replace any meat. You can also eat soy products - tofu, tempeh, miso.
- All red and purple vegetables and fruits contain polyphenols that stimulate the production of HDL: blueberries, viburnum, dogwood, raspberries, blackberries, strawberries, chokeberries, cranberries, lingonberries, red grapes, eggplants, red cabbage, beets, pomegranate. The champion in this regard is cranberry juice. Juices can be combined.
- Among vegetables, white cabbage is the leader. Its use is beneficial in any form, and it should be in the diet daily in an amount of at least 100 g.
- Garlic is a powerful natural statin , slowing the production of LDL. For a noticeable result, it must be consumed for up to 3 months, 2-3 cloves per day (caution for gastritis , peptic ulcers , pancreatitis and colitis ).
- Iodine has a hypocholesterolemic effect and prevents the deposition of lipids in the vascular wall. Its source is seafood: shrimp, sea cucumbers, fish, mussels, seaweed, the consumption of which helps meet the need for iodine.
- The role of chromium is also associated with hypocholesterolemic and hypoglycemic effects. The main sources are rye flour and coarse wheat flour, baker's yeast, meat, legumes, corn and pearl barley.
- Selenium is an antioxidant microelement and is found in wheat and oat bran, sunflower seeds, pink salmon, whole grain bread, eggs, chickpeas, beans, and lentils.
- Fermented milk products and yoghurts with sourdough containing Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus.
All of these foods will help lower your cholesterol . Of course, medications are more effective in this regard, but if you follow a diet, their effectiveness increases.
Folk remedies will also help with treatment to some extent.
Drinking ginger tea is beneficial. Ginger is grated and poured with boiling water. Usually take 1 tsp. ginger per glass, add a slice of lemon and leave for at least 30 minutes.
Ginger tea
Infusion of milk thistle herbs and seeds: 1 teaspoon of raw material per 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes. In the morning and evening, 30 minutes before meals, drink the infusion warm. You can eat milk thistle “meal” - 1 teaspoon of milk thistle meal, chewed thoroughly and washed down with water, taken before meals 2-3 times a day.
Garlic oil: 2 cups olive oil and 10 cloves of garlic, pressed through a press. This oil can be used as a seasoning and dressing for salads, cereals, and vegetables.
Dill seed infusion: 1 tbsp. seeds, pour 250 ml of boiling water, after infusing for 15 minutes, filter and take 0.25 cups before meals several times a day.
General recommendations in addition to nutrition are: increasing physical activity, getting enough sleep, giving up bad habits.
Cholesterol: what do we know about it?
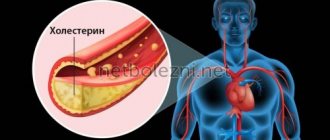
This is the second name for lipoprotein compounds - a fatty alcohol that dissolves not in water, but in lipids, which are its carriers through the bloodstream of the body. It plays not only a negative role - it causes the development of atherosclerosis - but also makes an invaluable contribution to strengthening cell membranes, is contained in the brain and acts as a structural element of the adrenal glands and gonads.
Cholesterol is also found in mother's milk, which allows the child to grow strong and healthy. So do not underestimate its effect on the functioning of our body.
Before finding out what you can’t eat if you have high cholesterol, and what you can, let’s look at the main functions of this compound:
Part of cell membranes and nerve endings.
- Strengthens the immune system and protects against cancer.
- Helps the adrenal glands and sex glands produce hormones: cortisol, estrogens, progesterone, etc.
- Stimulates brain function.
- Allows the production of vitamin D.
In total, our body contains about 350 g of cholesterol. Most of it is found in tissues, and only 10% circulates in the blood.
We produce cholesterol ourselves - such compounds are called endogenous. The liver, small intestine and other organs are responsible for their synthesis. Much less building material for cell membranes comes from food - this is exogenous fatty alcohol.
Not all cholesterol is bad. Experts divide it into two groups:
- The first includes lipoproteins that are characterized by high density. They cleanse our body of excess potentially dangerous substances, cleanse blood vessels, preventing the development of atherosclerosis.
- The second contains low-density lipoproteins, as well as triglycerides - compounds that harm our health by increasing cholesterol levels in the blood. This leads to the growth of atherosclerotic plaques, impaired blood circulation, fat and protein metabolism, blockage of blood vessels and the development of coronary heart disease.
At the same time, we should not forget that cholesterol in its free form is not dangerous. The nature of the effect on the body is determined at the stage of addition of fatty alcohol to a particular transport protein.
Authorized Products
- The basis of the weekly diet consists of fish and seafood dishes. Include tuna, mackerel, flounder, cod, salmon, salmon in your diet and eat 100 g of fish 2-3 times a week. At the same time, you need to give up fish and squid caviar or limit their consumption (for example, 2 times a year).
- Seaweed will be a useful addition to all salads.
- Include at least 400g of fresh fruits and vegetables. Eat fresh all vegetables that can be eaten raw. Prepare a side dish for meat and fish from all types of cabbage, beets, carrots, zucchini, pumpkin, eggplant, green peas, while limiting the consumption of potatoes. Legumes, which contain large amounts of vegetable protein, should be an obligatory component of the diet. If tolerated, include them in your diet daily.
- Fruits and berries are consumed raw or in the form of decoctions and compotes. There is a lot of pectin in citrus fruits, apples, dried dogwood berries, viburnum, grapes, and cranberries. They normalize intestinal function and stimulate metabolic processes. This substance does not dissolve in the intestines, and by absorbing toxins and cholesterol , removes them from the body.
- Juice therapy is also indispensable. Orange, grapefruit, apple and berry juices are especially useful. You can drink orange juice in the morning and grapefruit juice in the evening. Among vegetable juices, beet and carrot juices are recommended. Start drinking beet juice with 1 tablespoon.
- In addition to fruits and vegetables, take bran, fenugreek, sesame and flax seeds, ground in a coffee grinder - these are additional sources of fiber, oils and phytosterols that help fight the disease.
- Drink 2 teaspoons of bran before meals in the morning and at night, remembering to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- You can prepare vegetable soups, cabbage soup, beet soup, borscht, or soups with a small amount of cereal.
- Avoid meat broths and cook soups with water or vegetable broth. Soups are prepared transparent, not fried, and no flour is added to them.
- Meat and poultry only lean varieties. For adequate nutrition, it is enough to eat poultry and meat 2 times a week. Turkey meat is healthy (it contains very little fat) and should be preferred. You need to prepare dishes boiled or baked, after boiling the meat.
- Bread may be rye, grain, or with bran. You can bake your own bread or crispbread from soy flour. You can eat dry unsweetened cookies and whole grain bread. It is better to make homemade baked goods without salt and add bran, flax or sesame seeds.
- Milk, fermented milk products and cottage cheese are consumed with reduced fat content, cheeses should be chosen with a fat content of 20-30%, and low-fat sour cream and cream should be used sparingly and only in dishes. You can include up to 2 whole eggs and an unlimited amount of egg whites in your weekly menu.
- Crumbly porridges are prepared from buckwheat, oatmeal, and brown rice, but if you are interested in losing weight, the amount of cereals in your diet should be reduced. As an option for side dishes, you can use pasta made from wholemeal flour and durum wheat. It is good to include oatmeal broth or jelly in your diet - oats remove cholesterol.
- Use unrefined vegetable oils to season prepared foods. Olive, corn, sesame and flaxseeds are especially useful.
- Nuts contain monounsaturated fats that are healthy for the body. It is recommended to eat 30 g of nuts and seeds daily. Walnuts are especially useful for lowering cholesterol.
- Green tea with lemon, rosehip decoction, juices, and still mineral water should be drunk up to 2 liters per day.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| greenery | 2,6 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 36 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| cashew | 25,7 | 54,1 | 13,2 | 643 |
| sesame | 19,4 | 48,7 | 12,2 | 565 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Sausages | ||||
| boiled diet sausage | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 170 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Why do vegetarians have high cholesterol?
Vegetarians are people who completely give up eating meat. Every person who joins the ranks of vegetarians has his own reasons for this. Vegetarian food is predominantly plant-based, so it does not supply exogenous cholesterol. But it also happens that vegetarians suffer from hypercholesterolemia.
In such people, an increase in plasma cholesterol levels occurs against the background of a disruption in the production of its endogenous form. Normally, the liver produces the amount of cholesterol required by the body, which is used for metabolic processes. With pathology of the liver tissue or genetic disorders, excessive secretion of this substance begins, which causes its high serum level.
Fully or partially limited products
Excludes:
- baked goods, puff pastry and pastry products, cakes, cream pies;
- offal, fatty pork, duck, goose, cooking fats, smoked meats and sausages;
- all types of broths, fried foods, canned fish and caviar;
- fatty cottage cheese, sour cream, cheese and cream;
- chocolate, ice cream, cocoa, strong tea and coffee;
- white rice, pasta, semolina.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| red radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 20 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 11% | 16,0 | 11,0 | 1,0 | 170 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Cholesterol diet menu (Diet)
Organize 5-6 meals a day. When actively engaged in health improvement, avoid foods containing hidden fats (sausages, sausages, cheeses, ham, rolls, pates). By choosing lean meat and cooking it properly, you will know the approximate amount of fat and cholesterol in it.
Use a minimum of fat when cooking, which means using a steamer, oven or grill. Eliminate “fast” carbohydrates - they stimulate the production of insulin , which is involved in converting sugars into fat. Taking into account all the recommendations, you can create a varied menu.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Beneficial features
Meat has a lot of positive qualities. It is rich in proteins, essential amino acids that cannot be produced in the human body. The product also contains:
| Name of useful microelement | Beneficial action |
| Iron (Fe) | Prevention of anemia, increasing hemoglobin levels. |
| Zinc (Zn) | Strengthening the immune system, enhancing concentration and memory, normalizing blood sugar levels. |
| Potassium (K) | Stimulation of brain activity, stabilization of blood pressure (BP). |
| Sodium (Na) | Regulation of metabolism (in combination with K and Cl), normalization of heart rhythm, regulation of blood pressure. |
| Calcium (Ca) | Synthesis of neurotransmitters, improvement of the functioning of the endocrine system, strengthening of bones. |
| Manganese (Mn) | Improving the absorption of Fe in the gastrointestinal tract, normalizing cholesterol and sugar levels, improving blood quality. |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Removing toxins from the body, improving metabolism, regeneration of soft tissues. |
| B vitamins | Stimulates the functioning of the brain, saturates the body with energy, participates in the formation of red blood cells. |
| Vitamin D | Strengthening immune qualities, slowing down the aging process, improving the condition of hair, skin, and nail plates. |
| Vitamin A | Normalization of nervous system performance, stimulation of visual function. |
In most cases, when people completely abstain from meat, they experience iron deficiency anemia.
Cholesterol-free diet recipes
First meal
Light soup made from mixed vegetables
Green peas, potatoes, zucchini, carrots, onions, bell peppers, green beans.
Place chopped potatoes, bay leaves, beans, carrots and allspice into boiling water. After 8-10 minutes, add chopped onion, bell pepper and zucchini. Cook until the vegetables are ready.
Brussels sprouts soup with sweet peppers
Cabbage, potatoes, tomatoes, red peppers, onions.
Cut all the vegetables into cubes; the cabbage can be left whole if the heads are small. Bring the vegetable broth to a boil, add the prepared vegetables, except cabbage, to it. Add a little salt, bay leaf and nutmeg. Boil for 10-15 minutes and add Brussels sprouts.
Roast red lentils
Lentils, garlic, onions, paprika, turmeric, vegetable oil, pepper, cumin, tomatoes or tomato paste.
Boil the lentils until pureed. Place on a sieve, do not pour out the broth. Grate the onion, add 2 cloves of chopped garlic, 0.5 tsp of cumin, turmeric, paprika, coriander, black pepper, chopped peeled tomatoes. Mix everything with lentil puree and, if you need to boil it, simmer everything together for 10 minutes, adding vegetable oil at the end.
Cauliflower and eggplant stew
Cauliflower, eggplant, carrots, tomatoes, onions, garlic, spices, vegetable oil, herbs.
Cut the eggplants into cubes and add a little salt. After a while, squeeze out the bitterness and rinse them. Place chopped cauliflower, eggplant and carrots in a saucepan, add a little water and simmer covered for 10 minutes. Add spices to taste, chopped tomatoes, vegetable oil and continue to simmer until done.
Salads
Avocado salad with homemade cheese
Avocado, apple, low-fat homemade cheese, lemon juice, olive oil.
Cut the avocado, apple and cheese as desired. For the dressing, mix lemon juice, olive oil and a little mustard.
Salad with red beans and cucumbers
Boiled beans, onion, cucumber, red bell pepper, garlic, olive oil, lemon juice, black pepper, any spices to your taste.
Cut the pepper, onion and cucumber into strips, add the prepared beans. For dressing, mix 1 tsp. lemon juice, salt, pepper, olive oil, garlic squeezed through a press.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
The benefits of meat
The product contains the highest concentration of protein and amino acids required for the normal functioning of the body. In addition, meat is rich in the following useful components:
- iron;
- zinc;
- calcium;
- manganese;
- magnesium;
- vitamins from group A, B and D.
Products affect the body as follows:
- strengthen bone tissue;
- improve immunity and the functioning of hematopoietic organs;
- normalize visual functions.
Reviews and results
This diet should be viewed as a transition to healthy eating habits. Such nutrition should become the rule of life for patients who are overweight, have impaired lipid metabolism, and have problems with the cardiovascular system. It is balanced, and restriction in simple carbohydrates and fats does not negatively affect health. The positive aspects are that patients lose weight, feel more energetic and their lipid metabolism levels are normalized. Reviews often mention that the diet forced them to change their lifestyle.
- “... Hereditary hypercholesterolemia does not give me any dietary allowances. I have to monitor it very strictly, but thanks to this, I am the only one in my family who survived until the age of 55 without a heart attack. I was overweight and had fatty liver disease. The first achievement was to start eating right, the second step was to start walking a lot and skiing in the winter. In general, my condition has improved (vigor, activity) and I like my lifestyle”;
- “... My war against cholesterol began over the last 3 years, and all this time I have been cooking for myself separately. At first the menu was more free, but when this did not help, and cholesterol increased, I had to take nutrition more seriously. I excluded potatoes, pasta, rice and sugar immediately, as well as everything fried. If I used to eat 2 eggs a week, now I only eat whites, and for the last month I have removed cheese and cream from my diet. I don’t want to take drugs, so I limit myself this way. I’ll wait another 2 months, if it doesn’t help, I’ll take medicine”;
- “...Cholesterol is elevated and there are problems with the liver. I was on a diet for 3 months, lost 7 kg (the weight was initially heavy and the kilograms came off easily). I immediately felt great relief and my liver did not hurt. I cook for myself separately, because my family refuses to eat vegetable soups and boiled chicken breast. There is no time to cook if you work. I make diet yogurt myself, and it goes as a dressing on all salads. I eat rice crackers and bran bread with jam. I cook it with brown sugar. I constantly eat grapefruits, carrots, apples, celery in salads and beets.”