Causes of aneurysm in children
A cardiac aneurysm in a child occurs for a variety of reasons. The disease can be congenital or appear during the development of the child. Often the genetic predisposition of children leads to the development of pathology.
The following pathologies lead to a decrease in the elasticity of vascular walls:
- high blood pressure;
- chronic atherosclerosis;
- vasculitis;
- syphilis and sexually transmitted diseases.
Smoking in adolescence also becomes a serious risk factor. Such a bad habit leads to the accelerated development of an aneurysm, which becomes the main cause of hypertension. Blood clots and injuries to small vessels also lead to the disease. Pathologies quite often occur in adolescents who are involved in road accidents, emergencies, or engage in extreme sports.
The stages of aneurysm in children are closely related to the different stages of the ongoing impairment of the heart’s capabilities:
- stage of compensation, which is observed with a fairly stable size of the resulting aneurysm or with its slow growth. In these cases, the load on the organ increases slightly, which ultimately allows it to function within acceptable limits;
- the stage of decompensation is noted with a rapidly growing pathology with impaired contractile function of the heart. As a result, the organ stops normally releasing the required volume of blood into the circulatory system, which leads to complications.
Treatment of atrial septal defect
There are currently two types of surgical treatment:
- 1. Open heart surgery under artificial circulation with suturing of the defect or its plastic surgery with a patch from the pericardium.
- 2. Elimination of atrial septal defect using special devices (occluders) in the X-ray operating room through arterial punctures without sternotomy.
- It is necessary to understand that not every defect can be eliminated surgically, there are contraindications to surgery (small-diameter defects, severe pulmonary hypertension, right-left discharge through the defect), and not every defect can be eliminated using occluders (a combination of a defect with abnormal drainage pulmonary veins, primary defects with missing lower edge, large defects, combination of defect with another
- heart pathologies are an indication for open surgery).
- You can learn more about a specific case of the disease, indications and contraindications during a consultation with a cardiovascular surgeon (at an outpatient appointment).
Symptoms of aneurysm in children
Aneurysm in children is practically asymptomatic for many years and is most often detected after an X-ray examination performed to determine another disease. Pain in the pathological area can also become a symptom of the disease.
Congenital or acquired cardiac aneurysm can have a variety of forms, and each of them has certain characteristic symptoms.
- Abnormal areas in the brain lead to difficulties with normal blood flow and activity of this organ, problems with movement, severe headaches and sudden epileptic seizures. As a result, the mortality rate ranges from 10 to 30%.
- A cardiac aneurysm in a child most often occurs at the stage of intrauterine development. A serious symptom of the pathology is the presence of various signs of insufficient heart function due to a protruding, thinned and non-functioning heart wall.
- Aortic aneurysm is almost always completely asymptomatic or, in advanced forms, manifests itself in the form of coughing and incipient shortness of breath due to compression of the trachea and bronchi, severe pain in the back and during the process of swallowing. When an aortic aneurysm ruptures, immediate death almost always occurs.
- Pathological areas of the aorta located in the peritoneal cavity. With this type of aneurysm, the child feels pain in the abdomen, chest and lower back, and in some positions the discomfort intensifies.
A serious symptom of interatrial aneurysm in children is the appearance of a palpable pulsation in the abdominal cavity, increased body temperature, noticeable blueness of the fingertips and severe weight loss. Basically, the signs of this terrible disease appear with inflammation and the appearance of blood clots.
When a cardiac aneurysm suddenly ruptures, a child experiences severe acute pain in the chest, a drop in blood pressure, a strong increase in heart rate and disruption of the breathing process, the absence of any reaction to painful stimuli and noticeable bluish skin. If an aneurysm ruptures and there is no timely necessary medical care, the child dies.
Features of pathology in a newborn
An aneurysm of the interatrial septum in a newborn is primarily manifested by a slight cyanosis of the skin. Other symptoms appear in a child at the age of 3-4 months. The final diagnosis can be made for the patient when he reaches 2 years of age. The small size of the cardiac vessel defect does not cause symptoms, so the disease can only be determined through diagnosis.
As the defect enlarges and becomes larger than 15 mm, an aneurysm of the sac in a newborn may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Retarded physical development. The patient may experience weight loss and delayed psychomotor development.
- A decrease in the body's defenses, which causes frequent viral diseases.
- Pathological protrusion of the heart, which can be determined by palpation.
When should you see a doctor?
A visit to a pediatric cardiologist, pediatrician, and vascular surgeon is recommended if you have the following signs of an aneurysm in children:
- frequent and severe headaches in a child;
- a feeling of discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the chest;
- periodic loss of consciousness and frequent dizziness;
- shortness of breath even with mild physical exertion;
- pallor and some swelling of the skin.
An experienced pediatric cardiologist at Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic), located in the central district of Moscow, will carefully examine the child and record all his complaints. The specialist will talk with the parents and carefully study the provided medical documents. Based on the results, the necessary studies will be prescribed and appropriate treatment procedures will be carried out.
Diagnostics
- Examination of the patient with auscultation (listening) of the heart reveals a heart murmur.
- An ECG reveals right ventricular myocardial hypertrophy, right bundle branch block, arrhythmias of varying severity, and a sharp deviation of the electrical axis of the heart to the left.
- X-ray of the chest organs reveals dilation of the pulmonary artery trunk, enlargement of the heart, and increased pulmonary pattern.
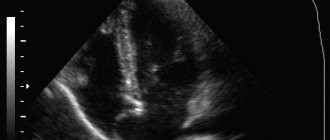
- Transthoracic echocardiography allows not only to visualize the atrial septal defect and clarify its nature (primary, secondary, venous sinus defect), but also to assess the direction of blood discharge through the defect and its hemodynamic significance (Qp/Qs).
- Transesophageal echocardiography in adults allows one to obtain detailed information about the edges of the defect, which is important for choosing a method of surgical treatment.
- Probing of the heart chambers and atriography is used when there is insufficient information from the research methods described above or as part of surgical treatment.
Complications of aneurysm in children
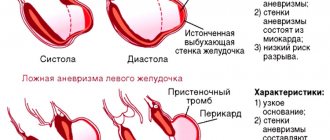
The main and most dangerous complication of an aneurysm in children is rupture of its wall, which leads to threatening internal bleeding. The large size of this pathology leads to a high risk of its development, and the consequences can be very severe, including death.
After rupture of the pathological area, the child may fall into a coma due to blood entering the existing subarachnoid space and mixing with the spinal cord fluid.
Another possible complication of an aneurysm is the risk of the formation of small blood clots in the form of thrombi, which are carried through the bloodstream and block the lumen of numerous small blood vessels. This leads to disruption of the blood supply to various internal organs, which may be the lower limbs, kidneys or organs located in the abdominal cavity. In most cases, patients die while still preparing for the upcoming operation.
Sudden vasospasm is the main cause of stroke and death. The patient's disability becomes a completely favorable outcome.
Diagnosis and treatment of aneurysm in children
Based on the symptoms, an accurate diagnosis of an aneurysm in a small child is almost impossible. All types of necessary examinations are prescribed only by a qualified doctor. With the help of differential diagnostics, a specialist can distinguish an aneurysm from various tumor neoplasms, which often have a threatening oncological nature.
At JSC “Medicine” (clinic of academician Roitberg), after a conversation with the parents, examination of the child and recording of his complaints, the pediatric cardiologist will prescribe the following types of tests for the child:
- echocardiography, ECHO-CG, daily ECG monitoring;
- ultrasound examination of joints;
- MRI and radiography;
- performing joint puncture;
- various laboratory tests.
To treat aneurysms, the clinic uses only high-quality medications and effective modern techniques. The experience and professionalism of doctors allows children to return health and joy of life.
Parents must pay close attention to the health of their child and regularly examine him with various medical specialists. This approach contributes to timely prevention and detection of the presence of this terrible disease.
Treatment of an aneurysm directly depends on the speed of development of this pathology. With rapid progression and large size of the affected area, competent surgical intervention is performed and its replacement with an artificial graft. Heart surgery in children is performed in a hospital, where the necessary modern equipment is available for careful monitoring of the child’s health condition and devices for the successful performance of the upcoming surgical intervention.
Most often, surgical intervention is performed as planned, and more rarely - as an emergency procedure. Before the operation and after it is performed, the patient must be under the supervision of an experienced cardiac surgeon or pediatrician while being registered at the dispensary.
Conservative methods are used to treat a small aneurysm. In this case, medications are prescribed that lower blood pressure and reduce the load on the walls of blood vessels. After surgery to relieve this pathology, the child’s condition is regularly monitored and a doctor is visited.
Types and consequences of pathology
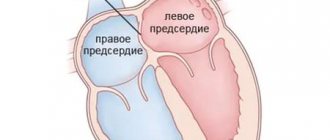
An atrial septal aneurysm is an abnormal bulging of the wall between the atria to one side. Most often, the protrusion occurs in the direction where the open oval window (OOF) was located, since in this place the heart muscle is not yet strong enough. The oval window between the atria is necessary for the fetus while it is in the womb, when pulmonary respiration is not yet functioning. It promotes the redistribution of blood flow between the left and right atria and should close after the baby is born.
However, in the practical activities of medical specialists in Makhachkala, there are cases when a newborn’s window remains open or not completely closed for quite a long time (a year or more). This leads to the fact that, under the pressure of the blood flow, the insufficiently strengthened myocardial wall begins to protrude in some direction. In medical practice, the combination of an aneurysm with an existing septal defect in children is much more common than AMPP alone without any additional heart pathologies. Types of aneurysm are classified depending on which direction the deflection of the interatrial septum is directed, such as:
- With protrusion into the right atrium.
- To the left atrium.
- S-shaped, in which different parts of the septum bulge in different directions.
If the occurrence of an aneurysm does not lead to a redistribution of blood flow from one cardiac chamber to another, then such a pathology does not pose a danger, and the prognosis can be called favorable. Otherwise, due to an increase in blood pressure in the pulmonary trunk, pulmonary hypertension may develop.
Prevention of aneurysm in children
With a congenital aneurysm, preventive measures are pointless, but such a disease can be prevented. Teenagers should never smoke, as this habit has a detrimental effect on the condition of the heart and blood vessels. If you have problems with blood pressure, constant monitoring is recommended.
The child's diet should be balanced and consist of healthy foods. Dishes with trans fats and semi-finished products are excluded from the diet, and the amount of sweets is reduced. The diet should consist of vegetables, fruits and unrefined carbohydrates.
The child should regularly engage in physical education or sports activities. Excess weight negatively affects the condition of the heart and blood vessels, so if such a problem arises, it is recommended to review the child’s diet. The teenager's height and weight should progress proportionally. To prevent aneurysm, children and adolescents should sleep at least 7 hours a day and, if possible, avoid stressful situations.
Clinical picture by age
In newborns, the course of an aneurysm without blood discharge is hidden. Symptoms in the presence of a pathological shunt:
- Tearfulness;
- Refusal to feed;
- Cry;
- Underweight;
- Frequent shallow breathing;
- Blue discoloration of the skin (the face may be red from crying);
- Fever (reflects the general reaction of the baby’s body to being unwell).
In children and adolescents, the disease, which is not accompanied by bleeding, is asymptomatic. In the presence of a shunt, the following manifestations are characteristic:
- Slow physical development;
- Dyspnea;
- Exercise intolerance;
- Complaints of stabbing pain in the heart, a feeling of irregularities and palpitations;
- Episodes of loss of consciousness;
- Insomnia;
- Cyanosis of lips, tip of nose, fingers.
Often, even with a shunt, children have no symptoms or complaints.
In adults, the clinical picture is determined by cardiopulmonary failure, which develops over many years, often in combination with other heart diseases. Symptoms:
- Dyspnea;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Chest pain;
- Exercise intolerance;
- Pain in the right hypochondrium;
- Swelling of the legs;
- Dilatation of superficial veins.
Adults are also characterized by an asymptomatic course, despite the presence of blood discharge, since the defect in the septum can be minor (2-3 mm).
How to make an appointment with a specialist?
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the center of Moscow in the Central Administrative District at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10 (Mayakovskaya metro station).
Our medical center employs doctors of the highest qualifications and extensive experience. All diagnostic measures are carried out with maximum efficiency. Especially when it comes to emergencies. All procedures are carried out on modern equipment using the latest technologies.
Doctors, having received the examination results, prescribe the optimal treatment method, which will be aimed exclusively at a positive result. Patients are always under the strict supervision of doctors. This allows you to quickly react if the child’s condition worsens.
If you have questions, you can make an appointment by phone.
Types of defects
There are primary and secondary violations of the structure of the septum. In the case of a primary change, the cause is underdevelopment of the primordial septum in the womb. This defect differs in localization - it is always located at the level of the fibrous ring of the atrioventricular valves. The defect may be accompanied by splitting of other valves.
An incorrectly formed secondary septum is responsible for the formation of a secondary defect. In this case, the lower edge of the hole falls on the height of the interatrial septum.
Make an appointment with a specialist without queues, at a convenient time
Sign up
+7