Cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is a specialized type of muscle tissue that forms the heart. This muscle tissue, which contracts and releases involuntarily, is responsible for maintaining the heart's pumping of blood throughout the body.
The human body contains three different types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth and cardiac. The only tissue present in the heart is cardiac muscle tissue containing cells called myocytes.
In this article, we will discuss the structure and function of heart muscle tissue. We also cover medical conditions that can affect heart muscle tissue.
Structure and functions
The cellular elements of muscle tissue are elongated, which is why they are called “fibers.” The cytoplasm of cells contains thin protein filaments of myofibril, which can lengthen and shorten (Table 1) . Special organelles and energy production by mitochondria provide contraction and elongation of fibers.
Table 1.
Structure and functions of muscle tissue
| Types of muscle tissue | Structure | Functions | Location in the body |
| Cross-striped | Consists of long and thick fibers (Fig. 1) . They are formed by the fusion of individual cells. There are a lot of nuclei. Striations are caused by alternating light and dark discs. The fibers are combined into bundles. | Voluntary body movements, breathing, facial expressions and a number of other actions. | The basis of skeletal muscles, tongue, pharynx, initial part of the esophagus. |
| Smooth | Individual spindle-shaped cells are small in size, united in bundles (5–10 pieces each). Each cell has one nucleus (Fig. 1) . Thin myofibrils stretch between the ends of the cell. The fabric is devoid of transverse stripes. | Involuntary contractions of the walls of internal organs under the influence of nerve impulses. | Muscular layers of the skin and internal organs (digestive system, bladder, blood and lymphatic vessels, uterus). |
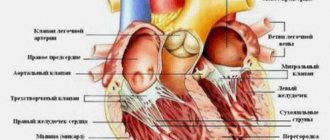
| Striated heart | The cells are elongated, branched, with a small number of nuclei, forming a single network (Fig. 1) . Transverse striation occurs due to shiny stripes at the junctions between cells. | "Engine" of blood circulation. Involuntary contractions of the heart muscle can occur under the control of the autonomic nervous system. | The bulk of the heart. |
Rice.
1. Structure and location of muscle tissue Muscle tissue ensures the movement of the body in space.
Muscle contractions are necessary to change the position of individual parts of the body. Muscles, in addition to motor function, perform protective and heat exchange functions.
Myocardial diseases
Since the myocardium has several important functions, any disruption in them can lead to a malfunction of the heart. The myocardium is influenced by many external and internal factors, which manifest themselves in the form of viruses or congenital pathologies. It is worth remembering that any chronic illness primarily affects the functioning of the heart and can disrupt the processes occurring in the myocardium. If the ability to contract is lost, the heart muscles weaken, the excitability of the fibers decreases, or the sending of impulses is disrupted, serious health problems may arise. Most often these are diseases of a cardiac nature, as well as those affecting the work and condition of blood flow and blood vessels. And these diseases are sometimes not easy to cure: they require time and financial costs, ensuring complete peace, changing lifestyle and other aspects that can radically change a person’s existing way of life.
Common myocardial diseases:
- Myocarditis. This is inflammation of the myocardium, which occurs due to pathological changes in the organ or due to infection. The disease is long and difficult to treat.
- Cardiomyopathy. Serious damage to the myocardium occurs, but doctors still do not know the causes of this disease. Therefore, it is quite difficult to treat it without knowing the exact causes.
- Myocardial infarction. It is the most common and best known ailment among cardiologists. This is an extremely “mean” disease that does not prepare a person for a fight, but strikes from around the corner, very unexpectedly and suddenly. Unfortunately, it is almost never possible to predict the approach of a heart attack. The only way to keep your heart healthy is to stick to good habits and an active lifestyle. Then, perhaps, a heart attack will bypass the person. It happens this way: first, a blood clot gets stuck in the coronary artery, and the patient feels incredibly severe pain, he lacks breathing and oxygen. After this, an important part of the heart becomes dead and ceases to function and perform its functions. Often, a heart attack instantly leads to death, and the person can no longer be saved. In other cases, the patient recovers from a heart attack, but for the rest of his life he must monitor his health, go on a diet and not drink alcohol. A heart attack significantly limits sports activities, but this does not mean that a person should become lethargic and inactive. All types of activities after suffering from such an illness are agreed upon with the doctor.
In this case, it is possible to prevent a heart attack if it is already known that the body is prone to thrombosis. If you eliminate all factors related to the formation or separation of a blood clot, you can protect yourself from the occurrence of many diseases. If it is possible to free the artery from the blood clot present in it, this should be done as soon as possible. There are special drugs that dissolve dangerous clots, as well as surgical intervention if conservative methods do not have the desired effect.
Properties
The muscle fiber stretches, but at rest returns to its original size. This property is the result of the interaction of protein filaments of myofibrils in the cytoplasm of cells. Each myofibril consists of protofibrils: thin ones formed by actin, and thicker ones formed by myosin.
Properties of muscle tissue:
- electrical excitability;
- contractility;
- conductivity;
- extensibility;
- elasticity.
Muscle tissue is capable of voluntary or involuntary contractions in response to nerve impulses. There is an interaction between fibrillar proteins - actin and myosin. Inorganic calcium ions necessarily participate in this process. During contraction, thin filaments of actin slide along thick myosin protofibrils.
Cardiomyopathy
There are diseases that attack the heart muscle tissue and impair the heart's ability to pump blood or relax normally. These include cardiomyopathy. Some symptoms of cardiomyopathy include:
- difficulty breathing or shortness of breath;
- fatigue;
- swelling of the legs, ankles and feet;
- inflammation in the abdomen or neck;
- arrhythmia;
- heart murmurs;
- dizziness.
Factors that may increase the risk of developing cardiomyopathy:
- diabetes;
- thyroid disease;
- cardiac ischemia;
- heart attack;
- high blood pressure;
- viral infections that affect the heart muscle;
- valvular heart disease;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- family history of cardiomyopathy.
A heart attack due to a blocked artery can stop blood supply to certain areas of the heart. Eventually, the cardiac muscle tissue in these areas will begin to die. Death of cardiac muscle tissue can also occur when the heart's demand for oxygen exceeds the supply of oxygen. This causes cardiac proteins such as troponin to be released into the bloodstream.
Smooth muscle tissue
Slow and prolonged muscle contractions are controlled by the autonomic nervous system. The purpose of such movements is to maintain or change the volume of hollow organs against tensile forces. Smooth muscles contract and stretch more than other types of muscle tissue. The contraction lasts much longer, which is associated with the rate of passage of calcium ions that regulate the process.
Properties of smooth muscles:
- contract 10–20 times slower than skeletal ones;
- capable of prolonged contractions;
- do not expend a lot of energy;
- Fatigue sets in more slowly.
Contractions of smooth muscle tissue occur involuntarily, that is, regardless of the will of the person. The signal from the nervous system passes through the entire mass of cells, which is explained by the peculiarities of the innervation of smooth muscles.
Some types of cardiomyopathy
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
causes stretching of the cardiac muscle tissue of the left ventricle and dilation of the chambers of the heart. - Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a genetic condition in which cardiomyocytes are not arranged in a coordinated manner but are disorganized. HCM can interrupt blood flow from the ventricles, cause arrhythmias (abnormal electrical rhythms), or lead to congestive heart failure.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
occurs when the walls of the ventricles become rigid. If this happens, the ventricles cannot relax to fill with enough blood. - Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
- This rare form of cardiomyopathy is caused by fatty infiltration of heart muscle tissue in the right ventricle. - Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy
occurs when amyloid proteins accumulate and form deposits in the walls of the left ventricle. Amyloid deposits cause the walls of the ventricle to harden, which prevents the ventricle from filling with blood and reduces its ability to pump blood out of the heart.
Cross-striped fabric
The cells have a thickness from 10 to 100 microns, a length from 10 to 40 cm. The cytoplasm contains a large number of nuclei and myofibrils, occupying a central position (Fig. 2) . Mature cells have hundreds of myofibrils and more than 100 nuclei. Actin and myosin filaments inside myofibrils are linked to each other (Fig. 3) . The ability for rapid contraction of this tissue is higher than that of others.
Rice. 3. Structure of skeletal muscle
Muscle fibers are covered with a membrane called sarcolemma. There are alternating plates of proteins of different densities that have unequal light refractive indices. Under an optical microscope, such muscles appear to be striated across. The contractile elements are united into muscle bundles covered with a connective tissue membrane. Skeletal muscles are well supplied with blood vessels and nerves.
Striated cardiac tissue
The special properties of the heart muscle are determined by the structure of the fibers. Cells up to 100 µm long are found only in the heart and do not merge, as in striated muscle tissue (Fig. 2) . The arrangement of actin and myosin discs in cardiac muscle is the same as in the fibers of skeletal muscle tissue. A distinctive feature is the presence of glossy stripes at the junctions of cells. Thanks to the connection of fibers into a single network, excitation in one area quickly covers the muscle mass involved in contraction.
The muscle tissue of the heart is capable of automatic operation. Between contractions there is a refractory period when the muscle is at rest. During contraction, the lumen of the heart cavities - the atria and ventricles - decreases.
Cardiac striated tissue contracts 10–15 times longer than skeletal muscle. Under normal conditions, a person contracts and relaxes 70–80 times per minute. Contraction is caused by electrical impulses originating in the heart itself. This process is associated with an energy carrier - adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Completely autonomous operation, continuous rhythmic activity are the physiological differences between the heart muscle and the skeletal muscle. Nerve impulses from the autonomic nervous system, which innervates the heart, are not required for the smooth functioning of the organ.
The effect of sports training on the myocardium
Studies have shown that the myocardium of an ordinary person, who is not inclined to exhaust himself with numerous and long-term training, is much different from the organ of a professional athlete.
It even works differently and acquires a specific structure, depending on daily loads. Despite the fact that sport itself has health benefits, professional training, frequent overexertion and participation in serious competitions can be very harmful. First of all, the heart suffers, which is faced with an impossible task: to withstand loads that exceed physical capabilities and pump blood under enormous strain. There are even fatal cases where athletes died from a broken heart during competitions or training. This suggests that, despite the importance of sport in a person’s life, it still needs to be treated wisely and used in moderation. Doctors recommend leading an active and sporty lifestyle, but not overdoing it. To maintain good body shape and healthy functioning of all organs, it is enough to use only 40% of the load that is the maximum for a particular organism. Then the myocardium will not suffer from overstrain, and all its functions will work normally. With increased power loads, the length of the myocardial fibers will remain the same and will not be subject to diffusion. But at the same time, important arteries in the heart are constantly strongly compressed, which is why the heart has to work several times faster and make a lot of effort to contract as before and supply oxygen to the cells. Athletics influences changes in the appearance of tissues. At the same time, the blood begins to circulate several times faster and more intensely. It is among track and field athletes that high blood pressure most often occurs, which is also not beneficial for the entire body. An abrupt stop in training is dangerous for the myocardium. If an athlete worked out intensely, and then suddenly decided to quit the sport and stopped loading his body even to a minimum, the heart will immediately react to this. The myocardial muscles can instantly weaken, the heart will stop contracting in a healthy manner, and as a result, the person will experience heart failure. This suggests that you need to quit sports gradually, reducing the time and intensity of training daily in small quantities. For healthy sports, it is enough to alternate difficult and easy exercises and be sure to give yourself rest.