The heart is a muscular pump that ensures continuous movement of blood through the vessels. Together, the heart and blood vessels make up the cardiovascular system. This system consists of the systemic and pulmonary circulation. From the left side of the heart, blood first moves through the aorta, then through large and small arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. In the capillaries, oxygen and other substances necessary for the body enter the organs and tissues, and from there carbon dioxide, metabolic products, are removed. After this, the blood turns from arterial to venous and again begins to move towards the heart. First along the venules, then through smaller and larger veins. Through the inferior and superior vena cava, blood again enters the heart, only this time into the right atrium. A large circle of blood circulation is formed.
Venous blood from the right side of the heart is sent through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs, where it is enriched with oxygen, and returns to the heart again - this is the pulmonary circulation.
Inside, the heart is divided by partitions into four chambers. The two atria are divided by the interatrial septum into the left and right atria. The left and right ventricles of the heart are separated by the interventricular septum. Normally, the left and right parts of the heart are completely separate. The atria and ventricles have different functions. The atria store blood that flows into the heart. When the volume of this blood is sufficient, it is pushed into the ventricles. And the ventricles push blood into the arteries, through which it moves throughout the body. The ventricles have to do more hard work, so the muscle layer in the ventricles is much thicker than in the atria. The atria and ventricles on each side of the heart are connected by the atrioventricular orifice. Blood moves through the heart in only one direction. In the systemic circle of blood circulation from the left side of the heart (left atrium and left ventricle) to the right, and in the small circle from the right to the left.
The correct direction of blood flow is ensured by the valve apparatus of the heart:
Valves:
- tricuspid
- pulmonary
- mitral
- aortic
They open at the right time and close, preventing blood flow in the opposite direction.
Aortic valve
Closes the entrance to the aorta. It also consists of three valves, which look like crescents. Opens when the left ventricle contracts. In this case, blood enters the aorta. When the left ventricle relaxes, it closes. Thus, venous blood (poor in oxygen) from the superior and inferior vena cava enters the right atrium. When the right atrium contracts, it moves through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. Contracting, the right ventricle ejects blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary arteries (pulmonary circulation). Enriched with oxygen in the lungs, the blood turns into arterial blood and moves through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium, then to the left ventricle. When the left ventricle contracts, arterial blood enters the aorta through the aortic valve under high pressure and spreads throughout the body (systemic circulation).
The heart muscle is called the myocardium
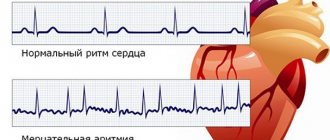
There are contractile and conductive myocardium. The contractile myocardium is the actual muscle that contracts and produces the work of the heart. In order for the heart to contract in a certain rhythm, it has a unique conduction system. The electrical impulse to contract the heart muscle occurs in the sinoatrial node, which is located in the upper part of the right atrium and spreads through the conduction system of the heart, reaching every muscle fiber
First, both atria contract, then both ventricles, thereby ensuring the flow of blood to all organs and tissues of the body. The heart muscle has two membranes (external and internal). The inner lining of the heart is called the endocardium. The outer lining of the heart is called the pericardium.
Treatment of coronary artery disease
Treatment for coronary heart disease includes lifestyle changes, medications and, in some cases, surgery.
All patients are advised to give up bad habits, spend more time in the fresh air, and reduce excess body weight. In your diet, you must avoid foods high in fat, very salty and sweet foods. Smoking and unauthorized discontinuation of prescribed medications are strictly prohibited. All this can lead to a sharp deterioration in the patient's condition. To stop an attack of angina, you need to immediately stop physical activity, provide access to fresh air and take nitroglycerin under the tongue or use nitrate in the form of a spray.
Basic drug therapy includes the following drugs:
- antiplatelet agents – drugs that thin the blood;
- beta blockers;
- ACE inhibitors or sartans;
- statins.
Long-acting nitrates can be used to prevent attacks.
In the presence of concomitant diseases, especially diabetes mellitus and hypertension, their treatment and achievement of target blood pressure and glucose levels are required.
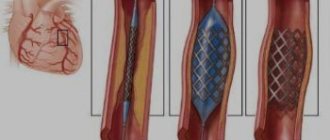
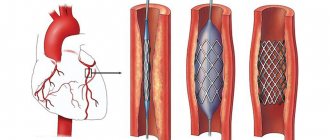
To restore cardiac blood flow, surgical intervention is necessary in some cases:
- Coronary artery bypass surgery is the creation of a bypass for blood at the site of narrowing of the coronary arteries using vascular prostheses.
- Coronary angioplasty and stenting - restoration of the diameter of the vessel, and, accordingly, the blood flow in it, by installing a special dilator.
Conduction system of the heart
The heart, like any organ, has its own nervous system. The nervous system of the heart has several levels. The first and main pacemaker of the heart is the sinus node, located in the right atrium. It is subject to the atrioventricular node, which is located on the border between the atria and ventricles and quite often slows down the heart rate set by the sinus node. Then the nerve impulse goes to the ventricles of the heart along the branches of the Hiss bundle, which are divided into the smallest nerve endings - Purkinje fibers.
Properties and types of muscle tissue
Morphological characteristics:
- Elongated shape of myocytes;
- myofibrils and myofilaments are located longitudinally;
- mitochondria are located near the contractile elements;
- polysaccharides, lipids and myoglobin are present.
Properties of muscle tissue:
- Contractility;
- excitability;
- conductivity;
- extensibility;
- elasticity.
The following types of muscle tissue are distinguished depending on their morphofunctional characteristics:
Muscle pain and cramps - possible causes and tactics
I want to get rid of these symptoms as quickly as possible. As a rule, muscle pain appears as a result of physical activity. But is this always the case? When is pain just a harmless physiological phenomenon, and when is it a sign of illness?
Muscle spasms
Muscle spasms are the most common cause of muscle pain. Muscle spasms can develop for various reasons. It develops acutely or over a long period of time with chronic overexertion. In this case, the pain can be dull, aching or, on the contrary, stabbing. It can last a few seconds or be protracted.
The most common reasons that lead to persistent muscle spasms:
- Prolonged muscle strain due to an uncomfortable position in which a person works. This is precisely the nature of back and neck pain among many office workers, leg pain among teachers and salespeople, hairdressers, and surgeons.
- Injuries as a response when muscles are forced to overstrain.
- Incorrect posture - as a result of this, certain muscle groups are constantly under heavy load and they are overstrained.
- Carrying a bag on one shoulder, and other asymmetrical physical activity.
- Hypothermia (fans, air conditioners and other cold air flows).
To get rid of the above unpleasant sensations, you first need to eliminate the causative factor. The next step should be rest, excluding additional physical activity and the use of warming ointments.
In some cases, massage will be helpful.
However, it should be said that sometimes it is easier to warn and be prepared for physical activity; for this you need to first perform warm-up exercises, or use ointment, elastic bandages, belts, bandages.
Lack of substances
Unpleasant sensations in the muscles can be caused by reasons that a person is not even aware of. Who would think that his arms and legs hurt because there is a lack of potassium or calcium salts in his body?
However, this is a very common reason. The most unpleasant thing is that a lack of potassium can cause discomfort in the heart, because the heart is the same muscle. A person goes to doctors, undergoes electrocardiographic and other examinations.
And he does not agree that the doctor prescribed him (in his opinion) a frivolous treatment - “vitamins”.
Distrust of the doctor and refusal to take the prescribed drug will exclude the opportunity to obtain the necessary complex of minerals, establish electrolyte balance, and will not contribute to healing.
Calcium deficiency develops for various reasons. Very often during periods of rapid growth of the body, during pregnancy during periods of hormonal changes in the body and especially in older people. Osteoporosis is a more catastrophic and later consequence of calcium deficiency. The harbingers are a banal aching, periodic muscle pain.
Mineral deficiency can be directly related to both lack of dietary intake, as well as as a result of forced metabolism (breakdown) in athletes and those who like to push themselves in a fitness club, irregular intense physical labor, adherence to various kinds of diets (refusal to eat), with the goal is to lose weight.
This explains the way to get rid of the problem. Seek advice from a doctor and, if necessary, undergo the necessary examination to confirm or refute the suspected deficiency of substances.
Thus, uncontrolled use of drugs can lead to an increased content of minerals, and sometimes this is worse than their deficiency (especially for potassium) and most often it is enough to limit yourself to eating foods rich in certain substances without resorting to taking medications.
Myositis
Painful sensations in the muscles that increase with movement can be caused by myositis. Myositis is inflammation of muscle tissue. At the same time, the pain is aching, occurring in the arms, legs, and muscles of the torso. Sometimes when palpating the muscle, you can feel nodules or cords.
Myositis occurs for various reasons. It appears as a result of injuries, muscle strain, as a complication after viral diseases, or a cold. Some parasites, such as Trichinella, also cause myositis.
At the same time, fever may develop with parasitic myositis.
The nature of myositis should be clarified by a doctor. And only after that start treatment.
Fibromyalgia
(a condition of the body caused by constant and sometimes debilitating muscle pain).
Such pains are common - some doctors even claim that 75% of people have experienced them in one way or another. Most often, fibromyalgia affects the muscles of the shoulders, chest, neck, back of the head, lower back, and hips.
And also often these aching pains cause restlessness at night and insomnia. The main difference between fibromyalgia is that the pain is distributed throughout the muscles and is associated with the act of movement, inhalation and exhalation. By pressing in areas of discomfort, you can even find the most painful points.
The pain is diffuse - that is, it can appear and disappear in one place and flow to other areas of the muscles.
A special place is occupied by the so-called “intercostal” fibromyolgia (neuralgia), which imitates pain in the chest and requires differentiation and cordiolgia (heart pain), which may hide a serious pathology.
Fibromyalgia can be caused by nervous and physical stress, frequent stress, injury, lack of sleep, emotional stress, exposure to cold or dampness, rheumatic and autoimmune diseases.
It is interesting that most often nervous and suspicious young women and teenage girls suffer from fibromyalgia. It's enough to be nervous before exams. But in men, fibromyalgia more often occurs due to nervous or physical stress.
Hard workouts or pressure at work are the main reasons for men.
Treatment of fibromyalgia on one side can be limited to taking valerian. On the other hand, it may require a more serious approach to treatment using rubbing ointments and tablet and injection forms of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and correction of physical activity.
Colds, flu and other infectious diseases
Many infectious diseases (one could say almost all!) are accompanied by the appearance of muscle pain.
This is explained by the fact that pathogenic microorganisms and viruses, during their vital activity in our body, cause its poisoning - intoxication of the body.
And with intoxication, muscle pain of varying intensity occurs. The more severe the cold, the more your body muscles may ache.
It is usually difficult to confuse muscle pain caused by infections, viruses, and others. After all, the symptoms of the disease itself are obvious: fever, chills, weakness.
And the main treatment is treatment of the disease itself: lowering body temperature, taking antiviral drugs, immunomodulators, vitamins, anti-inflammatory drugs, drinking plenty of fluids and other therapeutic measures that help remove toxic substances from the body that cause intoxication. However, the appearance of pain in simple forms of a cold can manifest itself as other concomitant diseases and complications. For example, pain in the chest area may indicate the onset of complications - bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia and other serious illnesses.