Acute heart failure (AHF) is an emergency condition that develops when the pumping function of the heart is severely impaired. Acute myocardial dysfunction entails circulatory disorders in the systemic and pulmonary circulation; as the pathological condition progresses, multiple organ failure develops, i.e., gradual failure of all organs and systems occurs. Acute heart failure can develop as a complication of cardiac diseases, sometimes occurring suddenly, without obvious preconditions for a catastrophe.
What is heart failure?
Heart failure is a disorder of the myocardium, which can be acute or chronic and is accompanied by insufficient blood supply to internal organs. In the acute form of the pathology, practically no blood flows to the organs, resulting in acute hypoxia (lack of oxygen) of all tissues and organs, which quickly leads to the death of the patient.
All forms of heart failure are associated with insufficient contractility of the myocardium, which may be the result of pathological factors (chronic diseases or disorders of internal organs) or other reasons not related to health. Acute heart failure almost always causes severe pathologies, which cause death.
These include:
- bilateral pulmonary edema;
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiac type asthma;
- cardiogenic shock.
To provide proper assistance, diagnosing the pathology, determining the type of heart failure and its symptoms is of great importance.
Diuretics for hypertension and heart failure are currently most widely used as drugs used to lower blood pressure and rid the body of excess fluid. Read more in the article: “diuretics for hypertension and heart failure.”
Who is at risk?
Among the risk factors for the development of CHF, the leading ones are arterial hypertension and lipid metabolism disorders, which are a prerequisite for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels. As a rule, the patient's history does not contain isolated exposure to a single factor. People with the following diseases are at risk. Diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- Arterial hypertension (primary and all secondary hypertension, especially renal);
- Coronary artery disease (all its varieties: stable and unstable angina, vasospastic angina and all forms of arrhythmic disease);
- Acute coronary syndrome;
- Heart attack (both large- and small-focal varieties);
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis;
- Congenital and acquired heart defects (aortic disease predominates among the causes as a consequence of rheumatism);
- Cardiomyopathies;
- A group of inflammatory diseases - myocarditis, pericarditis, endocarditis, pancarditis;
- Toxic heart disease (occupational factors, radiation).
Diseases of other organs: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); All types of severe anemia; Acute cerebrovascular accident. Chronic heart failure in developed countries is found in 1-2% of the adult population. It is a disease of older people and rarely occurs in patients under 50 years of age. The risk of developing this pathology increases with age; among people over 70 years of age, this figure exceeds 10%. There are also significant differences by gender: women get sick three times more often.
Papillomas are small growths of the skin and mucous membranes that arise as a result of human papillomavirus infection. The causative agent is the human papillomavirus (HPV). Read more in the article: “how to get rid of papillomas on the body.”
Money in fat
Unfortunately, the death of participants in weight loss shows is not uncommon. Last year, two participants in the show “I weigh 300 kilograms” already died. In addition, 90% of former fat people gain tens of kilograms again soon after filming ends, sometimes even more than before they began participating in the program. Medical experts have warned about these consequences of extreme weight loss methods more than once.
But such shows are eagerly watched all over the world. They follow the same pattern: weak-willed fat people who were given the opportunity by kind people to escape fat slavery, tough trainers who look like army sergeants, and thoughtful presenters who shake out revelations from the participants. These programs bring millions to their creators.
Money comes not only from high ratings (and they are high!) and advertising inserts. A New York Times study claims that the popular American fat show "The Biggest Loser" generates $100 million a year from show-related merchandise sales alone.
Classification of the syndrome
By nature of origin
| Type of pathology | Cause of occurrence |
| Reloading | The reason is increased stress that the heart cannot cope with. Often this type of pathology occurs with congenital heart defects, but sometimes it can develop with physical activity and strong emotional disturbances |
| Myocardial | Associated with metabolic disorders in the tissues of the heart muscle, due to which the contractility of the myocardium is impaired |
| Combined | Occurs against the background of average (sometimes moderate) loads that the organ cannot cope with due to chronic pathologies in the metabolic processes of myocardial tissue |
According to hemodynamic type
Advertising:
Hemodynamics is the term used to describe the movement of blood through arteries and vessels. Blood pressure depends on two factors: blood consistency and the resistance of the vascular walls. Based on the type of hemodynamics, two types of pathology are distinguished.
Congestive hemodynamics
| Type of pathology | Localization and cause of appearance |
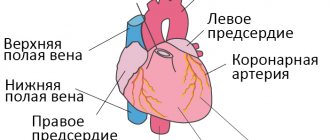
| Right ventricular failure (acute stage) | Stagnant processes are diagnosed in almost all organs and tissues. Defeat starts in a big circle |
| Left ventricular failure (acute stage) | Pathological changes occur in the small circle. The lungs are rapidly affected, and the patient develops pulmonary edema or cardiac-type asthma |
Hypokinetic type of hemodynamics
| How does the pathology manifest itself? | What does it represent? |
| Reflex shock | Response to pain resulting from pinched heart muscle |
| Arrhythmic shock | Occurs when the contractility of the heart is impaired and the heart rhythm is abnormal |
| Cardiogenic shock | Develops when half of the surface of the left ventricle is affected and is accompanied by intense pain under the right rib. |
Symptoms before death: cardiogenic shock
The symptomatic picture of true cardiogenic shock caused by myocardial infarction unfolds quickly and represents a chain of events, each of which, one after the other, aggravates the patient’s condition. Initially, in the most acute period of a heart attack, the patient experiences severe burning or pressing pain in the chest for 20 minutes or more, after which the feeling of lack of air quickly increases, mental agitation appears, fear of death, and panic develop. Almost immediately the skin becomes moist, perspiration appears on the forehead, the face turns pale, the pink color of the lips gives way to pale, and then bluish (cyanotic).
Advertising:
Breathing gradually becomes shallow and later stops completely after the development of asystole or ventricular fibrillation. The patient dies (clinical death). The time from the development of a heart attack to death is very short, although it depends on the development of fatal arrhythmias. Without arrhythmia, CABG can proceed in 40-60 minutes, although this time greatly depends on the initial volume of myocardial damage. With the rapid development of asystole, ventricular fibrillation, transverse block, idioventricular rhythm or electromechanical dissociation, as well as with ventricular tachycardia, death can occur suddenly.
Symptoms of acute heart failure: symptoms before death
Signs of the condition will differ depending on the form of pathology, location and extent of damage. The main symptom indicating the transition of the pathology to an acute form is a change in heart rhythm (sinus tachycardia). The patient's heart begins to beat faster, and the contraction frequency exceeds 100 beats per minute.
Determining the type of deficiency is important for first aid and subsequent treatment, so you need to know them and be able to distinguish them yourself.
How to recognize right ventricular heart failure?
If the right ventricle of the heart is affected, changes occur in the patient’s body, in most cases incompatible with life: a sharp decrease in the amount of protein in the blood plasma occurs, the salt balance changes, and general exhaustion of the body occurs.
A critical condition can be recognized by the following signs:
- increase in liver size;
- yellowing of the skin, eye sclera (looks like hepatitis and cirrhosis);
- swelling of veins in the neck and liver;
- high venous blood pressure;
- pain under the right rib (high intensity);
- severe swelling of the arms, legs and face;
- blueness of the fingers and toes, as well as the nose, chin, and ears.
Advertising:
The right ventricular form of pathology can be diagnosed with 100% accuracy using radiography and ECG. The electrocardiogram will show shock overloads from the right atrium and ventricle (drawn as teeth).
How to recognize left ventricular heart failure?
First aid for right ventricular heart failure:
- lay the patient down, raising the body on a pillow (so that the chest is at an angle of 50-60 degrees);
- give a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue.
First aid for left ventricular heart failure:
- sit the patient down (make sure that the person does not bend his legs and keeps them perpendicular);
- give Nitroglycerin under the tongue;
- Secure the hips with tourniquets.
For any form of pathology, it is important to ensure the supply of fresh air. To do this, you need to open all the windows in the room (if possible, take the patient outside). Remove all belts, bracelets and other accessories from the body that can compress the skin and interfere with the flow of blood through the vessels. The chest must be freed from clothing, all buttons must be undone.
The patient should not be left unattended until the ambulance arrives. If there are assistants, you need to prepare documents in advance and remember what the patient has been sick with recently, what medications he is currently taking, and whether there is a history of chronic diseases. This information will be needed by both the emergency team doctors and the hospital staff where the patient will be taken.
Sudden cardiac death. Chronic and acute heart failure: symptoms, treatment, signs.
Prevention of heart failure
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a serious disease that results in the accumulation of interstitial fluid in the lungs, abdomen, and lower extremities due to ineffective heart function. People with certain medical conditions have a higher risk of developing CHF. Making certain lifestyle changes can help prevent the development of congestive heart failure, so you can live a longer, more productive life.
Advertising:
- Exercise regularly
. One of the most important methods for preventing congestive heart failure is regular physical activity. Physical exercise strengthens the heart muscle, making it work more efficiently. Exercising for half an hour at least three times a week will help strengthen your heart. Reduce the amount of salt you consume. Sodium is the main enemy of heart health. Remember that excess salt promotes the accumulation of water in the body - Eat healthy
. In addition to reducing your sodium intake, it's important to maintain a healthy overall diet. - Stop smoking
. Smoking is the leading cause of heart disease, leading to congestive heart failure. Smoking causes the arteries of the heart to narrow and gradually become clogged with plaque. - Limit your alcohol intake
. It has been proven that one glass of wine at night before bed has a beneficial effect on heart function. However, in too large doses, alcohol has the opposite effect: it damages the coronary arteries, which increases the risk of developing CHF. - Blood pressure control
. A small increase in blood pressure, just 7 mmHg, increases the risk of cardiovascular disease by 27%. Increased peripheral pressure makes the heart work harder.
It should be emphasized that you should not take any prescription drugs without a doctor's prescription. Remember that some drugs, on the contrary, increase the risk of a heart attack, so you should always seek the advice of a good doctor.
Causes of the disease
In two thirds of all people with heart failure, the cause of the disease is myocardial infarction and ischemia. 14 percent of cases are caused by heart defects, 11 by dilated cardiomyopathy.
Among people over 60 years of age, four percent of cases are caused by hypertension. In elderly patients, a common cause is type 2 diabetes, especially if arterial hypertension is present at the same time. How heart failure is treated depends on the specific cause.
There are several factors that contribute to the formation of the disease. It usually manifests itself if there is a decrease in the compensatory mechanisms of the heart. These factors differ from the causes in their reversibility. If they are eliminated or even reduced, the development of the disease can be stopped. There are cases when this leads to saving the patient’s life.
Such factors include intense physical activity and stressful situations. Among them are pulmonary embolism, arrhythmia, and progressive ischemic disease. Factors include pneumonia, acute respiratory viral infections, and kidney failure. Negative consequences are caused by taking cardiotoxic drugs, as well as medications that retain fluid in the body and increase blood pressure. Addiction to alcohol and sudden weight gain have a negative effect. Predisposing factors are myocarditis, rheumatism, as well as neglect of the recommendations of a treatment specialist.