Almost every young person has encountered situations when the heart begins to beat faster than usual, especially during physical exertion, emotional outbursts, and excitement. Many conscripts are interested in advance, before undergoing a medical examination, when they can count on complete exemption from the upcoming military service with this pathology.
The decision of the military registration and enlistment office will be made after a detailed study of the diagnosis, so each case is considered individually.
Will arrhythmia become an obstacle to service in 2021?
Everyday life in the army, filled with increased physical and psychological stress, becomes a serious test for some.
For young men aged 18-27 years who have pathologies associated with cardiac activity, the question of fitness is especially relevant during the conscription campaign.
The disease is divided into different types, depending on the classification: the recruit will go along with the rest of the army or will receive a deferment.
What is taken into account when assigning a fitness category to a young man diagnosed with arrhythmia:
- the degree of the disease;
- frequency of recorded attacks;
- stage: persistent remission, exacerbation;
- undergoing the necessary diagnostics;
- detected concomitant diseases and complications.
It is worth noting that it will be possible to completely avoid service only in case of serious violations that are documented.
In any case, hoping to receive a non-conscription category, it is better for a young man to take care in advance of collecting medical certificates, extracts, research results, including an ECG.
How to get exemption for heart disease
Various types of cardiac pathologies require an equally large number of examinations and medical consultations when a young man undergoes a draft medical examination.
When diagnosing cardiac arrhythmia, it is first necessary to identify the presence of other, more complex diseases of the cardiovascular system. To do this, the conscript receives a referral for examination by a cardiologist. In this case, the doctor is guided by the provisions of articles 42-48 of the Schedule of Diseases dedicated to heart diseases.
After a detailed examination, the cardiologist makes a final diagnosis, which is the basis for members of the medical commission of the military registration and enlistment office when assigning a fitness category to a conscript.
IMPORTANT! The basis for exemption from military service can only be officially documented results of diagnostic studies of pathologies in the condition of the conscript’s cardiovascular system.
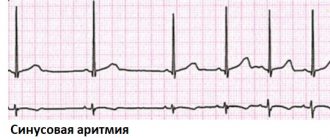
Are sinus arrhythmia and the army compatible?
The most common type of pathology among conscripts is sinus arrhythmia. In most cases, this form of the disease is not a contraindication to full performance of military duty.
Minor discomfort associated with sometimes rapid heartbeat, slightly deviating from normal values, will not be considered by the medical commission at the military registration and enlistment office as a reason for deferment or release. Usually, when asked by a future defender whether they are recruited into the army with sinus arrhythmia, one can hear a positive answer.
It is believed that the physical exercises included in the program, adherence to a daily routine, a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle will help strengthen the body and get rid of pathology.
The possibility of serving is also affected by the degree of progression of the disease, so it is impossible to say definitively whether someone with this type of arrhythmia will be accepted into the army.
You can hope to avoid conscription only if serious violations are identified:
- constantly occurring attacks of rapid or slow heart rate, documented;
- the presence of serious concomitant complications requiring treatment, control, and medical supervision.
Having proven a possible threat to the health of the recruit and incompatibility with the army at this stage, the guy receives category G and a temporary deferment for 6 or 12 months.
For more information about what category G means on a military ID, read our article.
After undergoing the necessary treatment, the young man must appear for a re-examination during the next conscription campaign, where a verdict will be made as to whether the guy with this stage of arrhythmia will be drafted into the army.
If there are obvious improvements, the future soldier is sent to the unit; if the therapy does not bring a positive result, the issue of extending the deferment or being assigned a non-conscription category is decided.
Characteristic signs
Sinus arrhythmia, which is the most common form of this disorder, can provoke the following symptoms in the patient:
- dyspnea;
- dizziness;
- tremor;
- pallor;
- feeling of lack of air;
- feeling of heart failure;
- fainting;
- chest pain.
The general condition of patients with arrhythmia is unstable. Any excitement or sudden physical activity can cause complications or a sharp deterioration in well-being.
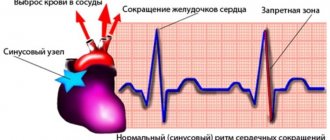
Sinus arrhythmia and the army
Sinus arrhythmia is one of the types of deviation during which the patient experiences the correct sinus rhythm, but with a faster heart rate (90-130 beats per minute).
If the conscript has an established and documented diagnosis of “sinus arrhythmia,” he will most likely be accepted for service. This is justified by the fact that usually such a deviation develops in insufficiently active people who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
Due to the lack of physical activity on the body, the heart muscles are weakened, which leads to an increased rhythm. This condition does not indicate deterioration in health.
Obtaining exemption from service is possible only with confirmed severe complications caused by arrhythmia in the conscript.
Extrasystole and service
Extrasystolic arrhythmia is the most common type of disease. It is accompanied by increased work of certain areas of the myocardium, which provokes premature contraction of the heart.
Manifestations of the disease can be quite different. Most often, patients suffer from a feeling of interruptions in heart rhythm, pain and tremors in the chest. Feelings of anxiety, weakness, and discomfort are also possible.
Conscripts in this condition are not accepted for service due to the high risk of cardiac arrest and other dangerous complications.
Remember! The military medical commission does not engage in primary diagnosis of diseases. She assesses the general health of the conscript based on the documents provided to her. That is why it is important to first take with you all the supporting papers with diagnoses and fixed conclusions of the attending physician.
It is impossible to hide any illness, as this can subsequently lead to serious deterioration in health.
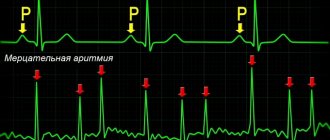
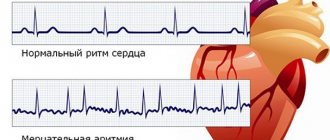
Atrial fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmias
In addition to sinus, there are other types of disease that are clearly incompatible with the army, which are prescribed in Article 44 of the “Schedule of Diseases.” After studying the medical record and research results, the doctors who are part of the military medical commission decide whether to take the guy with the detected rhythm disorder into the army or leave him in civilian life.
Young people with serious diagnoses are not called up for military service:
- atrial fibrillation and arrhythmia;
- ventricular extrasystoles in a pronounced form.
Constantly occurring attacks, regular disturbances in cardiac activity, requiring drug treatment, after which relapses occur, will become the basis for enlisting in the reserve or declaring the guy unfit for the army.
The letter “B” affixed to a military ID will mean that in peacetime the young man should not be afraid of receiving summonses. The letter “D” exempts the young man from conscription for life.
The category that determines the future of a particular citizen is assigned according to the list of “Schedule of Diseases”.
Read more about what military fitness categories mean here.
Diagnostics
Traditionally, arrhythmia is diagnosed by a cardiologist. This specialist must not only identify the disease, but also determine its etiology, type and degree of neglect. The following studies are used for this:
- ECG. This is a standard procedure that allows you to determine the possible causes of arrhythmia, monitor the frequency of ventricular contractions and record the heart rhythm.
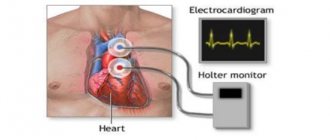
- Daily Holter monitoring. This is a painless test that records the work of the heart and deciphers the data obtained on a computer. Such an examination allows us to identify hidden interruptions in the functioning of the heart that occur during excitement, walking, or rest.
- Thyroid examination. Used for differential diagnosis.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- Exercise test.
Arrhythmia complications incompatible with military service
You should undergo all examinations to identify the presence or absence of concomitant diagnoses and possible complications.
Often complaining of periodic attacks in which a slow or, on the contrary, excessively rapid heartbeat is noted, young people are not aware of the presence of other serious diseases.
The fact is that arrhythmia may not be a separate pathology, but a symptom of other ailments that imply a non-vocational category:
- ischemia;
- neuroses;
- obesity;
- heart defects;
- mitral valve prolapse.
Read more about whether people with mitral valve prolapse are accepted into the army.
Having discovered diagnoses that pose a serious threat to the health, and in some cases the life of a young man, the doctors of the military registration and enlistment office will not ignore the dangerous pathology, releasing him from the army.
The main thing is to prepare documents in advance that can confirm the disease when going for a medical examination.
Having doubts about the diagnosis, doctors at the military registration and enlistment office issue a referral for additional examination of the conscript.
Is it possible to slant based on arrhythmia?
It's no secret that most young people are not eager to serve in the military. The most popular and safest way to avoid conscription is to feign some serious illness. Very often, conscripts are punished for heart disease.
Arrhythmia is definitely not the best diagnosis for simulation. It never starts just like that, but is a consequence or symptom of another disease, usually quite serious. Those with common sinus arrhythmia are recruited into the army. Only the most dangerous forms of rhythm disturbances, which do not arise suddenly and out of nowhere, are guaranteed exemption from conscription. If a young man does not have serious evidence of his diagnosis, then most likely they will not listen to him at all. But even in the presence of a serious pathology, a “military officer” is not issued immediately, but only after several checks and examinations. They are usually carried out in a hospital.
Installation of a pacemaker is considered one of the most effective treatments for severe heart rhythm disorders.
To confirm the diagnosis, the conscript will have to undergo several types of ECG (regular, under load, daily monitoring) and undergo a lot of tests. It’s definitely not possible to deceive complex equipment. And it’s not at all easy to deceive doctors who are well aware of all the tricks of the malingerers. You can also add that attempting to evade military service is a crime punishable by law.
Probability of avoiding service with arrhythmia
Except for cases where pronounced symptoms indicate a complex disease or the presence of concomitant diagnoses, evading military service is not so easy.
Attempts to mislead members of the medical-military commission are fraught with trouble: the law provides for serious punishment for “deviators,” ranging from impressive amounts of fines to criminal liability.
Verbal complaints about rapid rhythm without documentary evidence can be ignored and considered as a result of excitement. It is pointless to pretend in front of experienced doctors, and you should also not look for illegal ways to “slope” in the form of buying a military personnel or other dubious options.
Not wanting to undergo the tests of difficult everyday life in the army, a rational solution would be to turn to professionals in this field.
What diseases does it manifest itself in?
So, arrhythmia itself never occurs. It is important to establish the disease against which it develops. It is the underlying illness that determines whether a conscript will be accepted into the army or not. The conscript will receive a “white” ticket if, after the examination, the following diagnoses are confirmed:
- Rheumatic fever (Sokolsky-Buyo disease) in combination with heart failure. With this disease, muscle tissue becomes inflamed, which reduces their contractile functions, and blood circulation is impaired. As a result, frequent and prolonged attacks of arrhythmia occur, during which the patient requires medical supervision.
- Acute heart failure with severe arrhythmia.
- Dysfunction of the cardiac conduction system in severe form.
- Acquired or congenital heart defects.
- Incomplete closure of the mitral valve - prolapse.
- Cardiosclerosis is an extremely dangerous pathological process in which the muscle tissue of the heart is replaced by connective tissue.
- Cardiac ischemia in an advanced stage.
- Arterial hypertension in the third stage.
Any of the listed pathologies is the basis for assigning a category “D” (“White Sheet”) to a young person.
Extensive physical exertion and exposure to difficult living and climatic conditions, psycho-emotional stress can provoke an exacerbation, attack and a sharp deterioration in health
What other categories can a conscript with arrhythmia receive?
If the initial examination shows that the condition of a conscript suffering from arrhythmia is not critical, he may be assigned the status “G” or “B”. Status “G” means that the young man cannot be recruited until he undergoes the necessary examination, and, if necessary, emergency treatment. After this, his suitability for military service will be reviewed again. That is, this status provides only a temporary deferment from service, but not complete removal.
Status "B" does not provide for deferment. The young man will be called up, but he will serve only in peacetime and will be in rear positions, in benign conditions. If a young man's well-being changes for the worse, his status may be reviewed by a medical commission.