Our expert - Head of the Department of Surgical Treatment of Rhythm Disorders and Electrocardiostimulation No. 55 of the State Clinical Hospital named after. Botkin Igor Mayorov.
The beautiful word “arrhythmia,” which became widely known thanks to the famous Russian film about the hard everyday life of an ambulance doctor, denotes a pathology in which the heart rhythm differs from the normal sinus rhythm. As a result, the contractile activity of our motor is significantly impaired, which, in turn, can lead to dangerous complications.
What causes an attack?
The occurrence of an attack of cardiac arrhythmia can occur for completely different reasons, ranging from ordinary fatigue or physical exertion, to the presence of serious cardiac pathologies in which arrhythmia acts as a clinical manifestation. Consequently, etiological factors are divided into three main groups that cause increased heart rate:
- Organic heart lesions.
These include severe pathologies that, as a consequence of their course, disrupt the functioning of the heart, and especially its electrical system. These are myocardial infarction, heart defects, coronary disease, myocarditis, myocardiopathy, supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia, fibrillation.
- Disturbances of water-salt balance.
Pathological changes in water-salt balance lead to a deficiency or excess of magnesium, calcium, potassium and sodium in the body. Potassium is important for normal cardiac conduction and the normal cardiac cycle. Its compounds are responsible for favorable conduction of impulses in the heart muscle, and, consequently, control of heart rate.
- The influence of external factors on the body.
These include intense physical activity, stress, lack of sleep, overwork, and colds. Frequent emotional swings can provoke a psycho-emotional disorder, which disrupts the normal functioning of the nervous system and has a bad effect on the functioning of the heart.
There are many reasons that provoke a rhythm failure. Each of them leads to pathological changes in the main muscle and poses a threat to the general condition of the body. Therefore, it is important to know how arrhythmia attacks occur and what methods exist to stop them.
Diagnostics
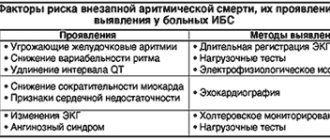
Symptoms of suspected arrhythmia need to be carefully checked. Alarming signs include not only rapid heartbeat, but also sudden cardiac arrest, pressure changes, weakness, alternating with drowsiness.
If you experience the above symptoms, it is time to see a doctor and undergo a full diagnosis. You should contact a cardiologist - first of all, he will begin to check the thyroid gland and identify possible heart diseases.
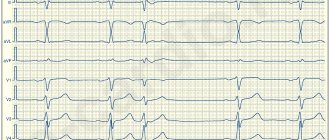
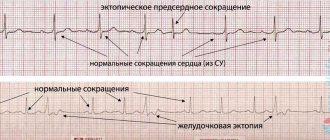
Many methods have been developed to diagnose arrhythmia. An electrocardiogram must be recorded - it can be short or long. Sometimes doctors provoke an arrhythmia to record readings and more accurately determine the source of the problem. Thus, diagnostics are divided into passive and active. Passive techniques include:
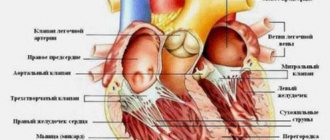
| Echocardiography | An ultrasonic sensor is used here. The doctor receives an image of the heart chambers, observes the movement of the valves and walls, and specifies their sizes. |
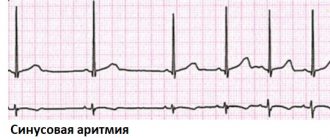
| Electrocardiography | Electrodes are attached to the patient's chest, arms and legs. The duration of the contraction phases of the heart muscle is studied and the intervals are recorded. |
| Daily ECG monitoring | This diagnosis is also called the Holter method. The patient carries a portable recorder with him at all times. This happens within 24 hours. Doctors receive information about heartbeats during sleep, rest and activity. |
In some cases, passive research is not enough. Then doctors induce arrhythmia by artificial means. Several standard tests have been developed for this purpose. Here they are:
- exercise stress;
- mapping;
- electrophysiological study;
- Tilt table test.
How does it go?
Many patients do not notice the passing of an arrhythmic attack, since they do not observe a significant deterioration in the body’s condition. Moreover, its occurrence can be irregular and appear very rarely, once a month or even a year. But over time, attacks of arrhythmia become more frequent and can be repeated daily (in severe forms).
To determine the onset of an attack, you should pay attention to the typical symptoms that accompany it:
- a significant fluctuation in the heartbeat is felt;
- increased pulsation of the neck veins;
- loss of muscle strength;
- excessive sweating;
- dizziness;
- heart pain of an angina nature (painful, pressing sensations behind the sternum, which can radiate to the left arm, jaw or neck);
- dyspnea;
- panic attacks, which manifest themselves as increased feelings of anxiety and fear;
- in rare cases, presyncope or fainting occurs.
Arrhythmia is divided into forms of its manifestation, in which the heart rhythm and heart rate are modified. There are also atypical symptoms of the passage of attacks.
- With bradycardia, a decrease in rhythm of less than 60 beats per minute is observed. This condition is characterized by convulsions and loss of consciousness, which can last no more than a minute, or even a couple of seconds.
- With tachycardia, the heart rate increases to 100 or more beats per minute. During this attack there is a severe lack of air.
- Irregular heart rhythm (atrial fibrillation), which is characterized by a sharp increase in heart rate, and then an equally sharp decrease. This is its distinguishing feature from other types of arrhythmias.
Any of the above arrhythmic paroxysms is life-threatening, since disturbances in the cardiac cycle can cause myocardial arrest.
Why is arrhythmia dangerous?
If we are talking about sinus tachycardia or bradycardia, the patient most often experiences severe discomfort during unexpected attacks: dizziness, rapid or slow heartbeat, nausea, fear. There is also general weakness and malaise.
These symptoms seriously affect your well-being, but are not life-threatening, and with the right regimen and treatment lead to complete recovery. Paroxysmal arrhythmia, which disrupts blood circulation and is an indicator of the presence of heart disease, requires a more serious attitude. Extrasystole can be deadly and indicate myocardial infarction or other serious pathologies.
How should I proceed?
Stopping an attack of arrhythmia is carried out in different ways, depending on the form of rhythm changes, its acceleration or deceleration. Doctors have developed techniques that the patient can perform independently. People who are at risk of arrhythmic conditions need to know well what to do during an attack and what manipulations can be performed.
For bradycardia
If a patient's heart rate decreases within the range of 35-40 beats per minute, the following recommendations should be followed to help increase the heart rate.
- Drink a cup of hot, strong and very sweet black tea.
- Take a bath with warm water.
- Do some physical exercises.
These manipulations help increase heart rate. However, if an attack occurs, you should call an ambulance. Attacks of bradycardia may conceal severe pathologies that, if left untreated, progress and can provoke cardiac arrest.
If the heart rate is less than 35 beats per minute, then you cannot do without outside help.
- The patient should be placed on his back, and a pillow or blanket rolled into a bolster should be placed under his feet, so that the elevation of the legs is 45 degrees.
- If the patient complains of pain in the heart or sternum, you should take the drug Nitroglycerin. The tablet is placed under the tongue, and a solution of two drops is dripped onto the sugar.
- If the patient has lost consciousness, artificial respiration must be performed. If there is no pulse, indirect cardiac massage is performed.
These measures are very limited and are used to delay time until the doctor arrives.
With tachycardia
Tachycardic attacks are marked by a strong increase in heart rate, more than 80 beats per minute. These increases can reach 200-220 beats per minute, which is very dangerous for the body.
During this attack of arrhythmia, it is important to calm down as much as possible if this is caused by an emotional change. If the condition
provoked by physical activity, you should immediately stop it and lie down to ensure complete rest. It is also necessary to ensure a full flow of fresh air: open windows and doors if the patient is indoors; unfasten the collar and belt, remove the tie, and if the clothes are too tight, take them off.
If after these manipulations the heart rate does not decrease, you should turn to pharmaceutical sedatives. This group includes herbal sedatives: valerian, motherwort, peony, hawthorn, as well as their complex infusions. If ineffective, you should resort to a combined sedative drug - Corvalol. The number of drops of the drug should correspond to the number of years of the patient.
The vagal technique will tell you how to relieve an attack of tachycardia. It is carried out in several steps:
- Holding your breath - you need to take a very deep breath and hold it for a while, performing a manipulation similar to pushing air.
- Pressing on the eyeballs - performed with slight force with two fingers for several minutes.
- Carotid sinus massage is a maneuver that gently massages the right carotid artery.
You should place your fingers in the area of the artery (located under the cheekbone in the cavity to the right of the Adam's apple) and massage this area with moderate pressure, periodically moving to the cervical part (located lower under the jaw). It is important not to compress the carotid artery, as this can cause loss of consciousness, which is very dangerous during an attack.
- immersion reflex - a maneuver of immersing the face in cold or ice water for several seconds, during which the heart rate automatically slows down.
A good calming move is the usual counting of numbers out loud. To do this, the patient must place the fingers of his right hand on his left wrist, feel the pulse, and count it, not paying attention to its loss. Doctors say that such manipulation is very effective for attacks due to emotional disorders.
Treatment of arrhythmia
Effective treatment of disorders of proper excitability and conduction in the heart requires not only an individual approach taking into account the existing pathology, but also a comprehensive examination for a targeted impact on the underlying cause of the disease.
The worst way to treat arrhythmias is considered to be advice from friends, because antiarrhythmic drugs require individual selection, which depends on the form of arrhythmia, the patient’s body’s response to treatment measures, the presence of concomitant diseases and simply one’s own sensitivity to the drug. One thing suits one, another suits another, so only a specialist in these matters can prescribe or advise.
However, some medications should still be considered, since patients follow new products and are very interested in their pharmacological effects.
- In case of overwhelming bradycardia, implantation of a pacemaker will be the most effective. It is recommended in cases where there are signs of AV block or heart rate drops below 40 times per minute. If the reduction in contractions is not so significant, then treatment is limited to medications.
- With atrial fibrillation, it is possible to prescribe medications during attacks, but if it is permanent, then drug therapy is required on an ongoing basis. Among the drugs, the most effective are novocainamide, quinidine, cordarone, propanorm, potassium preparations, and sedatives. In some cases, electrical cardioversion may be performed. It is most effective in the first 48 hours from the moment the flicker develops and can be medicinal or electrical. In both cases, it is aimed at coordinating the contractions of the ventricles and atria in the correct rhythm. At a later date, attempts to normalize heart function may be less effective due to the development of thrombus formation in the vessels and inevitable stroke.
As for respiratory arrhythmia, it does not require special treatment, and in the case of sinus tachycardia not associated with the act of breathing, treatment is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease that caused this pathology.