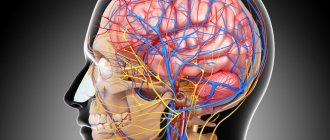
The heart is a muscular pump that ensures continuous movement of blood through the vessels. Together, the heart and blood vessels make up the cardiovascular system. This system consists of the systemic and pulmonary circulation. From the left side of the heart, blood first moves through the aorta, then through large and small arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. In the capillaries, oxygen and other substances necessary for the body enter the organs and tissues, and from there carbon dioxide, metabolic products, are removed. After this, the blood turns from arterial to venous and again begins to move towards the heart. First along the venules, then through smaller and larger veins. Through the inferior and superior vena cava, blood again enters the heart, only this time into the right atrium. A large circle of blood circulation is formed.
Venous blood from the right side of the heart is sent through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs, where it is enriched with oxygen, and returns to the heart again - this is the pulmonary circulation.
Inside, the heart is divided by partitions into four chambers. The two atria are divided by the interatrial septum into the left and right atria. The left and right ventricles of the heart are separated by the interventricular septum. Normally, the left and right parts of the heart are completely separate. The atria and ventricles have different functions. The atria store blood that flows into the heart. When the volume of this blood is sufficient, it is pushed into the ventricles. And the ventricles push blood into the arteries, through which it moves throughout the body. The ventricles have to do more hard work, so the muscle layer in the ventricles is much thicker than in the atria. The atria and ventricles on each side of the heart are connected by the atrioventricular orifice. Blood moves through the heart in only one direction. In the systemic circle of blood circulation from the left side of the heart (left atrium and left ventricle) to the right, and in the small circle from the right to the left.
The correct direction of blood flow is ensured by the valve apparatus of the heart:
Valves:
- tricuspid
- pulmonary
- mitral
- aortic
They open at the right time and close, preventing blood flow in the opposite direction.
Aortic valve
Closes the entrance to the aorta. It also consists of three valves, which look like crescents. Opens when the left ventricle contracts. In this case, blood enters the aorta. When the left ventricle relaxes, it closes. Thus, venous blood (poor in oxygen) from the superior and inferior vena cava enters the right atrium. When the right atrium contracts, it moves through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. Contracting, the right ventricle ejects blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary arteries (pulmonary circulation). Enriched with oxygen in the lungs, the blood turns into arterial blood and moves through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium, then to the left ventricle. When the left ventricle contracts, arterial blood enters the aorta through the aortic valve under high pressure and spreads throughout the body (systemic circulation).
The heart muscle is called the myocardium
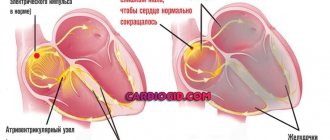
There are contractile and conductive myocardium. The contractile myocardium is the actual muscle that contracts and produces the work of the heart. In order for the heart to contract in a certain rhythm, it has a unique conduction system. The electrical impulse to contract the heart muscle occurs in the sinoatrial node, which is located in the upper part of the right atrium and spreads through the conduction system of the heart, reaching every muscle fiber
First, both atria contract, then both ventricles, thereby ensuring the flow of blood to all organs and tissues of the body. The heart muscle has two membranes (external and internal). The inner lining of the heart is called the endocardium. The outer lining of the heart is called the pericardium.
Causes and symptoms
Heart valve defects can be congenital or acquired. The main causes of the development of heart valve defects are rheumatism, infections, myocardial and cardiovascular diseases.
Congenital heart valve defects develop before birth and depend on how the pregnancy progressed. Congenital heart valve defects are an extremely rare diagnosis, diagnosed only in 1% of cases. Congenital defects include defects of the aortic and pulmonary valves, which are treated by surgical intervention in the first years of the patient’s life.
Purchased . Acquired heart valve defects include transformations of the valve structure due to infections, inflammation, previous heart attacks, etc. Most of them arise as a result of a gradual change in the structure of the heart; in some cases, rheumatism leads to the defect. All congenital and acquired defects have related symptoms that can appear at any age:
- increased heart rate,
- dyspnea,
- swelling,
- other manifestations of heart failure.
Initially, they appear during physical activity, but as pathologies develop, they will begin to appear in a calm state. Among the types of heart valve defects, mitral valve prolapse is the most common. It occurs during heart contractions when the valve leaflets in the left atrium sag. The walls of the valve lose elasticity and it “leaks”. Prolapse can be primary or secondary:
- Primary prolapse refers to congenital valve defects. Connective tissue pathologies in this case are a genetic predisposition.
- Secondary prolapse is an acquired defect. It occurs due to chest injury, rheumatism or myocardial infarction.
Prolapse does not have serious health consequences, and its symptoms do not interfere with life. However, they may not appear for a long time and most often bother people in old age, which is why they are written off as “age-related.” If you do not pay attention to the symptoms in time, complications may arise, such as arrhythmia and heart failure.
Symptoms also include complaints of pain in the heart area. They arise against the background of anxiety, are not associated with physical activity and are not relieved with medication. The pain is not intense, but long-lasting, accompanied by anxiety and rapid heartbeat.
Conduction system of the heart
The heart, like any organ, has its own nervous system. The nervous system of the heart has several levels. The first and main pacemaker of the heart is the sinus node, located in the right atrium. It is subject to the atrioventricular node, which is located on the border between the atria and ventricles and quite often slows down the heart rate set by the sinus node. Then the nerve impulse goes to the ventricles of the heart along the branches of the Hiss bundle, which are divided into the smallest nerve endings - Purkinje fibers.
Diagnosis and treatment
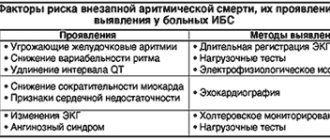
If you or your loved ones are experiencing the symptoms described above, we recommend getting tested. During diagnosis, the doctor monitors heart parameters at rest and during exercise.
The patient is prescribed:
- daily ECG monitoring,
- echocardiography (ECHO-CG),
- chest x-ray,
- CT and MRI using special equipment that allows you to examine the heart virtually between beats.
Such diagnostics are carried out not only during the initial examination of patients with suspected disease, but also in dispensary groups of patients with an already confirmed diagnosis.
Depending on the diagnostic results, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment: therapy or surgery.
- Therapy is aimed at preventing, preventing and alleviating relapses of the disease that became the root cause of the defect, as well as treating heart failure.
- Surgical intervention is an extreme necessity, which due to age or complications may not be prescribed for all patients.
Typically, heart valve disease is a mechanical problem that can only be solved with surgery performed by a surgeon. For stenosis, an operation is indicated to separate the fused valve leaflets and widen the atrioventricular opening - commissurotomy. If there is insufficiency, prosthetics are performed: replacement with a biological or mechanical analogue.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy does not occur due to myocardial malnutrition, tumor or inflammation. This diagnosis is largely collective and belongs to the group of heart diseases of unknown origin. It manifests itself as dystrophic changes in cardiomyocytes (heart cells) and against their background the performance of the cardiac ventricles is often impaired.
Understanding how to identify heart pain in cardiomyopathy is not easy because the disease changes as it progresses. It will not be possible to relieve discomfort by taking Nitroglycerin, and initially the loads do not in any way affect the intensity of the manifestations of the disease.
In the early stages, patients have ambiguous symptoms of heart pain, namely:
- the nature of the pain can be anything;
- unpleasant sensations are transmitted to various places;
- The pain is not severe, but it does not stop.
As cardiomyomaty develops, the heart does not hurt so often, but the disease begins to manifest itself in attacks, especially after physical exertion. The resulting unpleasant sensations are sometimes relieved by Nitroglycerin. At an advanced stage, it is easier to answer what exactly hurts, since the painful focus has already been formed and has a specific localization.
Muscles, skin
When a person smiles, 17 muscles work.
The strongest muscle in the human body is the tongue.
The smallest muscle is the stapes muscle. When the sounds are too strong, she turns the stirrup so that the ratio of the lengths of the arms of the bone-lever changes, and the sound amplification factor drops.
It is impossible to accurately indicate the number of muscles. Experts count from 400 to 680 muscles in humans. For comparison: grasshoppers have about 900 muscles, some caterpillars have up to 4000. The total muscle weight in a man is about 40% of his body weight, and in a woman it is about 30%.
Man is the only representative of the animal world capable of drawing straight lines.
During a lifetime, a person's skin changes approximately 1000 times.
Diseases
Cardiovascular diseases are the most common cause of death in the world. Of these, more than three-quarters are the result of coronary artery disease and stroke. Risk factors include:
- smoking;
- overweight, sedentary lifestyle;
- high cholesterol;
- high blood pressure and others.
Cardiovascular disease often has no symptoms but can cause chest pain and difficulty breathing.
The operation that changed everything
Surgeons dreamed of learning how to transplant a heart a century and a half ago. But Christian Barnard was the first to perform such a phenomenal operation, and it happened in South Africa, in the city of Cape Town, on December 3, 1967. The patient was businessman Louis Washkansky, and his posthumous donor was a 19-year-old woman who died in an accident. Alas, Louis died 18 days later, but the cause was not heart disease, but bilateral pneumonia. Today, after transplants, people live 10, 20 or more years. The world record for living with a “foreign” heart is 32 years, and, it should be noted, in the latter case the patient did not die from problems associated with the operation.
Stomach, intestines
Human gastric juice contains 0.4% hydrochloric acid (HCl).
For one square millimeter of the gastric mucosa there are about one hundred glands that secrete digestive juice.
The small intestine, where digested food is absorbed into the blood, has about 5 million villi on its inner surface - the finest hair-like outgrowths through which nutrients are absorbed.
During life, the human small intestine is about 2.5 meters long. After his death, when the muscles of the intestinal wall relax, its length reaches 6 meters.
Physiology - the principle of operation of the human heart
Let's take a closer look at the principles and patterns of heart function.
Cardiac cycle
When an adult is calm, his heart beats in the range of approximately 70-80 cycles per minute. One pulse beat equals one cardiac cycle. At this speed of contraction, one cycle is completed in approximately 0.8 seconds. Of which, the contraction time of the atria is 0.1 seconds, the ventricles are 0.3 seconds, and the relaxation period is 0.4 seconds.
The frequency of the cycle is set by the cardiac pacemaker (the area of the heart muscle in which impulses arise that regulate the heart rate).
The following concepts are distinguished:
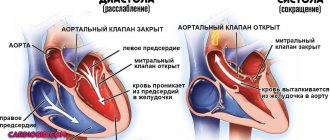
- Systole (contraction) - this concept almost always means contraction of the ventricles of the heart, which leads to a push of blood through the arterial bed and maximization of pressure in the arteries.
- Diastole (pause) is a period when the heart muscle is in the stage of relaxation. At this moment, the chambers of the heart fill with blood and the pressure in the arteries decreases.
So, when measuring blood pressure, two indicators are always recorded. Let's take the numbers 110/70 as an example, what do they mean?
- 110 is the top number (systolic pressure), that is, the pressure of the blood in the arteries at the moment of heart contraction.
- 70 is the lower number (diastolic pressure), that is, this is the pressure of the blood in the arteries at the moment the heart relaxes.
A simple description of the cardiac cycle:
- Cardiac cycle (animation)
At the moment of relaxation of the heart, the atria, and even the ventricles (through open valves), fill with blood.
- Atrial systole (contraction) occurs, allowing blood to completely move from the atria to the ventricles. Contraction of the atria begins at the point where the veins flow into it, which guarantees initial compression of their mouths and the inability of blood to flow back into the veins.
- The atria relax, and the valves separating the atria from the ventricles (tricuspid and mitral) close. Ventricular systole occurs.
- Ventricular systole pushes blood into the aorta through the left ventricle and into the pulmonary artery through the right ventricle.
- This is followed by a pause (diastole). The cycle repeats.
Conventionally, for one pulse beat there are two heart contractions (two systoles) - first the atria contract, and then the ventricles. In addition to ventricular systole, there is atrial systole. Contraction of the atria is of no value when the heart is working steadily, since in this case the time of relaxation (diastole) is enough to fill the ventricles with blood. However, once the heart starts beating faster, atrial systole becomes crucial - without it, the ventricles simply would not have time to fill with blood.
The push of blood through the arteries occurs only when the ventricles contract; it is these push-contractions that are called the pulse.
Heart muscle
The uniqueness of the heart muscle lies in its ability to perform rhythmic automatic contractions, alternating with relaxations, which occur continuously throughout life. The myocardium (the middle muscular layer of the heart) of the atria and ventricles is divided, which allows them to contract separately from each other.
Cardiomyocytes are muscle cells of the heart with a special structure that allows them to transmit a wave of excitation in a particularly coordinated manner. So there are two types of cardiomyocytes:
- ordinary workers (99% of the total number of cardiac muscle cells) - designed to receive a signal from the pacemaker through conducting cardiomyocytes.
- special conducting (1% of the total number of cardiac muscle cells) cardiomyocytes - form the conducting system. In their function they resemble neurons.
Like skeletal muscles, the heart muscle can increase in volume and increase its efficiency. The heart capacity of endurance athletes can be 40% larger than that of the average person! We are talking about beneficial hypertrophy of the heart, when it stretches and is able to pump more blood in one beat. There is another hypertrophy called “athletic heart” or “bull heart”.
The bottom line is that in some athletes the mass of the muscle itself increases, and not its ability to stretch and push large volumes of blood. The reason for this is irresponsibly designed training programs. Absolutely any physical exercise, especially strength training, should be based on cardio training. Otherwise, excessive physical stress on an unprepared heart causes myocardial dystrophy, which will lead to early death.
Conduction system of the heart
The conduction system of the heart is a group of special formations consisting of non-standard muscle fibers (conducting cardiomyocytes) and serving as a mechanism for ensuring the coordinated functioning of the parts of the heart.
Pulse path
This system ensures automatism of the heart - excitation of impulses generated in cardiomyocytes without an external stimulus. In a healthy heart, the main source of impulses is the sinoatrial (sinus) node. He is the leader and blocks the impulses from all other pacemakers. But if any disease occurs that leads to sick sinus syndrome, then other parts of the heart take over its function. Thus, the atrioventricular node (automatic center of the second order) and the His bundle (AC of the third order) are able to activate when the sinus node is weak. There are cases when secondary nodes enhance their own automaticity even during normal operation of the sinus node.
The sinus node is located in the upper posterior wall of the right atrium in close proximity to the mouth of the superior vena cava. This node initiates pulses with a frequency of approximately 80-100 times per minute.
The atrioventricular node (AV) is located in the lower part of the right atrium in the atrioventricular septum. This septum prevents the impulse from propagating directly into the ventricles, bypassing the AV node. If the sinus node is weakened, then the atrioventricular node will take over its function and begin to transmit impulses to the heart muscle at a frequency of 40-60 contractions per minute.
Next, the atrioventricular node passes into the His bundle (the atrioventricular bundle is divided into two legs). The right leg rushes towards the right ventricle. The left leg is divided into two more halves.
The situation with the left bundle branch has not been fully studied. It is believed that the left leg with fibers from the anterior branch rushes to the anterior and lateral wall of the left ventricle, and the posterior branch supplies fibers to the posterior wall of the left ventricle and the lower parts of the lateral wall.
In case of weakness of the sinus node and atrioventricular block, the His bundle is capable of creating impulses at a speed of 30-40 per minute.
The conduction system deepens and further branches into smaller branches, eventually passing into Purkinje fibers, which penetrate the entire myocardium and serve as a transmission mechanism for contraction of the ventricular muscles. Purkinje fibers are capable of initiating impulses at a frequency of 15-20 per minute.
Exceptionally trained athletes can have a normal resting heart rate down to the lowest recorded figure of just 28 beats per minute! However, for the average person, even one leading a very active lifestyle, a heart rate below 50 beats per minute may be a sign of bradycardia. If your heart rate is this low, you should be examined by a cardiologist.
Heartbeat
A newborn's heart rate may be around 120 beats per minute. As a person gets older, the pulse stabilizes between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Well-trained athletes (we are talking about people with well-trained cardiovascular and respiratory systems) have a heart rate of 40 to 100 beats per minute.
The rhythm of the heart is controlled by the nervous system - the sympathetic strengthens contractions, and the parasympathetic weakens.
Cardiac activity, to a certain extent, depends on the content of calcium and potassium ions in the blood. Other biologically active substances also contribute to the regulation of heart rhythm. Our heart may begin to beat faster under the influence of endorphins and hormones released when listening to our favorite music or kissing.
In addition, the endocrine system can have a significant impact on the heart rhythm - both the frequency of contractions and their strength. For example, the release of the well-known adrenaline by the adrenal glands causes an increase in heart rate. The hormone with the opposite effect is acetylcholine.
Heart sounds
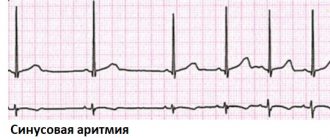
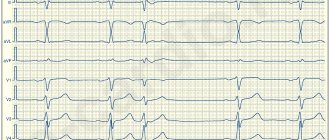
One of the simplest methods for diagnosing heart disease is to listen to the chest using a stethoscope (auscultation).
In a healthy heart, during standard auscultation, only two heart sounds are heard - they are called S1 and S2:
- S1 is the sound heard when the atrioventricular (mitral and tricuspid) valves close during ventricular systole (contraction).
- S2 - the sound heard when the semilunar (aortic and pulmonary) valves close during diastole (relaxation) of the ventricles.
Each sound consists of two components, but to the human ear they merge into one due to the very short period of time between them. If, under normal conditions of auscultation, additional tones become audible, this may indicate some kind of disease of the cardiovascular system.
Sometimes additional abnormal sounds may be heard in the heart, called a heart murmur. As a rule, the presence of murmurs indicates some kind of heart pathology. For example, noise can cause blood to flow back in the opposite direction (regurgitation) due to malfunction or damage to a valve. However, noise is not always a symptom of a disease. To clarify the reasons for the appearance of additional sounds in the heart, it is worth doing echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart).
Personality transplant?
Science still does not have a clear explanation for this fact, but people who have survived a heart transplant often experience radical changes in their tastes, habits and preferences. In particular, one of the magazines described the case of an American woman named Debbie, who was a staunch teetotaler, hated fast food restaurants and listened only to classics. She won the heart of an 18-year-old black boy who loved beer and fried chicken and only listened to rap. Opening her eyes after anesthesia, Debbie realized that she wanted a can of beer. When she left the hospital, the first thing she did was go to McDonald's, although she had previously hated it. Is it any wonder that she fell out of love with classical music and started listening to rap?
Hair
Human hair is approximately 5,000 times thicker than soap film.
The length of hair on the head grown by the average person over the course of a lifetime is 725 kilometers.
Blondes grow a beard faster than brunettes.
The hair growth rate is approximately 0.3-0.35 mm per day, that is, 12 cm per year, the lifespan of hair is 2-4 years; Considering that the total number of hairs on the head of redheads is about 80,000, that of brunettes is 100,000, and that of blondes is 140,000, then over the course of a lifetime, the average person grows hair to a total length of up to 1,008,000 kilometers (you can wrap the earth around the equator 22 times).
Every day a person loses from 30 to 120 hairs.
Hair grows fastest between the ages of 15 and 30. Hair growth slows down after 50. In summer, by the way, hair grows faster than in winter.
The hair can be stretched to 1/5 of its length, and after that it returns to its original state.
The strength of the hair is comparable to aluminum and can withstand a load of 100 to 200 g.
Hair is hygroscopic, that is, it is able to absorb moisture - this is due to the structure of the hair.
Hair is resistant to weak acids, but does not tolerate alkaline compounds well.
Hair can accumulate certain substances, which allows it to be used as an identifier.
The lifespan of hair is different: on average, men have 2 years on their heads, and women have 4-5 years.
Redheads have the thickest hair, but less hair than others.
Black hair is the largest of all, and can be 3 times thicker than blonde hair.
The baby's first hairs appear in the womb, at about 4-5 months of pregnancy.
Hair grows at an average rate of 0.4 mm per day.
As you age, your hair becomes shorter and thinner.
Women are less likely to go bald than men because women's hair roots are 2 millimeters deeper in the skin than men's.
Human skin is 95% covered with hair.
During the day, each hair lengthens by about 0.35 mm.
The optimal water temperature for washing hair is 35-45°C.
84% of women improve their mood by going to the hairdresser.
According to American experts, 60-70% of men and 25-40% of women suffer from hair loss.
From each hair follicle, about 20 hairs grow sequentially throughout life.
Ear, hearing
There are about 25,000 cells in the inner ear that respond to sound. The range of frequencies perceived by hearing lies between 16 and 20,000 hertz. It decreases with age, especially due to decreased sensitivity to high-pitched sounds. By the age of 35, the upper limit of hearing drops to 15,000 hertz.
The ear is most sensitive to the range of 2000-2300 hertz. The best ear for music (the ability to distinguish pitch) is in the region of 80-600 hertz. Here our ear is able to distinguish, for example, two sounds with a frequency of 100 hertz and 100.1 hertz. In total, a person distinguishes between 3-4 thousand sounds of different pitches.
We become aware of sound 35-175 milliseconds after it reaches the ear. It takes another 180-500 milliseconds for the ear to “tune in” to receive a given sound and achieve the best sensitivity.
Functions of the heart - why do we need a heart?
Our blood provides the entire body with oxygen and nutrients. In addition, it also has a cleansing function, helping in the removal of metabolic waste.
The function of the heart is to pump blood through blood vessels.
How much blood does the human heart pump?
The human heart pumps from 7,000 to 10,000 liters of blood in one day. This amounts to approximately 3 million liters per year. That works out to 200 million liters over a lifetime!
The amount of blood pumped per minute depends on the current physical and emotional load - the greater the load, the more blood the body requires. So the heart can conduct from 5 to 30 liters through itself in one minute.
The circulatory system consists of about 65 thousand vessels, their total length is about 100 thousand kilometers! Yes, we didn't make a mistake.
First aid for heart pain
Medicines for heart pain are prescribed by the attending physician based on the diagnosis. Trying to select medications on your own is prohibited, as you may worsen your condition. But what if the attack comes suddenly? In such a situation, the following instructions will help you understand how to get rid of heart pain:
- First you need to stop running around looking for medicine. Instead, you need to calm down and sit down.
- The room should be well ventilated.
- Breathing should not be limited by clothing, so it is better to unbutton the top buttons.
- If possible, you should lie down. If the pain subsides, then it is quite possible that the problem is not in the heart muscle. With increasing discomfort and a feeling of squeezing, we can talk about an imminent attack.
- To improve the condition, you need to put medicine for heart pain under your tongue - for example, a Nitroglycerin tablet, and then call an ambulance.
After the medical team arrives, it is necessary to list the painful symptoms to the doctors and tell them what actions have been taken since the onset of the attack. All this will help to quickly normalize the condition, since you can relieve pain in the heart only by knowing the whole picture.
Pain in the chest has different manifestations. From them you can roughly understand what is tormenting a person. However, only the attending physician can make an accurate diagnosis, focusing on the symptoms that arise and the results of examinations. Finding on your own what to take for heart pain is life-threatening - there are many diseases that only masquerade as pain in the chest area.
Eyes, vision
The human eye is capable of distinguishing 10,000,000 shades of color. Women blink approximately 2 times more often than men - 6,205,000 times a year, with each blink lasting 0.3 seconds. It is not difficult to calculate that by blinking, we keep our eyes closed for 21.5 days a year.
It is impossible to sneeze with your eyes open.
People with blue eyes are more sensitive to pain than others.
One eyeball weighs 28 grams.
If you like to download free books from the Internet, keep in mind that our eyes perceive printed information from a computer screen 25% slower than from a paper sheet.
Men are about 10 times more likely than women to suffer from color blindness.
The eye is able to distinguish a well-lit object with a diameter of one tenth of a millimeter at a distance of 25 centimeters. But if the object itself glows, it can be much smaller.
A hole with a diameter of 3-4 thousandths of a millimeter, pierced in a sheet of tin, behind which a light bulb is lit, is clearly visible to the normal eye.
The eye is capable of distinguishing 130-250 pure color tones and 5-10 million mixed shades.
Complete adaptation of the eye to darkness takes 60-80 minutes.