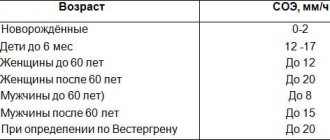
EDS (blood test) - what is it? How is it carried out? Why is it needed? To fully understand these issues, it is necessary to refer to some medical information and data provided by a variety of diagnostic laboratories. In fact, understanding what we are talking about is not as difficult as it seems. Almost every citizen of a particular country sooner or later encounters EDS diagnostics. What is she like?
Description
It's simple. EDS - blood test. What is it in general and what diseases is it used to diagnose? The thing is that a similar abbreviation is used to describe the method for determining syphilis in the blood. A kind of analogue of the name of the Wasserman reaction.
In diagnostic laboratories you can see this analysis in the form of the inscription “Reaction to RW”. Many people are familiar with this procedure. Especially women. The population is tested for syphilis not only if it is suspected, but also simply for the sake of checking the body. For example, during pregnancy.
EDS (blood test) - what is it? As already mentioned, a method for diagnosing syphilis in the blood. Or Wasserman's reaction. There are no special features for the patient. How is the analysis carried out?
Carrying out analysis
The diagnostic technique is extremely simple. Especially for patients. They are required to do a little preparation for submitting biological material, but nothing more. It will be discussed later.
EDS (blood test) - what is it? A test that helps determine the presence of syphilis in the human body. A unique method of diagnosing the disease using blood.
A person comes to the laboratory and donates some venous blood. Next, the laboratory begins to work with the resulting biomaterial. A special solution is mixed with the patient’s blood, then, after some time, the reaction is examined. If it is present, the person has encountered syphilis. Otherwise the patient is completely healthy. Diagnostic time in the laboratory is about half an hour.
Preparing for analysis
How to take a blood test for EDS? More precisely, how should you prepare for the study? The laboratory does not provide any special instructions or recommendations. But to obtain a more accurate result, it is advisable to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol several days before taking biological material for research.
It is also important to donate blood on an empty stomach. It is recommended not to eat food 8 hours before the test. It is advisable to exclude too spicy, salty and sweet foods from your diet 2-3 days before your visit to the laboratory. This is the only way to achieve maximum results.
Negative analysis
Next, we can talk a little about how this analysis is deciphered. It's not all that difficult to understand. EDS (blood test) - what is this test? It is clear for what purposes it is being carried out. And what it represents, too. But how to interpret the results obtained?
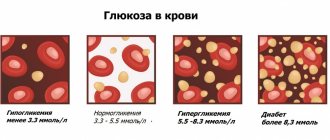
Using the previously stated method, the laboratory will look for antibodies to syphilis proteins in the blood. Blood test (EDS) negative? This means that the human body has not encountered the specified disease. That is, he is healthy. And I never had anything to do with syphilis.
This is exactly the result that patients expect when they take an EDS test. But this is not the only response. What other options might there be after research?
How to determine the extent of damage?
It can give both positive and negative results. The more serious the defeat is, the more advantages there are in the indicators.
- weakly positive reaction - + and ++ (if plus one, then the result is doubtful);
- positive — +++;
- strongly positive - ++++.
Based on the results of the analysis, antibody titers are indicated. When conducting a therapy monitoring study, titers help determine whether the patient is recovering. As a rule, after treatment the patient is under the supervision of specialists for a year. During this period, he is tested several times. The effectiveness of therapy is also evidenced by a decrease in titers over the year by four or more times. In the absence of IgM immunoglobulins in the blood, we can talk about the absence of resumption of infection. The presence of IgG is possible for a long time after treatment, and sometimes even throughout life.
Positive result
For example, a positive EDS blood test result. It occurs when a person’s blood, after mixing it with a special solution, produces antibodies to syphilis.
Accordingly, it can be judged that the patient’s body has encountered a disease. It makes no sense to talk about the norm for this analysis. After all, it shows whether there is syphilis or not.
Typically, laboratories simply provide the public with a printout that tells them whether antibodies to the disease have been found or not. But sometimes clinics offer an extended display of the result.
Cell classes
The man decided to take a blood test for EDS. What is this? How is the analysis by cell class interpreted? Understanding this is not as difficult as it seems. People with medical education know that in the presence of a particular disease, the body begins to produce either IgG cells or IgG cells. From them you can easily understand whether a person has encountered syphilis or any other disease.
Decryption can happen like this:
- Recent infection with syphilis. Then lgM antibodies are produced approximately 7 days after encountering the virus.
- A relatively recent disease. If syphilis has been living in the body for about a month, then IgG antibodies begin to be produced. IgG also persists after successful treatment of syphilis. In other words, the presence of such antibodies is not only an indicator of recent infection, but also an indicator of the development of stable immunity to the disease.
- Secondary disease. This is possible if the result is a negative reaction, but there is IgG. The so-called credits are also written nearby. Depending on them, the real result will be interpreted. Either the person simply has a strong immune system, or he gets sick with syphilis again.
What is EMF: explanation in simple words
EMF is understood as the specific work of external forces to move a single charge in the circuit of an electrical circuit. This concept in electricity involves many physical interpretations related to various areas of technical knowledge. In electrical engineering, this is the specific work of external forces that appears in inductive windings when an alternating field is induced in them. In chemistry, it means the potential difference that occurs during electrolysis, as well as during reactions accompanied by the separation of electrical charges.
What is a photoresistor?
Read more
Marking of SMD transistors.
Read more
How to make a motion sensor with your own hands.
Read more
In physics, it corresponds to the electromotive force created at the ends of an electrical thermocouple, for example. To explain the essence of EMF in simple words, you will need to consider each of the options for its interpretation. Before moving on to the main part of the article, we note that EMF and voltage are very similar concepts in meaning, but they are still somewhat different. In short, the EMF is on the power source without a load, and when a load is connected to it, it is already a voltage. Because the number of volts on the power supply under load is almost always slightly less than without it. This is due to the internal resistance of power sources such as transformers and galvanic cells.
Additional material on the topic: In simple words about voltage converters.
Electromotive force (emf), a physical quantity characterizing the action of third-party (non-potential) forces in direct or alternating current sources; in a closed conducting circuit is equal to the work of these forces to move a single positive charge along the circuit. If we denote the field strength of external forces by Etr, then the emf in a closed loop (L) is equal to , where dl is the element of the loop length. The potential forces of an electrostatic (or stationary) field cannot maintain a constant current in the circuit, since the work of these forces on a closed path is zero. The passage of current through the conductors is accompanied by the release of energy - heating of the conductors.
Third-party forces set in motion charged particles inside current sources: generators, galvanic cells, batteries, etc. The origin of third-party forces can be different. In generators, external forces are forces from the vortex electric field that arises when the magnetic field changes over time, or the Lorentz force acting from the magnetic field on electrons in a moving conductor; in galvanic cells and batteries - these are chemical forces, etc. Emf determines the current strength in the circuit at a given resistance (see Ohm's law). EMF, like voltage, is measured in volts.
What is EMF.
About credits
Now the answer to the question about EDS (blood test) “what is it” is clear. Its decoding is also more or less clear. What titers can be seen for antibodies of one type or another? And how can they determine whether a person has syphilis? It's simple, you just need to take into account the following indicators:
- with one minus, there is no syphilis;
- with one plus the result is doubtful;
- 2 pluses - weakly positive, the likelihood of disease is low;
- 3 pluses - there is syphilis;
- 4 pluses - strongly positive, recent infection.
In this case, you can carry out any other diagnosis of syphilis. And take into account all the results. If they are also positive, the person is sick. Otherwise there is nothing to be afraid of.
Electromotive force (EMF) of the energy source
To maintain an electric current in a conductor, an external energy source is required, which constantly creates a potential difference between the ends of this conductor. Such energy sources are called electrical energy sources (or current sources). Sources of electrical energy have a certain electromotive force (abbreviated EMF), which creates and maintains a potential difference between the ends of the conductor for a long time.
Expert commentary
Lagutin Vitaly Sergeevich
Engineer with a degree in Computer Software and Automated Systems, MEPhI, 2005–2010.
Ask a Question
It is sometimes said that emf creates an electric current in a circuit. We must remember that this definition is conventional, since we have already established above that the reason for the emergence and existence of electric current is the electric field.
A source of electrical energy produces a certain amount of work by moving electrical charges throughout a closed circuit. The unit of measurement of electromotive force is the volt (abbreviated volt is denoted by the letter B or V - “ve” in Latin). The emf of a source of electrical energy is equal to one volt if, when moving one coulomb of electricity throughout a closed circuit, the source of electrical energy does work equal to one joule:
Electromotive force (EMF) of an energy source.
In practice, both larger and smaller units are used to measure EMF, namely:
- 1 kilovolt (kV, kV), equal to 1000 V;
- 1 millivolt (mV, mV), equal to one thousandth of a volt (10-3 V),
- 1 microvolt (μV, μV), equal to one millionth of a volt (10-6 V).
Obviously, 1 kV = 1000 V; 1 V = 1000 mV = 1,000,000 μV; 1 mV = 1000 µV.
Currently, there are several types of electrical energy sources. For the first time, a galvanic battery was used as a source of electrical energy, consisting of several zinc and copper circles, between which skin soaked in acidified water was laid. In a galvanic battery, chemical energy was converted into electrical energy (this will be discussed in more detail in Chapter XVI). The galvanic battery got its name from the Italian physiologist Luigi Galvani (1737-1798), one of the founders of the doctrine of electricity.
Numerous experiments on the improvement and practical use of galvanic batteries were carried out by the Russian scientist Vasily Vladimirovich Petrov. At the beginning of the last century, he created the world's largest galvanic battery and used it for a number of brilliant experiments. Sources of electrical energy that work on the principle of converting chemical energy into electrical energy are called chemical sources of electrical energy.
Good to know: How to calculate the power of an electric current.
Another main source of electrical energy, widely used in electrical and radio engineering, is the generator. In generators, mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. In chemical sources of electrical energy and in generators, the electromotive force manifests itself in the same way, creating a potential difference at the source terminals and maintaining it for a long time.
These terminals are called the poles of the electrical energy source. One pole of an electrical energy source has a positive potential (lack of electrons), is indicated by a plus sign (+) and is called the positive pole.
The other pole has a negative potential (excess electrons), is indicated by a minus sign (—) and is called the negative pole. From sources of electrical energy, electrical energy is transmitted through wires to its consumers (electric lamps, electric motors, electric arcs, electric heating devices, etc.).
It will be interesting➡ What is a bridge rectifier and how does it work?
Examples of problem solving
For each position in the first column, select the corresponding position in the second:
| PHYSICAL QUANTITIES | FORMULAS |
| Electromotive force | |
| Current strength | |
| Resistance | |
| Potential difference |
Solution: The electromotive force of a galvanic cell is a quantity numerically equal to the work of external forces when moving a single positive charge inside the element from one pole to the other.
The work of external forces cannot be expressed through a potential difference, since external forces are non-potential and their work depends on the shape of the trajectory of the charges.
EMF is determined by the formula:
The current strength is determined by the formula:
Resistance is determined by the formula:
The potential difference is determined by the formula:
Correct answer:
| PHYSICAL QUANTITIES | FORMULAS |
| Electromotive force | |
| Current strength | |
| Resistance | |
| Potential difference |
FAQ
What is electromotive force?
This is the ratio of the work of external forces when moving a charge along a closed circuit to the absolute value of this charge.
What is an electrical circuit?
A set of devices that are connected by conductors, designed to allow current to flow.
What does Ohm's law sound like for a complete circuit?
The current strength in a complete circuit is equal to the ratio of the circuit's emf to its total resistance.
Errors
EDS (blood test) - what is it? A modern, although not entirely accurate, method for diagnosing syphilis in humans. It is worth paying attention to the fact that a positive result may be false. Therefore, there is no need to panic when you see that the body is producing antibodies to the disease.
First, it is recommended to retake the test. Or choose a different method for diagnosing syphilis. EDS is a study that has certain errors.
Secondly, as already mentioned, the presence of antibodies to a disease may mean the development of immunity to the disease. For example, due to the characteristics of the organism.
Thirdly, the presence of bad habits, as well as chronic diseases, can lead to a positive test result. In girls, even menstruation affects it.
Accordingly, EDS is a fairly quick rapid test for syphilis, which has certain errors. 100% accuracy is given only to perfectly healthy people. But in practice, such research is in great demand. Now it is clear how to donate blood for EDS, what it is, how the analysis is deciphered, and what are the factors influencing the accuracy of the study.
Laboratory detection of the causative agent of syphilis
Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis) belongs to gram-negative bacteria of the spirochete species. In 95% of cases, infection occurs through unprotected intimacy. Contagiousness (infectiousness) is manifested by the concentration of bacteria in the secretory fluids of an infected person (sperm, vaginal secretions) and microscopic damage to the mucous membranes of the partner.
The bacterium enters the intercellular junctions of the endothelium, cells and tissues, and multiplies in the lymph nodes. The high virulence of treponema pallidum ensures the rapid spread of infection throughout the body through the blood and lymph flow.
Treponema pallidum is not detected under a light microscope and does not grow on nutrient media, which excludes conventional microscopic analysis and bacteriological culture (bacteriological culture) from laboratory practice. The bacterium can only be detected in blood serum through serological tests.
RPR in the list of diagnostic methods for determining Treponema pallidum
Serological blood testing is based on the body’s immune reactions: the interaction of antigens (bacteria or viruses) that have entered the blood and Ig immunoglobulins - specific blood plasma proteins responsible for the differentiation and destruction of antigens.
Reference! Antibodies to foreign pathogens are called immunoglobulins, and serological reactions are called antigen-antibody reactions.
Treponemal and non-treponemal tests are used to diagnose syphilis. Treponemal testing is a complex and expensive method using actual Treponema pallidum antigens. They are necessary to confirm the diagnosis in case of false positive results.
The list includes reactions:
- immunofluorescence (RIF);
- immobilization of Treponema pallidum (RIBT);
- passive hemagglutination (RPHA).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunochemiluminescence (ICL) are similar. In non-treponemal tests, cheap nonspecific antigens are used for the antigen-antibody reaction and immunoglobulins are not separated by titers, but their total amount is determined. Non-treponemal studies include RPR, which is used to quickly diagnose syphilis.