Thyrotoxicosis
Hepatitis
Diabetes
51022 06 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable; the information below is for reference only.
Glucose (in blood) (Glucose): indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of results and normal indicators.
General information
In the body, all metabolic processes occur in close connection. When they are violated, various diseases and pathological conditions develop, including increased blood
glucose Nowadays people consume very large amounts of sugar, as well as easily digestible carbohydrates. There is even evidence that their consumption has increased 20 times over the last century. In addition, people's health has recently been negatively affected by the environment and the presence of large amounts of unnatural food in the diet. As a result, metabolic processes are disrupted in both children and adults. Lipid metabolism is disrupted, and the load on the pancreas, which produces the hormone insulin, .
Already in childhood, negative eating habits are developed - children consume sweet soda, fast food, chips, sweets, etc. As a result, too much fatty food contributes to the accumulation of fat in the body. The result is that symptoms of diabetes can appear even in teenagers, whereas previously diabetes was considered a disease of older people. Nowadays, people experience signs of increased blood sugar very often, and the number of cases of diabetes in developed countries is now increasing every year.
Glycemia is the level of glucose in a person’s blood. To understand the essence of this concept, it is important to know what glucose is and what the glucose levels should be.
Glucose - what it is for the body depends on how much of it a person consumes. Glucose is a monosaccharide , a substance that is a kind of fuel for the human body, a very important nutrient for the central nervous system.
However, its excess causes harm to the body.
How to prepare
In order for the analysis results to be reliable, the patient needs to know that the examination requires certain preparation:
- Blood donation occurs on an empty stomach. The last meal should be 8 hours before the start of the procedure. Therefore, the most convenient time is morning.
- It is forbidden to drink anything except plain water.
- In two days you need to eliminate fatty foods and alcoholic drinks.
- On the day of delivery, you should not brush your teeth or chew gum.
- It is prohibited to take medications 3 days before the test. This is especially true for glycemic medications. If it is impossible to cancel, then you need to inform your doctor.
- Avoid smoking on the day of delivery.
- Do not subject the body to increased mental and physical stress during the day.
- The analysis does not fail after the patient has had a massage, x-ray, or ultrasound.
- You should not donate blood if there are signs of inflammation and infection.
It is important to follow all these rules, because the amount of sugar may change. Certain foods, physical activity, and possible stressful situations can increase or decrease blood sugar.
Before donating, some patients try to reduce the monosaccharide readings in the body using folk remedies. Such actions are unacceptable, since the real picture of the condition is distorted and the results will be invalid.
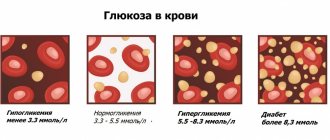
Normal blood sugar
To understand whether serious diseases are developing, you need to clearly know what the normal blood sugar level is in adults and children. The blood sugar level, the norm of which is important for the normal functioning of the body, is regulated by insulin. But if enough of this hormone is not produced, or tissues respond inadequately to insulin, then blood sugar levels increase. An increase in this indicator is influenced by smoking, poor diet, and stressful situations.
The answer to the question of what is the normal blood sugar level for an adult is given by the World Health Organization. There are approved glucose standards. How much sugar should be in blood taken from a vein on an empty stomach (blood can be either from a vein or from a finger) is indicated in the table below. Indicators are indicated in mmol/l.
| Age | Level |
| 2 days – 1 month. | 2,8-4,4 |
| 1 month - 14 years | 3,3-5,5 |
| From 14 years (for adults) | 3,5-5,5 |
So, if the readings are below normal, it means the person has hypoglycemia , if higher, it means hyperglycemia . You need to understand that any option is dangerous for the body, since this means that disturbances occur in the body, and sometimes irreversible.
The older a person gets, the less tissue sensitivity to insulin becomes due to the fact that some of the receptors die, and body weight also increases.
It is generally accepted that if capillary and venous blood is examined, the result may fluctuate slightly. Consequently, when determining what the normal glucose level is, the result is slightly overestimated. The average rate of venous blood is 3.5-6.1, capillary blood is 3.5-5.5. The norm of sugar after eating, if a person is healthy, differs slightly from these indicators, rising to 6.6. Sugar does not rise above this level in healthy people. But don’t panic that your blood sugar is 6.6, what to do – you need to ask your doctor. It is possible that in the next study the result will be lower. Also, if during a one-time test your blood sugar is, for example, 2.2, you need to do the test again.
Norms for determining blood sugar levels before and after meals
Therefore, it is not enough to do a single blood sugar test to diagnose diabetes. It is necessary to determine the level of glucose in the blood several times, the norm of which can be exceeded within different limits each time. A performance curve must be evaluated. It is also important to compare the results with symptoms and examination data. Therefore, when receiving the results of sugar tests, if it is 12, a specialist will tell you what to do. It is likely that with glucose levels of 9, 13, 14, 16, diabetes can be suspected.
But if the norm for glucose in the blood is slightly exceeded, and the readings from a finger test are 5.6-6.1, and from a vein are from 6.1 to 7, this condition is defined as prediabetes (impaired glucose tolerance).
If the result from the vein is more than 7 mmol/l (7.4, etc.), and from the finger – above 6.1, we are talking about diabetes mellitus. To reliably assess diabetes, a test is used - glycated hemoglobin .
However, when carrying out tests, the result is sometimes determined to be lower than the norm for blood sugar in children and adults. You can find out what children's sugar norm is from the table above. So if the sugar is lower, what does that mean? If the level is less than 3.5, this means that the patient has developed hypoglycemia. The reasons that sugar is low may be physiological, or may be associated with pathologies. Blood sugar levels are used both to diagnose the disease and to assess how effective diabetes treatment and diabetes compensation is. If glucose before meals or 1 hour or 2 hours after meals is no more than 10 mmol/l, then type 1 diabetes is compensated.
In type 2 diabetes, more stringent criteria for assessment apply. On an empty stomach, the level should not be higher than 6 mmol/l; during the day, the permissible level should not be higher than 8.25.
Glucometer
Diabetics should regularly monitor their blood sugar using a glucometer . A glucometer measurement table will help you correctly evaluate the results.
What is the normal amount of sugar per day for a person? Healthy people should adequately structure their diet without overindulging in sweets, while diabetics should strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Women should pay special attention to this indicator. Since the fair sex has certain physiological characteristics, blood sugar levels in women may vary. An elevated glucose level is not always a pathology. So, when determining the normal level of blood glucose in women by age, it is important that how much sugar is in the blood is not determined during menstruation. During this period, the analysis may be unreliable.
In women over 50 years of age, during menopause , serious hormonal fluctuations occur in the body. At this time, changes occur in the processes of carbohydrate metabolism. Therefore, women over 60 years of age should have a clear understanding that they need to check their sugar regularly, while understanding what the norm of blood sugar is in women.
Blood glucose levels may also vary in pregnant women. During pregnancy , a reading of up to 6.3 is considered a normal variant. If the sugar norm in pregnant women is exceeded to 7, this is a reason for constant monitoring and the appointment of additional studies.
The blood sugar level in men is more stable: 3.3-5.6 mmol/l. If a person is healthy, the blood glucose level in men should not be higher or lower than these indicators. The normal indicator is 4.5, 4.6, etc. Those who are interested in the table of norms for men by age should note that in men after 60 years of age it is higher.
Decoding the result
Increased glucose levels (hyperglycemia)
Observed in the following diseases and conditions:
- Diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy).
- Physiological hyperglycemia, causes: moderate physical activity, strong emotions, stress, smoking, adrenaline release after injection.
- Active infectious process.
- Trauma, recent surgery.
- Endocrine system diseases:
- a) pheochromocytoma - a tumor of the adrenal glands that produces adrenaline and is characterized primarily by a persistent increase in blood pressure; b) thyrotoxicosis – a pathological condition in which the thyroid gland begins to produce too many hormones (thyroxine and/or triiodothyronine); c) acromegaly is a disease associated with a violation of the synthetic activity of the pituitary gland (a gland located in the brain). It is characterized by excess production of growth hormone, leading to changes in facial features, enlargement of the hands and feet. d) gigantism - a pathology, also associated with the pituitary gland, is hereditary in nature, the first manifestations occur in early adolescence; e) Itsenko-Cushing syndrome is a condition in which the adrenal glands produce excessive amounts of cortisol. Characterized by a violation of carbohydrate metabolism; f) somatostatinoma - a tumor of hormonally active cells of the pancreas or cells located in the wall of the duodenum, secreting somatostatin; g) polycystic ovary syndrome - a symptom complex accompanied by the formation of cysts in the ovaries, menstrual irregularities, excess body weight, and infertility.
- Diseases of the pancreas (acute and chronic pancreatitis, pancreatitis with mumps, cystic fibrosis, hemochromatosis, pancreatic neoplasms).
- Chronic liver and kidney diseases.
- Cerebral hemorrhage, myocardial infarction.
- Taking thiazide diuretics, beta blockers, caffeine, oral contraceptives, glucocorticoids (a full list is presented in the section “What may affect the results”).
Low glucose levels (hypoglycemia)
- Patients with diabetes may experience low glucose levels in the following situations:
- a) insulin overdose; b) overdose of drugs that lower blood glucose levels; c) increased physical activity; d) skipping meals; d) drinking alcohol.
- Severe liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis, carcinoma, hemochromatosis).
- Tumor diseases: pancreatic cancer, adrenal cancer, stomach cancer, fibrosarcoma.
- Reactive hypoglycemia is a condition in which blood glucose levels decrease 1-3 hours after eating.
- Dietary disorders (prolonged fasting, malabsorption syndrome - impaired absorption of nutrients due to intestinal diseases).
- Taking large doses of alcohol.
- Intense physical activity.
- Feverish conditions.
- Taking a number of medications:
- a) beta blockers (atenolol, propranolol, etc.) – used in the treatment of coronary heart disease, hypertension; b) flecainide and quinidine (drugs for arrhythmia); c) indomethacin (painkiller); d) insulin and other hypoglycemic drugs; e) some antibiotics, antifungal drugs; e) aspirin; g) a number of antiepileptic, anti-anxiety drugs (pregabalin); h) monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of tumor or autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of high sugar
High blood sugar can be detected if a person exhibits certain symptoms. The following symptoms that appear in adults and children should alert a person:
- weakness, severe fatigue;
- increased appetite and at the same time weight loss;
- thirst and constant feeling of dry mouth;
- copious and very frequent urine output, frequent trips to the toilet at night;
- pustules , boils and other lesions on the skin, such lesions do not heal well;
- regular occurrence of itching in the groin and genitals;
- deterioration of immunity, deterioration of performance, frequent colds, allergies in adults;
- deterioration of vision, especially in people over 50 years of age.
The occurrence of such symptoms may indicate that there is increased glucose in the blood. It is important to note that signs of high blood sugar can only be expressed by some of the manifestations listed above. Therefore, even if only some symptoms of high sugar levels appear in an adult or a child, you need to get tested and determine glucose. What kind of sugar, if it is elevated, what to do - all this can be found out by consulting a specialist.
Symptoms of low sugar levels
The risk group for diabetes includes those who have a hereditary predisposition to diabetes , obesity , pancreatic disease , etc. If a person is included in this group, then a single normal value does not mean that the disease is absent. After all, diabetes mellitus very often occurs without visible signs and symptoms, in waves. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out several more tests at different times, since it is likely that in the presence of the described symptoms, elevated levels will still occur.
If such signs are present, high blood sugar during pregnancy is also possible. In this case, it is very important to determine the exact causes of high sugar. If glucose is elevated during pregnancy, your doctor should explain what this means and what to do to stabilize the levels.
It should also be taken into account that a false positive test result is also possible. Therefore, if the indicator, for example, is 6 or blood sugar is 7, what this means can be determined only after several repeated tests. What to do if in doubt, the doctor determines. For diagnosis, he may prescribe additional tests, for example, a glucose tolerance test, a sugar load test.
In what cases should you get checked?
You need to check for sugar levels in cases where the following symptoms are observed:
- frequent thirst;
- frequent urination;
- dry skin, itching;
- dry mucous membranes;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- deterioration of vision (decreased sharpness);
- fast fatiguability;
- decreased performance.
Checks are also carried out as planned, for example, during a medical examination, passing a commission, as part of a medical examination program, etc. Patients with diabetes regularly test their blood sugar - in some cases, daily monitoring is required.
How to perform a glucose tolerance test
The mentioned glucose tolerance test is carried out to determine the hidden process of diabetes mellitus; it is also used to determine malabsorption syndrome and hypoglycemia.
IGT (impaired glucose tolerance) - what it is, the attending physician will explain in detail. But if the tolerance norm is violated, then in half of the cases diabetes mellitus in such people develops within 10 years, in 25% this condition does not change, and in another 25% it completely disappears.
Tolerance analysis allows you to determine carbohydrate metabolism disorders, both hidden and obvious. It should be taken into account when conducting the test that this study allows you to clarify the diagnosis if there is doubt about it.
This diagnosis is especially important in the following cases:
- if there are no signs of an increase in blood sugar, and urine testing periodically reveals sugar;
- in the case when there are no symptoms of diabetes, but polyuria itself - the amount of urine per day increases, while the fasting glucose level is normal;
- increased sugar in the urine of the expectant mother during pregnancy, as well as in people with kidney disease and thyrotoxicosis ;
- if there are signs of diabetes, but there is no sugar in the urine, and its content in the blood is normal (for example, if sugar is 5.5, upon re-examination it is 4.4 or lower; if it is 5.5 during pregnancy, but there are signs of diabetes) ;
- if a person has a genetic predisposition to diabetes, but there are no signs of high sugar;
- in women and their children, if their weight at birth was more than 4 kg, subsequently the weight of the one-year-old child was also large;
- in people with neuropathy , retinopathy .
The test that determines IGT (impaired glucose tolerance) is carried out as follows: initially, blood is drawn from the capillaries of the person who is being tested on an empty stomach. After this, the person should consume 75 g of glucose. For children, the dose in grams is calculated differently: per 1 kg of weight 1.75 g of glucose.
Glucose tolerance test curve graph
Those who are interested in how much sugar 75 grams of glucose is, and whether it is harmful for a pregnant woman to consume such an amount, for example, should take into account that approximately the same amount of sugar is contained, for example, in a piece of cake.
Glucose tolerance is determined 1 and 2 hours after this. The most reliable result is obtained after 1 hour.
Glucose tolerance can be assessed using a special table of indicators, units – mmol/l.
| Evaluation of the result obtained | Blood capillary | Venous blood |
| Normal indicator | ||
| Before meals | 3,5 -5,5 | 3,5-6,1 |
| 2 hours after glucose, after food | up to 7.8 | up to 7.8 |
| Prediabetes condition | ||
| Before meals | 5,6-6,1 | 6,1-7 |
| 2 hours after glucose, after food | 7,8-11,1 | 7,8-11,1 |
| Diabetes | ||
| Before meals | from 6.1 | from 7 |
| 2 hours after glucose, after food | from 11, 1 | from 11, 1 |
Next, the state of carbohydrate metabolism is determined. For this, 2 coefficients are calculated:
- Hyperglycemic – shows how glucose 1 hour after a sugar load relates to fasting blood glucose. This indicator should not be higher than 1.7.
- Hypoglycemic – shows how glucose 2 hours after a sugar load relates to fasting blood glucose. This indicator should not be higher than 1.3.
It is important to be sure to calculate these coefficients, since in some cases, after a test for glucose tolerance in a person, violations are not determined by absolute indicators, and one of these coefficients is greater than the norm.
In this case, the determination of a questionable result is recorded, and then the person is at risk for diabetes mellitus.
Indications for use
If a patient exhibits symptoms similar to the characteristic features of diabetes mellitus, the doctor prescribes a sugar test. These symptoms include:
- decreased visual acuity;
- decreased level of performance, feeling of frequent fatigue;
- feeling of constant thirst;
- feeling of dryness in the mouth;
- rapid weight loss;
- itching and dry skin;
- frequent urination;
It is also recommended to take the test once a year for people at risk. These include:
- patients who have relatives with diabetes in their family;
- overweight women, men and children;
- women who gave birth to a child weighing more than four kilograms;
- patients taking glucocorticosteroids;
- people with tumor diseases;
- men and women who were diagnosed with heart or vascular disease in middle age.
Pregnancy is also a reason to examine the amount of monosaccharides in the body, since during this period there may be cases of hidden diabetes.
Glycated hemoglobin - what is it?
What blood sugar should be is determined from the tables given above. However, there is another test that is recommended for diagnosing diabetes in people. It is called a test for glycated hemoglobin - the one with which glucose is bound in the blood.
Wikipedia indicates that the analysis is called the hemoglobin HbA1C, this indicator is measured as a percentage. There is no difference by age: the norm is the same for both adults and children.
This study is very convenient for both the doctor and the patient. After all, it is permissible to donate blood at any time of the day and even in the evening, not necessarily on an empty stomach. The patient should not drink glucose and wait a certain time. Also, unlike the prohibitions that other methods suggest, the result does not depend on taking medications, stress, colds, infections - you can get tested even in this case and get the correct readings.
This study will show whether a patient with diabetes has clearly controlled blood glucose in the last 3 months.
However, there are certain disadvantages of this study:
- more expensive than other tests;
- if the patient has low levels of thyroid hormones, the result may be overestimated;
- if a person has anemia, low hemoglobin , a distorted result may be determined;
- It is not possible to go to every clinic;
- when a person takes large doses of vitamins C or E , a reduced indicator is determined, but this dependence has not been precisely proven.
What should be the level of glycated hemoglobin:
| From 6.5% | Diabetes mellitus is pre-diagnosed; observation and repeated studies are necessary. |
| 6,1-6,4% | There is a high risk of diabetes (so-called prediabetes), the patient urgently needs a low-carbohydrate diet . |
| 5,7-6,0 | There is no diabetes, but the risk of developing it is high. |
| Below 5.7 | Minimal risk. |
Measuring sugar levels with a glucometer
This method is the fastest and most convenient. For more accurate indicators, the following tips should be followed:
- Read the instructions carefully.
- It is recommended to perform a blood test on an empty stomach (on an empty stomach).
- Wash your hands with soap and rub your finger to warm it up.
- Wipe your finger with an alcohol solution.
- Prick your finger on the side with a piercing pen.
- Take a second drop of blood onto the test strip: the first is removed with cotton wool.
- After two seconds, the test result will appear on the meter screen.
To ensure accurate results, follow the specialist’s recommendations before taking the test.
Why does low blood sugar occur?
Hypoglycemia indicates that your blood sugar is low. This level of sugar is dangerous if it is critical.
If organs are not nourished due to low glucose levels, the human brain suffers. As a result, coma .
Serious consequences can occur if sugar drops to 1.9 and less - to 1.6, 1.7, 1.8. In this case, convulsions , stroke , and coma . The person’s condition is even more serious if the level is 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,
1.5 mmol/l. In this case, in the absence of adequate action, death is possible.
It is important to know not only why this indicator increases, but also the reasons why glucose can sharply decrease. Why does it happen that the test indicates that glucose is low in the body of a healthy person?
First of all, this may be due to limited food intake. With a strict diet, the body's internal reserves are gradually depleted. So, if for a large amount of time (how much depends on the characteristics of the body) a person abstains from eating, the sugar in the blood plasma decreases.
Active physical activity can also reduce sugar. Due to a very heavy load, even with a normal diet, sugar may decrease.
With excessive consumption of sweets, glucose levels increase greatly. But over a short period of time, sugar rapidly decreases. Soda and alcohol can also increase and then sharply decrease blood glucose.
If there is little sugar in the blood, especially in the morning, a person feels weak, drowsiness , and irritability . In this case, measurement with a glucometer will most likely show that the permissible value is reduced - less than 3.3 mmol/l. The value can be 2.2; 2.4; 2.5; 2.6, etc. But a healthy person, as a rule, only needs to have a normal breakfast in order for blood plasma sugar to normalize.
But if a hypoglycemia response develops, when the meter shows that the blood sugar concentration decreases when a person eats, this may be evidence that the patient is developing diabetes.
Preparing for analysis
The biomaterial for research is venous or capillary blood, which is collected according to standard algorithms.
- Blood sampling is performed in the morning (8.00 – 11.00) and strictly on an empty stomach. The last meal should be at least 8-14 hours before the procedure;
- The day before, you should not overindulge in sweets, fatty and fried foods;
- Also, the day before the test, it is necessary to exclude the consumption of alcohol and energy drinks;
- It is not recommended to smoke 3-4 hours before blood sampling;
- On the day of the examination, you need to protect yourself from any physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Insulin high and low
Why there is elevated insulin, what this means, you can understand by understanding what insulin . This hormone, which is one of the most important in the body, is produced by the pancreas. It is insulin that has a direct effect on lowering blood sugar, determining the process of transfer of glucose into body tissues from blood serum.
The normal level of insulin in the blood of women and men is from 3 to 20 µU/ml. In older people, the upper level of 30-35 units is considered normal. If the amount of the hormone decreases, the person develops diabetes .
With increased insulin, the processes of glucose synthesis from proteins and fats are inhibited. As a result, the patient exhibits signs of hypoglycemia .
Sometimes patients have elevated insulin with normal sugar levels; the reasons may be associated with various pathological phenomena. This may indicate the development of Cushing's disease , acromegaly , as well as diseases associated with liver dysfunction.
How to reduce insulin should be asked by a specialist who will prescribe treatment after a series of studies.
About glucose
Glucose nourishes the cells of the brain, nerve fibers, muscles, epidermis (skin), etc., and is the main energy resource for maintaining the vital functions of the human body. It is a monosaccharide that is formed from carbohydrates and amino acids during the breakdown of food into its constituent nutrients and other substances and fermentation (processing under the action of enzymes).
After glucose is released, most of it is absorbed into the blood and, with the help of insulin (an intrasecretory hormone of the pancreas), is delivered to the cells of the body. The liver transforms the remaining part of the monosaccharide into high molecular weight glycagon - a carbohydrate reserve. With the full production of insulin by the pancreas and the rational use of the hormone by the body's cells, a normal level of glucose is maintained in the blood, stable in relation to homeostasis (constancy of the internal environment of the body).
In the absence of disturbances, the amount of glucose formed is completely compensated by energy costs. A deviation of sugar levels from the norm in the direction of increase is called hyperglycemia, and in the direction of decrease - hypoglycemia. Glucose levels are directly affected by:
- Age.
- Nutrition.
- Neuropsychological state.
- Body mass.
- Physical activity.
- Work and rest schedule.
- Having bad habits.
- Chronic diseases.
- Pregnancy and menopause in women.
- Medicines used.
- Temporary disorders of psychosomatic health.
Abnormal blood sugar indicates a disruption in the body's metabolic processes and hormonal synthesis.
Differences between hyperglycemia after meals and on an empty stomach
Hyperglycemia is a pathological condition of the body in which the glucose level systematically exceeds the norm. If sugar levels do not return to normal within the allotted three-hour interval, it is necessary to be diagnosed with diabetes mellitus or prediabetes. The development of diabetes is considered the main cause of hyperglycemia. Other factors that influence abnormal sugar levels before and after meals include:
- chronic pancreatitis;
- hidden oncological diseases;
- increased synthesis of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism);
- incorrect hormonal therapy;
- chronic alcoholism;
- hypertension and atherosclerosis;
- deficiency of macro- and microelements and vitamins in the body;
- systematic physical overload;
- abuse of monosaccharides and disaccharides (simple carbohydrates);
- constant psycho-emotional stress (distress).
In the absence of disease, the minimum values are 3.9 mmol/l, from 2 to 4 am
The main reason for a stable increase in blood sugar and the development of diabetes is obesity. The main symptoms that may indicate hyperglycemia are:
- physical weakness, decreased ability to work and tone, quickly onset fatigue;
- dysania (sleep disorder), nervousness;
- polydipsia (permanent feeling of thirst);
- pollakiuria (frequent urge to urinate);
- systematic headaches, unstable blood pressure (blood pressure);
- polyphagia (increased appetite);
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating).
Due to the weak functioning of the immune system, acute respiratory viral infections and colds become more frequent.