Home » Departments » Hematology » Blood test for sugar, cholesterol - indications, preparation for delivery, results
Blood sugar level allows you to objectively assess the state of carbohydrate metabolism, which may be disrupted due to insufficient insulin production or a decrease in the response of cells to its effects in diabetes mellitus. Cholesterol in the blood is an equally important indicator, the increase of which indicates the risk of developing atherosclerosis - a pathology associated with its deposition on the inner wall of the arteries in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. They reduce the lumen of arterial vessels, which leads to a decrease in blood supply to the corresponding organs that feed the affected vessel.
During the consultation, a hematologist in Rostov-on-Don deciphers the results of tests showing sugar or cholesterol levels. Based on clinical data and the severity of changes in these indicators, a conclusion is made about the risk of developing metabolic disorders in the body associated with an increase in the concentration of these organic compounds.
High cholesterol - causes, consequences
The concentration of cholesterol reflects the state of fat metabolism, production, and utilization of cholesterol-containing hormones (hormones of the adrenal glands, gonads). An increase in its level develops under the influence of such provoking causal factors:
- Hereditary genetic predisposition.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Tendency to be overweight or a significant increase in a person’s body weight (obesity).
- Presence of bad habits (smoking or systematic drinking of alcohol).
- Preference for eating fatty, fried foods, pickles, and spices.
- Passion for refined carbohydrates (sweets, confectionery).
A prolonged increase in cholesterol leads to its gradual deposition in the inner wall of arterial vessels with a narrowing of their lumen. This significantly impairs the blood supply to the organs. Depending on the location of cholesterol atherosclerotic plaques, coronary heart disease, cerebral atherosclerosis (formation of plaques in the vessels of the brain), hypertension (the result of insufficient blood supply to the kidneys, which respond by producing substances that increase systemic blood pressure) can develop.
Glucose and cholesterol
What is glucose?
In the human body, glucose is the main and most universal source of energy for metabolic processes, the “single energy currency” of the body. All cells of the body have the ability to metabolize glucose.
Due to the exceptional importance of maintaining a stable level of glucose in the blood, humans have a complex system of hormonal regulation of carbohydrate metabolism parameters.
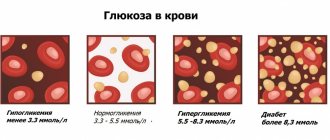
More than half of the energy consumed by a healthy body is generated through the oxidation of glucose. Glucose and its derivatives are present in most organs and tissues. The main sources of glucose are sucrose, starch from food, glycogen reserves in the liver, as well as glucose formed in synthesis reactions from amino acids and lactate. The concentration of glucose in the blood is a derivative of the activity of the processes of glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. The concentration of glucose in the blood is regulated by hormones: insulin is the main hypoglycemic factor, and other hormones - glucagon, somatotropin (GH), thyrotropin (TSH), thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), cortisol and adrenaline cause hyperglycemia (counterinsular effect). The concentration of glucose in arterial blood is higher than in venous blood, because There is a constant utilization of glucose by tissues. Glucose is not normally excreted in urine. When the level of glucose in the blood increases to 10 mmol/l (the renal threshold for glucose), it begins to appear in the urine.
Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (diagnosis and monitoring of the disease);
- pathology of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland;
- liver diseases;
- determination of glucose tolerance in individuals at risk of developing diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- pregnancy diabetes;
- impaired glucose tolerance.
Preparation for the study: on an empty stomach, no less than 8 hours (!) after the last meal, it is advisable to take blood in the morning. It is necessary to exclude increased psycho-emotional and physical stress. Material for research: serum or plasma. Execution time: 1 working day
What is total cholesterol (cholesterol, Cholesterol total)?
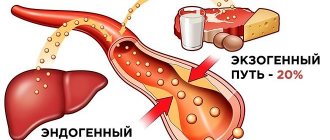
Cholesterol (cholesterol) is a secondary monohydric cyclic alcohol. It is found in the blood and tissues of the body in free and esterified forms. Free cholesterol is a component of cellular plasma membranes, as well as mitochondrial membranes and the endoplasmic reticulum. Its esters predominate in blood serum. Cholesterol is a precursor of sex hormones, corticosteroids, bile acids, vitamin D. Up to 80% of cholesterol is synthesized in the liver, and the rest enters the body with products of animal origin (fatty meat, butter, eggs). Cholesterol is insoluble in water; its transport between tissues and organs occurs due to the formation of lipoprotein complexes. There are low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol fractions that differ in composition and function. Cholesterol level at birth is below 3.0 mmol/L. With age, its level in the blood increases, and gender differences in concentration appear. In men, cholesterol levels rise in early and middle age and decline in old age. In women, the concentration of cholesterol increases more slowly with age, until menopause, and subsequently may exceed the level in men. This is due to the action of sex hormones. Estrogens reduce, and androgens increase, total cholesterol levels. Cholesterol accumulation is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease (CHD). A high risk of developing coronary artery disease in adults is a cholesterol concentration in the blood above 6.22 mmol/l. When the concentration of total cholesterol is in the range of borderline values and above, it is advisable to study cholesterol in combination with the determination of triglycerides, HDL and LDL cholesterol.
Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- atherosclerosis and related diseases of the cardiovascular system: coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction (prediction, risk assessment, diagnosis);
- liver and kidney diseases;
- endocrine pathology (myxedema, diabetes mellitus).
Preparation for the study: blood must be donated in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach, no less than 12 hours after the last meal. Material for research: serum. Execution time: 1 working day.
Increased sugar levels - causes, consequences
Glucose concentration mirrors the state of carbohydrate metabolism in the body as a whole. Its increase is the result of two main pathogenetic causative factors:
- A decrease in insulin production by intrasecretory cells of the pancreas is type 1 diabetes mellitus, which is the result of congenital genetic changes, viral or autoimmune damage to pancreatic tissue.
- A decrease in the response of body cells to the effects of insulin at normal concentrations (diabetes type 2) - develops with an increase in a person’s body weight, abuse of sweets, genetic predisposition, which is inherited from parents to children, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Elevated sugar levels over a certain long period of time lead to the development of a number of consequences, which include angiopathy (pathological changes in the walls of all blood vessels, including capillaries of the microvasculature), visual impairment, damage to brain tissue, and kidneys.
The reasons for the consequences for the body of increased concentrations of these organic compounds have certain similarities. Therefore, preventive measures aimed at reducing cholesterol and sugar are also similar. They include sufficient physical activity (sports, walking, running, morning exercises), dietary recommendations with preferential consumption of plant foods and limiting fatty, fried foods, sweets, and giving up bad habits. To monitor the level of these indicators, it is advisable to donate blood at least once a year for testing to determine cholesterol and sugar levels. It is advisable to decipher the obtained test results during a consultation with a hematologist, who will give appropriate recommendations or prescribe treatment.
The therapist explained whether high blood sugar and cholesterol are always dangerous
Photo: portal of the mayor and government of Moscow/Vladimir Novikov
A general practitioner of the highest category, Tatyana Romanenko, told Moscow 24 whether high cholesterol poses a threat to the body.
There is an opinion that when there is a lot of it, it is bad, says the doctor. However, according to her, such a judgment is not always correct. In particular, because the body needs cholesterol to build cell membranes.
“It is part of these membranes. Cholesterol is involved in the synthesis of bile acids. And the good effect of cholesterol will be that it improves digestion. There is some evidence that those who have adequate cholesterol levels are less likely to suffer from Alzheimer's disease. Therefore there are many advantages. The question is what kind of cholesterol it is,” explains Romanenko.
If you have high total cholesterol, it can be increased by both bad cholesterol, called low-density lipoproteins, and good cholesterol, called high-density lipoproteins. Tatiana Romanenko
therapist of the highest category
In order to understand which cholesterol predominates in a person, the therapist advises taking an extended test called the lipid spectrum.
“If your cholesterol levels are elevated due to high-density lipoproteins, then this is a very good prognostic sign. This means that your risk of atherosclerosis is minimal, which we cannot say about low-density lipoproteins. Thanks to them, inflammation develops and atherosclerosis forms. Triglycerides - neutral fat - are precisely the culprits in the formation of insidious plaques on the walls of your blood vessels,” says the specialist.
"Doctor 24": cholesterol and glucose
A person may also have elevated blood glucose levels, but, according to Romanenko, this does not always indicate diabetes. For example, the corresponding indicator may increase due to strong feelings, she continues.
In such cases, the hormone cortisol is produced, and it can increase glucose levels. Or, let’s say you get sick, you have some kind of mild cold, a viral infection. In this case, glucose levels may also be elevated. Tatiana Romanenko
therapist of the highest category
In order to find out the exact cause of the changes, the doctor recommended taking a clarifying test: glycated hemoglobin. This indicator will characterize your glucose level for two months, the therapist concluded.
Previously, nutritionist Elena Solomatina explained why you should not completely give up sugar. The expert noted that without it the human body cannot function normally. This also applies to the brain, which operates exclusively on glucose.
Cholesterol and blood sugar - is there a relationship?
Medicine has long noted the relationship between cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Sugar, of course, does not contain this natural lipophilic alcohol, but studies conducted among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus show that every person suffering from this disease has elevated cholesterol levels in the blood, that is, it is a concomitant disease. In addition, obesity, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, smoking and alcoholism affect the increase in cholesterol levels. Meanwhile, two of the above reasons, namely poor nutrition and obesity, often become prerequisites for the development of diabetes mellitus.
Studies conducted in diabetics allow us to conclude that this pathology is often found in people suffering from excess blood pressure, excess weight and, typically, high cholesterol. To date, the mechanism of interaction between these diseases has not been studied, and therefore in each specific case it is quite difficult to identify which disease provoked the appearance of the other. Therefore, if the patient has one of the abnormalities under consideration, it is important to monitor blood counts, trying to ensure that they correspond to the norm. By the way, the norms for cholesterol and sugar are quite similar and amount to 3.6–7.8 and 3.3–5.5 mmol/l, respectively. Even a slight deviation from the norm of any of the indicators can have a negative impact on human health.
Scientists have long come to the conclusion that a constant increase in cholesterol levels by at least 0.1 mmol/l negatively affects learning ability, concentration and memory, ultimately leading to the loss of the ability to think logically. In people with high sugar levels, the process of reduction in intellectual activity occurs more slowly, but when a patient is diagnosed with both of these ailments, there is a serious danger to brain performance. That is why it is important to maintain both indicators at normal levels.
Increased levels of blood sugar are compensated with the help of insulin, as well as a special diet, while 80% of cholesterol is produced by the body itself and only 20% of this lipophilic alcohol enters the body with food. However, very often it is this 20% that separates the indicator from the norm, and therefore people with high cholesterol levels also need to switch to a dietary diet, which is in many ways similar to the diet for diabetes.
Thus, a diet for diabetes involves giving up sugar, both in its pure form and in various confectionery products. In addition, you should limit the consumption of fatty meats, sweet fruits and juices from them, fast food and various sodas that contain sweeteners. If you have high cholesterol, you should not consume animal fats, which contain high levels of natural lipophilic alcohol. This means that you should give up fatty meats, and especially not eat offal (liver, kidneys and brains), which contain quite high cholesterol levels.
To lower cholesterol and lower blood glucose levels, it is useful to eat fibrous foods, that is, whole grains, beans, peas, lentils and other legumes, vegetables, herbs, fruits and nuts. Egg yolk contains a daily dose of cholesterol, but the white does not contain this substance at all. It is useful for persons with these ailments to consume dairy products: cottage cheese, fermented baked milk or kefir. An excellent drink that reduces cholesterol and blood sugar is green tea. Eat right and take care of yourself!
order an online consultation with our specialists
Additional Information