Classification of IHD
Coronary heart disease is divided into several types:
- Sudden coronary death - death occurs instantly or within an hour after the onset of a heart attack.
- Heart failure . Develops as a result of prolonged insufficiency of blood supply to the myocardium. Manifested by shortness of breath and swelling.
- Angina pectoris. This is one of the types of ischemic heart disease, which is manifested by pain and discomfort in the chest of a pressing, squeezing nature. The pain is localized behind the sternum and can radiate to the neck, left arm, epigastric region, and lower jaw. There are the following main types of angina:
- angina pectoris – pain in the heart occurs during physical exertion;
- Spontaneous angina - pain occurs against the background of the patient’s usual stress or at rest, the attack lasts more than twenty minutes.
- Violation of the rhythm and conductivity of the heart (tachycardia, bradycardia, arrhythmia).
- Painless coronary heart disease . A latent form of the disease that can only be detected using instrumental diagnostic methods.
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis . Myocardial damage, in which the muscle tissue of the heart is replaced by scar tissue.
- Myocardial infarction . Death of a part of the heart, which occurs as a result of an acute circulatory disorder in it.
- Syndrome X. A variant of coronary artery disease in which angina attacks are observed with unchanged large coronary vessels; pathological changes in this form of the disease develop in small arteries.
In addition, there are acute forms of IHD (myocardial infarction, focal acute dystrophy, unstable angina) and chronic forms of IHD (painless form of the disease, cardiac arrhythmias, stable angina).
Development of edema
Patients suffering from heart failure need to know that as the disease progresses, all accompanying symptoms worsen. If at the first stages of the disease the accumulation of fluid in the body is insignificant, then over time, this symptom manifests itself more and more. Patients are mistaken in believing that edema due to heart failure is a temporary phenomenon. Often, fluid accumulation in the legs is associated with fatigue. After all, after rest, the condition of the lower extremities improves, and the patient does not experience discomfort. But, over time, the disease progresses, and the accumulation of fluid does not seem so harmless. Legs swell not only at the end of the working day; this condition occurs at any time of the day, regardless of physical activity. Along with this condition, the patient notes a deterioration in health and the appearance of other symptoms of the disease.
Causes of IHD
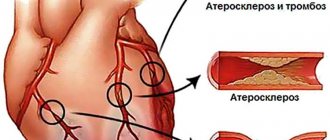
The main cause of IHD is considered to be blockage of one or several vessels at once by atherosclerotic plaques, which causes narrowing of their lumen, impaired blood flow and the development of myocardial ischemia. Experts say that atherosclerosis is the cause of ischemic heart disease in 95% of cases.
Other possible causes of coronary heart disease are:
- hereditary predisposition - the presence of cases of IHD in the family increases the risk of developing this disease;
- high blood pressure;
- age (50 years and older);
- excess weight;
- poor nutrition;
- diseases associated with metabolic disorders (for example, diabetes);
- physical inactivity;
- bad habits.
Symptoms of IHD
Clinical manifestations depend on the form of the disease . Common symptoms include the undulating course of IHD, when periods of normal well-being alternate with periods of exacerbation of the disease.
About a third of patients do not experience any symptoms at all . IHD can develop over decades and certain symptoms can appear just as slowly.
The main clinical signs of IHD are:
- arrhythmia;
- feeling of constriction in the heart area;
- physical weakness;
- shortness of breath, which occurs with light exertion and even at rest;
- nausea;
- feeling of lack of air;
- cold clammy sweat.
With angina pectoris, the patient feels intense paroxysmal pain that does not last long and a feeling of strong compression in the chest (which is why angina pectoris is popularly called “angina pectoris”).
In addition, with coronary artery disease, the patient feels causeless anxiety, he develops a fear of death, a state of apathy and melancholy.
Attacks of spontaneous angina, unlike exertional angina, can occur suddenly, for example, while taking a shower or leaving a warm apartment into the cold.
In case of sudden coronary death, a person suddenly loses consciousness, his heart sounds cannot be heard, there is no pulse, breathing stops, his pupils dilate, and his skin acquires a grayish tint.
Coronary heart disease (CHD), or angina (questions and advice for the patient)
Coronary heart disease is a disease that occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the heart due to narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels. Pain during angina appears most often in the center of the chest, but it can also be on the left, in the region of the heart, and can radiate (“give”) to the neck, lower jaw, left arm, between the shoulder blades. The sensation may be squeezing or pressing. Some patients feel as if something is falling on their chest. Sometimes, along with the pain, there is a feeling of lack of air, the inability to breathe. Angina almost always appears during stress - physical or emotional. It can begin during fast walking, running, climbing stairs, lifting heavy objects, or during severe stress or emotional distress. In later stages, when the disease becomes more severe, pain may also occur at rest. It is very important that if such sensations occur, be sure to consult a doctor as soon as possible!
What you need to know about coronary heart disease?
In order to function properly, the heart needs oxygen and nutrients. The blood supply to the heart is carried out through the arteries that surround the heart, like the crown, and are therefore called coronary. Blood enters the coronary arteries from the aorta, after which it is delivered through smaller vessels to the working myocardial cells. The diameter of the coronary arteries is very small - they are no thicker than a cocktail straw (3-5 mm), but disruption of their patency can cause serious damage to health. The main cause of impaired arterial patency is atherosclerosis (from the Greek words “ather” - gruel and “sclerosis” - hardening). The name accurately reflects the essence of the process - the accumulation of soft deposits on the walls of the arteries - lipids (fats, such as cholesterol), the subsequent proliferation of dense connective tissue and hardening - calcification. As a result, the arteries lose their elasticity and become stiff. Lipid (fat) deposits, called atherosclerotic plaques, bulging into the lumen of blood vessels lead to narrowing of the lumen or even blockage of the arteries. The mechanisms of the early stages of the development of the atherosclerotic process, due to which plaques and narrowing of the coronary vessels develop, have not yet been fully clarified. Nevertheless, today it has been proven that atherosclerosis develops, among other things, in response to damage to the vascular wall from the inside (damage or dysfunction of the endothelium). This can be caused by a number of reasons, in particular, smoking, a significant increase in blood lipid (cholesterol) levels, high Blood Pressure, psycho-emotional stress, viral or bacterial infection. Hereditary predisposition also plays a role. Narrowing (stenosis) of one or more coronary arteries by atherosclerotic plaque(s) reduces the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart muscle and causes myocardial ischemia (from the Greek words “ishe” - retain and “hemo” - blood). It is the lack of blood and oxygen that causes the pain a person feels during an angina attack.
What is angina and how to recognize it?
Angina pectoris is the main symptom of chronic coronary heart disease (CHD)
Angina is an acute feeling of discomfort in the chest (a feeling of squeezing, tightness, burning, pain), forcing a person to stop physical activity. Regardless of what kind of exercise causes angina, the attack should go away after stopping the exercise and/or taking nitroglycerin (spray or tablets). If the discomfort in the chest does not go away after this, immediately call an ambulance; a myocardial infarction may develop.
If any unpleasant sensations appear in the chest, you should consult a doctor for a routine, “standard” (ECG, blood tests, medical examination) or more in-depth examination (ECG or echocardiogram with stress, ECG monitoring throughout the day, coronary angiography of the arteries of the heart) . Coronary angiography is performed for severe manifestations of angina pectoris in order to clarify the possibility of using surgical methods to improve the blood supply to the heart, stenting or bypass surgery. (see more detailed information on “poststenta.rf”).
What to do if you have an angina attack?
Angina is a cry from the heart for help. Although an insufficient amount of blood flows through the heart artery narrowed by the plaque, under resting conditions it is enough to provide the heart muscle with oxygen supplied by the blood.
Therefore, the first action for angina pectoris is to stop the load that caused the attack. Second action: if the attack does not go away within 2-3 minutes with rest, you need to take 1 tablet of nitroglycerin, placing it under the tongue. It is more convenient to use nitroglycerin in the form of a spray. Nitroglycerin is quickly absorbed, enters the blood and causes dilation of the blood vessels of the heart. After 1-2 minutes the attack should stop. Short-term attacks of angina go away on their own when you stop exercising or after taking nitroglycerin for 2-3 minutes, sometimes up to 8-10 minutes.
Remember! You should always have an adequate supply of your medications with you!
With coronary heart disease (more precisely, with atherosclerosis, which narrows the arteries of the heart), myocardial ischemia occurs (bleeding of part of the heart muscle) of varying durations - from several minutes to 1 hour or more.
Ischemia for more than 40 minutes is most likely associated with the development of arterial thrombosis (blockage by a blood clot). This is a sure sign of a beginning or already occurring myocardial infarction (death of cells of part of the heart muscle).
What to do in this situation?
At the first sign of a heart attack, call 911. It is best to start treatment within the first hour after symptoms appear. Waiting increases heart damage and reduces the chance of survival. It is essential to prevent the artery from narrowing within 90 minutes to minimize the consequences.
Before the ambulance arrives, provide access to more oxygen: unfasten the collar, open the window.
Be sure to stop any physical activity, lie down with the head of the bed raised or sit in a chair with armrests, and relax as much as possible.
Do not eat, do not drink, do not smoke.
If pain persists, continue taking nitroglycerin every 7-10 minutes. If there is no pain, you do not need to take nitroglycerin.
Do not panic! Emotional stress can further increase ischemia.
Strictly follow the recommendations of the emergency doctor after an attack.
How to deal with angina pectoris?
It has been proven that modern treatment methods can prevent the progression of the disease, prolong life and maintain health.
To do this, first of all, it is necessary to change your lifestyle and give up bad habits, eliminating risk factors:
If there is hypertension, the blood pressure level should be brought to figures less than 130 mm. Hg / 90 mm. rtst.
Quit smoking
Stop drinking alcohol
Monitor your diet using a diet for patients with coronary artery disease
Get rid of excess weight
Consult your doctor for recommendations on physical activity
Non-drug methods (diet, physical training, blood pressure control, weight control) significantly increase the effectiveness of drug therapy. But the persistence of risk factors such as smoking, alcohol, hypertension, excess weight, low physical activity, and diabetes mellitus can reduce the effect of drug prevention!
What medications should be taken to relieve angina attacks?
Once you are diagnosed with angina, you may need to take medications indefinitely, long-term. Even if you have had coronary angioplasty (sometimes called PCI, PTCA, stenting) or coronary artery bypass grafting, you will need to continue taking your medications afterwards.
To reduce the number of angina attacks, there are a number of drugs called antianginal drugs.
Remember that prescribing, discontinuing and changing dosages for the treatment of angina pectoris is carried out only by your attending physician .
The purpose of these drugs is to prolong your life and eliminate (or significantly reduce) the symptoms of angina pectoris. Symptoms will decrease due to normalization of blood flow, pressure, pulse, and restoration of the metabolic state of heart cells.
What can the doctor prescribe for you? (only if indicated and after examinations!).
Fast-acting nitrates (spray or tablets).
These drugs are used to relieve angina attacks. The essence of their action is that they quickly dilate the blood vessels of the heart, which relieves pain. You should always have nitroglycerin spray (or tablets) with you. This could save your life. But remember that these drugs only relieve the symptoms of angina pectoris, but do not cure it. If you take them often and regularly, their effect may weaken. Be sure to tell your doctor how many times a day/week you use nitrates.
Beta blockers
They act on the sympathetic nervous system, somewhat slow down the heart and lower blood pressure. It is very important to take them constantly, for a long time, and under no circumstances stop taking them without consulting your doctor. Beta blockers are used to prevent angina attacks, but not to relieve them.
Calcium antagonists
They also prevent the development of angina attacks. Taking these drugs leads to dilation of the arteries, including the arteries of the heart. As a result, blood flow improves, the load on the heart decreases, and more blood flows to the heart. Calcium antagonists also lower blood pressure.
Myocardial cytoprotectors
These drugs have a fundamentally different mechanism of action. They prevent the development of attacks by influencing metabolic disorders caused by a lack of oxygen directly in the heart cells.
Without affecting blood pressure and pulse, these drugs enable the heart to work without ischemia by switching the heart to more economical use of scarce oxygen. They switch metabolic processes to use glucose as “fuel” for the heart, rather than fatty acids as is usually the case. With the same amount of work, the heart requires less oxygen (by about 20-30%) to oxidize (burn) “fuel” for the normal functioning of heart cells
If after your doctor prescribes/discontinues any pills you feel worse, do not make any independent adjustments to your treatment, but, if possible, contact your doctor as quickly as possible.
What to tell the doctor
Describe how you feel. Fill out the form on the back.
Show your blood pressure and heart rate monitoring diary.
Tell us in detail about the pain - where it hurts, what it is like, when it occurs, how you relieve it.
If you have had any examinations or tests, bring the results to your doctor.
What to ask your doctor
Do I need to take medications? When? How many times a day? What dosage?
When to come next time?
What to do if it gets worse?
Do you need a diet? Which? How much fluid to drink?
Are there any restrictions on physical activity?
It is important to control angina pectoris
Note how you feel in your diary every day, this is very important for controlling angina.
Download the Angina Control mobile application from the AppStore or GooglePlay. It is easy to use and will help you better evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.
Information for patients.
Fill out the questionnaire before your doctor’s appointment; this will make communication with a specialist more effective.
Gracheva Z.M. — cardiologist OGBUZ ARB
Print Email
- Back
- Forward
Diagnosis of IHD
Coronary heart disease requires complex diagnosis. First of all, it is necessary to find out the form of the disease. The correctness and effectiveness of the prescribed treatment depends on this.
Diagnosis of IHD includes the following steps:
- interviewing the patient;
- physical examination;
- laboratory research methods - blood and urine tests (biochemical, general);
- ECG;
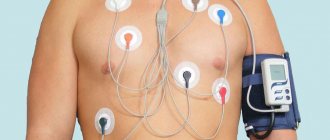
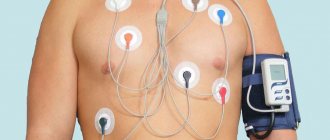
- Holter monitoring;
- intraesophageal electrocardiography;
- angiography;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- functional tests.
Treatment of coronary artery disease (classical medicine)
Treatment of IHD in the initial stages is carried out on an outpatient basis. In advanced forms of the disease, when there is a high probability of complications, treatment is carried out in a hospital setting.
Drug therapy includes the prescription of the following groups of drugs:
- antiplatelet agents – improve blood flow;
- statins and fibrins – slow down the formation of new atherosclerotic plaques and partially destroy old ones;
- adrenergic blockers – reduce heart rate and reduce myocardial oxygen demand;
- diuretics – remove excess fluid from the body;
- nitrates – effectively relieve angina attacks;
- Anticoagulants – thin the blood and prevent blood clots.
The attending physician must prescribe certain medications, determine their dosage and duration of treatment. Self-medication is unacceptable and can lead to the development of a number of serious complications.
Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where conservative therapy does not produce results and the patient’s condition continues to deteriorate.
The main method of surgical treatment of coronary artery disease is coronary artery bypass grafting . The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Its essence lies in suturing a special shunt to the coronary artery and thus creating a bypass for blood, which allows restoring blood supply to the myocardium.
In addition to coronary artery bypass grafting, treatment methods for coronary artery disease such as angioplasty and stenting are used. The disadvantages of these methods are the short-term effect.
If treatment for coronary artery disease is started in time, the prognosis is favorable. The patient’s quality of life increases, ability to work is restored, and the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke is reduced.
"Heart" products
- Banana . Regular consumption of this fruit can reduce the likelihood of developing myocardial infarction or stroke and helps normalize blood pressure. Banana is a storehouse of vitamins and useful elements; it contains: B vitamins, phosphorus, sodium, iron, calcium, carotene, magnesium and potassium. This fruit is truly a friend of the heart; it is almost a champion in potassium content. Banana will not only strengthen the heart muscle, but also fight the formation of cholesterol plaques, thereby protecting blood vessels.
Dried apricots . It is not only very tasty, but also very healthy, especially for the heart. It contains potassium, magnesium, calcium, carotene, pectin, iron, phosphorus, and many vitamins. This dried fruit will strengthen the nervous system, immunity, and increase hemoglobin levels. Dried apricot normalizes blood pressure, inhibits the development of atherosclerosis, cleanses blood vessels of cholesterol, improves blood circulation, and makes the main muscle in the human body more resilient.- Honey _ The affected myocardium can replenish its strength with glucose, which is found in abundance in honey. It promotes the expansion of coronary vessels, improving blood flow in them. A small amount of honey, when used regularly, can improve blood composition and increase muscle tone of the heart. Honey removes swelling, helps with shortness of breath, and relieves attacks of arrhythmia. It is also rich in B vitamins; A, E, C, H, K, potassium, magnesium, copper, fluorine, calcium, zinc, manganese, boron, iron, chromium.
- Walnut . It contains a lot of potassium, it is able to protect the nervous system, increase the endurance of the heart, bring its rhythm back to normal, lower blood pressure, minimize the possibility of blood clots, and get rid of cholesterol. Walnuts contain a lot of unsaturated omega-3 fats (reduce cholesterol, improve heart rate), vitamin E, fiber, protein, and the amino acid l-arginine, which makes blood vessels more elastic.
Traditional medicine for coronary heart disease
To treat coronary heart disease using traditional methods, methods based on herbal components are used. To achieve maximum effect and select the most suitable product, consultation with a specialist is necessary. Self-medication and IHD are incompatible. Therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor. Plants in this case are medicines, and they have side effects and contraindications.
A distinctive feature of treatment with folk remedies is that therapy must be carried out over a long period of time . Unlike medications, natural compounds do not provide an immediate effect, but, accumulating in the body, prevent the onset of symptoms and alleviate the patient’s condition. Complex action can be obtained using multifunctional compounds.
Hawthorn for ischemic heart disease
An effective remedy for angina pectoris, which is caused by ischemic heart disease, is hawthorn. It can be consumed in several ways - in the form of infusions, decoctions, teas.
- Hawthorn infusion . Pour 1 tbsp into a thermos. l. dried fruits of the plant and pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, stand for at least 2 hours, strain using several layers of gauze. Use 2 tbsp. l. in three doses half an hour before meals.
- Infusion of hawthorn and motherwort . The components in equal quantities (6 tablespoons each) are poured with boiling water (7 tablespoons). The container is well wrapped and left for a day in a warm place. Strain and squeeze using gauze. Take 3 tbsp. a day before meals. It is useful to add rosehip infusion prepared according to a similar recipe.
Herbal infusions
Collections of medicinal herbs are used to treat coronary artery disease, angina pectoris, and prevent the occurrence of atherosclerotic plaques.
- Buckwheat (flowers), mistletoe (leaves) . Combine the ingredients in a 2:1 ratio and mix. For 1 tbsp. boiling water you will need 1 tsp. herbs. Wrap well, leave overnight, strain. Take 2 tbsp orally in three doses. l. medicine.
- Dill (seeds), jaundice (herb), sunflower (reed flowers) - 2 tbsp. l., coltsfoot - 1 tbsp. l . Grind the ingredients and mix well. For 1 tbsp. boiling water take 1 tbsp. l. mixture, leave overnight, filter, squeeze. Drink 100-120 g in 5-6 doses. The duration of therapy is a month.
- Blue cornflower (flowers), birch buds, elecampane (root), bearberry, buckwheat (flowers), corn silk . Take 1 tbsp. l. all ingredients, chop well and stir. For 1 tbsp. boiling water you will need 2 tbsp. l. mixtures. Place in a water bath, boil, set aside and leave. Strain and pour in cooled boiled water in such an amount to bring the volume to the original volume. Drink within 30 minutes. before meals, 100-120 g in two doses.
- Horsetail (20 g), knotweed (30 g), hawthorn flowers (50 g) . Grind the ingredients well, mix, separate 2 tbsp. l. and pour 1 tbsp. boiling water Let stand for a couple of hours, cool, strain, squeeze. Drink 1 sip throughout the day.
- Motherwort, chamomile (flowers), hawthorn (flowers) . Take 100 g of ingredients and mix. Add 50 g of birch leaves, horse chestnut (flowers), piraeus (root), heather grass. Mix and pound in a mortar. Separate 1 tsp. mixture and pour boiling water, wrap in a towel and leave for an hour. Strain and take warm in two doses.
- 1 tbsp. l. centaury steamed 2 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 1 hour. Divide into 4 parts, drink half an hour before meals throughout the day. The course lasts 2-3 weeks.
- over the eryngium (collected during the flowering period). For 1 tsp. you will need 1 tbsp. water. Bring to a boil, simmer for 5 minutes. Drink up to 5 times a day, 1 tbsp. l. Course 2-3 weeks.
Cottage cheese and millet porridge
To maintain the health of this organ, it is recommended to include millet porridge prepared according to a special recipe in your diet. The millet is pierced over high heat so as to preserve its natural color. The third part of the glass is washed, 750 g of water is poured in and boiled. Salt, sugar to taste.
Also, for heart diseases, it is useful to eat at least 100 g of cottage cheese daily.
Horseradish for ischemic heart disease
An effective folk remedy for coronary artery disease and other heart pathologies is horseradish. For treatment use one of the following methods:
- 5 g of plant root is poured into 1 tbsp. boiling water, keep in a thermos for a couple of hours. The drug is used for inhalation.
- 1 tsp. mix grated horseradish and honey and consume daily with a small amount of water. The course is 1.5 months.
- 2 tbsp. l. grated horseradish, 1 tbsp. honey, 1 tbsp. freshly squeezed carrot juice. Horseradish is steamed with boiling water and left for a day. All ingredients are mixed and consumed 1 tbsp. l. an hour before meals.
Garlic tincture
You will need 50 g of garlic and 1 tbsp. vodka, leave for 3 days. Drink 8 drops, diluting the tincture in a small amount of water in three doses.
Properties of herbs
A visit to the doctor will help eliminate heart problems, but traditional medicine can be successfully supplemented with alternative medicine.
If the patient has recently become concerned about coronary heart disease, treatment with folk remedies will be very advisable. Why do heart patients turn to traditional medicine for help? Many believe in the healing power of nature and the wisdom of the people, who from time immemorial have used this power for their own benefit. Time-tested recipes are credited with magical properties, but the successful treatment of cardiac ischemia with folk remedies has a completely scientific explanation.
The plant world is rich in beneficial substances that can improve the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
Medicines that are used in traditional medicine are made from plant extracts. Vitamins and microelements contained in certain foods, vegetables, and fruits help strengthen the heart muscle.
Plants that can be used to treat coronary heart disease:
- hawthorn;
- motherwort;
- peppermint;
- fennel;
- rose hip;
- pharmaceutical camomile;
- Melissa;
- valerian;
- horsetail;
- Eleutherococcus
This is not a complete list of medicinal herbs. Some strengthen the heart, others relieve symptoms of arrhythmia, pain, calm the nervous system, lower blood pressure, and fight swelling. Often all these medicinal properties are combined in one plant.
Here are descriptions of some herbs and their beneficial properties.
Hawthorn . The plant helps the heart contract more strongly, activates blood flow in the vessels that supply the heart, and can relieve attacks of arrhythmia. Hawthorn has a beneficial effect on the nervous system and relieves pain accompanying angina pectoris. It contains hyperin (an antioxidant), which protects blood vessels from damage and prevents the development of atherosclerosis.- Rose hip . Contains a lot of useful things: vitamins and microelements. It will strengthen blood vessels and prevent atherosclerotic phenomena. Rosehip promotes active hematopoiesis and lowers blood pressure.
- Melissa . It is used for hypertension and also as a sedative. The composition includes vitamins B and C, microelements (copper, zinc, selenium, calcium, manganese), including magnesium and potassium, which are especially beneficial for the heart. Melissa fights anemia, relieves heart pain, eliminates dizziness, improves heart rhythm, and improves blood circulation.
- Horsetail . This is a good remedy for edema, including cardiac edema. The plant has a pronounced diuretic property, normalizes metabolic processes, relieves inflammation, helps stop internal bleeding, and fights atherosclerosis of the heart vessels. Horsetail is rich in the following beneficial substances: magnesium, manganese, potassium, selenium, iodine, carotene, zinc, iron, vitamin C.
Magnesium and potassium are very useful for the normal functioning of the heart and blood vessels. They:
- Provide nutrition to the heart.
- Activate the process of hematopoiesis.
- Adjusts the rhythm of heart contractions.
- Promotes blood thinning and increases blood circulation.
- Prevents the formation of blood clots.
- Reduce atherosclerotic plaques.
- Strengthens blood vessels and promotes the elasticity of their walls.
- Eliminate pain in the heart muscle.
It is not for nothing that traditional medicine recommends consuming foods containing magnesium and potassium for the treatment of ischemic heart disease.
Here are some of them: raisins, dried apricots, banana, walnuts, beans, buckwheat, honey. There are many recipes for treating heart disease that contain these beneficial foods.
Prevention of coronary artery disease
Prevention of coronary heart disease includes:
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper nutrition - avoiding fast food, fatty, fried, smoked, salty, pickled foods, including more fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- weight control;
- regular blood pressure measurement;
- walking, physical activity, physical education;
- cholesterol control;
- Regular preventive examinations and ECGs will help identify the disease in the early stages, which will significantly facilitate subsequent treatment and improve the prognosis.