Reception is conducted by:
Krivonosov Denis Sergeevich -
cardiologist, candidate of medical sciences
Make an appointment
A characteristic feature of modern society is physical inactivity - a disruption in the functioning of the body due to a lack of physical activity. The development of the transport network, automation of production and the increase in the number of “knowledge” workers have led to the fact that people began to lead a sedentary lifestyle. Unfortunately, this factor has a negative impact on the health of the human cardiovascular system. Diseases such as angina pectoris, stroke, and heart attack have become increasingly common. Therapeutic exercise for coronary artery disease is an important component of the rehabilitation of patients who have suffered heart disease.
The benefits of physical activity for cardiac ischemia
For physical rehabilitation, doctors prescribe light exercises at the very beginning of the post-infarction period. The purpose of such exercises is to restore breathing and bring the patient out of a serious condition.
It must be remembered that therapeutic exercises for ischemic heart disease are prescribed strictly by a specialist. Excessive physical activity and too intense exercise can negatively affect your health and lead to a relapse of the attack.
Regular physical activity is beneficial for everyone. For healthy people, it helps prevent the onset of diseases, and for those who have already suffered heart disease, physical education reduces the recovery period and prevents the development of relapse.
Physical activity for coronary artery disease helps:
- keep muscles toned;
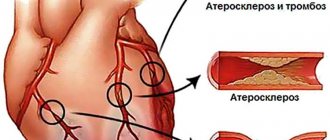
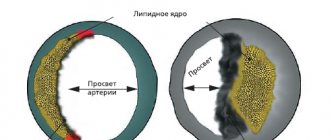
- reduce the level of atherogenic lipids in the blood (cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, etc.), thereby reducing the risk of atherosclerosis;
- normalize blood pressure;
- prevent the formation of blood clots;
- improve quality of life, improve mood;
- normalize sleep;
- prevent obesity and reduce the risk of diabetes.
According to medical research, people who engage in physical therapy after a heart attack are 7 times less likely to suffer a recurrence of such a heart attack and reduce the likelihood of death by 6 times. Exercise therapy for coronary heart disease can improve the general health of the patient. Regular exercise improves blood flow, minimizes the effects of heart failure, and strengthens the cardiovascular system.
Nutrition rules
A low-calorie diet with a high fiber content is the basis for the rehabilitation of patients after myocardial infarction. During the recovery period, it is important to control body weight and get enough potassium, polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins C and P. The attending physician will give basic recommendations on the diet. He will tell you what you can and cannot eat after a heart attack, how much liquid to drink, and what foods you need to avoid.
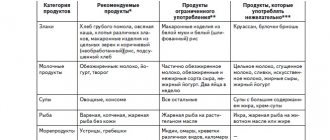
Authorized products:
- lean non-red meat, poultry without skin;
- fresh fish;
- fruits, vegetables, berries;
- egg whites (omelet);
- cereal porridge;
- whole grain, rye, bran bread;
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- greens and nuts.
Among the drinks allowed during the recovery period after myocardial infarction are weakly brewed teas, non-acidic fruit drinks and compotes, and natural juices without sugar. A decoction of dried fruits is recommended.
The following are strictly prohibited:
- strong tea, coffee, cocoa, chocolate, alcoholic drinks;
- fatty meat, animal fats, sausages;
- fresh, especially hot, baked goods, baked goods, all types of sweets and cookies;
- some vegetables - spinach, radishes, as well as mushrooms and legumes;
- spices, spicy foods, smoked meats, pickles, marinades.
Rehabilitation for myocardial infarction involves split meals in small portions, limiting fluid to 1 liter per day, steaming, stewing or boiling food. Salt should be limited to 5 grams per day.
Features of physical education for ischemic heart disease
Not all types of physical activity are suitable for patients suffering from coronary heart disease. The type of load and its intensity are determined by the attending physician based on the specific clinical picture.
For patients who have suffered heart disease, the nature of exercise therapy can be of decisive importance:
- With moderate activity, recovery speeds up, strength and endurance of the body increase.
- With excessive exercise, angina pectoris may occur, which often leads to a repeat attack.
The priority areas of physical education are exercises aimed at developing endurance. These include quiet walks, cycling, housework, and dancing. Loads should gradually increase. In this case, the heart rate should increase by no more than 15-20 beats per minute.
Prevention of heart attack and stroke
To prevent such serious pathologies, you need to take care of your lifestyle on an ongoing basis. Proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, and constant blood pressure monitoring are important. Physical activity also plays a role. Loads should be reasonable and moderate. Special exercises to prevent stroke and heart attack will help significantly reduce the likelihood of these problems. Those who are at risk are advised to select types of activity especially carefully. This should be done together with a specialist.
Exercises to prevent heart attack and stroke can be seen in the following videos.
Indications and contraindications
Coronary heart disease is a pathological condition that is characterized by disruptions in the blood supply to the myocardium due to damage to the coronary vessels. The reason for this situation is the lack of oxygen entering the heart with blood. Indications for performing therapeutic exercises are acute forms of coronary artery disease (with a history of myocardial infarction) and chronic forms (with periodic attacks of angina pectoris).
Contraindications for exercise therapy for ischemic heart disease:
- frequent attacks of angina pectoris;
- acute disturbances in coronary circulation;
- advanced stages of heart failure;
- persistent arrhythmia;
- cardiac aneurysm.
For patients suffering from angina, doctors recommend that they carry out therapeutic exercises in between attacks. So, with a mild attack, simple exercises can be done already on the second day, with a moderate attack - on the fourth, with a severe attack - on the eighth.
When to start classes
The time when the patient should begin physical therapy is determined by the doctor. In his decision, he relies on the following factors:
- The severity of the patient's condition;
- Patient's age;
- Gender;
- Features of the course of the disease;
- Degree of physical fitness.
Note!
3-4 days after the attack, any physical activity is prohibited!
After the fourth day of rehabilitation, the doctor consults with the patient, assesses his condition and makes a decision on prescribing a complex of therapeutic exercises. At the initial stage, recovery is carried out while the patient is still in a supine position.
The timing of active exercise depends on how many times a person has had a myocardial infarction. If an attack occurs for the first time, active training begins within a month. After a second heart attack, classes are resumed only 5 weeks after the attack.
Rules for performing physical exercises for ischemic heart disease
Physical education for patients with coronary heart disease is carried out only after the condition has been stabilized.
Initially, it is advisable to do breathing exercises and exercises aimed at the activity of individual muscle groups. Then, in a clinical setting, a submaximal test is performed to determine the permissible intensity and volume of loads as part of post-infarction rehabilitation.
The test ends when the heart rate increases to 120 beats per minute or when clear signs of intolerance appear. The heart rate recorded at the end of testing becomes the threshold value and subsequent physical activity should not exceed 75% of the experimentally established value.
At first, the optimal loads will be: therapeutic exercises, walking, exercise bike, swimming, jogging.
Prohibited loads, permitted loads - with the sign “+„. The number of “+” signs indicates the permissible intensity and volume of loads.
Daily physical activity
| Type of activity | Function class | |||
| I | II | III | IV | |
| Run | ++ | + | — | — |
| Walking: Fast (130 steps/min) Medium (100/120 steps/min) Slow (<= 80-90 steps/min) | +++ +++ +++ | ++ +++ +++ | — ++ +++ | — — — |
| Climbing stairs (floors) | 5 or more | up to 5 | 2-3 floors | — |
| Carrying heavy loads (kg) | 15-16 | 8-10 | 3 | — |
| Having sex | +++ | ++ | + | — |
Types of household work
| Type of activity | Function class | |||
| I | II | III | IV | |
| Sawing | + | — | — | — |
| Working with a hand drill: comfortable position, uncomfortable position | ++ ++ | + — | — — | — — |
| Working with a vacuum cleaner | ++ | + | — | — |
| Washing vertical surfaces (windows, walls, cars): comfortable position, uncomfortable position | ++ + | + — | — — | — — |
| Wiping dust | +++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| Washing dishes | +++ | +++ | ++ | + |
| Washing: comfortable position, uncomfortable position | ++ + | + — | — — | — — |
| Sewing, embroidery | +++ | ++ | + | — |
Work on a personal plot
| Type of activity | Function class | |||
| I | II | III | IV | |
| Excavation work (loosening the soil, digging the ground, digging holes) | ++ | + | — | — |
| Carrying loads manually (water, sand, cement, bricks, fertilizers, etc., in kg) | up to 15 | until 8-10 | until 3 | — |
| Transportation of goods by wheelbarrow (kg) | until 20-25 | up to 15 | until 6-7 | — |
| Watering: with a hose, with a large watering can (10 kg), with a small watering can (3 kg) | +++ +++ +++ | ++ ++ ++ | + — + | — — — |
| Planting: trees seedlings | ++ +++ | + ++ | — + | — — |
| Harvesting: from trees from bushes | +++ +++ | ++ +++ | + + | — — |
A set of exercises for coronary heart disease
Exercises for the treatment of coronary artery disease include a combination of breathing exercises and physical activity. Physical education can be carried out in a clinic or at home based on the recommendations of the attending physician. During classes, you need to monitor your breathing - it should be calm and even.
Here are some examples of exercises that speed up rehabilitation after heart disease:
- The patient lies down on a hard horizontal surface with his arms and legs spread wide. Then he slowly bends and straightens his fingers. The exercise is repeated 5-6 times.
- In a supine position, the patient does breathing exercises - alternating deep, slow breaths with exhalations. Number of repetitions – 3-4 times.
- Lying on his back and stretching his legs, the patient alternately pulls the sock towards himself and away from himself. The exercise is repeated 5-6 times.
- Sitting on a chair, the patient lowers his arms along the body. Then, inhaling deeply, he raises his hands up, exhaling - down. Number of repetitions 5 times.
- In a sitting position, the patient fixes his hands on his belt. Then he straightens his arms one by one and returns them to their starting position. Number of repetitions – 5-6 times.
- The patient takes a “standing” position and makes 3 slow rotations of the head in one direction and 3 in the other.
- In a standing position, the shoulders are alternately raised and lowered. Number of repetitions – 5-6 times.
- The patient puts his hands on his belt and makes 3 circular rotations of the body in one direction, 3 in the other.
- The patient stands next to the chair, leaning his arms on its back. Then he slowly sits down on a chair while inhaling and rises to his original position when exhaling. Number of repetitions – 4-5 times.
Stages of recovery after a heart attack
The rehabilitation period consists of three stages: inpatient, post-inpatient and maintenance.
Stationary stage
In the hospital, the patient undergoes drug therapy, gets used to moderate physical activity and receives psychological help, which allows him to stabilize his condition and adapt to the changes that have occurred.
The success of rehabilitation depends on the professionalism of doctors and medical personnel, constant monitoring of vital signs. It is necessary to pay attention to the patient and surround him with care.
Post-stationary stage
Post-inpatient recovery is possible in:
- Boarding house for the elderly;
- Specialized sanatorium;
- Rehabilitation center;
- At home.
It is much more difficult for older people to recover and adapt, which is why they require round-the-clock care. Therefore, it is advisable to temporarily place the patient in a boarding house for the elderly, where he will be provided with qualified, high-level care and leisure activities will be organized.
In the sanatorium, the patient can not only undergo treatment, but also relax and take part in recreational activities.
The rehabilitation center has all the necessary conditions for high-quality restoration of the body. Experienced, highly qualified specialists work here, there is modern equipment, and methods that have proven their effectiveness are used.
When undergoing rehabilitation after a myocardial infarction at home, it is necessary to provide systematic examinations by a cardiologist and psychological assistance. It is imperative to monitor compliance with the regimen and take medications prescribed by your doctor. All this is quite possible, but very difficult, since it requires maximum discipline from both the recovering person and his loved ones.
Most often, after the inpatient stage, doctors refer patients after a heart attack to a specialized rehabilitation center, after which they recommend continuing recovery at home, periodically visiting the clinic.
Support stage
This stage lasts a lifetime. To minimize the risk of relapse, you will have to constantly take maintenance medications, follow a diet, engage in feasible physical work, lead a healthy lifestyle, and regularly visit doctors.