General rules
Among cardiovascular diseases, the leading place is occupied by coronary heart disease and cerebral stroke . Coronary heart disease is myocardial dysfunction (acute or chronic) due to a decrease in blood supply to the myocardium, most often caused by atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries. Severe myocardial hypertrophy, as well as congenital anomalies of the coronary vessels, can also lead to worsening of coronary blood flow. IHD has many clinical forms: stable angina , progressive angina, myocardial infarction , asymptomatic IHD, vasospastic angina, sudden death.
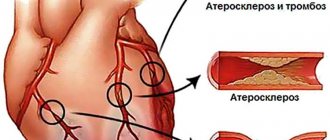
Elevated cholesterol are a leading factor in the progression of atherosclerosis and the occurrence of coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis begins at a young age and progresses. For a long time it proceeds secretly until it manifests itself as myocardial infarction, stroke or angina pectoris. The formation of atherosclerotic plaque in blood vessels is directly related to an increase in the content of LDL (low-density lipoproteins), which deliver increased amounts of cholesterol to the vascular wall. When the internal lumen of the coronary artery decreases by 50%, the oxygen supply to the heart muscle deteriorates and ischemia , which is clinically manifested by angina pain. It occurs more often during physical or mental stress, is localized behind the sternum, has a pressing or compressive nature and can radiate to the left shoulder, jaw or shoulder blade.
The main treatment strategy for stable coronary artery disease is to prevent progression, reduce the frequency and intensity of angina attacks, increase exercise tolerance and reduce the progression of atherosclerosis. By reducing the frequency and intensity of attacks, an improvement in the patient’s quality of life is achieved. It has been proven that reducing blood cholesterol levels by just 1% reduces mortality from CVD by 3%. Therefore, great importance is given to following an anti-atherogenic diet , which helps correct existing lipid metabolism disorders, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle (stop smoking, increase physical activity, control weight and blood pressure ).
Nutrition for coronary heart disease is organized within Table No. 10C , which is specially designed for patients suffering from atherosclerosis. The main nutritional points are:
- Reducing the consumption of animal fats and foods high in cholesterol.
- Reducing the total calorie content of food by reducing carbohydrate intake. It's not so much a low-fat diet that helps lower LDL cholesterol, but a low-carb diet.
- Increasing fiber intake. You need to eat up to 500 g of fruits and vegetables. Dietary fiber absorbs cholesterol and is excreted in feces. A large amount of fiber is found in beans, oatmeal (whole), wheat bran, nuts, dates, prunes, raisins, cranberries, raspberries, gooseberries, figs, dried apricots. Somewhat less - in barley, buckwheat, pearl barley, oatmeal, carrots, cabbage, peas, eggplants, sweet peppers, quince, pumpkin, mushrooms, oranges.
- An increase in vegetable fats in the diet, since in case of coronary artery disease it is important to maintain high-density cholesterol levels by consuming omega-3 PUFAs . Their daily requirement is 2 g. 100 g of flax seed contains 22.8 g, the same amount of walnuts - 6.8 g, mackerel - 2.5 g, tuna, soy and salmon - up to 1.6 g , in herring - 1.5-3.1 g. Enriching the diet with fish oil for a month (you can consult a doctor and use the drug) causes a significant decrease in cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL cholesterol. Thus, the following will help reduce cholesterol: fatty sea fish, avocados, greens, nuts (excluding peanuts and cashews), cabbage and olive oil.
- Limit salt to 6-8 g (cook without adding salt, and then add salt, using the norm during the day).
- There are two options for therapeutic nutrition. The first is for people with normal weight, which allows the consumption of fats up to 80 g per day (half vegetable) and carbohydrates within the physiological norm (350-400 g). The second option is prescribed for overweight and is characterized by a reduction in the amount of fat to 60 g, and carbohydrates to 250-300 g. Of course, this option of therapeutic nutrition has a lower calorie content.
All animal products contain cholesterol. A person cannot completely abandon them. It is necessary to exclude foods with a high content of it: brains, liver, kidneys, yolk, canned food in oil, fatty pork, mackerel, stellate sturgeon, carp, cuttlefish, squid, oysters, eel, pork fat, goose, lamb, beef, all sausages.
Eliminate artificial trans fats, which are undoubtedly associated with the risk of coronary events. During industrial curing of liquid oils, trans isomers of fatty acids are formed. They are present in margarine, mayonnaise, and many sausages.
It is necessary to take into account not only the amount of fat and cholesterol , but also the salt and sugar content in foods. The main enemies of atherosclerosis are refined carbohydrates. Therefore, the following are limited: sugar, preserves, jams, flour products, sweets, potatoes and baked goods. If possible, eliminate completely simple carbohydrates, since they stimulate the production of insulin , under the influence of which excess sugars are converted into fat. Salt makes it difficult to break down fats; in addition, under its influence, the wall of blood vessels becomes loose and more susceptible to the deposition of cholesterol in it.
According to research, the danger in atherosclerosis is the lack of sufficient fiber in food, so the diet for IHD should be rich in vegetables, fruits, berries, bran, pectin (apples, dried dogwood), whole grains, walnuts, almonds.
The most important elements for normal heart function are potassium and magnesium. The function of the “sodium-potassium pump” (it is not possible without the presence of magnesium) provides intracellular potassium content, which is necessary for neuromuscular contractility. Potassium deficiency leads to cardiovascular disorders, primarily rhythm disturbances and inhibition of cardiac contractility. With hypokalemia, fluid retention occurs and blood pressure increases. It has been found that a low-salt diet is more effective in reducing blood pressure if it is supported by additional potassium, for example, through food.
Its daily requirement is 1.2-2 g. We get potassium by eating dried apricots, raisins, pine and walnuts, almonds, peanuts, jacket potatoes, porcini mushrooms, sunflower seeds, bananas, oatmeal and buckwheat, peaches, watermelon, apples , pears, prunes, apricots, melon, eggplant, cucumbers, apple juice, citrus fruits, Brussels sprouts and kohlrabi, peas, lentils, beans, spinach, carrots.
Magnesium is necessary for people who have suffered a myocardial infarction , hypertensive patients, for the prevention of stroke , for those who take diuretics or are exposed to stress. Its high content is in wheat bran, pumpkin and sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, almonds, pine nuts, peanuts, walnuts, spinach, beans, dates.
In this disease, antioxidants - vitamins E , A , C and selenium. Vitamin C is found in all vegetables and fruits, but most of all in black currants, rose hips, sea buckthorn, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower, green peas, red peppers.
Sources of vitamin A are sea fish, all citrus fruits, carrots, tomatoes, egg yolks, apricots, spinach, pumpkin.
Vitamin E can be obtained by consuming vegetable oils, cereals, legumes, almonds, peanuts, and sunflower seeds. Sources of selenium are: tuna, sardines, sunflower seeds, beef, milk, bran, pink salmon, whole grain bread, chickpeas, beans, eggs, lentils. All these products are available and try to constantly introduce them into your diet.
Moderate physical activity (walking) is a unique remedy for atherosclerosis and heart attack prevention. No diet or medication can replace physical activity. You need to exercise carefully to avoid attacks of chest pain. But a sedentary lifestyle is not acceptable either. Discuss your exercise program with your doctor.
General principles of nutrition
Cardiac ischemia is a malfunction of the coronary circulation, damage to the middle layer of the heart muscle, which occurs due to insufficient oxygen levels in the blood and its entry into the myocardium.
After the first signs of pathology, measures are taken to eliminate it. Proper nutrition for coronary heart disease plays one of the main roles in the fight against it. The basic principles of constructing a patient’s diet are moderate nutrition with the exclusion of products saturated with animal fats, cholesterol and salt. A diet for coronary heart disease is a balanced intake of food that completely saturates the body with essential vitamins and minerals. The main element in this regime is ascorbic acid, which is found in many products of plant origin.
Doctors recommend eating small and frequent meals during cardiac ischemia. During the day, take 200 ml of food at least five times. At the same time, a temporary restriction of meals in the evening is established. Dinner should take place at least three hours before bedtime.
The recommended method of preparing dishes is steam and boiled cooking, stewing. Baking is also a useful method.
Authorized Products
The diet for coronary heart disease includes:
- Fish and seafood dishes that should prevail in the diet. omega-3 fatty acids from fatty sea fish (herring, salmon, salmon, sardine, mackerel, halibut). You should eat fish 3 times a week, but exclude caviar and squid. The benefits of seaweed for this disease are great (give preference to dried and prepare it yourself, since industrially produced salads contain sodium nitrite).
- 400-500 g of vegetables, which are a source of dietary fiber (you need to get 30-50 g of them per day).
- Additionally, you can increase the amount of dietary fiber in your diet through pure pectin or wheat bran. When consuming bran, you need to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day. It is worth remembering that prolonged use and large quantities (more than 60 g) disrupts the absorption of vitamins and microelements.
- In addition to fiber, flax, fenugreek and sesame seeds contain oils and phytosterols , which are useful for atherosclerosis. Use all kinds of vegetable salads as a side dish for meat and fish.
- Among vegetables, give preference to white cabbage, the use of which is useful in any form; include it daily up to 100 g. Prepare stewed cabbage, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, eggplant or a mix of vegetables.
- Limit your consumption of potatoes as a carbohydrate product. All red-purple vegetables contain polyphenols, and they stimulate the production of HDL. Therefore, eggplants, beets, and red cabbage would be useful additions.
- Fruits include pomegranate, viburnum, dogwood, blueberries, raspberries, strawberries, blackberries, chokeberries, lingonberries, red grapes, cranberries and their juice.
- Beans, cereals and soy products can lower cholesterol due to their high fiber content. The high protein content of legumes can replace the consumption of meat, so they should be included in the diet daily. Feel free to eat soy products - tempeh, tofu, miso.
- Unrefined vegetable oils, which should make up the majority of the fat component. They are used to season ready-made dishes. A representative of MUFA is oleic acid , which olive oil is rich in.
- Sources of omega-6 PUFAs are: corn, sunflower, cottonseed oil - they also help reduce cholesterol levels.
- Omega-3 fatty acids contain flaxseed, rapeseed, sesame, mustard, soybean, and nut oils. Alternating oils will give dishes different flavors.
- Nuts and seeds are rich in monounsaturated fats, so they should be included in your diet daily, but limited due to their high calorie content - up to 30 g. Some oils and seeds, among other things, contain phytosterols and phytostanols (coconut, corn, soybean, fir, rapeseed, cedar oils) , sunflower and pumpkin seeds, pistachios, pine nuts, almonds), which have a hypolipidemic effect and can reduce cholesterol by 10%, subject to a low-calorie diet.
- Fruits and berries are mainly raw, as well as decoctions and compotes made from them. If we talk about the content of pectins, which absorb cholesterol and remove it from the body, there are a lot of them in apples, citrus fruits, viburnum, dried dogwood berries, cranberries, and grapes.
- First courses with water or vegetable broth; prefer vegetable first courses to cereal ones due to their lower calorie content (cabbage soup, beet soup, borscht, green borscht). From a dietary point of view, you cannot add vegetables to soups.
- Eating poultry and meat once a week. Choose dietary meat of low-fat varieties and cook it boiled or baked. To reduce cholesterol and fat in meat, it is first boiled and then baked.
- Rye, grain and bran bread, but limited. As a dessert, you can have savory cookies or whole grain bread.
- Milk, cottage cheese, fermented milk products and low-fat yoghurts. The benefits of kefir and yogurt prepared independently using sourdough are invaluable. Cheeses can also be low-fat (20-30%), cream is used sparingly when preparing dishes. According to classic dietary recommendations, you can eat 2 whole eggs per week and an unlimited amount of protein. However, the question of the dangers of egg yolk remains open.
- There are various cereals in the form of porridges and casseroles, but given the need to lose weight, their quantity is reduced. It is rare to include wholemeal pasta.
- Green tea with lemon, rosehip decoction, juices, and still mineral water should be drunk up to 2 liters per day.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| greenery | 2,6 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 36 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| cashew | 25,7 | 54,1 | 13,2 | 643 |
| sesame | 19,4 | 48,7 | 12,2 | 565 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Sausages | ||||
| boiled diet sausage | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 170 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Features of therapeutic nutrition for heart and vascular diseases
Therapeutic nutrition for cardiovascular diseases is based on the correct ratio of nutrients in the diet, increasing the amount of fruits and vegetables in the daily menu, reducing the consumption of salt, simple carbohydrates and saturated fats.
In some cases, it is necessary to reduce the amount of fluid you drink, but such a decision is made only on the basis of a doctor’s conclusion after examining and examining the person. For heart disease, it is recommended to follow diet No. 10, 10a, 10c, 10i. Potassium, fruit and vegetable, and hyposodium diets are sometimes used.
Diet Goal #10:
- quickly restore normal blood circulation after a heart attack, with hypertension, rheumatism, heart defects and atherosclerosis (be sure to read how to eat with atherosclerosis
; - reduce the load on the heart during digestion;
- improve metabolism for effective weight correction;
- remove metabolic products from the body;
- normalize the functioning of the excretory system (liver and kidneys).
Based on the goals set, the nutritional principles for this diet are as follows:
- limiting salt to 5 g and liquid to 1.5 liters per day;
- maximum variety of diet with fractional meals;
- restriction of coarse fiber (legumes, eggplants, mushrooms, etc.);
- increasing the number of foods that normalize fat metabolism;
- adding to the menu products containing alkaline compounds, in particular cabbage, milk, lemons, carrots, apples;
- increase in foods that contain vitamins B, A, PP, E, C, retinol, calcium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus.
Typically, the calorie content of such a diet does not exceed 2800 kcal per day. Food is best boiled, steamed or baked.
Fully or partially limited products
- Exclude products made from puff pastry, pastries, cakes, cream pies, confectionery (sweets, waffles, halva, chocolate), sugar, jam, ice cream, white rice, semolina.
- Highly extractive meat/fish/mushroom broths.
- Fatty meats, cooking fats, mayonnaise, margarine, kidneys, brains, liver, sausages, canned food and smoked meats.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Canned fish, caviar, smoked fish.
Limit egg yolks, strong tea and coffee, cocoa, grapes, honey, raisins.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| red radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 20 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 11% | 16,0 | 11,0 | 1,0 | 170 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
What foods are prohibited for heart and vascular diseases
Prohibited foods for cardiovascular diseases and diet No. 10 include:
- marinades, pickles, canned food;
- meat and mushroom soups and broths;
- fried meat and fish, fatty meats;
- legumes in large quantities;
- fish roe;
- store-bought sauces and ketchups;
- instant products, snacks and fast food;
- fried potatoes;
- liver, brains, kidneys, sausages and smoked meats;
- baked goods and chocolate, cakes and cream pies;
- restrictions on onions, garlic, radishes, sorrel;
- strong coffee and tea, cocoa, sweet soda.
Menu (Power Mode)
Developing healthy eating habits involves avoiding sausage, ham, smoked meats, meatloaves, fast food, and pates. Instead, the diet should include properly cooked fish and meat - boiled or baked without adding fat. You should choose vegetables in any form as a side dish. Eliminating simple carbohydrates and limiting fat will immediately have a positive effect on weight, and eating five to six times a day will prevent you from feeling hungry, and the diet will be easily tolerated.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Why is it important to adhere to therapeutic nutrition for heart disease?
One of the main goals of therapeutic nutrition is to enhance the effect of taking medications prescribed by a doctor. In some cases, with a properly selected diet, it is possible to do without medications altogether or significantly reduce their amount and period of use. For this reason alone, it is worth listening to the advice of an experienced nutritionist and switching to a therapeutic diet immediately after making the appropriate diagnosis.
A nutritionist will help develop a treatment menu and the required level of physical activity at which the load on the heart and blood vessels will be optimal. In addition, a nutrition consultant will tell you which habits you should give up right now.
These include smoking, drinking alcohol, overeating, abuse of simple carbohydrates, leading to obesity and insulin resistance ( diabetes mellitus
is an aggravating factor in cardiovascular diseases).
Another important task of diet therapy is the correction of metabolic disorders that inevitably arise with such diagnoses, relieving the heart from excessive stress, and improving the absorption of food through proper diet.
Thanks to a special diet, it will be possible to normalize weight, lower blood pressure, reduce lipid and blood sugar levels, and reduce the susceptibility to thrombosis. All this will certainly affect your well-being and general health, and will also significantly reduce the risk of developing serious cardiovascular pathologies and complications, disease progression and death.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Example of a daily menu for diet No. 10
Here's what your menu might look like if you follow diet No. 10:
- Breakfast (8 a.m.)
– cottage cheese with sour cream, semolina or rice porridge with water or milk, bread and butter, tea with milk. - Snack (10 am)
– a glass of kefir or yogurt, fruit. - Lunch (12 hours)
- pureed vegetable soup, steamed turkey meatballs, porridge, baked apple. - Afternoon snack (15:00)
– one-egg omelette, applesauce, rosehip drink. - Dinner (18:00)
– buckwheat or vegetable cutlet, cottage cheese pudding or potatoes with boiled fish and jelly.
Reviews and results
This food is designed for a long time, as it is balanced. Vegetables and fruits, nuts, seeds, all kinds of vegetable salads dressed with vegetable oil, fish, chicken, egg dishes - all this makes the diet varied, nutritious and healthy. Limiting carbohydrates, fats and meat, as well as proper cooking methods, can help you lose weight and normalize cholesterol levels.
The diet is well tolerated, but some find it difficult to reduce the amount of salt, avoid sweets and favorite foods. Since nutrition does not have strict restrictions, you can very rarely allow yourself “dietary liberties”. All these points, as well as the results of treatment, are noted in the reviews of patients.
- “... Angina attacks began to occur more often. At this time, a burning pain appears and the hand goes numb. The attacks last 4-5 minutes and can happen anywhere, so I always carry pills with me. The examination revealed slightly elevated cholesterol and blood pressure. I have also gained weight over the past 5 years. The doctor advised me to go on a diet and said that I could try to bring my cholesterol back to normal. The transition to a healthy diet was not easy (due to salt, lack of sweets, smoked meats and sausages). The craving for this disappeared only after a month. I eat a lot of vegetables, replace sweets with dried fruits and honey, bread and cookies with bread made from grain flour with bran and flax or sesame seeds. I liked eating this way. As a result, I lost weight and improved my health. Cholesterol returned to normal only after six months of being on a diet”;
- “... I regularly see a cardiologist for angina and take treatment. I try not to get nervous and don’t eat before physical activity or going outside. In addition to the pills, a diet was prescribed. I realized that I couldn’t do without it (weight, periodically high sugar levels and slightly elevated cholesterol). As a result, in six months the weight dropped, cholesterol was normalized without pills, so I’m happy with the results.”
What do they enrich the diet with?
To improve the condition of coronary artery disease, eat foods that help remove cholesterol from the body:
- fish - it does not contain cholesterol, but contains polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega-3 and omega-6), which have a beneficial effect on the walls of blood vessels and destroy cholesterol accumulations and plaques. You can consume any types of fish, even fatty ones (flounder, mackerel);
- fresh vegetables and fruits - rich in fiber, which enhances intestinal motor function, quickly removes cholesterol and other harmful products of intestinal metabolism;
- cereals - buckwheat, wheat and oatmeal - contain a huge amount of useful vitamins and minerals, help the body cope with excess cholesterol;
- bran - used as a food additive in ready-made dishes, but not more than 3 tbsp. l. in a day.
It is important to consume large amounts of vitamins B, C and P. They restore damaged walls of coronary vessels, reduce their fragility and prevent rapid aging of myocardial cells. B vitamins strengthen the heart and increase its elasticity. An excess of such substances may not only not have the necessary effect, but also harm the general condition of the body.
The essence and rules of the diet
Angina pectoris is one of the manifestations of coronary heart disease that develops due to atherosclerosis. The disease occurs when fat metabolism is disrupted - the body receives a lot of fatty fats, which contribute to the formation of “bad” cholesterol, which is deposited on the walls of blood vessels in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. Thus, the lumen of blood vessels decreases, so the heart muscle receives insufficient oxygen, and chronic oxygen starvation gradually develops.
By correcting your diet, you can prevent the progression of angina pectoris. This requires compliance with the following rules:
- Diet for blood type 2 negative: food table and diet
- with a normal initial weight, reduce the daily calorie content to 2800-2900 kcal, and correctly distribute the chemical composition of the diet: proteins - up to 100 g, fats - up to 90 g, carbohydrates - up to 350 g;
- if you are overweight, reduce your daily caloric intake so that it does not exceed 2000 kcal, with the amount of fat per day up to 70 g, and carbohydrates up to 300 g;
- switch to fractional meals - in addition to the 3 main meals, you can have 1-2 snacks, and the diet should be varied, including products of predominantly plant origin;
- maintain the correct water regime - drink about 2 liters of liquid during the day;
- exclude fats of animal origin from the diet, with the exception of fatty sea fish and seafood, since they contain omega-3 acids, which have a positive effect on cholesterol metabolism;
- prepare food through proper heat treatment, such as stewing, boiling and steaming, but frying is not recommended.
By following these rules, you can get rid of extra pounds and maintain a healthy weight. This will improve metabolic processes in the body, avoid the development of complications of angina pectoris and maintain stable health.
Product selection
The key point in the diet is the correct choice of foods, because some of them are prohibited, others are acceptable in small quantities, and others should prevail in the daily menu. Each option should be considered separately.
Prohibited
It is necessary to exclude those foods that increase cholesterol levels in the blood, impair blood circulation and promote the formation of blood clots, which impede blood flow and impair the nutrition of the heart muscle. These are:
- fatty meats, such as pork and lamb;
- fatty poultry - duck, goose;
- sausages;
- offal, including liver and brains;
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- cream;
- fried eggs;
- flour and confectionery products;
- chocolate;
- ice cream;
- lemonade and sweet carbonated drinks;
- alcohol.
The listed products are also prohibited due to their high content of easily digestible carbohydrates, which are often the cause of obesity.
Limited
There are foods that can be consumed in limited quantities:
- Proper nutrition of a patient with heart failure and edema
- drinks with a high caffeine content (coffee, strong tea) - 1-2 cups per day, as they have a strong diuretic effect and remove a lot of fluid from the body;
- fatty fish (mackerel, trout, sardine), seafood – up to 3-4 times a week;
- meat (beef, veal, turkey, rabbit) – once a week;
- eggs, chicken - up to 2-3 times a week;
- salt - up to 5-6 g per day, since it prevents the removal of fluid from the body.
Any leafy green is worth using as a salt substitute as it contains vitamins A, B, C and PP, as well as many minerals, including folic acid, phosphorus, calcium, potassium and iron.
Recommended
The basis of the daily diet consists of products that meet the following criteria:
- contain minerals (phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, iron, potassium, sodium, zinc);
- are sources of vitamins A, B, C, E, PP;
Vitamin C is especially useful for angina, which is a strong antioxidant, prevents blood vessels from narrowing, reduces their permeability and has a relaxing effect on the arteries.
- rich in fiber and coarse fibers, which remove excess “bad” cholesterol from the body, cleanse the intestines, normalize metabolism, and slow down the process of vascular damage.
The following products meet these criteria:
- beans, bran and cereals (especially oatmeal, buckwheat, millet, barley);
- milk and fermented milk products are valuable sources of lactose, thiamine, vitamin A, calcium;
- vegetables, especially leafy vegetables (any cabbage, spinach);
- fruits, especially banana, as it is high in potassium;
- vegetable oils (sunflower, olive, corn) – sources of mono- and polyunsaturated fats, as well as vitamins A, D, E, K and F, involved in cell formation and metabolism;
- nuts (walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts);
- honey, since it is a valuable source of potassium and successfully replaces sugar;
- dried fruits (raisins, prunes, dried apricots).
It is worth noting that this set of products requires a therapeutic diet - table No. 10. It is anti-atherosclerotic and is prescribed to normalize metabolism, reduce blood clotting and restore the metabolism of blood vessels and heart muscle.
Nutritional Features
Products for cardiac ischemia should contain increased amounts of vitamin C. It prevents vasoconstriction, has a relaxing effect on the arteries, reducing pressure, and also reduces the permeability of blood vessels.
In addition, it is a powerful antioxidant. The menu includes foods rich in potassium, magnesium, iodine, manganese and zinc. The body also needs methionine, an essential amino acid that is part of proteins, and B vitamins. The introduction of seafood, rich in cholesterol that is beneficial for the human body, into the diet is also necessary.