Increased hemoglobin is a rather dangerous condition, which in 90% of cases indicates disruptions in the metabolic processes occurring in the body.
This may also mean that tissues and organs experience oxygen starvation, and increased hemoglobin is the body’s protective reaction to a decrease in the amount of micronutrients received.
In any case, according to research , it is possible, in most cases, to lower hemoglobin levels in men and women with the help of a specialized diet. What products best reduce it? And which ones, on the contrary, should not be consumed?
When should hemoglobin be reduced?
In most cases, an increase in hemoglobin levels in adults is complemented by an increase in blood viscosity due to impaired water-salt metabolism. And thick blood leads to an increased risk of blood clots and plaques, and coagulation also increases. All this can be supplemented:
- hypertension (increased blood pressure to a critical level);
- thrombosis (if the blood flow slows down to the point where the blood literally coagulates in some vessels);
- heart attack (if thrombosis affects the heart muscle or the blood vessels that supply it);
- stroke (if thrombosis affects the circulatory system of the brain);
- atherosclerosis (when cholesterol plaques form on the walls of blood vessels, thereby impeding normal blood flow).
At the same time, an increase in hemoglobin may indicate pathologies in metabolic processes when the body receives insufficient amounts of oxygen and other micronutrients.
In some cases, elevated hemoglobin is normal. This happens, for example, among residents of mountainous regions, where the oxygen content in the air is significantly lower.
Also, hemoglobin and red blood cells naturally increase in smokers, since they inhale fumes while smoking. It, in turn, creates inseparable compounds with hemoglobin, thereby deactivating the molecule. In these cases, the hemoglobin level should not be reduced, since the body will experience constant oxygen starvation.
Hemoglobin also often increases in the summer or during regular physical activity, when the body actively loses water and minerals (along with sweat). But normalizing hemoglobin concentration in this case is quite simple - you need to drink as much water as possible (in summer - from 3 liters or more).
Why and how much?
Iron acts as a catalyst (accelerator) for many metabolic processes. Without it, full breathing is impossible. Not only the lungs participate in respiration; every cell “breathes” as long as it is endowed with oxygen.
But iron is not synthesized independently; its source is certain foods.
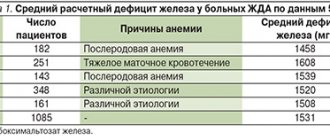
Approximately 15 mg of the element is needed per day for women (the dosage is doubled for pregnant and lactating women), 10 mg for men, and for children from 5 to 15 mg.
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, iron deficiency is observed in a large part of the world's population (more than 50%).
General nutrition rules
With elevated hemoglobin, nutritionists recommend following the following tips and recommendations:
- Consume foods and dishes rich in calcium. This element reduces the bioavailability of iron. That is, it slows down its absorption. Namely, iron is the main component of hemoglobin and it is with its help that oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported to/from the lungs.
- Eliminate foods rich in vitamins B12 and B9 from your diet. This will also help reduce the bioavailability of iron and slow down the processes of generating new hemoglobin molecules.
- Eliminate iron-rich foods from your diet. These include apples, greens, beef, pork, meat by-products (liver, lungs, heart), fish. Preference should be given to porridge (with the exception of buckwheat), dairy products, and pasta. The diet for each patient must be prepared individually by a nutritionist.
If we are talking about infants, then breast milk helps them normalize hemoglobin. If artificial feeding (formulas) is used, then you should consult a pediatrician about this - he will recommend formulas that contain a minimum of iron and B vitamins.
First harbingers
Lack of iron in the body can lead to various diseases. It is a mistake to believe that a low level of iron in the blood is already anemia. The first signs of element deficiency appear long before anemia occurs. Among them:
- Dyspnea.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Noise in ears.
- Floaters before the eyes.
- Clear signs.
If you do not attach importance to these symptoms, then in the future, with insufficient iron intake in the body, serious consequences will develop.
- Iron-deficiency anemia. This disease can occur in different ways. The mild form is treated by adjusting the diet. For moderate anemia, you need to take special medications under the supervision of a doctor and constantly monitor your blood tests. For very low hemoglobin, hospital treatment is indicated.
- Decrease in the body's defenses. The immune system guards the entire body. Failure in its operation leads not only to frequent colds, but also to allergic reactions and inflammatory processes.
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system. The consequence of severe iron deficiency with concomitant anemia may be the development of heart failure. If there were heart problems (for example, hypertension) before the development of anemia, the risk of developing heart failure increases, as well as the development of other pathologies (heart attack, stroke).
- Chronic headaches. This is not just a symptom, a malfunction of the vascular system, it is a serious problem that affects the quality of life. Headaches can often be accompanied by pressure surges and the development of neurological symptoms.
- Depression. The functioning of brain neurotransmitters is impaired due to iron deficiency. The balance of amino acids, adrenaline, dopamine, serotonin and other mediators responsible for important functions changes. The consequence is the gradual development of depression. This is not just a bad mood in rainy weather, it is a clinically confirmed diagnosis with characteristic symptoms.
- Developmental defects in a child. They occur when iron levels are very low in children. During intrauterine development, the child receives iron from the mother. If the baby was born on time, then the supply of the element should be normal. If the birth is premature, there may be problems, since the fetus receives a considerable amount of iron in the last week before birth. If the mother has an iron deficiency during pregnancy, the child will not receive enough iron, and autism and mental retardation may develop.
According to the above, it can be argued that the lack of iron is due to the fault of the person himself. Therefore it is important:
- Eat a balanced diet.
- When playing sports, you need to understand the importance of nutrition for the body to fully recover after exercise.
- During pregnancy, you need to pay special attention to your health, regularly get tested and visit a doctor to prevent all sorts of risks for mother and child.
- Caring for children includes providing them with nutritious, healthy food, especially during critical age periods; all this is in the hands of parents, their responsibility.
- A timely medical examination will allow you to identify many diseases in the early stages.
It all comes down to one thing - vigilance in relation to health. It is better to prevent a problem than to eliminate its serious consequences.
What should be excluded from the diet?
For greater effectiveness, when following a diet, be sure to exclude from the diet foods that cannot be eaten with increased hemoglobin:
- Fat meat. Particularly “dangerous” are beef, pork, as well as meat by-products (liver, lungs, heart, kidneys, and so on). Meat is rich in iron, as well as B-group vitamins (therefore, iron from such products is easily absorbed).
- Pomegranate and pomegranate juice. Pomegranate increases hemoglobin and blood pressure. For hypotension, it is extremely useful to include in the diet, but with increased blood viscosity, it should be completely excluded.
- Fatty fish. Rich in omega-3 acids, which accelerate most intercellular metabolic processes. Their use should be minimized. You can also include other seafood here, including oysters, shrimp, red and black sparkle, and seaweed.
- Chicken eggs. More precisely, it is the yolks (but the whites – slightly, but still reduce hemoglobin). It is also better to exclude quail from the diet.
- Spices. Turmeric especially strongly increases hemoglobin (it contains not only iron and herbs (parsley, dill, basil), but also B-group vitamins). It is better to temporarily stop using them altogether.
- Cherries and sweet cherries. These berries raise hemoglobin levels no worse than pomegranate and pomegranate juice.
Foods that increase the bioavailability of iron
In order for iron from food to be better absorbed by the body, you need to combine foods correctly.
Products with vitamin C
Vitamin C promotes better absorption of iron from plant foods. It captures it and stores it in a form that is easily absorbed by cells.
These are products such as:
- Citrus.
- Leafy vegetables are dark green in color.
- Bell pepper.
- Melon.
- Strawberry.
Read more: Which fruits and vegetables have the most vitamin C?
A study was conducted that showed that taking 100 mg of vitamin C with meals can increase iron absorption by up to 67%. [8].
Therefore, when eating a meal rich in iron, you can wash it down with, for example, orange juice or combine it with other foods from the list.
Foods - sources of vitamin A and beta-carotene
Vitamin A is necessary for the body to maintain visual function, skeletal system and immunity. Beta keratin is an orange-red pigment found in fruits and vegetables. It can be converted into vitamin A.
Beta-carotene and vitamin A are found in the following foods:
- Carrot;
- Potato;
- Spinach and cabbage;
- Zucchini;
- Red pepper;
- Melons;
- Apricots and peaches;
- Oranges.
Scientists observed 100 subjects who ate cereals. The study showed that vitamin A increases the bioavailability of iron from rice to 200%, from wheat to 80%, and from corn to 140%. With the addition of beta-carotene, the bioavailability of iron increased for rice by more than 300%, and for corn and wheat by 180% [9].
Animal products
Fish, meat and poultry themselves act as a source of heme iron, and also contribute to the absorption of its non-heme form. There is evidence that the combination of animal products with cereals increases the absorption of non-heme iron from plant foods by 2-3 times [10].
In addition, it was found that adding 75 g of meat to food increases the bioavailability of iron by 2.5 times. Scientists have concluded that 1 g of meat or other animal food has an effect comparable to the effect of taking 1 mg of vitamin C [11].
Other recommendations
Doctors with elevated hemoglobin also recommend:
- Minimize physical activity. This will help normalize the water-salt balance, reduce blood pressure and blood viscosity.
- Drink as much water as possible. And most importantly - without gas, since the carbon dioxide contained in such water slightly increases the bioavailability of iron (due to stimulation of the gastrointestinal mucosa).
- Refusal of multivitamin complexes. It is especially important to avoid taking B vitamins.
Who is most at risk of getting sick due to lack of iron in the body?
- Women of childbearing age, especially with heavy menstruation;
- Pregnant, recently given birth and breastfeeding women;
- People who have undergone major surgery or physical trauma;
- People with inflammatory bowel disease or celiac disease;
- Those who follow an unbalanced diet. This is especially true for vegetarians and vegans, who do not eat meat, fish or poultry and do not add plant sources of iron to their diet.
- Infants and toddlers who drink more than 700 milliliters of cow's milk every day. Cow's milk is low in iron and may reduce the absorption of iron from other sources.