One of the effective methods for diagnosing many diseases is the Valsalva maneuver.
This is a pretty simple test. Does not require the use of special instrumental equipment. Moreover, as a result of its implementation, the doctor has the opportunity to establish the cause of the disease and make a diagnosis at the initial stages of the pathological process.
This method is widely used in cardiology, surgery, neurology, urology and otolaryngology.
What is the Valsalva maneuver, how does it affect a person’s condition, when should it be used and when should it not be used? The answers to these questions are contained in the article.
The essence of the method
The differences between such concepts as the test and the Valsalva maneuver are as follows:
- The study is a diagnostic method that allows you to identify pathological processes.
- Reception is a certain human activity that causes high pressure in the middle ear, as well as in the abdominal and thoracic areas.
Initially, this technique was successfully used in obstetrics during childbirth and to free the ear from earwax or purulent plugs.
Operating principle
The pressure created in the chest and abdominal areas as a result of deep inhalation, subsequent breath holding and pressure changes blood flow. This state is accompanied by phases of tension and relaxation.
During stress, the blood supply to the vessels of the heart decreases, which leads to a drop in blood pressure and a simultaneous increase in intracranial pressure. During relaxation, blood flow is restored and blood pressure rises accordingly.
During this stage, receptors in the cervix sense changes in blood pressure, which send a signal to the vagus nerve in the brain, helping to further reduce the heart rate. This is how a healthy body reacts to the Valsalva maneuver.
The inability of the heart muscle to change the rhythm of the heart indicates the likelihood of developing pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system.
Holding your breath and exercising also affects the pressure in the lower extremities. Abnormal changes in the venous valves of the legs and thighs reverse blood flow, indicating dysfunction.
The Valsalva technique simultaneously increases pressure in the nasopharynx and middle ear, which, when pus accumulates in it, causes perforation of the membrane and its expulsion from the auricle.
Decoding the results
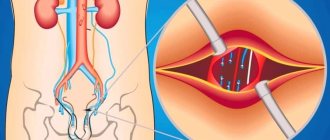
Positive test. Normally, the diameter of the vessels of the pampiniform plexus ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 mm. If, when straining, they expand to 3 mm or more, then a varicocele is diagnosed. The diameter of healthy veins should not increase by more than 1 mm under tension. With varicocele, during an ultrasound near the testicle, you can see many convoluted dark-colored structures that do not reflect ultrasound waves. Blood moves slowly around them. On an ultrasound in the supine position, the flow may become retrograde - blood flows backwards. This means that the channel's reserves have been exhausted. Another possible type of reaction to Valsalva is an increase in blood flow speed. This happens if there is an additional outflow pathway that is activated when straining.
Varicocele scoring system
Stages of varicocele determined by the Valsalva test:
- The veins are not dilated, but the direction of blood flow changes when straining. This phenomenon is called "reverse".
- A slight expansion of the veins in the area of the upper pole of the testicle is noticeable. Reverse is present during testing.
- The veins expand from the upper to the lower pole only in a standing position. There is a reverse.
- Dilated veins are also observed in the supine position. The testicle is reduced in size.
- The veins are dilated from the upper to the lower pole in the supine position, there is no reverse, since initially the blood flow was in the opposite direction. This is a very bad sign.
Dilated vessels on ultrasound
Varicocele grade 4. Possible testicular hypotrophy
Negative test. When straining, the vessels of the scrotum expand within normal limits, the blood flow is normal.
Indications for use
The Valsalva method is used to diagnose the following pathological conditions:
- Varicocele;
- different types of tachycardia;
- Possibility of death after a heart attack;
- determination of the functional state of the venous valves of the lower extremities;
- determination of the condition of the ear canals.
In addition, release is used to relieve symptoms of arrhythmias, reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure.
With tachycardia, rapid heartbeat can occur both in connection with physical activity and as a symptom characteristic of myocardial dysfunction. The Valsalva maneuver not only helps classify the types of this pathology, but also helps stabilize the heart rhythm.
The essence of the method
During the examination, the patient is in a standing or sitting position (rarely lying down). He is asked to exhale all the air. This is followed by a long, deep breath (with your nose and mouth closed). Breathing after inhalation should be held for 15-18 seconds. Then exhale slowly, followed by sweat.
Rapid entry of air into the lungs speeds up blood flow to the heart, and stopping breathing slows down its movement. This may cause slight dizziness and weakness.
Treatment is preceded by recommendations from a specialist doctor.
Recovery after
No special manipulations, medications or folk remedies are required after the ear blowing procedure.
After the procedure, the patient feels well and does not require a recovery period; he can go home. If, after carrying out the blowing procedure using any of the existing methods, undesirable manifestations appear, then it is necessary to urgently seek help from a specialist.
Among these symptoms:
- nose bleed;
- severe tinnitus;
- dizziness;
- discharge from the ears;
- convulsions.
Any discomfort in the ears or nasopharynx should force a person to consult an otolaryngologist about this.
Sample options
Depending on the purpose (diagnostic or therapeutic), the procedure is performed differently for different diseases.
Detection of varicocele
The functional Valsalva test allows you to determine not only the presence, but also the degree of development of varicocele, which is manifested by dysfunction of the venous valves located in the testicles and spermatic cord.
The diagnosis is checked while standing. Vein retention increases blood flow to the testicles, allowing palpation of their dilated veins. If we are dealing with valve disease, an enlargement of one of the testicles (often the left one) is clearly visible even to the naked eye. Very rarely there is a defect in the right testicle or both.
When a conscript is recommended to be diagnosed with varicose veins of the 2nd degree, the operation is the basis for rescheduling the service.
In the supine position, the examination is carried out if grade 3 varicose veins are suspected. To clarify the diagnosis, ultrasound is used to determine the size of the lumen of the testicular veins.
The Valsalva maneuver and ultrasound findings are important for the choice of surgical intervention.
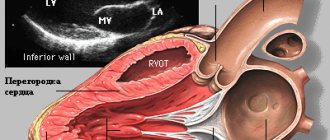
Cardiac test
A patient's examination in cardiology is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor. Cardiogram and blood pressure readings are recorded simultaneously.
The procedure is slightly different from the previous version (for varicocele). After taking a deep breath, you slowly (over 10-20 seconds) exhale through a special mouthpiece. This is followed by relaxation, as a result of which breathing is restored.
To determine the result, ECG readings and blood pressure are analyzed.
The test is considered positive if the pulse and blood pressure drop during inspiration but then rise.
Valsalva ratio
The ratio of long and short ventricular contractions (R - R) is used to determine the likelihood of sudden cardiac arrest.
Under normal conditions, this coefficient should not exceed 1.7. A range below 1.3 indicates possible death.
Vascular surgery
In the case of varicose veins, before using the Valsalva technique, a preliminary examination of the condition of the veins of the lower extremities is carried out - ultrasound. Then, performing the technique described above leads to an increase in pressure in the vena cava.
At this stage, the ultrasound procedure is repeated on problem areas. This makes it possible to diagnose insufficient functioning of the venous valves, which provokes the accumulation of excess blood in the vessels.
The combined use of the test and ultrasound allows you to determine the rate of blood release from vessels damaged by varicose veins.
A positive test result is the observation of regurgitation of blood, which is an indication for surgery.
A negative test indicates leg fatigue with symptoms similar to those of varicose veins.
The test is performed for early detection of the disease when the patient complains of fatigue and swelling in the limbs, but does not yet have visible vasodilation. In the case of varicose veins, the appointment also allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment procedure.
Advanced stages of diseases of the lower extremities and thrombophlebitis are contraindications for the Valsalva maneuver, since the clot may detach. This has serious complications.
Application in neurosurgery
The test is also performed during chest surgery. It allows you to detect a pleural defect. If its shell is accidentally damaged, a sound characteristic of air entering the pleural cavity is heard.
Previously, this method was used to assess the condition of cerebral vessels. Currently, it is not used due to the advent of more advanced research methods in this direction.
However, the Valsalva technique is still effective in studying congenital brain defects. Its action is accompanied by a significant increase in headaches.
Osteochondrosis
The test is based on a load that increases in the lower back due to pressure generated in the abdomen. This leads to compression of the nerve roots of the spinal cord. The pain radiates to the limbs, which indicates an exacerbation of osteochondrosis.
A herniated disc in the lumbar region also causes pain symptoms. However, to confirm the diagnosis it is necessary to use other research methods.
Otolaryngology
The test is used as a diagnostic and therapeutic method by ENT doctors. With its help, it determines the patency of the ear canals. Additionally, purulent formations from the ear cavity are removed.
When else is it used?
Underwater divers and airline passengers use the Valsalva technique to relieve unpleasant symptoms caused by pressure fluctuations.
A positive effect during takeoff and landing of an airplane is achieved through the following actions: after inhaling, the air should not be inhaled through the mouth or nose, but exhaled through the ears.
Determining the source of reverse flow
The Valsalva maneuver along with ultrasound also helps to determine the cause of the violation of venous outflow from the scrotum. The doctor's actions are as follows:
- In a standing position during peak strain during straining, the speed and duration of passage of the wave of reverse blood flow in the area of the external inguinal ring is assessed.
- After 30 seconds of rest, the patient is transferred to a supine position and the testicular vein is clamped approximately in the middle of the inguinal canal.
- Repeat point one.
If there is no return blood flow when the vein is compressed, then renal-testicular reflux is determined. If the rate of reverse blood flow with a free and compressed vein is approximately the same, then ileotesticular reflux is diagnosed. In other cases, the simultaneous presence of both types is likely.
The leftmost photo below shows an echogram of dilated vessels of the veins of the pampiniform plexus at rest, corresponding to grade 3 varicocele. The middle photo shows them during the Valsalva maneuver. The third photo shows the abdominal cavity, where the dilated left renal vein (labeled LPV) is visible, which is sandwiched between the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) and the aorta. This is called Nutcracker syndrome, which is a common cause of varicocele.
The photo below on the left shows the vessels of the pampiniform plexus at rest, on the middle - dilated vessels of testicular tissue, on the right - reverse blood flow in the left testicular vein in a standing position. In this case, grade 5 varicocele was caused by a tumor of the left kidney.
Contraindications
It is strictly forbidden to use the Valsalva technique in patients prone to sudden fluctuations in pressure. In addition, the following pathologies are contraindications to the procedure:
- Stroke;
- myocardial infarction;
- thrombosis of blood vessels;
- retinal disinsertion;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- chronic illnesses.
Despite its simplicity, the test cannot be used without the participation and advice of a specialist.
Its effectiveness in making a diagnosis and choosing treatment tactics can hardly be overestimated. It provides maximum information about the state of the organs and systems of the human body.