The heart begins to beat long before we are born. Surprising and even magical, right? However, this means that this organ works longer and harder than others. And not only the quality of our life, but also life itself depends on how carefully we pay attention to his condition!
More than 17 million people die every year from heart and vascular diseases. It has been proven that 80% of premature heart attacks and strokes could be prevented!
Fortunately, most cardiovascular diseases are successfully diagnosed thanks to modern innovative equipment and the professionalism of doctors. And as you know, establishing an accurate diagnosis means taking an important step towards healing.
One of the most informative and safe studies is cardiac echocardiography (EchoCG) or, in other words, ultrasound of the heart.
1 ECHO-KG in "MedicCity"
2 Echocardiography at MedicCity
3 Ultrasound of the heart at MedicCity
The essence of echocardiography
Ultrasound of the heart is the process of studying all the main parameters and structures of this organ using ultrasound.
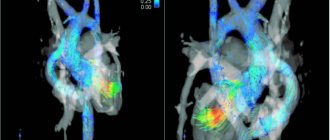
When exposed to electrical energy, the echocardiograph transducer emits high-frequency sound that travels through the structures of the heart, is reflected from them, captured by the same transducer and transmitted to the computer. He, in turn, analyzes the received data and displays it on the monitor in the form of a two- or three-dimensional image.
In recent years, echocardiography has been increasingly used for preventive purposes, which makes it possible to identify cardiac abnormalities at an early stage.
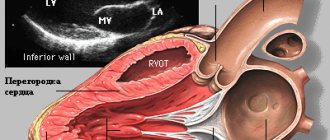
What does an ultrasound of the heart show:
- heart size;
- integrity, structure and thickness of its walls;
- sizes of the cavities of the atria and ventricles;
- contractility of the heart muscle;
- operation and structure of valves;
- condition of the pulmonary artery and aorta;
- pulmonary artery pressure level (to diagnose pulmonary hypertension, which can occur with pulmonary embolism, for example, when blood clots from the veins of the legs enter the pulmonary artery);
- direction and speed of cardiac blood flow;
- condition of the outer shell, pericardium.
1 ECHO-KG in "MedicCity"
2 Echocardiography at MedicCity
3 Ultrasound of the heart at MedicCity
Operating principle of an ultrasonic device
Thanks to the spread of technical capabilities for ultrasound diagnostics, visualization of the heart and its valve apparatus has become a cheap, fast and popular practice. Echocardiography is considered a separate branch of ultrasound, although there are no significant differences in the technique of conducting and processing information.
Ultrasound is based on the functionality of ultrasound. These are high-frequency sound vibrations that are inaccessible to the human ear. Our hearing organs perceive sound with a frequency of 16,000 to 20,000 hertz, and the frequency of ultrasound exceeds 20,000 hertz and is outside the zone of acoustic perception.
Representatives of the animal world (for example, dolphins, whales, rodents and tarsiers) can communicate using high-frequency sound waves. Humanity has learned to use ultrasound in several fields: medicine, biology, industry.
An important feature of sound waves is their free movement through the soft tissues of living organisms. Unimpeded distribution has become key for ultrasound diagnostics. How exactly does this happen? The human body is a heterogeneous structure consisting of hard and soft tissues, air, and water. Each of these structures represents a kind of barrier to the sound wave and prevents its propagation, which is called acoustic resistance. The acoustic resistance of liquids and bone structures will be different, which means the indicator depends on the density, elasticity and structure of the barrier.
As soon as the sound wave reaches the barrier, one part of it is absorbed by the new medium, and the other is reflected. Ultrasound equipment records changes in sound vibrations, processes the information and transforms it into a two-dimensional or three-dimensional image. The process itself is so fast and simple for modern technology that the doctor and patient can observe what is happening in the body in real time.
A sector sensor is used to study the heart. It operates at a frequency of 1.5 to 5 MHz. It is used in cases where it is necessary to diagnose a small area of the body located at depth. The size of the probe and the final image is different, which is important to consider when assessing anatomical structures.
Before the procedure, a special liquid gel is applied, which acts as a transition medium. Without it, diagnostics are impossible, since human skin reflects 99.99% of sound waves. The gel improves signal quality due to its viscous structure and allows the sensor to slide freely over the surface.
The sensor generates ultrasound and redirects the information to reconstruction systems, which create a black and white image. An interesting fact is that 64 different shades of the black and white scale are used for this. The shade depends on the intensity of acoustic vibrations and the specifics of the barrier. The most intense waves that are absorbed by the medium are depicted in white (liquids, soft tissues), and weak vibrations are recorded in black (bone structures).
Who is prescribed echocardiography?
The following are routinely examined:
- infants - if congenital defects are suspected;
- teenagers are a time of intensive growth;
- pregnant women with existing chronic diseases - to decide on the method of childbirth;
- professional athletes - to monitor the state of the cardiovascular system.
An echocardiogram is required if:
- anomalies of the endocardium and valve apparatus:
- heart tumors;
- arrhythmias;
- threat of a heart attack or a heart attack;
- IHD;
- failures of cardiac activity due to various intoxications;
- attacks of angina pectoris;
- pericarditis of various origins;
- hypertension;
- heart failure.
And also in the process of treating heart diseases, before and after cardiac surgery.
When is a cardiac ultrasound performed?
Indications for cardiac ultrasound are:
- alarming changes in health (increased or interrupted heartbeat, shortness of breath, swelling, weakness, prolonged fever, chest pain, cases of loss of consciousness);
- changes detected in the last ECG;
- increased blood pressure;
- heart murmurs;
- cardiomyopathy;
- manifestations of coronary heart disease;
- heart defects (congenital, acquired);
- pericardial diseases;
- lung diseases.
Preparation for cardiac echocardiography
Ultrasound of the heart does not require special preparations. On the eve of the procedure, the patient is free to eat as usual and perform normal activities. The only thing that will be asked of him is to give up alcohol, caffeine-containing drinks, and strong tea.
If the patient is constantly taking medications, this must be warned in advance so that the results of the study are not distorted.
For each subsequent ultrasound of the heart, you should take a transcript of the previous one. This will help the doctor see the process over time and draw the right conclusions about your condition.
The examination itself takes from 15 to 30 minutes.
The patient, undressed to the waist, is lying on his back or side. A special gel is applied to his chest, ensuring easier sliding of the sensor over the area under study (the patient does not experience discomfort).
The specialist performing echocardiography has access to any areas of the heart muscle - this is achieved by changing the angle of the sensor.
Sometimes standard ultrasound of the heart does not provide complete information about the functioning of the heart, so other types of echocardiography are used. For example, fat on the chest of an obese person can interfere with the passage of ultrasound waves. In this case, transesophageal echocardiography is indicated. As the name suggests, the ultrasound probe is inserted directly into the esophagus, as close to the left atrium as possible.
And to screen cardiac function under stress, the patient may be prescribed stress echocardiography. This study differs from the usual one in that it is performed with a load on the heart, achieved by physical exercise, special medications or under the influence of electrical impulses. It is used primarily to identify myocardial ischemia and the risk of complications of coronary artery disease, as well as for certain heart defects to confirm the need for surgery.
April 28, 2018
Modern diagnostic techniques make it possible to assess the functioning of the heart, identify disorders and causes of deviations in the functioning of this human organ. Ultrasound examination is one of them.
Ultrasound of the heart, or echocardiography, is painless and harmless. With the help of special equipment, the doctor is able to monitor the main functional processes of the organ. The progress of the examination is displayed on the computer monitor. Thanks to a sensor that transmits high-frequency sound waves, a clear picture appears on the screen. At the end of the diagnosis, the doctor gives the patient a conclusion, on the basis of which a diagnosis is made and a treatment program is developed. You can find out where to get a heart ultrasound in Moscow on our website.
Medical clinics are open from morning until late evening. Sign up for the procedure at any time convenient for you.
What does ultrasound of blood vessels and heart show:
- The work of the main muscle.
- The thickness of the walls of the organ.
- The speed of blood movement.
- Condition of valves and chambers.
- Parameters of cavities and pressure in them.
Why do you need an ultrasound of the heart?
To evaluate the characteristics of organ contractions.
Deterioration and disruption in the functioning of the cardiovascular system are visible even at the initial stage of the disease. During an ultrasound examination, congenital and acquired defects, blood clots, areas of asynergy, and valvular changes become apparent.
An ultrasound assessment of an organ is carried out not only if patients have symptoms of pathologies, but also if they do not. The method allows you to measure the pressure of the pulmonary artery. Repeated echo diagnostics demonstrates the dynamics of the pathology and the success of therapy.
Advantages of the technique
Patients are referred for echocardiography even in serious condition. Explanation for this:
- safety - no negative impact on the body and no side effects;
- information content - an accurate reflection of the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- painlessness - physical and moral comfort.
Echocardia is good because it does not take much time, the patient immediately receives a conclusion. The duration of the procedure varies between 5–45 minutes. The duration depends on the purpose of the procedure, the patient’s condition and the symptoms of the pathologies.
List of indications
Symptoms of diseases of the cardiovascular system are the main reasons to visit an uzologist. Both adult and young patients receive referrals. Indications for echocardiography are as follows:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- pain in the chest and ribs;
- heart murmurs;
- swelling, enlargement of the liver and other manifestations of failure;
- acute and chronic ischemia;
- shortness of breath, lack of air;
- increased fatigue;
- pallor;
- blue tint to the skin around the ears and eyes.
Patients are referred for ultrasound after heart surgery and chest injuries, and people suffering from frequent headaches are also recommended to undergo echocardiography in the therapist’s office. Why?
The causes of unpleasant painful sensations are sometimes microemboli. This disorder is treated by a cardiologist, drawing up a therapeutic program based on the ultrasound findings.
EchoCG is indicated for patients:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- cancer;
- dystrophy;
- anorexia.
Ultrasound of the heart during pregnancy is performed mainly at the end of the first trimester. The study demonstrates the number of chambers, the rhythm of the fetal organ.
It is recommended that professional athletes undergo an ultrasound scan at least once a year. The explanation for this is the increased load on the heart. Based on the diagnostic findings, serious illnesses can be prevented and a preventive program can be drawn up.
Are there any contraindications
Diagnosis of the heart using ultrasound is safe and prompt, so there are no restrictions on its implementation. Over the many years of existence of ultrasound, no contraindications have been identified. However, in some cases the procedure is technically difficult. We are talking about examination of newborns. The cabinets are equipped with traditionally sized sensors. Using such equipment, it is difficult to diagnose the state of the heart of a small patient.
Carrying out an ultrasound examination
Let's take a closer look at how heart ultrasound is performed.
Once you receive a referral for an echocardiogram, there is no need to worry. Diagnostics will not cause any discomfort. There is no need to carry out any preparatory activities. However, you should not abuse fatty foods, smoke, or drink alcohol.
In the office, the ultrasound specialist will ask you to remove clothing from your upper body and lie down on the couch slightly on your left side. This position allows you to get a better picture. Before the examination begins, gel is applied to the chest and sensors are attached. After placing these pieces of equipment, all parts of the heart are viewed. Information about dimensions and functional features becomes available. Connecting the sensors is a painless procedure. There is also no discomfort during startup of the equipment.
The picture on the monitor screen is obtained due to the movement of acoustic waves. They are converted into electrical signals, which, after processing by an echocardiograph, become an image. At the same time, the doctor moves a sensor in the area of the heart.
This type of diagnosis should not be confused with electrocardiography. In the latter case, information about heart activity becomes known, presented in the form of a graphical recording. The ultrasound described earlier is called transthoracic.
There are the following types of echocardiography:
- Transfood type. This is not the most pleasant procedure, as the uzologist inserts a thin tube into the esophagus through the oral cavity.
- Stress analysis. Analysis of the organ’s functioning is carried out under conditions of increased stress on the body.
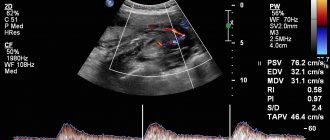
- Dopplerography. Allows you to monitor blood flow processes.
But most often patients are examined transthoracically.
Classification of areas of methodology according to the method of implementation
Echocardiography, as a diagnostic technique, can be one- or two-chamber. In the first case, the study is carried out in the “M” mode.
What is special about single-chamber technology? The ultrasound sensor emits waves along a single axis, which is determined by the doctor. A picture with a top view is displayed on the screen. If you change the direction of the sensor movements, the following become visible:
- ventricles of the heart;
- aorta;
- atrium.
Ultrasound in M-mode is performed on patients of any age.
Dual-chamber echocardiography differs from the previous technique in the type of image. The picture is obtained in two planes. The scanned plane is perpendicular to the 4-chamber position. With this type of ultrasound, a sensor with a wave frequency of 30 units. in 1 second they are directed in an arc of 90 degrees. When the trajectory of movement changes, the current processes of the cardiac structures are viewed.
During the previously mentioned Doppler assessment, turbulence and blood flow velocity become clear. What do deviations from the norm of such an ultrasound indicate? About the fullness of the left stomach and hidden heart defects.
The attending physician should decipher the conclusion of a particular ultrasound examination. During the analysis of a medical document, he compares the indicators with the established generally accepted norm. Discrepancies in values indicate the presence of diseases.
If the ultrasound specialist sees a clear deviation on the computer monitor, he displays this in the conclusion.
You can obtain more detailed information about the examination from the Delomedic administrators. Sign up for a cardiac ultrasound in advance or come during business hours. If necessary, our experienced doctors will decipher the conclusion.
Decoding EchoCG
After the examination, the doctor draws up a conclusion. First, a visual picture with the presumed diagnosis is described. The second part of the study protocol indicates the patient’s individual indicators and their compliance with standards.
Decoding the data obtained is not a final diagnosis, since the study can be done not by a cardiologist, but by an ultrasound diagnostic specialist.
It is the cardiologist, based on the collected medical history, examination results, interpretation of tests and data from all prescribed studies, who can draw accurate conclusions about your condition and prescribe the necessary treatment!
What indicators are considered normal?
Having received the results in hand, the cardiologist can interpret them. In this case, the specialist takes into account anamnesis, medical history, the effect of medications taken and many other related factors. To evaluate the results of cardiac ultrasound, the norm of indicators is prescribed in its standard version. Deviations from the norm do not always indicate the presence of serious pathologies. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and start a correctly selected treatment, there is every chance of bringing the abnormal indicators back to normal.
| Indicator name | Women | Men |
| Left ventricular myocardial mass | From 95 to 142 g | From 135 to 180 g |
| Left ventricular mass index | From 71 to 88 g/m2 | From 71 to 92 g/m2 |
| Left ventricular end-systolic size | From 31 to 42 mm | |
| End diastolic size | From 45 to 58 mm | From 46 to 58 mm |
| Left ventricular wall thickness in diastole | Max 10mm | Max 11mm |
| Volume of blood ejection during left ventricular systole | From 60 to 100 ml | |
| Right ventricular wall thickness | 4.8 to 5 mm | 5 mm |
| Left atrium size | From 17.5 to 33 mm | From 18.5 to 33 mm |
| Left atrial end-diastolic volume | From 38 to 57 ml | From 50 to 82 ml |
| Right atrial end-diastolic volume | From 20 to 100 ml | |
| Thickness of the interventricular septum in systole | 5 to 9.0 mm | From 5 to 9.5 mm |
| Thickness of the interventricular septum in diastole | From 7.5 to 11 mm | |
| Aortic opening area | From 20 to 35 mm2 | |
| Thickness of the outer membrane of the pericardium | 1.2 to 1.7 mm | |
| Volume of fluid in the pericardial cavity | From 10 to 30 ml | |
Ultrasound parameters of the heart, normal for children from birth to 14 years
| Index | 0-1 m | 1-3 m | 3-6 m | 6-12 m | 1-3 g | 3-6 years | 6-10 years | 11-14 years old |
| LV EDC | 13-23 | 16-26 | 19-29 | 20-32 | 23-34 | 25-36 | 29-44 | 34-51 |
| TZS LV | 2-5 | 2-5 | 3-6 | 3-6 | 3-7 | 3-8 | 4-8 | 5-9 |
| LV ESD | 8-16 | 9-18 | 11-20 | 12-22 | 13-22 | 14-25 | 15-29 | 21-35 |
| Diameter AO | 7-13 | 9-15 | 10-16 | 10-17 | 11-18 | 13-21 | 13-26 | 15-30 |
| TM ZhPd | 2-6 | 2-6 | 2-6 | 2-6 | 2-6 | 3-7 | 4-8 | 5-8 |
| LA diameter | 9-17 | 10-19 | 12-21 | 14-24 | 14-26 | 15-27 | 16-31 | 19-32 |
| TSS PZhd | 1-3 | 1-3 | 1-3 | 1-4 | 1-4 | 1-4 | 1-4 | 1-4 |
| Pancreas diameter | 2-13 | 2-13 | 2-14 | 3-14 | 3-14 | 4-15 | 5-16 | 7-18 |
EchoCG norm: what some parameters indicate
There is a range of normal values for one or another cardiac ultrasound indicator for adults (in children the norms are different and directly depend on age).
Thus, along with other important parameters, echocardiography helps to obtain information about the ejection fraction of the heart - this indicator determines the efficiency of the work performed by the heart with each beat.
Ejection fraction (EF) is the percentage of blood volume ejected into the vessels from the heart ventricle during each contraction. If there were 100 ml of blood in the ventricle, and after the heart contracted, 55 ml entered the aorta, it is considered that the ejection fraction was 55%.
When the term ejection fraction is heard, we are usually talking about the left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction, since it is the left ventricle that ejects blood into the systemic circulation.
A healthy heart, even at rest, pumps more than half of the blood from the left ventricle into the vessels with each beat. As the ejection fraction decreases, heart failure develops.
The normal left ventricular ejection fraction for an adult is 55-70%. A value of 40-55% indicates that EF is below normal. An ejection fraction of less than 40% and even lower ejection fractions indicate heart failure in the patient.
General characteristics of the study area
The heart is the central muscular organ of the blood circulation. It pumps blood through the veins and arteries, providing vital substances to the entire body. A healthy heart continuously contracts and unclenches, forming a cardiac cycle. In a person at rest, about 55-70 cardiac cycles per minute can be recorded.
The shape of the heart is variable and depends on body type, age, gender, and health status. Its weight varies from 274 to 385 grams in men and from 203 to 302 grams in women.
Content:
- General characteristics of the study area
- Operating principle of an ultrasonic device
- Indications/contraindications for the study
- Specifics of echocardiography
- Preparation and carrying out manipulations
The human heart consists of four chambers, which are separated by valves and septa. Blood circulates throughout the organ, passing from one valve to another, is saturated with vital elements and is distributed throughout the body. On average, 7,000 to 10,000 liters of blood pass through the heart per day.
The organ is susceptible to a large number of pathologies - from congenital defects to cancer. To track and prevent the disease in time, doctors prescribe an ultrasound examination. How practical is this? Echocardiography is a fast, accurate and painless method for diagnosing the central circulatory organ. With its help, the doctor will be able to assess the condition of the blood vessels, monitor the blood flow, and identify pathological changes in the valve apparatus or the structure of the myocardium. The main advantage of the method is safety. There are no side effects, pain, discomfort or complications after the ultrasound.
Is cardiac echocardiography safe?
During this study, there is no radiation or other load on the organ. Therefore, if necessary, it can be prescribed even several times a week.
This study is characterized by the absence of complications and side effects.
EchoCG does not harm either the expectant mother or the fetus during pregnancy.
Limitations for the procedure may include inflammatory diseases of the skin of the chest, chest deformities and some other reasons.
How to prepare for ECHO CG
A list of dos and don’ts before the examination is usually given by the doctor. The thing is that preparation depends on the chosen method. When performing traditional, superficial echocardiography, special preparation is not required. Enough:
- sleep well;
- avoid overload (both physical and psychological);
- do not overeat (however, in general you can eat and drink before the procedure);
- do not drink alcohol, coffee, energy drinks.
Special preparation is needed only when conducting internal diagnostics in a hospital setting. The attending physician informs you about it.
How to do an ultrasound of the heart at the MedicCity clinic?
It is advisable for every person to have an echocardiogram at least once in their life. The fairly low cost of cardiac ultrasound is another reason to prefer this particular diagnostic method.
At MedicCity you can undergo all types of cardiac diagnostics - ECG, EchoCG, bicycle ergometry, HOLTER, ABPM, etc.
Just type in a search engine: “Ultrasound of the heart, Savelovskaya metro station, Dynamo metro station.” Or call us at: +7 (495) 604-12-12.
The doctors of our multidisciplinary clinic will do everything possible to relieve your heart pain!
ECHO at home
If your doctor has prescribed a classic transthoracic examination method, or you are undergoing a procedure to prevent cardiovascular diseases, you can perform an ECHO or cardiac ultrasound at home .
Doctors at the Ultrasound+ clinic use modern portable ultrasound machines, which are not inferior to stationary ones in terms of diagnostic accuracy. They will allow you to accurately visualize the organ and identify pathologies. In our clinic, examinations are carried out by doctors, so you can immediately receive a transcript and diagnosis. If you have been diagnosed with a disease, the doctor will tell you how to proceed.