All about frozen pregnancy
I will talk about not the most pleasant, but, unfortunately, very relevant topic - frozen pregnancy after IVF. Quite a lot of questions arise about this, including the connection between IVF and the risks of miscarriage.
Spontaneous miscarriage is the most common complication of pregnancy, from 10 to 20%, i.e., in fact, almost every fifth! pregnancy ends in miscarriage. Most often, they are caused by chromosomal damage that is possible during the formation of embryos. Nature makes especially many of these “mistakes” at a late reproductive age, after 36 years. In patients over 40 years of age, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo can range from 80 to 100%.
Termination of pregnancy can be caused by a number of diseases, infections, pathology of the blood coagulation system, problems with the endocrine system, diseases of the uterus and appendages, etc. There are also a number of additional risk factors that lead to early miscarriages:
- late reproductive age (if the risk of miscarriage at 20–30 years old is on average 10%, at 35 years old - already 20%, at 40 years old - 40%, over 40 years old - up to 80%);
- drinking coffee (a dose of more than 100 mg of caffeine or 4-5 cups of coffee per day is considered aggressive);
- smoking;
- medicines (itroconazole - a remedy for thrush, NSAIDs (analgin, etc.), retinoids (including vitamin A) - substances that are widely used in cosmetology, are included in many creams, for acne, for example. They are teratogenic effect, i.e. they can lead to disruption of embryo development;
- increased body temperature more than 37.7C°;
- folic acid deficiency.
And there are a number of factors that many mistakenly consider dangerous for pregnancy, but in fact they are not. These include:
- air travel;
- blunt abdominal trauma (the well-worn movie standard for pregnancy problems);
- use of contraceptives before pregnancy (including hormonal contraceptives, IUD, etc.);
- physical activity (provided that the woman was involved in sports/fitness in the same way before pregnancy);
- vaccination against papillomavirus before planning pregnancy;
- sex;
- stress;
- history of abortions before planning this pregnancy.
When is a miscarriage diagnosed?
- If on ultrasound the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus is more than 7 mm, but there is no heartbeat.
- If a control ultrasound 11–14 days after detecting the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity does not reveal a fetal heartbeat.
- If the size of the embryo is less than 7 mm, the ovum is less than 16–24 mm, there is no heartbeat.
- If the fertilized egg measures 25 mm or more, and the embryo in it is not visualized.
It is important to remember that for a reliable diagnosis of a frozen pregnancy, dynamic monitoring is required! You should never despair ahead of time, after the first ultrasound, at which it seemed that the baby was too small. I know many cases when a woman was given a terrible verdict that the pregnancy was not developing, but she still refused curettage, had a control ultrasound in another clinic and it turned out that everything was fine with the baby.
But expectant management is possible only in cases where there is no bleeding or pain in the lower abdomen - i.e., symptoms of an incipient miscarriage. If such complaints are present, hospitalization in a hospital is required. There they can save the pregnancy if the embryo is in order, or it is safe for health to remove the non-developing embryo and send it for histological examination, which will help to understand the cause of this tragedy and take measures to try to avoid it in the future.
How to be examined after a non-developing pregnancy? The list of analyzes is very long and I will not give it to you here, since there is no universal scheme, an individual approach is needed. You can, of course, come to the laboratory and submit everything that is offered there, from smears to karyotype, but is this necessary?
The European Society for Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE), the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) and the clinical guidelines of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation do not recommend ANY EXAMINATION after the first case of frozen pregnancy at short term, since in 70% of cases it can be associated with an error in embryo formation , is random and does not repeat in the future.
If the episode of miscarriage or frozen pregnancy occurs again, here you need to look for the reasons. It is recommended to start with a study of the fetal karyotype - a histological study of the removed material, which determines whether the embryo had any abnormalities or not.
If they were, then the prognosis is considered favorable, the chances that it will be possible to report safely next time are quite high.
If the embryo was normal, a comprehensive clinical examination of the couple should be performed. Everything is already assessed here, infections, hormonal disorders, autoimmune pathology, hemostasis disorders are excluded, diagnostic hysteroscopy with endometrial biopsy, etc. is performed. And the more thoroughly the research is carried out, the greater the chances of a successful outcome of the subsequent pregnancy.
Well, a few words about the connection between a frozen pregnancy and the IVF program. Is the risk of miscarriage higher after IVF compared to spontaneous conception?
There are statistical data indicating that the number of miscarriages after IVF is higher than with spontaneous conception for patients of the same age groups (from 18 to 32% of all pregnancies after IVF are short term). But this does not take into account the results of PGD, which significantly reduces the risk of miscarriage (for example, when comparing groups with recurrent miscarriage in couples with spontaneous conception, the miscarriage rate reached 28%, and in couples after IVF with PGD, the average abortion rate was 9%).
The rate of miscarriage after IVF is not directly related to IVF. It is directly related to the factors that caused the couple to resort to IVF treatment: late reproductive age, endocrine pathology, impaired sperm quality, chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, etc. IVF does not eliminate the disease itself, unfortunately.
We try to bring all chronic diseases into a state of stable remission before planning IVF, but pregnancy again activates a number of diseases and they enter into an unequal battle with it. Therefore, pregnancy after IVF, unfortunately, does not always proceed smoothly. But high-quality preparation for the protocol, adequate support after embryo transfer and individual pregnancy management increase your chances of success. So let’s put aside unnecessary fears and move towards long-awaited motherhood!
What's happening to the baby
Six weeks is the “age” in which the baby’s development occurs very quickly and intensively. Now the fetus is becoming more and more like a small person.
Fetal development.
At this stage, the child’s facial features have already been formed. Of course, this is not yet the face that mom and dad will see when they first hold the baby in their arms, but the eyes and nose, as well as the upper and lower jaws, are already quite well developed. True, the eyes are still closed; the child will learn to open them a little later. The baby is already making active movements. True, he is still too small for the mother to feel this: at this stage the length of the fetus is about 4 mm. In the sixth week, every day is very important. After all, the organs of the endocrine system begin to form in the embryo, and the nervous system and digestive tract are actively formed. And at this stage, an important event occurs: the placenta begins to form, the baby begins to receive all the nutrients it needs through the mother’s bloodstream. Therefore, everything that enters the mother’s body goes to the baby.
Fetal heartbeat.
Although the fetus is still very tiny, it already has a heart. It is not fully formed, but is already fully occupied with “training.” An ultrasound can detect a heartbeat that reaches 110–130 beats per minute.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of a frozen pregnancy are the same in any trimester. The main signs that may indicate such a pathology are:
- vaginal discharge with blood;
- general weakness, chills, increased body temperature;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- cessation of swelling and soreness of the mammary glands;
- sudden disappearance of toxicosis manifestations;
- absence of fetal movements (with pathology in the second trimester).
Despite the existence of characteristic symptoms of the pathology, often the cessation of fetal development goes unnoticed, since the basal temperature can remain within 37 degrees, and the hCG level remains high for several more weeks. In this case, the woman learns about the problem only at her next doctor’s appointment or routine ultrasound.
How to determine the sex of a child by heartbeat
According to the theory, there is a close connection between the work of the heart and gender. There are significant differences in the heartbeat of boys and girls. The main ones:
- Beat frequency
. The heart rate of girls is higher than that of boys - 140 beats versus 120. It is believed that this information is reliable only until the 20th week of pregnancy, although there is an opinion that the period does not matter. - Heart rhythms
. Male power manifests itself already in the womb. A boy's heart is more powerful, so its contractions are more rhythmic and loud. The girls' heartbeat is somewhat chaotic; doctors compare it to alarming music. It is also quieter than boys. However, determining the sound level is quite difficult. - Sound location.
A number of experts believe that girls and boys occupy different positions in the womb. A boy's heart can be listened to on the left, and a girl's heart on the right. The reliability of this method is questionable, because at the beginning of the term the baby has enough space in the uterus and can actively move, unlike later stages, where the fetus is limited in maneuvers.
There is an opinion that the mother’s heart beats simultaneously with the rhythm of her son’s heart and resonates with the girl’s heartbeat.
Dangerous timing: when can it happen?
Fetal development can stop at any time up to 28 weeks (in rare cases, cessation of development can occur later), but the greatest likelihood of such a pathology occurs in the first trimester. There are also several periods with the highest risks of frozen pregnancy, these include the following periods:
- 3-4 weeks;
- 8-10 week;
- 16-18 weeks.
It is these periods that most often become critical for pregnancy.
What tests should I take after?
Before becoming pregnant after a frozen pregnancy, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a recurrence of what happened. Treatment must be appropriate to the problem that caused the pathology. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo a full examination, which will help determine the reason for the fading of fetal development. Based on the results of the examination, doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with the detected diseases.
It is recommended to undergo examination after the woman’s menstrual cycle has returned (usually this takes about 30 days after cleansing). But both spouses should get tested. A full examination includes:
- genetic examination of spouses;
- tests for TORCH infections;
- study of hormonal levels;
- blood coagulogram;
- Gynecological ultrasound;
- spermogram;
- immunogram.
Such an examination is usually sufficient to determine the causes of frozen pregnancy both in the early and late stages. The attending physician may prescribe additional tests if necessary. All these examinations can be completed at the IVF and infertility treatment clinic of Academician V.I. Grishchenko.
A frozen pregnancy is not a death sentence - in 90% of cases, after the occurrence of such a pathology, spouses in the near future become happy parents of healthy babies. The main thing is to undergo a full examination and eliminate the cause of the pathology. And if necessary, you can undergo the procedure of artificial insemination (IVF).
Lifestyle of an expectant mother
Control over your health and lifestyle adjustments are necessary from the very beginning of pregnancy. The doctor gives personal recommendations to each woman, taking into account all the features identified during the examination. But a few universal tips will be useful to all expectant mothers.
Nutritional features.
Of course, the diet should be complete and healthy. But during the period of toxicosis, it is important to adapt your diet to your condition so as not to provoke attacks of nausea and vomiting. It makes sense to give up all foods that increase toxicosis and replace them with nutritional analogues. For example, if you feel sick from fish, you can completely switch to lean boiled meat, and replace whole milk with fermented milk products.
Surveys
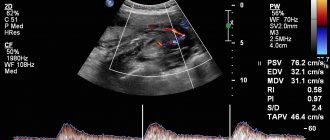
Ultrasound in the sixth week of pregnancy.
At this stage, the fact of pregnancy is usually beyond doubt. And although an ultrasound examination is rather general in nature, since the size of the fetus does not allow us to assess the features of its development, ultrasound can:
- confirm pregnancy in doubtful cases;
- determine the location of the fetus and its size;
- determine single or multiple pregnancy;
- determine fetal heartbeat and heart rate.
Laboratory diagnostics.
When registering at the antenatal clinic, the doctor prescribes tests necessary to assess the health of the expectant mother and identify any factors that could threaten pregnancy. This is a general blood and urine test, an analysis to determine the level of hCG, blood type and Rh factor, as well as a study to detect sexually transmitted diseases. At this time, the baby’s father may also be involved in laboratory tests if the doctor sees the need for this. For example, this is necessary when the parents have different Rh factors or a woman is diagnosed with an STD, the treatment of which must be carried out in both partners.
It is important!
Nausea and vomiting are experienced by approximately 70% of pregnant women, usually occurring in the first trimester of pregnancy*.
The severity of toxicosis varies widely. An expectant mother may experience nausea only from the taste of a certain product, only in the morning or only in hot weather, etc. But attacks of severe nausea can be overcome by any strong smell, even from one that she previously liked (from her favorite perfume, the aroma of fresh baked goods and etc.).
Increased fatigue.
A growing fetus needs energy. But he is completely dependent on the mother, so she has to share her resources with the baby. If a woman has no problems with her health, and her lifestyle can be called healthy, then such energy consumption is not very noticeable. But if a pregnant woman suffers from toxicosis, often experiences stress or is exposed to physical exertion, then the feeling of fatigue and drowsiness is quite pronounced.
Frequent urination.
Frequent urge to urinate can be observed already in the very early stages of pregnancy. This is due to both hormonal changes in the body and an enlarged uterus, which irritates the bladder.
Mood swings.
Again, hormones are to blame. In most cases, the body adapts to its new status, and mood swings stop or become less pronounced. But in the first trimester, the expectant mother needs to be prepared for the fact that emotions will not depend on objective circumstances. Causeless euphoria and sadness can replace each other just like that and several times over a short period of time.
New taste preferences
. The need for a pregnant woman to eat something strange has become almost a legend. But this phenomenon has a completely understandable explanation. A woman's body becomes a vessel in which new life develops. And this life requires a variety of substances that are not always fully present in the diet of the expectant mother. With such an irresistible need to eat something unusual, the baby signals his own needs. Doctors recommend listening to such signals. But if they are too frequent and urgent, then it makes sense to reconsider your diet and adjust your diet in general.
How does a mother feel in the sixth week of pregnancy?
Although the pregnancy has not yet manifested itself externally, the expectant mother may notice more or less pronounced changes in her health.
Breast tenderness.
The mammary glands begin to prepare for feeding the baby from the first weeks of pregnancy. They may increase by 1-2 sizes and become sensitive. In some cases, even the touch of clothing to the breast causes pain to a woman. The nipples and areolas may darken and the skin of the areola becomes rougher. Such changes are normal, because this is another stage in preparing the breasts for feeding the baby.
Early toxicosis.
Even women who feel great in the first five weeks of pregnancy often experience nausea in the sixth or seventh week. It is caused by hormonal changes, which, among other things, affect the digestive organs and make the nervous system particularly “reactive.”