What is diabetes mellitus
There are two types of diabetes.
First type
When it occurs, the pancreas stops producing insulin in the required volume, which leads to chronic accumulation of glucose in the blood. Such disturbances in the body occur quite early.
In particular, type 1 diabetes is regularly diagnosed in children under ten years of age and in adolescents. Fortunately, according to statistics, among all people with diabetes, the first type is found in only ten percent of people. Doctors cannot yet say for sure what causes the appearance of such diabetes, but they agree that this occurs due to genetic abnormalities of the pancreas. This type is often accompanied by pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
Second type
The most common type of diabetes. When the disease occurs, insulin production in the body does not stop completely, but is reduced to critical levels. This mainly occurs due to the aging of a person; it can begin after forty years, but it also happens in young people, especially in office workers whose work does not involve regular physical activity. You may be diagnosed with prediabetes when your body produces higher levels of glucose than normal. Hemoglobin in type 2 diabetes mellitus may deviate slightly from the norm during the primary period of the disease.
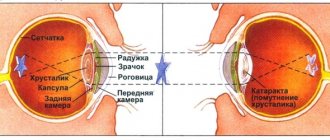
Developing diabetes increases your risk of heart disease. Excessive amounts of sugar in the blood can damage the walls of blood vessels, which can lead to coronary artery disease. But diabetes means that blood in normal quantities does not flow to the nerve cells, and this threatens a complete loss of sensitivity in the limbs and tissue death.
The number of diabetics is increasing every year. In 2019, there are already half a billion of them. In Russia, the number of patients is also increasing every year.
Interesting! In the last five years alone, the number of people diagnosed with diabetes has increased by 23 percent.
What concomitant diseases can lead to anemia?
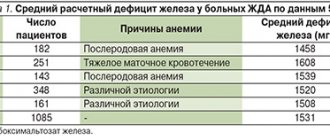
Diabetes mellitus is only one of the reasons predisposing to the development of anemia. This pathology is accompanied by concomitant diseases and complications, which, in turn, contribute to the development of anemia.
Concomitant diseases leading to a decrease in Hb:
- Lack of vitamin B12, iron, folic acid and protein foods. Usually observed with poor and monotonous diet, especially during pregnancy and during physical exertion, as well as in children and adolescents.
- Infectious diseases of a chronic or acute nature. Anemia is especially often observed after influenza, scarlet fever, diphtheria, and tuberculosis.
- Blood loss - due to injury or chronic diseases. Large blood losses can be observed, for example, in various gynecological pathologies, gastrointestinal diseases, and tumors.
- Oncological and renal diseases.
Common causes of decreased glycated hemoglobin
Glycated hemoglobin is the result of a reaction between amino acids and sugar in the body. Doctors say that testing for this type of hemoglobin has become the most important when diagnosing hidden diabetes. It will show the amount of sugar in the blood over a certain period and how correctly the hydrocarbon metabolism process is proceeding. And if the level of glycated hemoglobin is elevated, this means that the sugar level in the body is not normal. This analysis is rather preventive in nature, since with its help it is possible to identify the early development of diabetes and prevent its further development.
It’s not just diabetes that can lead to a low level of glycated hemoglobin. Lack of regular physical activity, sedentary work, vitamin deficiency, cardiovascular diseases, leukemia, age and stress. These factors can become catalysts for the development of diabetes. To avoid elevated levels of glycated hemoglobin, you need to obtain individual prescriptions from your doctor. The doctor may prescribe special insulin injections, certain types of exercise, and also help normalize sleep phases.
The level of this type of hemoglobin can be not only increased, but also decreased. In this case, the body does not receive the full range of nutrients, which is why a person regularly experiences fatigue, dizziness, and various types of pain. It is very simple to neutralize the negative effect of this diabetes; just eat something containing sugar.
How to increase hemoglobin during pregnancy
During the period of bearing a child, the indicator is of particular importance: as the fetus grows, it needs more nutrients and oxygen, and the woman’s body lacks the necessary substances. Complications during pregnancy and bleeding can also cause a decrease in hemoglobin. For these reasons, the expectant mother is prescribed folic acid, vitamin B12, iron supplements and is advised to adhere to a diet. Be sure to consume red meat, liver, spinach, freshly squeezed juices, nuts, and cereals.
If hemoglobin still decreases, then special drugs are prescribed: Sorbifer, Maltofer, Ferroplex. Complex medications containing vitamin C, B12, B9, and fructose are indicated.
Sugar level analysis
To donate blood for a hemoglobin level test, no special preparation is required. The same rules apply as for general blood donation. The only exception is food. When donating blood for analysis of hemoglobin levels, there is no requirement to fast for the last few hours; you can even drink alcohol in reasonable quantities. There is no need to abstain from stress and psycho-emotional stress.
Blood is taken from a vein. The result will reflect the amount of HbA1C in the blood over the past three months (this is the average lifespan of red blood cells), and can be obtained in just four days. Using the test results, your doctor will make a diagnosis and also determine steps for further treatment or prevention of diabetes. Depending on the results, the doctor may send you for a repeat blood donation. The patient can independently monitor all changes in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, but the lack of necessary knowledge will make it impossible to make a correct diagnosis.
Diet to increase hemoglobin
Diabetes mellitus requires special dietary nutrition, and dietary dishes for diabetics. You can raise your hemoglobin level using this sample menu:
Breakfast: oatmeal with water and steamed prunes, apple juice.
Second breakfast: bread with bran, Adyghe cheese, blackcurrant compote with xylitol.
Lunch: lentil and carrot soup, chicken liver, lettuce, tomato juice.
Dinner: boiled squid salad with herbs, buckwheat porridge, rosehip infusion.
Folk remedies for increasing hemoglobin Herbalists and traditional healers know how to increase hemoglobin in natural ways:
- Take a teaspoon of pollen in the morning.
- Prepare an infusion of nettle and yarrow. Take a teaspoon of each herb and pour boiling water over it. Leave for 25 minutes and drink a third of a glass twice a day.
- Instead of tea, brew fireweed leaf.
- Drink half a glass of raw potato juice before meals. Only freshly prepared ones are used.
- Infusion of meadow clover. Ten flower heads per 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for an hour. Drink 30 ml 4 times a day.
- Mix equal parts of rosehip and rowan. Pour a tablespoon of the crushed mixture with boiling water (250 ml) in a thermos overnight. In the morning before breakfast, drink half a glass.
- Eat half a pomegranate every day.
- Sprout wheat, grind and take a tablespoon or add to porridge.
Signs of low hemoglobin levels
A reduced number of red blood cells in the blood is called anemia. This syndrome is characterized by all the symptoms that can appear with a general weakening of the body:
- Problems with concentration. Losing concentration occasionally is normal for the body. But if you cannot read several pages without being distracted by any irritating factor, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
- Dyspnea. Periodic short-term oxygen starvation is normal. But walking a couple of steps and starting to noisily swallow air, and so on several times a day, is a reason to be wary and visit the clinic.
- Drowsiness. Sleeping for several days in a row in a normal mode, for eight hours, and at the same time feeling tired and overwhelmed is an alarm bell.
- Regular respiratory diseases. Frequent colds or seasonal acute respiratory infections indicate low hemoglobin.
- Brittle, fragile nails indicate not only a lack of calcium in the body, it is also a syndrome of low hemoglobin content.
Prevention of changes in the blood
Once faced with anemia, you should adhere to general recommendations throughout your life:
- Have a medical examination twice a year
- Form a balanced, varied diet.
- Monitor your work and rest schedule, take walks in the fresh air.
- Eliminate bad habits
- Maintain normal body weight.
Walking is good prevention
Treatment of anemia in diabetics
90% of patients with second-degree diabetes develop anemia, which worsens the quality of life. A lack of red blood cells and low hemoglobin have an impact on the quality of the patient’s sexual, physical and mental-intellectual activity.
Anemia is treatable. This does not apply to patients with renal failure, which is not treated with mineral and vitamin complexes; without proper medical supervision, it goes into a severe stage and can lead to disability. In cases where anemia develops due to a lack of the hormone erythropoietin in the body, it is treated with the complex use of medications containing this hormone. Erythropoietin is prescribed by the attending physician if there is no effect after using other drugs containing iron. However, most doctors are inclined to start treatment with erythropoietin immediately, believing that this will prevent the destruction of the walls of small vessels in the patient and prevent the development of nephropathy (kidney damage).
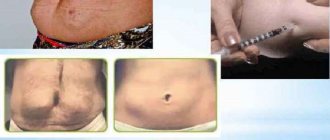
Erythropoietin is administered either intravenously or subcutaneously. The second method allows patients not to seek the help of a doctor, but to carry out injections on their own. The hormone is administered three times a week. To increase the effectiveness of treatment, doctors recommend combining hormone injections with the use of medications containing iron.