People often wonder if diabetics can drink alcohol. If yes, then in what quantities, what strength, and how often. The relevance of this topic is clear, because ethanol easily interacts with glucose, which leads to the formation of glucoside and water and a sharp decrease in blood sugar levels. At first glance, it seems that drinking alcohol for diabetes has a positive effect. But is this really so? Let's figure it out.
Content:
- Features of the disease
- Alcohol and type 2 diabetes
- Dangerous symptoms of delayed hypoglycemia
- Is it possible to drink alcohol if you have diabetes 4.1 Dry wine 4.2 Vodka 4.3 Beer
- Prohibited types of alcohol
- How to drink correctly if you have non-insulin-dependent diabetes
- When you should absolutely not drink if you have diabetes
The intake of “hot” drinks should always be within reasonable limits.
It is especially important to remember this principle for people who have chronic diseases. Let's try to figure it out: if diabetes is diagnosed, is alcohol allowed or not? Doctors' opinions on this matter differ slightly.
Some believe that ethanol should not be used under any circumstances in this condition, while others give patients relief. In fact, everything depends on the unique characteristics of the patient’s body, indicators of his health status, and the therapy used.
What are the dangers of obesity
“Alcohol is also a high-calorie drink, since the breakdown of 1 g of alcohol releases 7 kcal. For comparison, 1 g of fat produces 9 kcal, and 1 g of protein or 1 g of carbohydrates provides 4 kcal,” the endocrinologist recalled. It should be noted that overeating is dangerous to health even in the absence of chronic diseases. Obesity remains one of the most pressing problems globally. Thus, according to the Regional Office for Europe of the World Health Organization (WHO), in the countries of the European Union, 30–70% of the adult population is overweight and 10–30% are obese.
This problem also worries Russian society. On September 30, Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Federation Tatyana Golikova, at a meeting of the Council of the Government of the Russian Federation on issues of guardianship in the social sphere, reported that the rate of increase in the prevalence of obesity in Russian children on average per year is almost 9%. “Based on the results of a selective survey of schoolchildren, excess body weight was detected in 18% of the schoolchildren surveyed, obesity in 8%, and in some regions, children with excess body weight in grades 1–4 exceed 30%,” stated the Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Federation.
Conditional release
Photo: Global Look Press/Angelika Antl/imagebroker
Straight to the bull's eye: fruit reduces the risk of diabetes
Scientists advise consuming these gifts of nature twice a day
Diabetes mellitus types I and II also remain a serious problem threatening the health of people around the world. According to WHO, between 1980 and 2014 the number of people with diabetes grew from 108 million to 422 million, with the incidence growing fastest in low- and middle-income countries. Diabetes is a leading cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke and lower limb amputations. Additionally, if undiagnosed and untreated, diabetes can be fatal. Thus, in 2021, 1.5 million people died due to diabetes in the world. Additionally, in 2012, 2.2 million deaths were attributed to high blood glucose levels.
Features of the disease
Before we figure out whether it’s possible to drink alcohol if you have diabetes, let’s describe the disease itself. It is a serious metabolic disorder manifested by chronic hyperglycemia. The latter is the result of a disruption in the interaction of tissue cells with insulin.
Glucose is a source of energy in the human body. Penetrating into the gastrointestinal tract, complex carbohydrates are metabolized and transformed into monosaccharides, which go directly into the bloodstream. They cannot immediately penetrate cells because their molecules are too large. To make this happen, insulin is involved in the process. This is a peptide hormone produced by the pancreas. It has a multifaceted effect on metabolic reactions in almost all tissues.
In the non-insulin-dependent form, insulin deficiency is not observed, but the cells lose sensitivity to it. Because of this, glucose cannot directly penetrate into tissues and provide the body with the required energy charge. As a result, tissues are damaged due to increased blood sugar levels, metabolic processes are disrupted, and there is a lack of energy.
What to do
Diabetes mellitus is a serious disorder in the functioning of body systems. A person should give up alcohol completely. If a person with alcoholism is diagnosed with diabetes, he needs to combine treatment with getting rid of addiction.
Detoxification will cleanse the body of harmful toxins, and rehabilitation will help cope with psychological cravings for alcohol. To recover, you must adhere to a diet and an active lifestyle. All these factors will help a person live a long life.
Do your loved ones need help treating alcohol addiction? Sign up for a free consultation by calling the hotline: 8-800-775-32-63 . Specialists will answer your questions, select an effective treatment plan and accompany you throughout the entire program. We guarantee results if all our recommendations are followed.
Alcohol and type 2 diabetes
The disease leads to damage to blood vessels:
- kidney;
- liver;
- brain;
- eye;
- myocardium.
For this reason, diabetics are not recommended to drink alcohol-containing drinks. You also need to remember that alcohol can lower blood sugar levels. It would seem that there is nothing wrong with this - after all, this is what people with such a diagnosis need. But it's not that simple. The fact is that hypoglycemia usually does not occur immediately, but after some period of time. Sometimes more than 20 hours pass before the sugar-lowering effect appears.
This delayed effect of alcohol in type 2 diabetes is fraught with danger. After all, surges in blood sugar can be unpredictable, which means that the likelihood of a deterioration in the patient’s physical condition increases.
Alcohol depletes the compensatory capabilities of the human body. It promotes the breakdown of large amounts of glycogen, but does not allow new reserves to form.
Norm and restrictions
Within an hour, the liver is capable of converting no more than 75 ml of vodka, that is, 30 ml of alcohol. If you do not “add”, biochemical processes safely return to their original positions.
In the course of the studies, acceptable norms for diabetics to consume alcoholic beverages with different sugar and alcohol contents were determined. High strength drinks can be drunk in accordance with strict dosages. A serving of vodka (cognac, whiskey) per week is 50 ml for women and 100 ml for men.
Safe standards for alcoholic drinks for diabetics
Additional Information
Low-alcohol drinks always contain a sugar component. Excessive consumption of wine will invariably lead to an increase in glycemic levels. The GI of dry wine is 44 units, fortified – 35, sparkling – 50. Diabetics should choose high-quality red varieties of dry blended wines.
The norm is 0.2 liters (one glass). The presence of beer in a diabetic menu is extremely undesirable. The product has the highest glycemic index (110 units), energy value of about 50 kcal and provokes polygapia. A half-liter can of beer can increase sugar levels by an average of 4 mmol/l and add 250 kcal to the diet.
Dangerous symptoms of delayed hypoglycemia
It can be difficult to distinguish normal intoxication from hypoglycemia, because the symptoms of these conditions are similar. Typically, when there is a sharp drop in blood sugar, a diabetic is concerned about:
hand tremors (start to shake);- increased sweating;
- severe headaches;
- dizziness;
- vomit;
- frequent nausea;
- confusion;
- difficulties with orientation in space;
- speech impairment (becomes unclear and incoherent).
It is good if people who are close to a diabetic know about his diagnosis. Then, if his physical condition sharply deteriorates, they will be able to adequately respond to the situation and take first aid measures.
Features of taking medications
Alcohol can interact with hypoglycemic medications and affect their effectiveness. For example, in combination with clopramamide it causes a sharp deterioration in health with symptoms of acute intoxication.
In combination with metformin and thiazolidinediones, which reduce insulin resistance, ethanol increases the chemical load on the damaged liver.
If you are taking any hypoglycemic medications, you should avoid drinking vodka.
Vodka is prohibited while taking medications.
Is it possible to drink alcohol if you have diabetes?
Since the disease described is unpredictable, it is best to completely avoid drinks containing ethanol. If a person has at least one of the listed diagnoses, he is 100% prohibited from taking “hot” drinks:
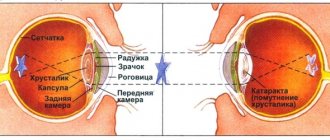
nephropathy;- cirrhosis;
- encephalopathy;
- diabetic retinopathy.
It is permissible to use alcohol-containing compounds if the patient knows exactly how his body reacts to drinking and glycemia is under complete control.
In rare cases, you can drink alcohol if you have the following types of diabetes:
- quality wine;
- vodka.
Dry wine
It is the best alcohol-containing drink allowed for diabetics. But you can take it occasionally and no more than one glass (200-250 ml). High-quality natural wine products:
dilate blood vessels;- promote the elimination of toxins;
- enrich the body with useful microelements and amino acids;
- lower the level of bad cholesterol;
- make the negative impact of stress on overall health less pronounced.
It is very important that the sugar content in the drink is less than 5%.
Vodka
It is permissible to use up to 100 ml of vodka at one time. This is the maximum dose for a man who has non-insulin-dependent diabetes. For a woman, the established dosage is two times lower.
In this case, it is necessary to first determine the quality of the product. It should not contain chemical impurities, as they can cause negative changes in the functioning of internal organs.
You can drink vodka in the specified amount once a week.
Beer
This drink, which young people love so much, is best not used by diabetics at all. Despite the fact that it has a low degree, its glycemic index is off the charts. This means that beer contributes to a rapid increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, and this is dangerous.
Rules for safe use
The main conditions for a diabetic to drink alcohol are:
- moderation. Do not exceed the permitted dose.
- normal sugar levels. A small amount of vodka is allowed only in the compensated stage of the disease.
Important! Stable hyperglycemia is the basis for complete abstinence from alcohol.
Drinking vodka if you have diabetes is allowed only in accordance with the rules:
- consult with the doctor with whom the patient is registered;
- do not exceed the permitted portion;
- do not drink the drink with juices, fruit drinks, soda and do not add them to vodka;
- exclude the possibility of drinking alcohol on an empty stomach;
- adjust the dosage of insulin and hypoglycemic medications before the feast;
- limit physical activity before the intended consumption of ethanol-containing drinks and during the feast;
- control glycemia (at least once every 90–120 minutes);
- choose your drink carefully; questionable (falsified) products should be discarded;
- bite tightly.
Suitable snacks include meals consisting of complex carbohydrates and proteins. Cereals and legumes promote partial absorption of harmful substances, and protein products will slow down the absorption of ethanol into the blood. Examples include:
Alcohol and the pancreas
- brown rice with vegetables and boiled chicken;
- cabbage stewed with turkey and red beans;
- boyar style buckwheat (with mushrooms and vegetables).
When drinking vodka, you must have with you:
- portable glucometer for monitoring glucose levels during and after an event accompanied by alcohol consumption;
- a prepared syringe with insulin (in case of increased blood glucose levels);
- a couple of pieces of sugar (to relieve possible hypoglycemia).
It is important to avoid drinking alcohol alone. When a diabetic crisis develops from an excessive amount of vodka or its dubious quality, the risk of being left without medical care increases.
How to drink correctly if you have non-insulin-dependent diabetes
Narcologists advise patients to adhere to certain rules that will sometimes allow them to relax with the help of “hot drinks” without causing harm to their health. This means recommendations:
Take alcohol with food, not on an empty stomach. Eat only those foods that are allowed for diabetes.- Drink only high-quality and proven alcohol. You cannot buy cheap wines, formulations with various additives and impurities, preservatives. Poor quality products often cause unpredictable reactions from the body.
- Don't drink before bed. This is associated with an increased risk of delayed hypoglycemia during nighttime sleep.
- Always carry medications with you that help quickly normalize your sugar levels.
- On the day of the feast, take glucose measurements according to the standard scheme, do not forget about their importance.
Following these tips will help minimize possible risks.
Main contraindications
In some cases, alcohol is not acceptable at all , and it is better not to experiment with it. Therefore they need to be listed separately.
- High risks of hypoglycemia.
- Kidney problems, especially nephropathy.
- Gout.
- High triglycerides under the influence of alcohol, which causes problems with fat metabolism.
- Cirrhosis and hepatitis.
- Use of the drug Metformin.
- Diabetic neuropathy.
It is important to monitor your diet at the time of drinking alcohol, before this moment and thereafter. You need to eat well, 3-5 times a day. It is also important that the food is varied . This measure allows you to minimize risks. However, in any case, you should be careful and carefully monitor your condition.
When you should absolutely not drink if you have diabetes
There are situations in which a diabetic must completely abstain from alcohol. Among them:
chronic pancreatitis;- gout;
- liver cirrhosis, hepatitis;
- pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
- ketonuria, acetonuria;
- detection of any of the complications of type 2 diabetes (cardiosclerosis, retinopathy, nephropathy, encephalopathy, etc.).
All diabetics should see a doctor regularly. They need to take responsibility for their health. By leading a healthy lifestyle, they will feel much better and avoid many problems.
Absolute contraindications for drinking alcohol
One of the causes of “sweet” disease type 2 is chronic alcoholism, which causes loss of pancreatic function and the development of alcoholic diabetes and pancreatitis. Patients with a history of such a set of pathologies should not drink even minimal doses of alcohol, since alcohol will provoke activation of the primary disease in them and, as a result, aggravation of the pathological process. Also, absolute contraindications that strictly prohibit the consumption of alcohol include :
- patient age under 21 years;
- any metabolic disorders;
- periods of pregnancy and lactation;
- concomitant cirrhosis, hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis;
- ketonuria, the presence of ketone bodies in the urine, indicating that glucose levels have dropped to critical levels.
Of particular danger is the development of late hypoglycemia. If you have this condition, you should also completely stop drinking alcohol, because it is very difficult to stop an attack that occurs several hours after the patient drinks.
How to avoid diabetes, 13 ways
This leaves many wondering how to minimize the risks of developing diabetes. Prevention is the best way to preserve both your own health and that of your loved ones. This aspect is especially important given that many people are predisposed to the disease. This means that sugar is high, but has not yet reached the level when the patient is diagnosed with diabetes.
Prevention of diabetes
Seventy percent of people with a predisposition to this disease may develop type 2 diabetes. However, by taking certain steps, this can be avoided. It will not be possible to influence age, genes, or lifestyle prior to the moment when a person decides to pay increased attention to his health, but everyone can eliminate certain bad habits and acquire useful ones that help minimize the risks of developing the disease.
#1 Avoid refined carbohydrates and sugar
Reviewing your diet is the first step towards preventing diabetes. Foods in which sugar and refined carbohydrates are present in large quantities can give a significant impetus to the development of the disease. Sugar molecules formed as a result of the breakdown of such products enter directly into the circulatory system. This causes a sharp increase in blood sugar levels and the synthesis of insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that performs a “transport” function, as a result of which sugar from the blood enters other cells.
Insulin is not accepted by the body of people with a predisposition to diabetes, and, instead of being distributed, sugar obtained from “junk” food remains entirely in the blood. The pancreas, trying to restore balance, begins to produce insulin even more actively. This does not lead to normalization of sugar, but, on the contrary, increases it even more. In addition, the amount of insulin begins to go off scale. Such a scheme becomes the impetus for the development of diabetes.
The existence of a connection between the consumption of foods rich in refined carbohydrates and sugar and an increase in the likelihood of illness has been proven in various studies. If you refrain from eating such foods, this risk is significantly minimized. Of the thirty-seven studies conducted to date, all have confirmed that people who eat fast carbohydrates are forty percent more likely to develop diabetes.
#2 Exercise regularly
Physical activity increases the sensitivity of cells to insulin, which allows the pancreas not to produce this hormone in large quantities, and, therefore, maintaining sugar levels becomes much easier. Doesn't necessarily become a professional athlete. The main thing is to simply do various exercises. Scientists have found that high-intensity exercise increases the body's sensitivity to insulin by 85 percent, and moderate-intensity exercise increases the body's sensitivity to insulin by 51 percent. The effect, unfortunately, only lasts on training days.
Engaging in various types of physical activity lowers sugar levels not only in people predisposed to diabetes, but also in obese people. Strength, high-intensity and aerobic training gives this result. If you make sports a part of your life, insulin will begin to be produced without any disturbances. This result can be achieved by increasing the number of calories burned during exercise to two thousand per week. To make this easier to achieve, you should choose exactly the type of activity that you like most.
#3 Make water the main source of fluid intake
You should not get carried away with various drinks. They, unlike ordinary drinking water, especially store-bought ones, contain sugar, preservatives and other additives not always known to the buyer. Drinking carbonated drinks increases the likelihood of developing LADA, that is, type 1 diabetes, which affects people 18 years of age and older. It begins to develop in childhood, but without any pronounced symptoms and rather slowly, requiring complex treatment.
The largest study on this aspect covered about 2,800 people. In people who drank two bottles of carbonated sweet juices per day, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes increased by 20 percent, and type 1 diabetes by 99 percent. It should also be taken into account that fruit juices can also become a provoking factor. Water has a completely different effect on the body.
Unlike other sweet and carbonated liquids, water has many positive qualities. It not only quenches thirst, but allows you to keep insulin and sugar under control. A similar effect was revealed experimentally when a group of people suffering from excess weight, instead of soda, were given plain water to drink during a diet. All participants noted not only a decrease in sugar levels, but also an increase in insulin sensitivity.
No. 4 Bring your weight to the optimal level
Diabetes affects not only people with excess body weight, but they make up the vast majority. And if there is a predisposition to the disease, then fat accumulates around the liver and abdominal cavity. Its excess becomes the main reason that the body becomes less sensitive to insulin, which increases the risk of diabetes.
Considering this fact, even a few lost kilograms cause significant improvements and disease prevention. The more weight lost, the better. In one experiment with about a thousand participants, it was found that losing one kilogram of weight reduced the risk of developing the disease by 16%. The maximum achievement that was identified during the study was an impressive 96%.
To get rid of excess body weight, you should adhere to a diet. You can follow a Mediterranean, vegetarian or any other diet that does not harm your health. It is important not only to lose weight, but also to maintain the results achieved. Along with the returning kilograms, old problems will make themselves known when the concentration of both insulin and sugar in the body increases again.
#5 Quit smoking
Smokers are at risk of developing many health problems, including type 2 diabetes. This applies to both active and passive smoking, that is, inhalation of tobacco smoke. As studies have shown, covering over a million smokers, the risk of disease in people who smoke a moderate number of cigarettes per day increases by 44, and from 20 or more cigarettes - by 61%.
There is also evidence of how giving up this bad habit affects a decrease in the manifestation of the disease in a middle-aged person. 5 years after stopping smoking, the likelihood of developing the disease decreases by 13%, and after 20 years this figure does not exceed that of people who have never smoked.
It is necessary to understand that quitting smoking will have a positive effect on both normal and overweight people. A person who quits a bad habit and then gains weight will always have much lower risks than if he continued to smoke.
#6 Try a low-carb diet
A low-carbohydrate diet is also called a ketogenic diet. It is the most effective and efficient for those who want to lose weight without any consequences or harm, since they should worry about their general condition, and not just about high sugar and insulin. This diet is recommended as a preventive measure both due to its good results in losing kilograms and because it reduces insulin resistance.
A three-month experiment during which people ate a low-carbohydrate diet found a 12% decrease in sugar levels and a 50% decrease in insulin levels compared to those on a low-fat diet for the same period of time. The indicators of the second group turned out to be much more modest and amounted to a 1% drop in sugar levels and a 19% drop in insulin levels. This best demonstrates the benefits of a low-carb diet. An artificially created carbohydrate deficiency allows you to maintain sugar levels both before and after meals almost the same. Thus, the pancreas will not produce large amounts of insulin, which is a prevention of diabetes.
This is not the only experiment on the relationship between carbohydrates and the concentration of insulin and sugar in the body. Another study showed that following a ketogenic diet in people prone to diabetes, blood sugar dropped to 92 mmol/L, which is down to normal, although it was previously at 118. Other health improvements were noted, as well as weight loss.
#7 Eat small portions
This applies to both dietary and regular nutrition. Portions of food placed on a plate should be small. This is fundamentally important for overweight people. The more food you eat at a time, the higher your sugar and insulin rise. And if you eat food in small portions, you can avoid sudden surges.
The study lasted for two whole years, which proved that the volume of food intake affects the likelihood of developing diabetes. An experiment found a 46% reduction in the risk of diabetes after switching from large to small portions. If you don’t change anything in your diet, you won’t have to count on such changes. Another experiment proved that thanks to small portions, after three months you can notice a difference in the level of both insulin and blood.
#8 Switch from a sedentary to an active lifestyle
You can’t practically stay still and prevent the onset of diabetes. Lack of movement, as scientists have found out, plays an important role in the development of the disease. There were about 47 different studies, but all of them showed a connection between a sedentary lifestyle and an increase in risk factors by 91%.
Of course, changing this is a completely feasible task. It’s enough to just get up and walk around once an hour. The main thing is to overcome your own habits, which, as has been proven, is very difficult. Young people who took part in a year-long lifestyle change experiment returned to a similar lifestyle after the study ended.
The power of habits is sometimes stronger than even the best intentions. And to avoid a “breakdown”, you should not overpower yourself, but rather set realistically achievable goals. If it is difficult to get up from your desk every hour and walk around your study or office, then walking up the stairs rather than taking the elevator, or talking on the phone while standing rather than sitting is much easier.
#9 Eat fiber-rich foods
High-fiber foods are healthy and help maintain both insulin and sugar levels at optimal levels. Depending on its ability to absorb water, fiber can be soluble or insoluble.
The peculiarity of the first is that, when it absorbs liquid, it forms a kind of jelly mixture in the digestive tract, which slows down the digestion process, which affects the slower flow of sugar into the blood. Insoluble fiber also prevents sugar from spiking, but the exact mechanism of action of this substance is not fully known.
Therefore, foods high in fiber, regardless of type, must be included in the diet, given that the maximum concentration of plant fiber is found in food when it has not been heat-treated.
#10 Avoid vitamin D deficiency
Cholecalciferol is one of the most important vitamins directly involved in blood sugar control. And if a person does not receive enough of it, then the risks of developing the disease increase significantly. The optimal level of its content is considered to be at least 30ng/ml.
Studies have shown that due to the high concentration of vitamin D in the blood, the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes is reduced by 43%. This applies to adults. In Finland, a study of the health of children taking cholecalciferol supplements showed that their risks of developing type 1 diabetes decreased by 78%.
Vitamin D, scientists believe, has a positive effect on cells that synthesize insulin, normalizes sugar, and reduces the likelihood of diabetes. The daily requirement of 2000 to 4000 IU can be replenished by exposure to the sun, consumption of cod liver and fatty fish.
#11 Minimize the amount of processed food
The method of preparing food directly affects a person's health. It is believed that additives and vegetable oils used in cooking have a negative effect on the process of obesity and the development of diabetes.
Eating plant foods, vegetables, nuts and fruits—that is, whole foods—prevents these risks. The main thing is that they are not exposed to heat. Prepared foods increase the likelihood of illness by 30%, while “raw” foods, on the contrary, reduce it.
No. 12 Drink tea and coffee
Along with water, it is necessary to include coffee and tea in your daily diet. Numerous studies show that coffee can reduce the risk of diabetes from 8 to 54%. The variation is due to the amount of consumption of this invigorating drink. Tea has a similar effect, especially on overweight people and women.
Tea and coffee contain antioxidants called polyphenols. They resist diabetes, protecting the body from this disease. Another antioxidant component, but present only in green tea, is EGCG or epigallocatechin gallate, which lowers sugar and increases the body's sensitivity to insulin.
#13 Include curcumin and berberine in your diet
Curcumin
It is one of the components of turmeric, a spice that is the basis of curry. It exhibits powerful anti-inflammatory properties and is used in Ayurveda. This substance perfectly helps to cope with arthritis and has a positive effect on many markers responsible for the occurrence and progression of diabetes. These properties of the substance have been proven experimentally.
The study, which lasted 9 months, involved 240 people. All of them were at risk, that is, they had a predisposition to diabetes. During the entire experiment, participants took 750 mg of the substance per day, as a result, everyone experienced zero progression of the chronic disease. In addition, each participant had an increased degree of insulin sensitivity, and the functions of the cells responsible for the production of this hormone improved.
Berberine
is part of some herbs traditionally used in Chinese folk medicine for several millennia. It, like curcumin, reduces inflammation, but also helps get rid of bad cholesterol. The uniqueness of the substance is that it lowers sugar even in those who suffer from type 2 diabetes.
There are about fourteen scientific studies that have confirmed the fact that berberine has properties similar to metformin, the most famous of the ancient drugs for the treatment of diabetes, that is, it lowers sugar. However, it should be understood that no direct studies have been carried out to test the effect of the substance on people who are at risk.
The supposed benefits of berberine are based on its ability to increase insulin sensitivity and lower sugar concentrations. This is quite enough to draw appropriate conclusions and recommend the component for inclusion in the diet of both patients and those with a predisposition to diabetes. However, if you decide to take berberine, you should first consult your doctor, as it is a potent substance.
Conclusion
It is impossible to completely eliminate the risk if there is a predisposition to diabetes, but it is possible to control the factors that can lead to the development of this disease. If you analyze your daily routine, bad habits, nutrition, physical activity, and make changes to your already habitual lifestyle, then it is quite possible to prevent the development of the disease. The main thing is to make every effort, since your health depends on this.