The "golf ball" phenomenon
The "golf ball" phenomenon
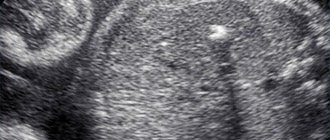
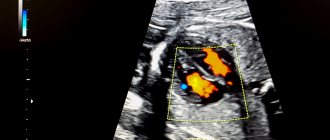
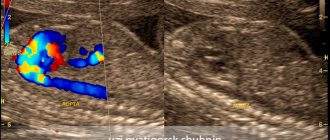
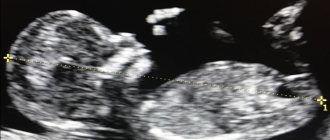
You come for the second screening, and they tell you that the child has a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle. “Hyperechoic” means that the area has increased brightness (density) against the background of heart tissue. The “golf ball” phenomenon arose because such a hyperechoic inclusion is shaped like a golf ball and bounces like a ball when the heart beats. Most often, a hyperechoic focus (HEF) is found in the left ventricle (LV), less often in the right ventricle (RV) and other chambers of the heart. It still remains a mystery why such a hyperechoic focus (HEF) in the heart muscle, which has bone density, disappears without a trace after birth.
GEF in the ventricles of the fetal heart: medical tactics
In most cases, if a “golf ball” is detected in the area of the child’s heart, it is necessary to continue observation: a control ultrasound examination during pregnancy should be performed by a certified diagnostician using a modern 3D device. If there is a suspicion of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, one must agree to invasive research methods.
After the birth of a child, it is important in the first days and during the first years of the baby’s life to be regularly examined by a pediatrician and cardiologist.
Detection of any changes in the baby’s heart is a significant reason for a careful assessment of the child’s intrauterine development.
Developmental defect or sign of chromosomal abnormalities
Excessive impregnation with calcium salts
Yes, yes, this is exactly the reaction that a similar conclusion from an ultrasound diagnostic doctor can cause in parents. In fact, neither one nor the other is true. A hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is not a malformation or an anomaly. Many parents are afraid that this kind of finding in the child’s heart is a sign of severe chromosomal pathology, for example, the presence of Down syndrome. To date, there is no scientific evidence that the presence of a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart is a reliable sign of chromosomal pathology in the absence of other signs.
Why does such a focus of increased density occur in the prenatal period? There are several possible reasons.
- Excessive impregnation of calcium salts (calcification) of a certain area of the heart muscle. Most often, such changes are localized in the area of the papillary (papillary) muscles. The second trimester of pregnancy, during which such changes are most often detected, is characterized by active mineralization of the child’s musculoskeletal system.
- The presence of an additional or false chord in the ventricle of the child’s heart. Such a false or additional chord does not carry a functional load, and is not a pathology, but refers to minor anomalies of cardiac development (MADC). This phenomenon is a common finding during ultrasound examination. The chords themselves in the prenatal period can provoke the deposition of calcium salts, as well as increase the brightness of the hyperechoic focus.
- One of the signs indicating chromosomal pathology. Let us remind you once again that in the absence of other reliable signs of chromosomal pathologies, the presence of a compaction or hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart does not indicate genetic disorders.
What are the main syndromes identified by NIPT?
- Down syndrome (trisomy 21)
The frequency of occurrence is 1:600 births. Moreover, the risk of trisomy 21 in the fetus increases with the woman’s age. One of the forms of genomic pathology, in which most often the karyotype is represented by 47 chromosomes instead of the normal 46, since the chromosomes of the 21st pair, instead of the normal two, are represented by three copies. There are two more forms of this syndrome: translocation of chromosome 21 to other chromosomes (usually on 15, less often on 14, even less often on 21, 22 and Y chromosome) - 4% of cases, and a mosaic variant of the syndrome - 5%. Characteristic features associated with Down syndrome: “flat face”, abnormal shortening of the skull, skin folds on the neck in newborns, short limbs, open mouth and other signs that can be accurately diagnosed by a geneticist.
- Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18)
The chromosomal disease is characterized by a complex of multiple malformations and trisomy 18 chromosomes. Described in 1960 by John Edwards. The worldwide population frequency is 1:5000 as of 2021. Children with trisomy 18 are more often born to older mothers, and the relationship with maternal age is less pronounced than in cases of trisomy 21. The main signs of Edwards syndrome: low weight, abnormalities in the shape of the skull, heart defects, ventricular septal defects, mental retardation.
- Patau syndrome (trisomy 13)
Frequency – 1:16000 births. Characterized by developmental disorders of the nervous system, eyes, severe facial deformation, malformations of the heart and other internal organs. Characterized by profound mental retardation. 90% of children die before the age of 1 year.
What to do next
Genetic blood test
If an ultrasound examination reveals a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart, further examination is necessary. What and how to do next will be determined by your attending physician. If necessary, a number of additional examination methods may include:
- A genetic blood test aimed at identifying chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus.
- Echocardioscopy is a diagnostic method performed from 18 to 25 weeks. Important parameters of the fetal heart are assessed. There are certain indications for this method: age over 35 years, diabetes mellitus (DM), infections of the pregnant woman in the early stages, detection of pathology of the heart muscle (myocardium) of the fetus in the early stages, delay in fetal development according to the timing, there is a heart defect in the pregnant woman or relatives relatives.
In more rare cases, the following diagnostic methods may be prescribed:
- Study of placental cells for the genetic characteristics of the fetus. This method (placentocentesis) allows you to determine the diagnosis as early as possible.
- Fetoscopy is an examination of the amniotic sac. Amniocentesis - analysis of the composition of amniotic fluid. The level of hormones, biochemical and immunological parameters is studied. It is possible to assess the risk of a chromosomal abnormality.
HGLOS - Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Until recently, this defect was fatal in absolutely all cases. The child died during the first week of life, and it was impossible to provide him with any surgical assistance.
Today the situation is different and, if everything is done on time and correctly, then there is a good chance of saving it. Precisely to save, because Immediately after birth, the time of his life counts not months and days, but hours and even minutes.
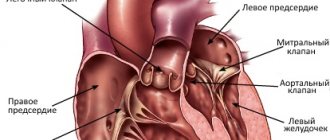
The word hypoplasia means “reduction in size.” With this defect, the left ventricle, i.e. the main one, the main one, was almost completely undeveloped. But this is not enough. Neither the entrance to it, i.e. mitral valve, nor outlet, i.e. section of the ascending aorta along with its valve. Instead of the aorta, there is a small vessel with a diameter of 1-3 millimeters, through which blood flows into the coronary arteries, but there is no section of the ascending aorta.
The huge right ventricle, receiving blood from the right atrium and left atrium through a defect in the interatrial septum, pumps all the blood into the pulmonary artery and lungs. Some of it enters the systemic circle through the open ductus arteriosus, but only a small part. Life, therefore, depends on the presence of two communications - interatrial and interarterial, which, firstly, are insufficient, and secondly, immediately after birth they can close, as is normal. Otherwise, as a hemodynamic catastrophe
it cannot be called, and without the most urgent measures the child will die.
The diagnosis can be made in utero, and this is an extremely important moment when both parents and doctors must weigh all available options for providing immediate assistance. What is important here is not only preparation for immediate action, but also absolute determination to go through with the child the entire difficult step-by-step path of his further treatment, which will take the first few years of his life.
Each of these stages may be the last for a child, since they are all associated with enormous risk. But always, even if this is little consolation, we must remember that both you and the doctors did everything possible today to save him.
Stages of treatment
The first operation is performed in the first days of life. Approaches to the first stage of surgical correction can be different and depend on the clinic, the skill of the surgeon, and the readiness of the cardiac surgery hospital to care for and manage this extremely complex category of patients. This can also be an operation with artificial circulation, sometimes quite long, because it is necessary to perform a complete reconstruction of the sharply narrowed ascending aorta. This is achieved by sewing in an elastic biological prosthesis of such a shape that, as a result, the pulmonary artery and aorta become the only vessel extending from the right (single) ventricle. To ensure sufficient mixing of blood, a large atrial septal defect is created, and blood flow to the lungs is directed through an arteriopulmonary anastomosis. As can be seen from this description, this is a very large and complex operation that can only be performed in centers with extensive experience in heart surgery on newborns.
But even in the largest and world-famous US institutions, the mortality rate after this stage reaches 20-40 percent.
We present these figures to emphasize that for hypoplastic left heart syndrome, surgery is the only possible, but far from safe, path. But, since we are talking about saving lives, even the attempts themselves are always justified.
In recent years, several clinics around the world have introduced a method, the survival rate of which is close to 90% - the so-called hybrid operation of patent ductus arteriosus stenting and bilateral separate narrowing of the pulmonary arteries .
If everything went well, then the second operation is recommended to be done at 4-10 months. This involves an anastomosis between the superior vena cava and the pulmonary artery, or “half” of the Fontan procedure. And finally, at the age of one and a half to two years, the child undergoes the third stage - the final Fontan palliation, after which the blood circulation is completely separated.
In clinics with extensive experience in such operations, the second and third stages are much less risky than the first, the most difficult. The child will have to live with one ventricle, and everything said above about the defects for which the Fontan operation is the final stage of surgical treatment applies in full to this defect.
Just 10-15 years ago, children with hypoplastic left heart syndrome were not subject to surgery at all. But the syndrome is one of the five most common congenital heart defects
.
Today, helping these children is possible, although not always. But if you and your cardiologists know this, then you need to act. And let the “little orchestra of hope led by love” never leave you on this difficult path. How to get treatment at the Scientific Center named after.
A.N. Bakuleva? Online consultations