Doctors around the world use palpation, percussion and auscultation to diagnose various diseases. During pregnancy, the gynecologist also uses these objective examination methods to determine your baby’s vital signs. You are probably familiar with palpation (from the Latin palpatio - stroking, feeling), and percussion (from the Latin percussio - blow, tapping), and auscultation (from the Latin auscultare - listen, listen) from childhood. But you will only have to encounter auscultation in the form in which it is practiced in gynecology during routine visits to the antenatal clinic. What is this term and what is this method? Of course, you are interested in delving into the essence of all the manipulations carried out during examinations by your attending physician, because now you are responsible not only for yourself, but also for the little person growing and developing in your womb.
- 2 Listening to the belly of a pregnant woman: why is this necessary?
- 3 Main determined indicators
- 4 Listening points
- 5 Preparation for manipulation
- 6 Algorithm for performing auscultation
- 7 Video “Technique for listening to the fetal heartbeat”
Auscultation: what is it?
Auscultation (from the Latin “auscultare”) in translation sounds like listening. In midwifery practice, this is listening to fetal heart sounds
Auscultation (listening) is one of the methods of examining a patient for the purpose of diagnosing diseases. In therapy, surgery, pediatrics and other areas of medicine, auscultation is carried out using a stethoscope - a device invented in 1816 by the French physician and anatomist Dr. Laennec, who was the discoverer of the auscultation method. He also named and described all the main auscultatory phenomena.
In gynecology, auscultation is performed with an obstetric stethoscope. It differs from a conventional stethoscope in the width of the funnel, which the doctor firmly applies to the pregnant woman’s exposed abdomen during auscultation.
In addition, this manipulation can be successfully carried out using a stethophonendoscope - an invariable attribute of all doctors, a device with which we have all been familiar for a long time.
Causes.
This anomaly can be caused by various factors that contribute to excessive or, conversely, insufficient activity of the baby in the womb. The main reasons for the anomaly:
- hypotonia of the abdominal muscles;
- oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios;
- fetal hypotrophy;
- tumors of the uterus and pelvic bones;
- increased myometrial tone;
- risk of spontaneous abortion;
- large fruit;
- clinically narrow pelvis;
- multiple births;
- abnormal attachment of the placenta;
- fetal development abnormalities;
- structural defects of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle-shaped).
Listening to a pregnant woman's belly: why is it necessary?
What does the doctor hear during auscultation of the expectant mother’s abdomen? And he can hear uterine and intestinal sounds, the beating of the abdominal aorta, which coincides with the woman’s pulse, the noise of the vessels of the fetal umbilical cord, its dull jerking movements in the mother’s womb, and, most importantly, the heart sounds of the fetus. They should be audible well and clearly with a stethoscope. A decrease in sound conductivity can be caused by a large amount of amniotic fluid, the location of the placenta on the anterior wall of the uterus, or significant fat deposits in the abdominal cavity. During multiple pregnancy, the heart sounds of the fetuses are dried in different parts of the uterus.
Auscultation of the fetal heartbeat can tell the doctor a lot about its development and physical condition. In particular, it can be used to determine the presence of congenital heart defects and pathologies of large blood vessels in a child. The baby's muffled heart sounds usually dry out due to hypoxia.
The fetal heartbeat during auscultation becomes clearly visible at the beginning of the second half of pregnancy, but no later than 18–19 weeks. Every week these sounds get better and better. The heart rate of the baby in your belly is normally 120–140 beats per minute.
At earlier stages, it is better to use phonocardiography or fetal cardiotocography to determine the cardiac activity of the embryo. The indicators from these studies will be more accurate.
Fetal heart rate can be used to determine gestational age
Ultrasound of the fetal heart
Early in pregnancy, the fetal heartbeat can be detected using ultrasound (ultrasound). Normally, with a transvaginal ultrasound (the sensor is inserted into the vagina), contractions of the fetal heart are detected at 5-6 weeks of pregnancy, and with a transabdominal ultrasound (the sensor is placed on the abdomen) - at 6-7 weeks. During the first trimester of pregnancy (up to 13 weeks), the heart rate (HR) of the embryo varies depending on the stage of pregnancy. At 6-8 weeks, heart rate is 110-130 beats per minute, at 9-10 weeks - 170-190 beats per minute, from the 11th week of pregnancy until birth - 140-160 beats per minute .
Such changes in heart rate are associated with the development and formation of the function of the autonomic nervous system (that part of the nervous system that is responsible for the functioning of the internal organs of the fetus). Heart rate is an important indicator of embryo viability. Thus, unfavorable prognostic signs are a decrease in heart rate to 85-100 beats per minute and an increase over 200 beats. In this case, it is necessary to carry out treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of the change in heart rate. The absence of heartbeats when the length of the embryo is over 8 mm is a sign of a non-developing pregnancy. In order to confirm a non-developing pregnancy, a repeat ultrasound is performed after 5-7 days, based on the results of which a final diagnosis is made. In the II-III trimesters of pregnancy, an ultrasound scan examines the location of the heart in the chest (the heart is located on the left and occupies approximately 1/3 of the chest during transverse scanning), heart rate (normal - 140-160 beats per minute), the nature of contractions (rhythmic or irregular). Heart rate in the later stages depends on many factors (fetal movements, physical activity of the mother, exposure to various factors on the mother: heat, cold, various diseases). With a lack of oxygen, the heart rate first compensatory increases above 160 beats per minute (this condition is called tachycardia), and then, as the fetal condition worsens, it becomes below 120 beats per minute (bradycardia).
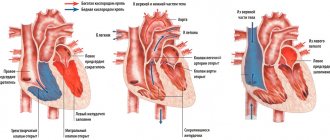
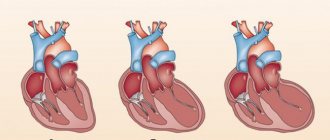
To identify cardiac malformations, a so-called “four-chamber slice” is examined. This is an ultrasound image of the heart in which you can see all four chambers of the heart at the same time - two atria and two ventricles. A conventional four-chamber ultrasound of the heart can detect approximately 75% of heart defects. According to indications, an additional study is performed - echocardiography of the fetus.
Listening points
The place where the fetal heartbeat is best heard is called the auscultation point. The location of such points on the pregnant woman’s abdomen depends on the position of the baby in the mother’s uterine cavity.
There are two types of fetal presentation.
- The main thing. It, in turn, can have the following positions: facial (the head is thrown back, the chest is as close as possible to the wall of the uterus) and occipital (fetal position).
- Pelvic. When the fetal pelvis is directed towards the exit of the uterus.
During auscultation, the doctor tries to listen to the fetus with a facial presentation - from the side of its chest, and with an occipital presentation - from the back. But there are listening points on the expectant mother’s belly, where you can almost always hear the fetal heartbeat.
Where are these points located?
- Just below the navel to the left.
- Just below the navel on the right.
- Along a line drawn through the navel parallel to the horizon, on the left.
- Along a line drawn through the navel parallel to the horizon, on the right.
Preparation for manipulation includes disinfection of the instrument and the doctor’s hands
Changes in fetal activity
Changes in fetal activity may be associated with external influences. For example, if a pregnant woman lies on her back for a long time, then the enlarged uterus compresses a large vessel - the inferior vena cava, and the flow of blood to the fetus is disrupted, which immediately causes its violent reaction - active movements. The same changes in the baby's activity can occur in any other uncomfortable position of the mother - if she leans forward, squeezing her stomach, or sits with her legs crossed, the child, with her activity, forces the mother to change her position. A similar situation arises if the baby himself squeezes or presses the loops of the umbilical cord, limiting the flow of blood through it. He begins to move more actively, changes his position and relieves pressure on the umbilical cord. However, in some cases, an increase or, conversely, a decrease in fetal movements can be a sign of a serious pathology.
If after 28 weeks of pregnancy the baby does not make itself known for 3-4 hours, perhaps he is just sleeping. In this case, the expectant mother needs to eat something sweet and lie on her left side for half an hour. If these simple manipulations do not lead to results, you should repeat them again after 2-3 hours. If this time the baby does not make itself known, this is a reason to consult a doctor. Rare and weak movements may also indicate unwellness of the fetus, most often a lack of oxygen for the baby, that is, fetal hypoxia.
Preparation for manipulation
During auscultation, the pregnant woman should be in a horizontal position, so it is advisable to have an individual sheet with you to cover the couch on which you will lie. Before visiting the antenatal clinic, you need to empty your bowels and bladder so that bowel sounds do not interfere with the examination.
And one more condition for obtaining reliable results. During auscultation, the expectant mother should be completely calm. When a pregnant woman is psycho-emotionally excited, the fetal heart rate may increase.
Phonocardiography is a modern analogue of auscultation
Gymnastics with the transverse position of the fetus.
Until 34 weeks of gestation, the position of the fetus is unstable, so there is a high probability that the baby will be placed longitudinally. For this purpose, expectant mothers are prescribed corrective gymnastics during the period 30-31 weeks. This is a group of exercises that help correct the incorrect position of the fetus.
Most often recommended:
- lie on the floor, bend your legs and rest your heels on the floor, raise your pelvis above head level;
- “cat” - get on all fours, while inhaling, raise your tailbone and head, and bend your lower back, while exhaling - the opposite movements;
- take a knee-elbow position, the pelvis is placed above the head - hold for up to 20 minutes.
These exercises are performed for 1-1.5 weeks three times a day. During this period, the fetus must acquire the correct position. If this happens, the stomach must be secured with a bandage.
Correct position while sleeping is also important. The baby is more accustomed to being head down, so the mother should sleep on the side on which the baby's head is located.
Corrective gymnastics is contraindicated in the following cases:
- abnormal placement of the placenta;
- multiple births;
- umbilical cord abnormalities;
- scar on the uterus;
- presence of bloody discharge from the vagina;
- abnormalities of amniotic fluid;
- severe chronic diseases of women;
- increased uterine tone;
- uterine fibroids.
Auscultation algorithm
How is auscultation performed? The patient lies with her back on the couch, her legs slightly bent at the knees. The doctor is located to the right of the expectant mother and first, using Leopold’s techniques, determines the presentation of the fetus and the level of the uterine fundus. Then, applying the wide bell of the stethoscope to the pregnant woman’s belly, and the narrow bell to her ear, the gynecologist searches for the listening point. In the place where the fetal heartbeat is best heard, the doctor calculates the baby’s heart rate characteristics.
Important! The doctor does not hold the stethoscope directly during the listening session.
After auscultation, the expectant mother is helped to rise from the couch, and the doctor washes his hands and disinfects the equipment.
Normal fetal movement
The baby in the mother’s belly moves almost constantly. At the 20th week of pregnancy, the fetus makes about 200 movements per day, and between the 28th and 32nd weeks the number of movements reaches 600 per day. Naturally, a pregnant woman does not feel all the movements of the fetus, but only a small part of them. So, after 28 weeks, the frequency of fetal movement, as a woman feels, is usually from 4 to 8 times per hour, with the exception of periods of fetal sleep (3-4 hours in a row).
During the third trimester, a pregnant woman may notice that her baby has certain sleep and wake cycles. Children are usually most active from 19:00 to 4:00 in the morning, and the period of “rest” occurs more often from 4:00 to 9:00 am. Of course, the movements of the fetus depend on the mother’s mood; if the mother is worried or happy, the baby may move more actively, or, conversely, become quiet. The fact is that when a mother is happy, the amount of joy hormones in her body increases significantly - endorphins, which regulate the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, including the blood vessels of the placenta. During times of stress or expressed negative emotions, biologically active substances are also produced - stress hormones; they also affect the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. It is thanks to this biological interaction between the mother and baby that the fetus senses the mother’s condition. When the expectant mother is resting, the baby usually becomes more active; if a pregnant woman is active and busy with some kind of work, the child most often becomes quiet. The movements also change depending on the satiety of the expectant mother. Usually the baby begins to move actively after the mother eats, especially something sweet. At the same time, the level of glucose in the blood increases sharply, which causes the fetus to be more active.
Fetal movements are the language in which the unborn baby speaks to his mother. Naturally, a pregnant woman should listen to movements because in some cases, changes in fetal movements may indicate a violation of its intrauterine state and a not entirely successful course of pregnancy.
If after 20 weeks of pregnancy the expectant mother does not feel the fetus moving, it may be worth consulting a doctor and making sure that everything is fine with the baby.
Video “Technique for listening to the fetal heartbeat”
- Author: Polina
Hello. My name is Polina. Having once heard the truth that a pediatrician is the main doctor for any family with small children, I realized that I had something to strive for. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Chlamydia during pregnancy: what does a woman need to know?
Fetal heart rate during pregnancy
Childbirth with a transverse position of the fetus.
If the position of the fetus does not change, then natural childbirth is not recommended and most often a planned caesarean section is prescribed.
Natural childbirth is possible with a low baby weight, but even then it is necessary to monitor the dilation of the cervix. If the dilatation does not allow birth on its own, then an emergency caesarean section is prescribed.
In the case of premature birth with a transverse position of the fetus, a decision is usually made on an emergency caesarean section.
Surgical intervention in the case of a transverse position of the fetus is quite justified, because there is a significant risk of complications during natural childbirth.
The transverse position of the fetus entails many difficulties, but they can be easily avoided if you follow all the instructions of your obstetrician-gynecologist.