Diagnostics
A general urine test will help identify renal pathology. To make a correct diagnosis, a complete history and examination of the cause of shortness of breath are fundamentally important. This will help to establish the factor that provokes this condition without resorting to additional research and analysis. Depending on the initial cause, examinations are carried out:
- X-ray;
- Ultrasound;
- general urine and blood tests to identify pathologies in the kidneys and determine hemoglobin levels.
Return to contents
Other symptoms
Swelling of the legs often occurs with diseases of the cardiovascular system.
In addition to cough and tachycardia, the following symptoms are observed with such cardiac disorders:
- swelling;
- blueness of fingers and toes;
- dyspnea;
- the occurrence of tachycardia;
- the veins in the neck become larger;
- loss of consciousness;
A dangerous symptom is a cough, which is accompanied by pink foam. This characterizes a severe form of untreated heart disease.
Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, it is important to consult a doctor to find out the cause and prescribe treatment. This will allow you to avoid serious consequences, which are often incompatible with life. After the first examination and assessment of the patient's complaints, a list of procedures will be prescribed to identify the problem.
Return to contents
Anemia
A disease that develops due to insufficient hemoglobin in the body. It is provoked by problems with the intestines, various infectious diseases, deficiency of vitamins and microelements.
Classification of anemia
Thus, vitamin deficiency anemia can cause shortness of breath and a number of other unfavorable symptoms, including:
- increased heart rate;
- impaired coordination and reflexes;
- general weakness;
- temperature increase.
Anemia - symptoms
Problems such as an increase in liver size and various types of mental disorders may occur.
Diagnostic stages
The first step is to contact a specialist. The doctor will examine the patient and clarify his complaints about his general health. If necessary, he will redirect the patient to specialists from a medical institution specializing in a different profile.
To diagnose lack of air during inspiration at rest, the following are used:
- general blood and urine analysis,
- spirography,
- ECG,
- echocardiography,
- radiography,
- Ultrasound,
- CT.
Secondary studies can be prescribed in accordance with the individual characteristics of the body and the course of the disease.
The heart beats often and it’s difficult to breathe: what’s the matter?
Normal breathing rate is 16-20 movements per minute. Shortness of breath or dyspnea is a disorder that is characterized by changes in the depth and rhythm of the respiratory process. Inspiratory type disturbance occurs on inspiration, expiratory type - on exhalation. Sometimes a mixed form is observed. In everyday life, shortness of breath periodically appears in every healthy person - adult or child. As a variant of the norm, it is called physiological and goes away after the cause is eliminated (running, physical activity). In situations where difficulty breathing persists for a long time and causes discomfort, you should think about the presence of some pathology.
- Rheumatoid arthritis and anemia. What you need to know
More about symptoms
Shortness of breath due to arrhythmia is a symptom that accompanies many different diseases. Doctors call the main signs of this condition:
- rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath;
- the growing feeling of suffocation that a person experiences;
- change in breathing pattern - it becomes more frequent;
- combination with swelling, wheezing, whistling.
Dyspnea can occur in various forms (subacute, acute and chronic) and has several degrees. The severe stage is detected in patients who experience discomfort at rest, with slight movement or the slightest household stress.
The most common causes of the condition
There are many pathological conditions that manifest themselves in the form of shortness of breath. Conventionally, they can be divided into three main groups:
- cardiovascular disorders;
- respiratory diseases;
- anemia.
Shortness of breath may appear in case of hyperthermia, be a consequence of smoking or drinking alcohol, or develop while taking medications or osteochondrosis. Depending on the etiology of the condition, treatment tactics are selected.
Lung problems
Pulmonary dyspnea is an inspiratory disorder caused by almost all diseases of the respiratory system. When it occurs, a person’s breathing becomes difficult and the heart beats rapidly. The reasons for this condition are:
- smoking;
- respiratory tract infections;
- bronchitis;
- obstructive pulmonary disease;
- pneumonia.
Attention! Against the background of these symptoms, tumor processes, emphysema, tuberculosis, pulmonary actinomycosis, pneumothorax, and sarcoidosis can develop.
Cardiovascular pathologies
Shortness of breath caused by heart pathologies is considered the most important symptom, and in most cases has a chronic course. By the degree of its severity and combination with tachycardia, one can judge the nature and stage of heart failure. The most common causes of difficulty breathing and rapid heartbeat are the following cardiac phenomena:
- heart failure;
- heart defects;
- myocarditis;
- atrial fibrillation;
- acute coronary syndrome;
- cardiomyopathy.
Heart failure is a term that describes not a specific disease, but disorders of the heart caused by the development of its morphological changes. The syndrome is characterized by difficulty breathing, which is initially observed only during walking or physical activity. As it progresses, shortness of breath becomes permanent and appears even at rest.
Symptoms of cardiac dysfunction that often accompany shortness of breath include:
- What to do when your hand joints hurt
- weakness in the legs and arms, drowsiness, palpitations;
- arterial hypo- or hypertension;
- cyanosis - a bluish tint of the skin on the fingers, toes, earlobes, nose, feet;
- frequent dizziness, fainting;
- paroxysmal dry cough, especially during rest hours;
- nocturia – increased urine production at night;
- periodic pain in the heart.
The problem of shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat that occurs against the background of heart failure is dealt with by therapists, cardiologists, and neurologists.
Attacks of VSD and neuroses
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a syndrome that combines many diseases that are similar in their manifestations. It develops against the background of stress, neuroses, endocrine pathologies, physical and mental overload. Paroxysms occur suddenly and can last from 10-15 minutes to 2-3 days, and all this time the heart continues to beat at an increased rate. During the attack and after it ends, hemodynamic deterioration occurs, due to which the organs do not receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients.
The most common type of VSD is tachycardia, namely the sinus type. Shortness of breath against the background of an accelerated myocardial rhythm is mild and does not cause discomfort. The most dangerous type is considered to be the paroxysmal type, in which the heart rate reaches 220-250 beats per minute. Most often it is diagnosed in older people. An increase in myocardial rhythm can be observed even at rest. During an exacerbation, a person suffers from the following symptoms:
- general weakness, drowsiness, fatigue;
- rapid pulse;
- severe shortness of breath;
- tremor of the limbs;
- mild nausea, vomiting;
- panic attacks;
- increased sweating;
- feeling of lack of oxygen.
Attacks are repeated frequently, which is caused by stress and fatigue due to young age and immaturity of the nervous system.
Hormonal imbalance
Humoral regulation is an important link in the chain of vital processes in the body. When hormonal levels change due to a delay in menstruation, menopause, or late pregnancy, cardiac activity primarily suffers, while organic damage to the myocardium is detected in rare cases. Such phenomena lead to increased heart rate, which is called hormonal tachycardia.
Its appearance can be determined by an increased heart rate, which is complemented by symptoms of autonomic disorder:
- headache;
- feeling of lack of air;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- strong noise of blows, echoing in the ears;
- painful sensations in the area behind the sternum;
- "heart jumping out of the chest."
With organic damage to the myocardium, symptoms may be supplemented by fainting states.
Temperature increase
Hyperthermia is considered one of the symptoms of many diseases. Almost always, it indicates the development of an inflammatory process, which, regardless of etiology, provokes increased production of various enzymes and specific substances. Together, they have a special effect on the thermoregulation center, causing an increase in temperature. Trying to cope with the changes occurring, the body begins to intensively secrete sweat.
- Movalis: composition of the drug, release form and pharmacological action
Due to the lack of oxygen, which is necessary for the reaction to proceed normally, breathing becomes more frequent and the load on the heart increases.
It is important to know! When the temperature rises even by one degree, the frequency of myocardial contraction in an adult increases by 10 beats. The child suffers even more; this figure is 50% higher. In a newborn and a year old, the heartbeat can reach 150 beats/min.
Anemia
Anemia is characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood. It acts as an independent disease, or is a symptom of pathological disorders. It can develop against the background of problems with the digestive system, infectious diseases or vitamin and mineral deficiency. Iron deficiency anemia occurs most often.
Shortness of breath is formed due to a violation of hemoglobin synthesis and the production of red blood cells. As a result, the transport of oxygen molecules to the cellular structures of organs and tissues deteriorates, which inevitably leads to hypoxia.
A person develops shortness of breath and a number of other signs appear:
- general weakness;
- fever, chills;
- impaired coordination and reflexes;
- trembling in the body and palpitations.
An increase in the size of the liver can often be observed, and mental disorders are also detected.
Bad habits
Chronic fatigue, excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, caffeine-containing products, smoking strong tobacco or a large number of cigarettes, addiction to drugs (even light ones), lack of sleep and wakefulness negatively affect well-being and over time lead to the development of shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. Getting rid of addictions, restoring the correct alternation of periods of active activity and rest will help eliminate unpleasant manifestations.
Side effects from taking medications
The occurrence of shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat can be provoked by medications such as corticosteroids, diuretics, as well as medications prescribed for the treatment of asthma and thyroid diseases. This is due to increased metabolic processes, in which the body experiences an increased need for oxygen, and a stimulating effect on the sympathetic nervous system. As a result, the heart rate reflexively increases, which leads to shortness of breath.
Most often, such symptoms appear at night, when a person is resting. If they occur regularly, you should contact a specialist to replace the medications you are using with other, safer ones.
Variant of the norm
Every healthy person experiences shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat from time to time. In this case, it is called physiological, and can appear under the following circumstances:
- in a closed room with a high concentration of carbon dioxide;
- at high altitudes, where there is a lack of oxygen and hypoxic conditions are created;
- with excessive physical exertion, climbing stairs.
To prevent the development of dizziness, nausea, palpitations, and weakness in the future, you should change your lifestyle - move more, engage in active sports, adapt to significant altitudes, adjust your diet, and lose weight. The manifestation of strong emotions (joy, pain, fear, anger) can also provoke these states. Posing no threat to health, they go away on their own within a few minutes and do not require medical intervention.
Difficulty breathing - causes of the disorder
The feeling that there is not enough air in the lungs is not always due to any disease. This phenomenon can occur during physical exertion, emotional shock, or sudden climate change. If the feeling of shortness of breath bothers you regularly, this may be due to serious problems:
- diseases of the heart muscle;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- pulmonary pathologies;
- the presence of foreign bodies in the respiratory tract;
- diabetes mellitus;
- oncology;
- infectious processes.
Other causes of difficulty breathing are active smoking, a tendency to allergies, excess body weight, and nervous disorders. The problem often occurs during pregnancy and is associated with bearing a large fetus, twins or triplets, and polyhydramnios.
Symptoms of shortness of breath
In order to timely determine caused shortness of breath from abnormal shortness of breath, you need to calm down and not panic, carry out an analysis of the condition if possible and identify the signs:
- rapid pulse;
- difficult air intake;
- suffocation;
- cardiopalmus;
- weakness;
- unstable breathing when walking;
- dizziness;
- chest pain;
- pale skin;
- panic attacks;
- profuse sweating.
Return to contents
Atrial fibrillation
This pathology is often diagnosed in people after 40 years of age.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cause of heart rhythm disturbances. This is a common deviation in people over 40. There is a significant risk factor for stroke, so timely consultation with a doctor becomes a vital measure. The pathology does not occur on its own, but manifests itself against the background of an existing disease or disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and rapid pulse. Signs are identical to those above, but are complicated by possible loss of consciousness and abnormally pronounced heartbeat.
Return to contents
Atherosclerosis
In the initial stages, the patient does not feel any symptoms or changes in his condition. Atherosclerosis or the accumulation of cholesterol provokes shortness of breath and heart rate due to atherosclerotic plaques sticking to the walls of blood vessels. As a result, blood circulation is disrupted, which gradually turns into oxygen starvation. The occurrence of such a disease is provoked by many factors: from bad habits and age-related changes to metabolic disorders, stress, a passive lifestyle and poor nutrition.
Return to contents
Lung problems
Pulmonary diseases often manifest as breathing problems.
Severe shortness of breath is a natural concept for patients suffering from dryness and respiratory tract diseases. There are pathologies that are not acquired, for example, low compliance of the lungs. Dyspnea occurs in people who have injured the thoracic region, have inflammation in the lungs, or suffered from dryness. Often these patients experience shortness of breath at night. The problem is also aggravated by difficulty in exhaling, as phlegm and mucus are found in the respiratory tract.
Return to contents
Anemia and its types
This disease develops in people with insufficient hemoglobin in the blood. The condition occurs due to intestinal problems, infectious diseases, due to a lack of vitamins and microelements. Anemia can be: microcytic, normocytic and macrocytic. They are classified according to the causes of occurrence and indicators of microelements in the blood. Signs and manifestations of the disease can be aggravated by an increase in the size of the liver and mental disorders.
Return to contents
Heart failure
Shortness of breath with this pathology appears against the background of fluid stagnation in the lung tissues, which occurs as a result of the inability of the heart to pump blood in the required volume. In the initial stages, dyspnea is typical after physical activity, and as it develops, it is also observed at rest. Depending on the degree of load on the heart and lungs, there are 4 stages, more details about which are in the table:
| Degrees | When does it appear? |
| 1 | After exercise |
| 2 | After moderate physical activity |
| 3 | Due to active manipulations and movements |
| 4 | At rest and during sleep |
Return to contents
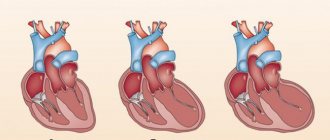
Mitral valve prolapse
In most cases, the pathology does not pose a danger to the patient.
MVP is one of the heart defects in which contraction of the left ventricle occurs with pronounced bending of one or both leaflets. The pathology is moderate and not dangerous; many patients live with it all their lives. Main causes: congenital or acquired prolapse. The symptoms of the disease are identical, sometimes the patient experiences a burning sensation in the chest, and disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system appear. Main features:
- prolonged or short-term tingling in the heart;
- increased heart rate;
- radiating pain in the chest area.
Return to contents
Other diseases
Dyspnea is caused by many other reasons that negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system and the person’s condition as a whole. The pathology often occurs in people with symptoms of tachycardia, increased emotional instability, and patients who drink large quantities of alcoholic beverages and caffeine-containing substances. In some cases, shortness of breath occurs while taking certain medications, such as corticosteroids and diuretics. This negatively affects the functioning of the heart and causes a rapid pulse.
Return to contents
Help that should be provided to the patient independently
Before the ambulance arrives, the patient should provide first aid independently. At the first sign of spasms, there are several remedies to normalize the condition.
- Create complete silence and peace for the patient.
- Freshen the air in the room.
- Apply ammonia.
- Give me some water to drink.
If the patient's condition worsens, it is necessary to give a small clap on the back and wait for the specialists to arrive.
Only after a correct diagnosis can qualified treatment be carried out. The patient’s health depends not only on the treatment and consultation of the doctor, but also on the patient himself. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and take medications according to the prescribed schedule, all symptoms will soon disappear completely.