Obstructive bronchitis is an inflammatory disease of the lower respiratory tract with damage to the bronchi. Bronchitis, in which the bronchi are narrowed, is called obstructive. Obstruction (literally this is a narrowing, overlap) - occurs under the influence of the inflammatory process in the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles, they thicken due to edema. Edema leads to concentration of sputum in the lumen of the bronchus. Sputum “clogs” the bronchi. Air passes through the bronchi with difficulty. The patient hears whistling and wheezing in the chest, as if bagpipes are being played inside.
In an adult patient it can be acute or chronic.
Acute obstructive bronchitis
This is an inflammation in the bronchi that begins quickly and is not preceded by several years of regular coughing. To the doctor’s question “How long have you been coughing?”, the patient will answer no more than a week.
The inflammatory process in the bronchi leads to swelling and irritation. A cough appears lasting no more than 3 weeks. In acute bronchitis, inflammation does not last long, and the structure of the bronchi will be completely restored after recovery.
In 80% of cases, acute obstructive bronchitis is caused by a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract. For example, influenza, parainfluenza, rhinovirus infection. Usually, people call all these pathogens, except influenza, colds. Less common causes of acute bronchitis are bacteria - mycoplasma or chlamydia pneumonia, the causative agent of whooping cough, staphylococcus, streptococcus and Haemophilus influenzae.
Chronic obstructive bronchitis
This is a chronic bronchial disease of an inflammatory nature. In this case, chronic (long-term) inflammation and swelling develop in the bronchial tree. Chronic inflammation and swelling narrow the lumen of the bronchi, which limits the flow of air into the lungs. The mechanism of obstruction coincides with the acute process that we described above. Against the background of obstruction, cough and shortness of breath intensify. Whistles and wheezing are heard in the chest. Sometimes wheezing and whistling can be heard even by people nearby. The patient has been suffering from cough for several years. The frequency of exacerbations of cough and other symptoms is two or three times a year, more than three weeks in a row.
Chronic bronchitis happens
- Obstructive
- Simple recurrent
- Asthmatic.
There are several causes of chronic obstructive bronchitis in adults. In the first place is the influence of external factors - tobacco smoking (active and passive). The second involves work related to inorganic dust (metallurgy, coal industry, etc.), the use of coal for home heating.
Other causes of this disease are infections. For example, previously suffered, poorly or lately treated bronchopulmonary diseases (consequences of untreated acute respiratory viral infections, pneumonia or childhood infections).
Asthmatic bronchitis is either undetected asthma or its onset, or pre-asthma.
Content:
- Symptoms of pathology
- Options for shortness of breath after Covid-19
- How to assess lung function after COVID-19 3.1. Difficulties in self-diagnosis
- How to treat shortness of breath after coronavirus 4.1. Medicines for shortness of breath 4.2. Oxygenation 4.3. Inhalations 4.4. Physiotherapeutic procedures 4.5. Breathing exercises
- Ways to improve lung function on your own
COVID-19 takes its toll throughout the body, but it most commonly affects the lungs. Shortness of breath after Covid is common. It occurs both in people who have had pneumonia and in those who have not encountered serious complications during their illness.
Scientists have found that in approximately 20% of those recovering, the function of the lung tissues has worsened. Patients gasp for air if they are in a hurry, are unable to lie on their back for a long time, and quickly get tired when doing even simple physical work. Things are especially bad for people diagnosed with pulmonary fibrosis, which leads to scarring of the paired organ.
Under normal conditions, fibrosis is rare. It is most often encountered by people over the age of sixty. With this diagnosis, shortness of breath is a concern. It can be so strong that it is difficult for a person to talk and move.
We suggest you figure out why difficulty breathing after coronavirus bothers you, and how to recognize and eliminate dangerous symptoms. It is important to know this information to prevent complications from Covid-19 from progressing.
Symptoms of pathology
With difficulty breathing, the patient cannot take a deep breath. He makes at least 22 breathing movements per minute. This is typical for moderate pneumonia. In severe cases of the disease, the number of inhalations and exhalations per minute exceeds 30.
A severe inflammatory process is recorded in the lung tissues. A person’s body temperature rises and a nonproductive dry cough occurs. It also happens that there are no accompanying symptoms. Then we can assume that shortness of breath is caused by panic attacks, psychosomatics, and fear.
If, when listening to the lungs, the doctor hears wheezing or whistling, it means there is coronavirus pneumonia and the bronchi are affected. This clinical picture is often observed in individuals with concomitant bronchitis, bronchial asthma, and secondary bacterial infection. It often precedes pulmonary edema.
Difficulties with breathing after coronavirus can be described as follows:
- feeling of tightness in the chest;
- rapid breathing;
- performing shallow breathing movements;
- heaviness when trying to take a deep breath.
Shortness of breath in itself is not a disorder in healthy people. Runners and athletes encounter it. If the onset of the symptom was preceded by difficult physical work, then shortness of breath is the norm. During and after coronavirus, the problem manifests itself even at rest. And this is a dangerous sign. It indicates that the body is suffering due to oxygen deficiency. As you know, in conditions of oxygen deficiency, not a single internal organ works fully.
Treatment of obstructive bronchitis
The main tasks that must be solved in case of obstructive bronchitis
- The cough is relieved - it should not interfere with sleep, do household chores, irritate or disturb loved ones.
- It is necessary to restore the normal passage of air through the bronchi - reduce obstruction, improve expectoration of sputum.
- The infection must be destroyed.
- After recovery, prescribe a program to strengthen the immune system, conduct rehabilitation and give recommendations for vaccination against influenza and pneumonia.
Acute uncomplicated bronchitis can be cured without active treatment and without consequences. It is better for the patient not to go to work at this time, but to stay at home. Drink plenty of warm drinks and recovery usually occurs within 7 days.
Remember: Obstructive bronchitis carried on the “legs” can be complicated by pneumonia!
To treat obstruction, Berodual is used through a nebulizer. Expectorants are ineffective in acute cases. The decision on use is made by the doctor.
If the illness is accompanied by an increase in body temperature for more than 4 days, consult a pulmonologist. You may have pneumonia and need other medications.
With an exacerbation of a chronic obstructive process in the lungs, the task is different. Treatment is mandatory. To prevent the disease from progressing, active treatment is necessary. The causes of exacerbation of this disease are usually associated with a bacterial infection due to a cold or hypothermia. Treatment cannot be achieved without antibiotics. Modern expectorants will be required. Inhaled bronchodilators, especially through a nebulizer, will quickly reduce cough.
For asthmatic bronchitis, treatment is aimed at stopping a sudden narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi. The disease develops in response to inhalation of an allergen, chemicals with a strong odor, or organic dust. It is necessary to exclude the patient's contact with the irritant. Symptoms of this disease are coughing attacks, wheezing and whistling in the chest. The clinical picture is bright. For therapy, bronchi dilators, expectorants, and inhaled or intravenous steroids will be effective. Antibiotic therapy is rarely used.
Treatment methods
Medicines
Antibiotics are necessary to destroy bacteria that cause inflammation in the bronchi. Due to the high percentage of thoughtless use of antibiotics, the number of bacteria resistant to treatment has increased.
Don't self-medicate! Antibiotics must be prescribed by a doctor! In the medical scientific community, there are clear recommendations for prescribing antibiotics for regions of our country.
Antiviral drugs are necessary only for the treatment of influenza and bronchial inflammation accompanying this disease. Only two drugs with proven effectiveness against this virus are used - Oseltamivir and Zanamivir. These medications only treat influenza; they are useless for other acute respiratory viral infections.
Prescribing immune stimulants will not bring tangible results. Therefore, you will not find these drugs in the recommendations of medical societies.
In case of bronchial obstruction, drugs that resolve this obstruction are needed and effective - they dilate the bronchi.
Bronchiodilators (bronchodilators)
These medications are inhaled through nebulizers. These include Berodual, Atrovent and Salbutamol. The doctor prescribes treatment because they have side effects.
Steroid medications are effective for chronic asthmatic bronchitis. They are inhaled by inhalation or administered intravenously.
Expectorants - ambroxol, acetylcesteine or carbocesteine. The drugs can be used in the form of inhalations or parenterally (intravenously). The dosage and frequency of taking these medications is determined by a pulmonologist.
Inhalations
In the treatment of obstructive bronchitis, the role of inhalation is difficult to overestimate. Compressor nebulizers spray antibiotics, bronchodilators, expectorants, corticosteroids into microparticles and inject a therapeutic aerosol into the bronchi. The advantage of this delivery method is that the medicine is delivered precisely to the site of inflammation. Therefore, when treated through a nebulizer, it is possible to quickly reduce cough, normalize expectoration of sputum, and reduce its viscosity.
Massage
A massage that has proven to be very effective and simple to treat is cupping massage. Cupping massage came to us a long time ago from Chinese medicine. Irritation of the reflex zones of the skin of the back stimulates expectoration of mucus, reduces cough and leads to recovery.
“Ventum Vest Vibration” is a complex effect of vibration massage and pressure on the chest at the same time. The patient is put on a special vest into which air is pumped under pressure. By changing the frequency of air supply to the vest and the pressure on the chest, the immune system is activated. This occurs due to improved microcirculation in the affected bronchi. Improves lymph circulation and regeneration of damaged bronchial mucosa. If vibration massage is combined with inhalation of antibiotics and expectorant medications, their concentration in the affected bronchi will increase. The complex effect on the bronchi promotes rapid recovery without complications.
Exercise therapy and breathing exercises
At the stage of reducing the severity of the disease or exacerbation, exercise therapy and breathing exercises will increase expectoration of sputum and improve blood supply to the bronchi. This will reduce inflammation, shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. This effect is obtained by training the respiratory muscles. These muscles include the diaphragm, intercostal muscles and back muscles. The main audience for whom exercise therapy helps are patients with chronic smoker's cough and COPD.
Possible consequences and complications of obstructive bronchitis
If bronchial obstruction is treated incorrectly, serious complications are possible. Pneumonia comes first. Pneumonia is an acute infectious disease that leads to rapid death. The risk of developing pneumonia if treatment is not started in a timely manner or is incorrect is high. To prevent the development of pneumonia, the patient must consult a pulmonologist. The doctor will be able to diagnose and rule out pneumonia. Perhaps he will prescribe a course of antibiotics without waiting for pneumonia to develop. If your body temperature does not decrease for more than 3-4 days or constantly increases, your cough intensifies and purulent or brown sputum appears, then there is a very high probability that you have pneumonia.
Against the background of bronchitis, a possible complication is pneumothorax - a rupture of the pleura due to a strong and intense cough. This is a resuscitation situation. Pneumothorax is observed in patients with bullous transformation, COPD, but cases of pneumothorax due to prolonged cough are common. Due to long-term obstruction and inflammation, the lung tissue loses its elasticity and becomes rigid. Lung tissue is easily damaged by coughing. Therefore, if symptoms such as sudden shortness of breath and chest pain appear, you should urgently consult a pulmonologist.
Frequent exacerbations of obstructive bronchitis lead to the emergence or progression of COPD, a disease that leads to the development of respiratory failure and death.
Options for shortness of breath after Covid-19
To date, doctors have described two types of difficulty breathing after coronavirus:
- Gradual. A person feels that he is breathing “insufficiently.” Difficulties with inhalation and exhalation occur even at rest. The situation gets worse at night. If the patient raises his hands up, he feels a little better. Worried about decreased performance.
- Sudden. At first the patient feels well, but at some point his body temperature rises, severe headache, and sweating occur. Full breathing becomes impossible. There is a panicky fear of dying from suffocation.
Both the first and second options require receiving qualified medical care. At the same time, you cannot hesitate, since even with mild symptoms, a moment may come when full breathing becomes impossible.
Why us
- Doctors. We receive specialists of the highest qualification category, holders of academic degrees, with extensive experience in leading Russian clinics.
- Individual approach. The doctor will develop an individual examination and treatment plan for each patient in accordance with the cause of development and clinical picture of the disease.
- Complexity. The therapists at our clinic work in close collaboration with other specialists - cardiologists, hematologists, psychotherapists. This provides effective treatment for shortness of breath of various origins.
- Expert equipment. All studies are carried out using modern equipment and are highly accurate.
- Comfort. All consultations, studies and treatment are carried out within our hospital, which allows our patients to save energy and time.
You can see prices for services
How to assess lung function after COVID-19
There is a no-false breath test that anyone can do on their own. According to its terms, it is necessary:
- Take a deep breath through your nose.
- Hold your breath for ten seconds.
- Exhale slowly.
If during testing no discomfort arises, a cough does not start, or a strong sore throat does not appear, then everything is fine with the lungs. If your health worsens when you try to hold in air, a medical examination is indicated.
Difficulties in self-diagnosis
Shortness of breath, which occurs due to narrowing of the nasal passages and swelling of the mucous membranes during a runny nose, and which manifests itself due to deterioration of the lungs - these are two completely different problems. A person is not able to independently understand what causes his illness.
Therefore, if you have difficulty breathing, you should still seek help from a therapist or pulmonologist. Self-medication for such symptoms is unacceptable.
Carrying out diagnostics
To find out why breathing is difficult and to select effective methods for normalizing it, a thorough diagnosis is carried out. To clarify the causes of shortness of breath, the KRH Dental & Medica clinic performs:
- examination of the larynx using direct and indirect laryngoscopy;
- chest x-ray, fluoroscopy, bronchoscopy;
- spirometry, which allows you to assess the state of respiratory function;
- electrocardiography, daily Holter monitoring, determining the characteristics of the heart.
It is also provided for a test to determine the gas composition of the blood. To find out the reason why breathing is difficult, an MRI, tests for allergic reactions, and testing for tumor markers may be required.
How to treat shortness of breath after coronavirus
When helping people who have difficulty taking deep breaths, doctors use:
- drug therapy;
- oxygenation;
- inhalation;
- physiotherapy;
- breathing exercises.
Let's look at each method in more detail.
Medicines for shortness of breath
To improve pulmonary function, doctors prescribe drugs belonging to such pharmacological groups as:
- antiviral;
- immunomodulators;
- bronchodilators;
- expectorants;
- thinning phlegm;
- antibiotics.
Drugs and their dosages are always selected individually, taking into account the severity of the symptoms of the disease and the patient’s health status.
Oxygenation
It is inhaled oxygen therapy. Used if a person is unable to breathe on their own. Then oxygen is introduced directly into the respiratory tract through a special catheter.
Oxygenation is required only for seriously ill patients. If a person controls his condition and follows all medical prescriptions, the risk of sudden suffocation will be minimal.
Inhalations
During inhalation, a nebulizer is used, breaking the medicinal solution into tiny particles that easily penetrate into the deep tissues of the lungs. A good effect can be achieved by:
- agents that thin viscous sputum;
- antiseptics;
- sea water;
- saline solution;
- bronchodilators;
- coughing
Inhalations should not be carried out unless prescribed by a doctor, since if the inhaled drug is selected incorrectly, lung function may deteriorate.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
To speed up the resorption of inflammatory foci and abnormal compactions, during and after coronavirus, you need to do the following:
- massage of the chest area;
- UHF therapy;
- electrophoresis with enzyme solutions;
- SMT.
It is important to follow the physiotherapy course to the very end. If you abandon the procedures immediately after you feel better, the negative symptoms will most likely return again.
Breathing exercises
You should do breathing exercises during illness and for at least one month after receiving a negative test for COVID-19. They activate the muscles of the chest and increase blood flow to the lung tissues.
If a patient suffers from severe shortness of breath, the doctor may recommend using a respirometer, a device that measures the intensity in cells and tissues.
Not enough air - treatment methods
If it is difficult to breathe for physiological reasons, but there are no diseases, no special therapy is required. Many people are interested in what to do if breathing is a little difficult, but there are no serious disorders in the body. To improve your well-being, you should use simple methods (ventilation, humidification, taking sedatives, agreed with the doctor).
Patients who have difficulty breathing due to certain diseases are prescribed complex treatment. Main goals of therapy:
- eliminate foci of infection and inflammation;
- clear the airways;
- speed up the discharge of sputum;
- improve blood composition;
- stabilize the functioning of the heart muscle;
- normalize the condition of blood vessels.
To eliminate lack of air during breathing, specialists at the KRH Dental & Medical clinic use effective and safe medications and prescribe effective procedures. Each patient is guaranteed attentive attention and an individual approach. After the treatment is completed, recommendations are given to correct the lifestyle and prevent the recurrence of the pathology.
Ways to improve lung function on your own
What can a person suffering from shortness of breath after coronavirus do? There are simple ways to normalize pulmonary activity:
- Eating foods that increase lung capacity. Preference should be given to fruits and vegetables. Tomatoes, blueberries, nuts, onions, and citrus fruits are especially useful. Spices and fatty foods should be avoided.
- No smoking. Tobacco smoke and the toxins it contains make the lungs extremely vulnerable. In order for the tissue to recover and the inflammatory process to stop progressing, it is important to stop smoking.
- Do cardio workouts. You need to start them only if you are in good physical health. Cardio increases lung capacity, normalizes blood circulation, and increases heart rate. It is good if the exercises are performed in the fresh air. But the load should be increased gradually.
- Respiratory protection from environmental pollution. A person who has recently had Covid-19 should not be in polluted conditions. If his professional activity involves being in harmful conditions, it is better to take a long vacation.
Patients who strictly follow the doctor's instructions, take medications, perform breathing exercises and eat properly quickly stop suffering from shortness of breath. Take care of your health and don't let the coronavirus deprive you of your ability to breathe deeply.
What happens in this case?
Since central sleep apnea
is a consequence of a disorder of the central nervous system and differs from obstructive apnea in that it is dependent on a neurological plan, and not a physiological one, this means that breathing disorder during sleep occurs from the brain.
Sleep and breathing disorders occur in the part of the brain that controls breathing. With central sleep apnea, the airways are completely free for air to enter. Central sleep apnea syndrome
It is much less common, but doctors who deal with sleep problems should certainly know the nature of your “bad sleep.”
For this purpose, several years ago, a unique diagnostic device was introduced into the circulation of somnologists - polysomnography
.
Literature:
- COVID-19, coronavirus infection caused by SARS-CoV-2 / 2020 / ORGZDRAV: News. Opinions. Education. VSHOUZ Bulletin.
- COVID-19: respiratory infection caused by a new coronavirus: new data on epidemiology, clinical course, patient management.
- Medical rehabilitation for new coronavirus infection (Covid-19) / Ivanova G. E., Balandina I. N., Bakhtina I. S., Belkin A. A., Belyaev A. F., et al. / 2021 / Physical and rehabilitation medicine, medical rehabilitation
The text was checked by expert doctors: Head of the socio-psychological service of the Alkoklinik MC, psychologist Yu.P. Baranova, L.A. Serova, a psychiatrist-narcologist.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 798-30-80
Call! We work around the clock!
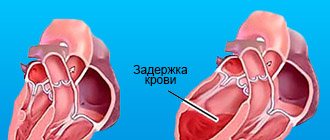
The mechanism of shortness of breath.
In most cases, shortness of breath is due to hypoxia (low oxygen in the body) or hypoxemia (low oxygen in the blood). Low oxygen levels cause irritation of the respiratory center in the brain, resulting in a feeling of lack of air and breathing involuntarily quickens. The causes of hypoxia can be diseases of the lungs, heart or extrapulmonary diseases that limit the mobility of the chest and lungs (pregnancy, obesity, etc.).