If a woman continues to have low or high blood pressure after childbirth, under no circumstances should she ignore this condition or try to cope with the problem herself. The reasons for this situation can be very diverse, so it is the doctor who must determine which factor influenced the change in indicators and eliminate it. Let's consider what factors influence blood pressure readings after childbirth, what symptoms bother a woman during this period, what treatment will help get rid of the pathology without harm to health.
Normal pressure
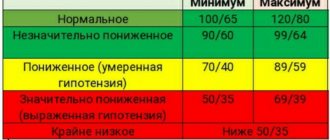
Both during the period of bearing a child and after his birth, if a young mother practices breastfeeding, the pressure should be within normal limits, this means that the body can fully cope with the loads, and no pathological changes occur in it. In healthy people, blood pressure should not be lower than or exceed the normal range of 90/60-140/60. Blood pressure can fluctuate within acceptable values; such changes depend on the characteristics of the body, age, weight and many other factors.
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
120
on
80
LACTOSTASIS OR MASTITIS - WHAT TO DO AND HOW TO AVOID?
Painful lump in the breast, redness, temperature - these words frighten almost every expectant mother. And it is with these complaints that nursing mothers very often turn to specialists. The diagnosis they hear is “lactostasis” or “mastitis”. These two diagnoses are often confused and even considered synonymous. Confusion also exists in specialized literature, and even more so in the stories of nursing and breastfeeding women.
Lactostasis is stagnation of milk caused by blockage of the duct. Milk accumulates, does not come out, and bursts the “locked” lobule, causing pain. Reabsorption of milk can provoke a rise in temperature. The filled lobule compresses the surrounding tissues, this causes swelling, which further complicates the release of milk.
Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue . Characteristic signs of inflammation are pain, redness and temperature, although often the picture can be blurry, for example, a slight temperature. Mastitis in a nursing mother is most often the result of prolonged lactostasis (swollen, injured tissues easily become inflamed), but it can also occur without previous stagnation, due to infection (for example, through cracks in the nipple or from foci of infection inside the body, as a consequence of an acute or chronic disease).
Understanding what exactly is happening to the breasts is not as easy as it seems. This is difficult to do by eye. Lactostasis can occur with severe pain and high fever, while mastitis can occur without fever. It is not always possible to palpate a lump, especially a deep one, and a specialist cannot always differentiate for sure what kind of lump it is - a lobule full of milk, or edematous tissue, or an abscess. Ultrasound comes to the rescue today, so if you have the slightest doubt, it is advisable to undergo an ultrasound examination. Moreover, in addition to its diagnostic role, it can also help therapeutically - ultrasound often “breaks” the plug and helps cope with lactostasis.
What to do?
But the nursing mother herself is usually not interested in the complexities of diagnosis. What is more important to her is what to do in a particular situation. Does it really matter what exactly happened? Yes. Because the treatment tactics are different. And if lactostasis can most often be dealt with on your own in a day or two, then mastitis usually requires the help of a specialist and often the use of antibiotics.
So, the first day after the onset of symptoms (pain, redness, thickening, rise in temperature) most often suggests lactostasis . You can try to cope with it with the following measures:
- The first and most important thing is to empty the sore breast well.
People often think that this requires a super-master of pumping or a mega-cool breast pump. However, the best assistant in emptying the breast is a properly sucking baby. Therefore, our first remedy will be frequent feeding from the sore breast.
If the baby sucks ineffectively (incorrectly attached to the breast, weak), rarely (for example, a child of the second half of the year or older than a year may breastfeed quite rarely), additional pumping may be useful. If there is a lot of milk and the baby's sucking is not enough to solve the situation, it is better to express the milk before feeding, and leave the baby the difficult job of sucking the milk out of the problematic ducts.
- Warmth before feeding/pumping (warm shower, warm diaper on the chest) may help;
- Cold after feeding/pumping has worked well (a bag of frozen berries wrapped in a diaper, a cloth soaked in cold water);
- You can massage the lump, but carefully - a hard massage increases the swelling and worsens the situation;
- drink when thirsty, it is better to drink plain cool water (hot drinks can increase the flow of milk) Limiting drinking will not help, on the contrary, if dehydrated, the milk may become thick, and it will begin to leak out even worse;
- If there is no improvement within 24 hours, you should seek help.
What should not be done if milk stagnation occurs?
- You can't stop feeding
- It may be risky to make vodka, alcohol, camphor compresses (may worsen milk secretion, there may be burns to the skin of the breast)
- There is no need to resort to hard, traumatic “kneading” of the chest - this can lead to injury and worsening the situation.
- Don't expect spontaneous improvement. If no progress is visible within a day or two, especially if it gets worse, you need to seek help.
Who should I turn to for help ?
- In case of mastitis, a woman needs to see a doctor , mammologist or gynecologist to make a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe antibiotics. Antibiotics are prescribed that are compatible with breastfeeding (that is, the active substance either does not penetrate into milk or penetrates in such small doses that it has no effect on the child).
- Be sure to continue feeding from the affected breast. An exception is made in the case of purulent mastitis - during the period of discharge of pus from the ducts, it is necessary to stop feeding the affected breast and express milk; after the end of the discharge of pus, feeding resumes. With healthy breasts, feeding is not interrupted.
Minimize risk
Expectant mothers are very concerned about how this situation can be prevented. There are no guaranteed methods. It happens that despite all efforts, stagnation of milk still occurs. But you can try to minimize the risks.
- Put your baby to your breast frequently (in the first month, breaks of more than 2 hours are undesirable).
- Make sure your baby is properly attached to the breast. An incorrectly sucked baby will empty it. If you are unable to put your baby to your breast, if congestion appears in the first month, it makes sense to seek help from a lactation consultant.
- Try to drink enough water.
- Avoid chest compression (tight underwear, underwired bra, pressure from the shoulder strap of a bag, backpack or baby carrier, sleeping on your stomach can lead to congestion).
- Do not let your baby suck on anything other than the breast (sucking on nipples and pacifiers increases the risk of lactostasis).
Let all these tips remain just “general information” information and feeding will be easy and problem-free. But even at the first signs of problems, there is no need to panic - with competent actions and timely seeking qualified help, most difficulties are quickly resolved.
Health to all nursing mothers and their wonderful babies!
Anastasia Vtulova, consultant on breastfeeding and child care (Center for Natural Development and Child Health)
You can consult our breastfeeding hotline:
+7 (daily from 7.00 to 23.00).
Previous
Next
Causes of low and high blood pressure after childbirth
After the birth of a child, it is possible that residual effects after pregnancy and childbirth will be observed for six months to a year, since the mother’s body takes a long time to return to normal, and this takes time. But if more time has passed after pregnancy, and blood pressure is still fluctuating, this indicates that not everything is in order with the body, and medical intervention is required. After the birth of a child, blood pressure can remain either high or low, let’s look at the main reasons.
Increased
Weight gain during pregnancy leads to blood pressure problems after childbirth.
High blood pressure after the birth of a child is most often caused by the following factors:
- A woman’s weight gain, especially if she does not follow the rules of a healthy diet and lifestyle. In this case, the load on the heart and blood vessels increases, as blood volumes become larger. Therefore, gynecologists so carefully monitor how a pregnant woman gains weight, so that later, after the birth of the child, she does not have problems with the health and functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- If in the last trimester a woman’s blood pressure began to increase abnormally and gestosis developed, then after childbirth the condition may not stabilize for some time. In this case, you should be under constant supervision by a doctor, and if you follow all the recommendations, your blood pressure will gradually return to normal.
- After the birth of a baby, some women do not immediately return to normal psycho-emotional health, as a result of which, due to stress and constant nervous strain, the load on the heart and blood vessels increases, and arterial hypertension develops.
- Some women notice that their blood pressure has increased during breastfeeding, which is affected by lack of sleep at night, fatigue, and disruption of sleep and wakefulness.
- Hereditary predisposition, when in the female line there were cases of increased blood pressure after childbirth.
- Chronic pathologies that worsened and became aggravated during pregnancy and after (chronic kidney failure, hypertension).
- If a woman takes heavy medications after giving birth, this also provokes a rise in blood pressure as a side effect.
Decreased
Low blood pressure after childbirth is less dangerous than high blood pressure, but still, you should not ignore the symptom and try to cope with the problem yourself. The pathology most often worries women of fragile build, prone to depression, and scrupulously monitoring their weight. If you severely limit yourself to normal food, anemia develops, as a result of which your blood pressure drops below normal levels. The cause may be a difficult, complicated birth, during which the woman has lost enough blood. Since the body needs time to recover, hypotension after childbirth will continue to bother you for some time.
If a woman suffered from vegetative-vascular dystonia before pregnancy, this condition may recur after the birth of a child, causing characteristic symptoms. Pathology can also arise as a consequence of a malfunction of the thyroid gland. In this case, only an endocrinologist can help cope with the situation; you can only make the situation worse on your own.
Methods to combat low blood pressure during breastfeeding
Most often, a decrease in pressure (hypotension) does not require correction, since with normal rest and nutrition, indicators are restored independently due to compensatory mechanisms.
Main symptoms of hypotension:
- weakness;
- sleep phase disturbances (nighttime insomnia and pathological daytime sleepiness);
- apathy - lack of desire to do anything, lack of interest in anything;
- diffuse headache;
- visual impairment (double vision, blurred contours);
- dizziness.
Reduced blood pressure disrupts the blood supply to organs and tissues, including the mammary gland, so long-term persistence of these symptoms is accompanied by the risk of a decrease in milk supply.
How can you raise a woman’s blood pressure during lactation?
The period of breastfeeding is characterized by the presence of many restrictions in the mother's lifestyle, therefore traditional methods of blood pressure correction are prohibited.
The safest methods to raise the blood pressure of a nursing mother are presented in the table below.
| Way | Mechanism of action |
| Increased drinking regimen (up to 2.5 liters per day). Allowed: compote, juice (natural), uzvar, fruit juice, clean water | Increasing the volume of circulating fluid in the vessels |
| Balanced nutrition (daily caloric intake of at least 2500 kcal) | Adequate intake of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and mineral salts with foods ensures the normal functioning of the vascular wall and endocrine glands responsible for blood pressure levels |
| Physical activity (morning exercises, special fitness for women in labor) | Increased blood flow in working muscles increases vascular tone throughout the body |
A common cause of low blood pressure in women after childbirth is dysfunction of the thyroid gland. In this case, you can raise the values by systematically using iodized salt or iodine preparations (after preliminary consultation and laboratory tests with a doctor).
How to relieve discomfort during hepatitis B due to low blood pressure at home?
Sudden signs of hypotension, which significantly worsen a woman’s condition and complicate child care, require immediate correction.
A nursing mother can raise her blood pressure at home using several methods:
- drink a cup of coffee. One mug of weak coffee a day will not affect the quality of milk (large quantities make it bitter), but will improve the mother’s condition;
- drink a cup of strong black or green tea with sugar;
- use tincture of ginseng or lemongrass (1 tablespoon, dissolved in a glass of water). The products can only be used after consulting a doctor;
- shake your abs (for women during the first month after a caesarean section or complicated childbirth - it is strictly contraindicated).
Drug treatment using pharmacological drugs is carried out only against the background of concomitant pathology and pronounced changes. Often, women must stop breastfeeding during therapy.
Symptoms
| Pressure | Symptoms |
| Increased |
|
| Decreased |
|
How to measure?
Correct measurement of pressure will allow you to make a reliable diagnosis.
Before measuring blood pressure, you should sit down and relax. Place a cuff on the arm, above the bend of the elbow, fixing the stethoscope on the inside where the large vein passes. Next, we pump up the air with the bulb so that the cuff fits snugly to the arm. Then the air slowly descends, and the tone is listened to through a stethoscope. The first beat shows the systolic pressure, and the last beat shows the dystolic pressure. For ease of use and obtaining accurate data, it is recommended to use an electronic tonometer. This will help avoid data inaccuracies, and the procedure will not bring any difficulties to a person who does not know how to measure blood pressure.
What to do?
If a woman’s blood pressure sharply increases or decreases after childbirth, she should consult a doctor who will conduct the necessary diagnostic tests that will help determine the root cause of this condition. For treatment to be effective, it is worth making an effort yourself and starting to monitor your health. First of all, after the birth of the baby, it is important to get plenty of rest, take off the extra burden and shift some of the family worries to your husband. It is also worth eating well so that the menu is healthy and balanced. This does not mean that you need to eat everything and gain weight rapidly. Meals should be healthy, consisting of healthy carbohydrates, proteins and fats. By eating right, you won't be able to gain excess weight, but your health and blood pressure will be fine.
conclusions
A decrease in blood pressure in a woman during breastfeeding is a common occurrence, which is accompanied by characteristic complaints. Traditional correction methods using large amounts of coffee, alcohol, and medications are contraindicated during lactation. Doctors recommend that a nursing mother drink strong tea, a lot of compote or juice for blood pressure. The main ways to correct the condition are proper rest, balanced nutrition and adequate physical activity. The methods will help not only raise blood pressure, but also speed up recovery after childbirth.