Increased blood pressure in a healthy person is a natural reaction to stress and physical activity. A problem is indicated if, after three control measurements, the blood pressure exceeds 140/90. Then the most likely diagnosis is hypertension.
For most people, the disease does not produce symptoms, hence its second name: the silent or invisible killer. The first symptoms appear when the body ceases to independently withstand such a load and critical changes occur in the blood vessels. The first signs are:
- Increased anxiety.
- Cardiopalmus.
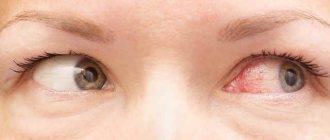
- Facial redness.
- Shortness of breath and dizziness.
- Headache and feeling of pressure in the temples.
- Chest pain in the region of the heart.
- Visual acuity decreases.
Fatigue, similar to the onset of a cold, is also a characteristic symptom. Accompanied by redness of the eyes, drowsiness and irritability. If the pressure approaches the extreme level, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
High blood pressure is divided into two categories: primary (essential) hypertension and symptomatic. The first is a chronic process, which is characterized by constant high blood pressure. The second is a symptom of other diseases of the human body.
Arterial pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure that blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels. This is one of the vital health indicators. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is interpreted based on two values:
- systolic pressure (“top”): the pressure of the blood when your heart contracts and pushes blood into the arteries;
- diastolic pressure (“lower”) is the blood pressure at the moment the heart muscle relaxes between two contractions.
The ratio of these indicators is usually considered in the context of norm, pathology or temporary disorder.
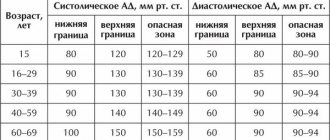
Blood pressure levels are individual for each age and gender. But the World Health Organization scale is considered to be a general guideline for assessing blood pressure.
Disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system, and with it cardiac activity and blood pressure, can occur in humans regardless of gender and age. However, you should understand in which case high blood pressure is associated with the development of the disease, and in which cases jumps in blood pressure occur situationally (emotional shock, alcohol and tobacco use, nervous tension, active physical activity).
In a healthy person, an increase in normal values by 10–15 mmHg is acceptable with age. If an age-related increase in pressure is indicated by a sharp jump, frequent attacks of hypertension, then this is not associated with age, but often with the development of a disease of the cardiovascular system. Ignoring such symptoms and waiting for age-related stabilization of blood pressure to occur is dangerous.
Treatment of hypertension
Arterial hypertension cannot be left untreated. Normalizing high blood pressure can delay or even prevent serious illness. In past years, until the early 90s, hypertension was considered only as a problem of lowering blood pressure. Today it should be considered and treated in conjunction with risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. High blood pressure can be reduced without medication, especially in patients who are significantly overweight, heavy smokers and alcohol drinkers. But these cases are rare and are rather a happy exception, since the vast majority of patients require drug treatment.
Causes of high blood pressure
Depending on which of the two pressure indicators is elevated (upper or lower), it is customary to consider the picture of the state of health.
Common causes of high blood pressure include:
- being in a state of prolonged, chronic stress and nervous tension;
- short-term bursts of emotional or mental activity, since adrenaline (stress hormone) speeds up the heart, affecting the tone of blood vessels;
- a high concentration of sodium and calcium in the blood, at which frequent spasms of the smooth muscles from which the entire vascular system is “woven” occurs.
- high cholesterol, the formation and accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels, which over time leads to a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which impairs blood flow. In this case, the heart is forced to work harder to move blood through the vessels, which causes the development of chronic hypertension.
- regular use of alcohol, tobacco, smoking mixtures, psychotropic substances. Under the influence of the chemical composition of which fluctuations in vascular tone occur, the functioning of the kidneys and other body systems is disrupted.
- course or frequent use of medications: oral contraceptives, appetite suppressants, glucocorticoids.
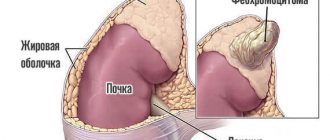
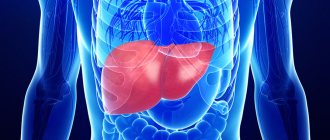
- diabetes mellitus, kidney and liver diseases, thyroid diseases
- excess weight and inactive lifestyle, asthenia
- blood thickening and dehydration, which make it difficult for the cardiovascular system to pump blood
- violation of diet, consumption of mineral salts, smoked spicy foods on a regular basis
- diseases of the spine, in which pinched nerve roots occur, increased muscle tone, which lead to impaired blood supply to blood vessels.
- heredity
However, looking at the readings of the measuring instruments, one should distinguish between high upper pressure and high lower pressure. Because both the risks of health complications and the choice of therapy depend on this.
High top pressure
When the upper (systal) pressure increases, aching headaches appear, with pulsation occurring. There may be pressure on the eyeballs, a feeling of swelling of the face.
The symptoms of high upper pressure are similar to intracranial pressure. Which develops as a consequence of impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
- if the upper pressure is increased, an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia) and aching chest pain may occur. Some people, if they have such symptoms, may panic and attribute their occurrence to heart problems.
- when the upper pressure increases to 150 mm Hg. Art. an adult may develop a hypertensive crisis, which causes pathological changes in the coronary arteries and heart muscles.
- angina pectoris develops, the left ventricle enlarges and cardiac output decreases, therefore heart failure develops, and with it the risks of developing myocardial infarction arise.
High bottom pressure
Lower pressure means the pressure in the blood vessels during maximum relaxation of the heart, before a new contraction. An increase in this indicator means that fluid is poorly removed from the body. Lower pressure is also called “renal pressure”. The kidneys, passing blood through themselves, act as a filter, regulate the water-salt balance of the body and remove toxins from the blood along with urine. If the lower pressure indicator fails, then you should start looking for problems in the kidneys, which for some reason cannot cope with their work.
Possible complications
Due to increased blood pressure, the walls of the arteries lose their elasticity, and the heart muscle works too hard. This increases the risk of angina, acute heart failure, and heart attack. Due to impaired blood supply to the brain, transient ischemic attacks and strokes are possible. The severity of hypertension will increase without treatment and lifestyle correction: pressure will continue to rise, and this will lead to damage to internal organs and worsen overall health and well-being. Smoking, drinking alcohol, overeating, lack of physical activity and high levels of stress accelerate the development of hypertension and make its course more complex.
Figure 2. Visually: what are the complications of hypertension. Source: CC0 Public Domain
Symptoms of high blood pressure
There are no specific symptoms typical for hypertension. Therefore, sometimes, seemingly without apparent reason or alarm bells, strokes and heart attacks occur even in young people. And those symptoms that may indicate high blood pressure are ignored.
Among the common ones:
- headache in the temporal or occipital part of the head
- dizziness
- weakness and tremors
- nausea
- dyspnea
- blurred vision, flashing spots before the eyes
- tachycardia
- swelling (in case of increased lower pressure)
Risk group
Regular high blood pressure occurs more often in men than in women. Arterial hypertension develops at any age. If previously elevated blood levels were found in older people, today young men aged 20–30 years are increasingly turning to the doctor. Reducing the age of the disease is associated with a fast pace of life, poor diet, and stress.
The earlier hypertension develops, the more difficult it is to tolerate. The risk group includes men who lead an unhealthy lifestyle, are obese, smoke, abuse alcohol and neglect physical activity. Most often, high blood pressure occurs in men with a hereditary predisposition.
Regular high blood pressure is more common in men than in women
How to reduce high blood pressure at home
High blood pressure is a very serious symptom. Therefore, any therapy should be prescribed strictly under supervision and on the recommendation of a specialist!
However, regular blood pressure medications should be in your home medicine cabinet, especially if there are real prerequisites.
- If the increase in pressure is situational in nature and caused by emotional or nervous shock. First of all, you should balance your breathing, find ways to calm down and relax as much as possible. Among the medications you can use: sedatives of plant origin, for example: novo-passit, persen, valerian tab, motherwort extarct tablet and others.
- To reduce blood pressure, diuretics can be used as part of complex therapy or as an independent remedy: Their selection and prescription, as well as the choice of dosage, is carried out by the doctor.
- If hypertension is an established chronic disease and another attack occurs, it is important to take as quickly as possible: Emergency drug Captopril 25 mg sublingually 0.5-1 tablet, and consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Preventing high blood pressure
Preventing high blood pressure is an important measure to prevent dangerous conditions and negative health consequences. Paying close attention to your body will protect it from dangerous diseases of the cardiovascular system. Considering that any disease can be aggravated by unfavorable heredity, it is important to approach the issue of preventing systemic diseases with particular care.
Primary prevention of high blood pressure
Primary prevention of hypertension involves preventive measures against blood pressure disorders in principle, exclusion of potential risk factors from lifestyle: bad habits, excessive physical activity, uncontrolled diet and diet.
Secondary prevention of high blood pressure
Secondary prevention means control of an existing disease and strengthening the stage of remission of hypertension, eliminating risk factors for the development of coronary heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. In addition to lifestyle correction measures, it also includes medications, vitamin health support, and physical therapy. Due to the great capabilities of modern medical equipment production, physiotherapy can be carried out at home.
The concept of mental hygiene plays an important role in the prevention of high blood pressure. Which implies reducing psychological and emotional tension, minimizing stressful situations and the ability to respond correctly to them.
Be healthy!
Still have questions? Ask them to us in the comments, we will definitely answer!
Consequences
Without treatment, arterial hypertension provokes serious consequences. Constant spasm of cerebral vessels leads to ischemia and stroke. They are dangerous with severe disability and even death. When the load on the heart muscle becomes too high, tachycardia, arrhythmia, and heart failure occur. Without treatment, myocardial infarction is possible.
The severity of hypertensive crises increases, they become complicated, life-threatening and can be accompanied by stroke, acute coronary syndrome and other serious conditions. The quality of life against the background of hypertension without adequate therapy and restoration of a normal state of health decreases sharply, even to severe disability.