Authors:
Currie KD, Floras JS, La Gerche A, Goodman JM.
Translation
- Sergei Strukov.
Current guidelines defining indicators for exercise testing and the prognostic importance of excessive blood pressure response to exercise lack contextual references and require updating.
- The magnitude and rate of change in blood pressure varies depending on age, gender, baseline values, training level, heart rate, comorbidities, and exercise protocol.
- The clinical utility of blood pressure measurement during exercise may increase with the establishment of normative ranges that integrate similar variables and defining models with better prediction of cardiovascular events.
How does increased blood pressure (BP) occur?
Many people are not even aware that they have high blood pressure, even if it is sometimes measured. That's why doctors call hypertension the silent killer. The pathology is insidious: 70% of people suffering from the disease die in the first 5 years after the official diagnosis. 89% die in their sleep. High blood pressure is a direct path to heart attacks and strokes.
General idea of pressure
The human heart is a pump for pumping blood in the body and providing it to all organs and systems. When it contracts, the chambers contract and blood is released into the vascular bed. This contraction is systole. Then the heart muscle relaxes (diastole) and blood enters the chambers of the heart again for subsequent release. From here, 2 pressure indicators are obtained: systolic and diastolic - upper and lower, respectively.
The normal blood pressure of an adult should not exceed 120/80 mmHg. Art., values below these numbers (for example, 110/70) are also normal. But a fall below 110 or a rise above 130 mmHg. Art. is no longer considered the norm.
130/80 is still the norm, but already borderline. Excess values of more than 130/90 indicate hypertension.
Blood pressure 140/95 is definitely grade 1-2 hypertension, which requires treatment. A person’s blood pressure may rise at times, for example, when they are nervous, scared, or even cleaning the room. During exercise, pressure in athletes increases not only in terms of indicators, but also in frequency, i.e. it increases many times during training. In sports, the heart experiences similar stress constantly, working in extreme mode. Hypertension develops if the norm of pressure in athletes is exceeded more than 2 times in a row during training.
Does blood pressure increase during exercise?
After physical activity, blood pressure increases. This happens according to the following scheme:
- During exercise, muscle contraction increases and they require more oxygen. Receptors send an impulse about the need to increase the amount of nutrients.
- Like the adrenal glands, the endothelium lining the inner surface of blood vessels synthesizes adrenaline and norepinephrine. These hormones cause the contractions of the vessel walls to become faster.
- Hormones affect the heart. The contraction of the heart muscle becomes more intense and accelerates.
- With the help of hormones, the walls of blood vessels adapt to changes in blood flow and regulate its changes.
The circulatory system satisfies the body's needs by redistributing blood movement. After exercise, blood pressure rises, the heartbeat accelerates, and the muscles seem to become stronger. At first, a positive effect is felt, but the body suffers from excessive tension.
Excessive stress when playing sports can be caused by the following factors:
- Physical labor that is unexpected for the body, for which the circulatory system, including the vessels, is not adapted.
- A drop in pressure due to abnormal volume of circulating blood, especially when the disorder is decompensated.
- Impaired ability of blood vessels to contract (inflammation, atrophy, arterial stiffness).
- Cardiac pathologies (inflammation, sclerosis, impaired innervation).
- Disorders associated with improper hormone production. Pheochromocytoma and Cushing's disease, localized in the adrenal glands, and polycystic ovary syndrome are more common.
- Increased renin synthesis due to pathology in the kidneys. Converted to angiotensin II, it increases the production of adrenaline.
Blood pressure cannot help but increase during physical activity. However, it must remain within certain limits.
Measurement of pressure during physical activity
Etiology of the phenomenon
The reasons are determined by the intensity of the load, nutrition and lifestyle of the athlete. Active sports are automatically a risk group for hypertension. Strength and extreme sports contribute to the development of the disease.
- Bodybuilding and arm wrestling are direct provocateurs of hypertension. How this happens: a huge weight is lifted with a jerk, holding your breath and strong muscle tension. After the jerk, an equally sharp throw with lowering the weight and relaxing the heart muscle. This gives a sharp jump in pressure and can end in disaster. If you have hypertension, intense and long-term fitness and lifting weights are prohibited.
- Diving. The pattern of blood pressure rise here is similar to that described. The only difference is that the body is under water with the additional action of external pressure.
- Parachuting. At altitude there is always not enough oxygen, and parachutists combine this with a surge of adrenaline. All internal organs are working to the limit.
Working hard - that's what competitions and demonstrations are all about. This has the most negative effect on the heart and vascular system, because in order to pump blood in large volumes, the heart must increase its output and contraction frequency. And this is nothing more than tachycardia and hypertension.
Athletes’ blood pressure also increases due to additional negative factors:
- nervous tension from fear of losing;
- fluctuations in body weight;
- lack of sleep;
- salty food.
For example, a strict diet allows the body to be at the desired size and weight. This means a lack of nutrients in the diet, which means increased blood pressure.
Disruption of sleep patterns also leads to pressure surges. Stress is present in all competitions, so it is correct to measure blood pressure at rest.
Taking anabolic steroids definitely increases blood pressure; a jump can be provoked by prolonged sleep or constipation.
Taking a bath or shower is also a reason; after water procedures, recovery time is required. New technologies increase blood pressure - gadgets with electromagnetic fields. The cold in the sleeping area causes vasospasm and also increases blood pressure. The optimal temperature in the room should be about 20 degrees.
Smoking, strong tea and coffee, especially on an empty stomach, are obligatory provocateurs of hypertension.
Blood pressure is not measured while lying down or crossing your legs - this will always increase the readings. Ideally, you should sit upright.
Sports training: how not to harm?
Sports training is an integral part of a healthy lifestyle. Every person needs some physical activity. Another question is that exercises and types of activities should be selected taking into account a number of factors.
Load is an individual concept
Each of us has our own way of life. Some people spend long working hours in an office chair or behind the wheel of a vehicle, while others have to lift serious weights. A postman or a local therapist walks more than one kilometer a day, while a store clerk remains in place, but is constantly on his feet.
Accordingly, physical activity should be selected individually. It is best to choose activities that best balance physical activity throughout the day. For example, a builder should hardly get involved in lifting weights in the gym. For him, loads like running or walking will be more relevant.
Health status is also an important factor. The main goal of any sports activity is to increase muscle tone and endurance, and saturate tissues with oxygen. The result of exercise should be an improvement in well-being, not a deterioration. Muscle soreness is quite acceptable, and fluctuations in blood pressure or pulse within normal limits are also not a cause for concern. But if the indicators exceed normal values, it is worth reviewing the training program.
Normal blood pressure levels when playing sports
The ideal pressure value is 120/80. True, this indicator is typical only for completely healthy people, but a deviation of 10 units in both directions is considered acceptable. With such indicators, a person usually feels comfortable.
A change in pressure during physical activity, as well as in stressful situations, as well as under the influence of some external factors, is not a deviation. Sports activities can cause deviations of the tonometer readings by up to 20 units from the normal state. This means that the values increased before training will become even higher after it. An increase in blood pressure to 160/100 and above is already considered dangerous.
It is worth monitoring the indicators not only for hypertensive patients, but also for people who do not have problems with blood pressure. Often, hypertension does not manifest itself in any way, and a person allows himself high-intensity exercise. You should not risk your own health; it is better to make sure that the body reacts normally to such exercises or to promptly identify malfunctions in the cardiovascular system.
Why is sport dangerous for hypertensive patients?
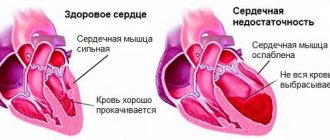
People suffering from hypertension or other blood pressure problems should be especially careful when approaching sports training. Such pathologies may be associated with negative external factors or heredity. In any case, the disease is accompanied by a decrease in vascular tone and the appearance of sclerotic plaques on them. Due to such changes, the vascular lumen decreases and blood circulation worsens.
During physical activity, the blood vessels contract even more, and the volume of blood circulating in the body increases. To provide tissues with oxygen, the heart begins to work more actively. All this together leads to increased blood pressure. And if in a healthy person the numbers return to normal a short time after exercise, then in a hypertensive person this will not happen immediately.
During intense sports, blood vessels that are overfilled with blood and do not have the ability to stretch may even burst, leading to hemorrhages. This means that an incorrectly calculated load can cause harm to health, and very serious one.
Why is it necessary to measure blood pressure during training?
It turns out that if you have problems with blood pressure, you should give up sports? In fact, hypertensive patients need physical activity no less, and sometimes more, than other people. With regular training, the heart muscle develops and the walls of blood vessels thicken. This allows the heart to pump blood more easily. Scientific research confirms that with systematic sports activities it is possible to reduce blood pressure by up to 10 units.
But exercises should be selected in such a way that they contribute to a smooth and not too significant increase in pressure, improving the condition of the heart, blood vessels and other body systems. To select optimal loads, you need, firstly, to consult a doctor, and secondly, keep your blood pressure under control during and after sports activities.
It is necessary to measure blood pressure for several reasons:
- By monitoring indicators, you can determine which type of training has a positive effect on the body, and which causes a negative reaction from the body;
- Analysis of the values allows you to select the correct intensity of exercise;
- Checking pressure makes it possible to avoid sudden changes in readings;
- A graph of pressure changes under the influence of sports will help the doctor give more detailed recommendations.
It is also very important to consider how long after completing the workout the pressure returns to normal.
A simple way to control pressure
However, measuring blood pressure during sports can seem quite complicated. True, only those who have not yet had time to verify and buy a tonometer on their wrist think so. Such models are designed for people who lead an active lifestyle and want to get the benefits of sports without compromising their health.
The electronic tonometer is easily attached to the wrist. It can be used for almost any type of physical activity, during exercise in the gym or outdoors.
Using such a tonometer provides many advantages:
- The Inflation technology function and a special resting indicator provide fast and accurate measurements right while the cuff is being inflated;
- Even the simplest and most affordable model is capable of not only measuring pressure, but also storing the obtained values for two people;
- The tonometer can be used not only to monitor blood pressure, but also to detect arrhythmia;
- Measurement results can be stored in the device's memory and can also be sent directly from the tonometer to a computer or smartphone using the free beurer HealthManager app. The program makes it possible to conduct full monitoring of the work of the heart and blood vessels before training, during the training itself and after it. Based on these data, the doctor will be able to accurately calculate the types and intensity of the load, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient.
Heart rate monitoring
To choose the right load during sports, you should also monitor your pulse - heart rate. The normal rate is 60-90 beats per minute. If under load your heart rate is lower or higher than these values, you should consult your doctor. It should be borne in mind that with different types of load, the pulse will also change differently. Heart rate shows how effective a workout is for each individual, and also helps to choose the optimal intensity of training.
You can measure your pulse using the traditional method: bring your fingertips to the places where the walls of the arteries are located closest to the skin. But during training, it is not always convenient to compare the number of hits with the numbers on the stopwatch. It will be much easier to use a heart rate monitor equipped with many useful functions:
- Pulse measurement via finger sensor;
- Measurement of average and maximum indicators;
- Determination of energy consumption in kcal;
- Volume of fat burned;
- Distance traveled;
- Current and average speed.
The heart rate monitor allows you to set up an individual training program. If the set values are exceeded, acoustic and visual signals will be triggered.
How and why to control weight?
Pulse and blood pressure are important indicators in terms of load selection. But very often the goal of sports activities is not only to maintain good health, but also to get rid of excess weight. True, it also happens that a person is actively involved in sports, but the volume does not go away, and sometimes even increases.
To achieve the desired changes, you need to correctly evaluate the results of your training. For example, weighing shows the total body weight, i.e. fat, bone, muscle and other tissues. Special diagnostic scales will help determine which of these components is increasing and which is decreasing.
Their main difference from conventional mechanical scales is their more advanced functionality. Thus, weighing makes it possible to determine not only body weight, but also body mass index, the values of basal and active metabolism in kcal. It is worth buying scales to obtain information about the proportion of muscles, bones, tissue fluid, as well as the proportion of fat mass in the body. Such data makes it easy to understand during any training how exactly this or that load affects these indicators. Knowing them, it is very convenient to adjust individual training programs.
Fitness bracelet for effective workouts
Perhaps the most popular device among fans of a healthy lifestyle is fitness bracelets. With their help, you can easily monitor many indicators, not only during training, but also during ordinary activities that are in no way related to sports.
For example, these bracelets show:
- The number of steps taken over a certain period (usually this period is a day);
- Distance traveled in km;
- Duration of training;
- Calories burned;
- Quality and duration of sleep.
You can buy a fitness bracelet to set goals for the day and track their completion in %. If there is insufficient physical activity, the reminder function will work. The bracelet also serves as a watch with an alarm clock. With it, you will not miss an important call or message: the bracelet will notify you with vibration about information received on your phone or via instant messengers. Through pairing with a special mobile application, all data is sent to the smartphone. You can view data about your activity for the selected period at any convenient time.
Virtual trainer and time saving
But what if you don’t have enough time for sports activities? The hours we spend in an office chair have a negative impact on our well-being. In this case, the body definitely needs activity and an individually selected load, however, in an often busy work schedule, it can be difficult to find at least an hour for training.
Don't deny your body what it really needs. The problem is solved with the help of the EMS simulator myostimulator EM 95. The device stimulates different muscle groups with electrical impulses, causing them to contract, similar to work during training. Such a simulator can become your personal trainer, helping you choose an individual load. For this purpose, the myostimulator provides 40 different programs, differing in time and frequency of exposure, designed for both beginners and professional athletes.
Your personal virtual trainer Beurer EM 95 EMS-HomeStudio will develop an individual training program, show a suitable video lesson, and provide safe and effective training without leaving your home. To get results, a 20-minute session 1-2 times a week is enough.
Payloads only
The benefits of playing sports are undeniable, but training if done unreasonably can be harmful. This is especially true for people who have health problems, but others should also monitor the body’s reaction to stress. Measuring heart rate, blood pressure and other indicators will help you choose exactly the types and intensity of exercise that will provide the desired result.
Strength sports
Strength sports are a great and constant stress for the body, after which time is required for long-term recovery of the heart and blood vessels. But the problem is that professional athletes cannot afford long breaks. That is why, before the age of 30, all security officials often develop hypertension - pathologically high blood pressure in athletes. The optimal sport for preventing the disease is aerobic exercise (such as walking, swimming and yoga). At the same time, the vessels dilate, blood pressure normalizes, and the cardiovascular system (CVS) is trained. But security forces do not have such a luxury, because during aerobics they will lose their shape and muscle volume.
Even during one training session, athletes’ blood pressure changes dozens of times and often increases. The heart gradually wears out.
Causes of hypertension in sports
Professional athletes are at risk for developing arterial hypertension.
This is due to the fact that during or after active training the body works for wear and tear. The cardiovascular system is especially affected, as the heart has to increase its rate of contraction and pump more blood. In addition, symptoms of hypertension are associated with:
- with nervous overstrain;
- with chronic lack of sleep;
- with excessive salt intake;
- taking medications (steroids, stimulants)
- with fear and stress;
- large body weight.
Along with these reasons, excessive physical activity can cause the development of hypertension or other complex diseases.
Alarming symptoms
In order to detect a disturbance in the heart’s function in time and the onset of an increase in blood pressure, in the gym you need to have water, a blood pressure monitor, validol, nitroglycerin or prescribed hypotensive drugs with you. You need to measure the pressure several times. It is very convenient to simply wear a bracelet with a tonometer on your arm. It is lightweight, automated, compact and especially relevant for professional athletes.
It is necessary to stop training, or better yet call a doctor, if:
- behind the sternum, with a return to the shoulder blade, arm, there was an acute pressing pain;
- sudden nausea appeared, sometimes with vomiting;
- it’s dark in the eyes and spots flicker;
- deafness and ringing in the ears;
- cold sweat;
- feeling of lack of air and fear of death.
Try to go out into the fresh air or sit near an open door or window. Try to calm down and relax.
Ask for a glass of cold water to sip and wipe your hands and face. You need to take validol or valocordin drops.
Another option: your health is normal, but your blood pressure is elevated on the tonometer. This does not change the algorithm of actions. Sports training is stopped immediately.
What sports are prohibited for hypertensive patients, and what precautions should be taken?
In case of hypertension, some sports are strictly contraindicated. There are also a number of exercises that are allowed to be performed with certain restrictions. The ban applies to excessive and prolonged exercise, for example, intense fitness classes, training for weightlifters and weightlifters, which involve lifting heavy weights.
Emotional stress and physical activity without breaks can also cause hypertension, so it is important to set aside time for rest and recovery.
Athletes should not drink coffee or strong tea, because caffeine causes vasospasm and can increase blood pressure.
You need to follow precautionary measures, monitor changes in your health in order to stop physical activity in time and take measures to lower your blood pressure.
We train the heart muscle
During aerobics, blood vessels become elastic due to the development of vascular endothelium and the appearance of new capillaries. At the same time, the performance of the heart increases. This also improves the blood supply to skeletal muscles.
The most beneficial for the heart and blood vessels are:
- swimming;
- race walking;
- yoga (not all asanas);
- water aerobics;
- calm running;
- qigong gymnastics;
- stretching;
- breathing exercises;
- cycling;
- skiing;
- sports dancing and skating.
The list is quite impressive, but running, walking and yoga are still of particular importance.
Running is the most popular and useful sport for hypertension. A moderate jogging pace strengthens the heart, improves general condition, lowers blood pressure, and increases oxygen supply to the brain. When running, it's not the speed that matters, but the duration. Fresh air also improves your health.
Race walking is also a choice for hypertensive non-athletes. By the way, blood pressure in former athletes often remains significantly elevated and requires not only control, but also treatment. Therefore, these recommendations are useful for them too.
Payloads
Depending on the stage of the disease, after consultation with a doctor, an individual training program can be selected for the athlete.
Typically, sports that involve all muscle groups at the same time are approved:
- race walking;
- water gymnastics;
- stretching;
- yoga;
- skiing;
- dance Sport;
- moderate running;
- swimming;
- breathing exercises;
- cycling;
- skating.
The benefits of sports with high blood pressure are reflected in the functioning of the heart. Exercise helps blood vessels carry oxygen to brain cells. This effect is an excellent therapy for hypertension.
The most common sport chosen by hypertensive patients is moderate running.
It helps improve heart function, corrects vascular tone and provides the brain with oxygen. Perfectly improves overall health and reduces blood pressure.
The effect of anabolic steroids on blood pressure
Anabolic steroids are popular not only among bodybuilders. The results with their use, of course, improve, but at a high cost.
A clear increase in achievements produces the opposite effect in that anabolic steroids increase blood pressure in 50% of cases of use and the risk of heart and vascular pathologies.
It is strictly not recommended to combine anabolic steroids and sports for the following categories of people:
- Over 35 years old.
- With poor heredity, a predisposition to hypertension in the family. If the parents were hypertensive, the offspring have a 75% chance of hypertension.
- Who already have at least 2 risk factors for developing hypertension.
The same applies to sports nutrition: if the jar contains instructions for containing caffeine and ephedrine, put it back on the shelf. Even with hypertension (hypertension) of the 1st degree, this cannot be taken. But glutamine, phosphates and creatine are not dangerous.
Strength training and atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is directly related to an increase in blood pressure, since this disease is characterized by the deposition of cholesterol plaques that narrow the vascular lumen. To maintain normal blood pressure in all tissues and organs, the heart pushes large volumes of blood through narrowed vessels, thereby increasing the pressure. Thus, it can be argued that an increase in blood pressure is only a small part of the consequences that can be a consequence of atherosclerosis. Strength dynamic training with a high degree of intensity (70-80% of 1RM), as well as static training, can become a factor in the development of atherosclerosis. Although today this conclusion is often refuted by new research data. There is an assumption that static training helps to increase levels of “bad” cholesterol (LDL - low-density lipoprotein). This type of cholesterol is called “bad” because it is deposited on the inside of blood vessels and forms plaques. Strength training with a moderate degree of intensity (50-60% of 1RM), on the contrary, reduces the level of “bad” cholesterol. In this case, incorporating pumping into your workouts to lower cholesterol levels may come to mind. Pumping just means working at 50-60% of 1RM. In addition, pumping with alternating antagonist muscles (biceps-triceps, chest-back) has a beneficial effect on blood pressure, normalizing it to normal values. In addition to “bad” cholesterol, the body also contains “good” cholesterol or HDL (high-density lipoprotein). The main difference between “good” cholesterol and “bad” is that “good” cannot be deposited on the walls of blood vessels, but it takes part in most physiological processes, plus it is involved in the production of sex hormones - testosterone and estrogen. Cholesterol is a transport agent for many biological substances. However, a large amount of HDL (“good” cholesterol) is more harmful to the body than beneficial. The HDL level increases due to aerobic and static-dynamic loads and, as a rule, rarely goes beyond the reference values.
Clinical trials conducted under the leadership of Dr. Nekorkina, during which participants performed static exercises, fully confirm the direct dependence of HDL and LDL levels on the effects of physical activity. Participants from group 1 did both static and dynamic exercises. For one static exercise there were 2-3 dynamic ones followed by a long rest. The duration of static work in each exercise was 5-8 seconds. The 2nd group performed only dynamic work. The test results demonstrate that aerobic and static-dynamic work lead to an increase in HDL. However, in group 1, which performed only statodynamic exercises, the HDL/LDL ratio was better.
Pressure after load: norm and permissibility
An athlete's normal blood pressure should be 120-130/80-90 mmHg. Art. After physical activity, the acceptable change is 140-150/90-100 mmHg. Art. It is important not only to monitor and control the tonometer readings, but also the time during which the numbers return to normal, that is, the period during which the pressure is restored. Normally, it should be no more than an hour. The indicators after and before the load are unequal. Blood pressure tends to rise.
In general, athletes have lower blood pressure than ordinary people due to constant vascular training. After active physical activity, blood pressure increases - this is natural and normal if over a certain period of time everything returns to normal. It is the sharp jumps that are dangerous for athletes, which can provoke a stroke even with a small load.
Pressure norm
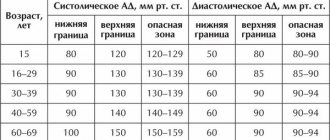
What blood pressure is considered safe for athletes? To determine its level, two indicators are used - the upper limit (systolic blood pressure) and the lower limit (diastolic blood pressure).
In healthy people, normal blood pressure is 120 to 80 mmHg.
Table: Normal blood pressure in men and women depending on age
| Age | Men (in mmHg) | Women (in mmHg) |
| 18-29 years old | 126/79 | 120/75 |
| 30-39 years old | 129/81 | 127/80 |
| 40-49 years old | 135/83 | 137/84 |
| 50-59 years old | 142/85 | 144/85 |
| 60-69 years old | 145/82 | 159/85 |
| 70-79 years old | 147/82 | 157/83 |
| 80 years and older | 145/78 | 150/79 |
The upper value can rise by 10 units, this is considered an acceptable norm. Moreover, if when measuring blood pressure on a tonometer, 140/90 mm Hg is regularly displayed. Art. and higher, this indicates the first stage of hypertension. This situation requires consultation with a general practitioner and treatment. Constantly pumping the heart in this mode can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Pulse
The pulse and blood pressure of an athlete professionally involved in strength sports are always elevated. The system begins to work hard, so beginners may be afraid of their off-scale heart rate.
A person's heart rate decreases slightly with age. In old age it increases slightly again. Women in menopause have an increased heart rate. At the same time, endurance also decreases.
If at the beginning of a sports journey, at 15-25 years old, the pulse can be 75-80 beats per minute, then at 30 years old - 45-50 beats. This is considered normal blood pressure in athletes; in an ordinary person it is bradycardia. In women in the same age group as men, the pulse is always 7-10 beats less.
A weak pulse is the result of insufficient heart function. Blood pressure and pulse are not directly related - you cannot think that lowering your heart rate will also lower your blood pressure.
With significant physical activity, the pulse of professional athletes can reach 200 beats; in weightlifters, when lifting loads, it can reach 120-135 beats per minute. At these moments, it is important to control your breathing.
Prevention
The best prevention of hypertension is dietary adjustments. It is best to exclude foods high in animal fats and sugar from your daily menu, and also avoid caffeine.
It is worth dedicating about 30 minutes of time daily for running and morning exercises.
High blood pressure in athletes requires hospitalization and treatment under the supervision of a cardiologist.
Professional athletes are required to see a personal physician to monitor their workload and prevent the development of dangerous diseases. This is especially true for the work of the cardiovascular system, which during training begins to work in an enhanced mode. Author of the article Svetlana Anatolyevna Ivanova, general practitioner
Is it possible to exercise with low blood pressure?
Not all sports are beneficial for hypotension. By the way, hypotensive people live longer.
If with hypertension the vessels experience stress on the walls and can rupture, then with hypotension the blood, on the contrary, flows poorly into the brain, which provokes hypoxia with subsequent fainting and dizziness.
Low blood pressure in an athlete will lead to a drop during training, so if you have hypotension, exercises with bending, lowering your head, somersaults, hanging your body on a horizontal bar, squats - anything related to balance are excluded. Fatigue and lack of sleep, dieting and fasting for various purposes aggravate the condition.
Sports under control
Any physical activity can be divided into two types:
- Static exercises. This is a set of exercises for increasing physical mass. These include weightlifting, kettlebell lifting, and powerlifting. In people who choose this sport, blood pressure is always higher than normal, so if persistent hypertension occurs, you should stop exercising.
- Dynamic exercises. They use all the muscles of the arms and legs. For example, running, swimming and walking. These types of physical activity improve blood circulation and lower blood pressure.
Even with the correct calculation of your own strength and caution, some exercises should be excluded from daily training.
You should refuse:
- jerks and sudden loads;
- strong tension when exercising on exercise machines;
- loads under which the muscles contract and the limbs are not involved in any way.
Ignoring these recommendations, a person will not be able to avoid sudden jumps in blood pressure. There is a risk of hypertensive crisis, persistent hypertension and headaches. And that's not the worst thing!
High blood pressure in athletes is a common sign of sudden stroke and death.
How to recognize hypertension
High blood pressure in athletes manifests itself as characteristic headaches in the back of the head and temples, and dizziness. Manifestations intensify during training; they may be absent at rest. Other signs of high blood pressure:
- nosebleeds;
- noise in ears;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- nausea or vomiting;
- sleep disorders;
- swelling of the limbs;
- hyperemic face during exercise;
- pain in the heart area and increased heart rate even at rest.
How to control blood pressure during exercise
To maintain good health both during and after training, you must adhere to some rules:
- Increase the load gradually, even if we are talking about running.
- Consult with a knowledgeable person or trainer.
- Choose a suitable sport.
- Don't stop after the first workout.
- Do not eat anything for an hour before physical activity, but do not fast.
- Avoid dehydration due to sweating. If necessary, pause for a minute rather than drink directly during the exercise.
- Do not sit down or lie down to take a break in the middle of class. The pressure changes with changes in body position.
Before each sports training, it is recommended to measure your pulse, blood pressure and breathing rate. Measurements can be repeated if strenuous exercise has been done or the person feels worse. You can complete your training with an inspection.
Constant or slightly elevated readings are completely normal. The athlete's general condition must remain satisfactory.
Often, with excessive loads above the permissible level of difficulty, pulse and blood pressure rise. It is even possible to rise to a hypertensive crisis. This condition is dangerous, but does not necessarily indicate pathology. It may indicate that the body is not sufficiently prepared.
Treatment of hypertension
Therapy is carried out comprehensively, but antihypertensive drugs prevail. They are selected only by a doctor, individually, taking into account the stage of hypertension, age and concomitant diseases.
Sartans, ACE inhibitors, adrenergic blockers (alpha and beta), calcium antagonists, diuretics, and combination drugs may be prescribed.
The list is huge, and they all have certain indications and contraindications. Self-medication is excluded.
It is also recommended to regularly measure blood pressure - 3 times a day: immediately after waking up, during the day and before bed.
Therapy is successful if blood pressure does not rise above 120-130/80-90 mmHg. Art. Unstable blood pressure may indicate the possibility of complications or improper treatment.
Is it possible to exercise with high blood pressure: study
To answer this question, researchers asked 32 women aged 60 to 75, all of whom had high blood pressure, to do strength training three times a week for four months. Each session, participants trained major muscle groups by performing ten simple compound exercises: upright rows, leg extensions, chest presses, hip abductions, leg curls, leg presses, and calf raises. The women performed three sets of each exercise. They started with 60 percent of the weight, one-rep maximum, and gradually increased it to 80 percent. The control group did not exercise at all [CG].
Recommendations for monitoring blood pressure during training
During training, you should adhere to the following rules:
- Maintaining proper water regime - 2.5 liters of clean water per day.
- The permissible heart rate value is no more than 76 beats/min 2 hours after physical activity.
- To reduce blood pressure, breathing exercises can be used: slow deep breathing with hands on knees. This way you can reduce blood pressure by 20 mm. There is another option - put your hands behind your head and, straightening up, breathe deeply.
So, what blood pressure should athletes have? The characteristic norm after exercise is 131/84 mm Hg. Art.
High blood pressure training
Exercise can help prevent high blood pressure, and people who already have high blood pressure can reduce it slightly by starting to do more exercise. For example, endurance exercise—40 minutes of cycling at an intensity of 60 percent of VO2max—helps lower blood pressure.
There is less information about the effects of strength training on blood pressure, although it is known that during sets with heavy weights, blood pressure can skyrocket. For people with vulnerable blood vessels, the temporary spike in blood pressure may be too much. However, there are studies that show that good breathing techniques and the use of blood pressure-lowering medications such as propranolol can help smooth out this peak.