Skip to content
Normalize your blood pressure
effective tips to avoid suffering
Main Menu
Article publication date: 08/31/2018
Article updated date: 02/17/2019
Author of the article: Yulia Dmitrieva (Sych) – practicing cardiologist
Often people, especially those with cardiovascular diseases, complain that they feel worse with the change in weather.
But not everyone knows why and how atmospheric pressure affects a person. However, these events are interconnected and this connection has a simple rationale: climate change means a change in atmospheric pressure, which, in turn, affects the walls of human blood vessels.
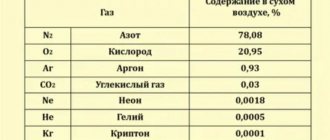
Normally, air pressure ranges from 750 to 760 mmHg. st (mercury column). Over the course of a day, it can change by an average of 3 mm, and over a year, fluctuations reach 30 mm.
Not really
Increased
Barometric pressure is considered elevated if its reading exceeds 760 mmHg. Art., in meteorology it is present in areas of anticyclones.
Under anticyclone conditions, there are almost no sharp jumps in temperature and precipitation. The weather is clear, there is no wind. At the same time, the content of harmful substances in the air increases.
Due to an increase in atmospheric pressure, the number of leukocytes in the blood decreases. This means that the body’s immune capabilities decrease – it becomes vulnerable to various infectious pathogens.
The effect of high atmospheric pressure on a person is marked by certain symptoms: headache, a feeling of weakness throughout the body, decreased ability to work, and increased blood pressure.
On days like these, it is recommended to protect yourself from emotional overload and avoid physical fatigue.
Decreased
Low air pressure is less than 750 mmHg. Art. Forecasters call the area where it is observed a cyclone.
A cyclone is accompanied by a high level of air humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, and a slight decrease in temperature. The oxygen concentration in the air decreases and the carbon dioxide content increases. This provokes insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood, and the heart muscle functions under increased stress.
The cyclone affects humans as follows:
- the breathing rhythm becomes more frequent;
- heart rate increases;
- the striking force of the heart decreases.
Effect on hypertensive and hypotensive patients
The dependence of blood pressure on barometric pressure exists in three variations:
- Straight. As atmospheric pressure increases, arterial pressure also increases. Similarly, when the atmospheric pressure decreases, blood pressure also decreases. Hypotonics are usually directly dependent.
- Partially the opposite. Only the values of the upper limit of blood pressure respond to changes in barometric indicators, while the lower limit remains unchanged. And the second situation is that a change in atmospheric pressure provokes a change in the lower values of blood pressure in the vessels, while the upper values remain unchanged. This situation is typical for people with normal blood pressure levels.
- Reverse. As atmospheric pressure decreases, the upper and lower limits of blood pressure increase. As atmospheric pressure increases, both blood pressure limits decrease. This dependence is observed in hypertensive patients.
In anticyclone conditions, people with hypertension and hypotension feel unwell to varying degrees of severity. But the manifestations of deterioration in well-being vary.
It is much more difficult for people with hypertension to survive an anticyclone, because in this situation, high barometric pressure provokes an increase in their own levels in the arteries. Such climatic conditions have a particularly difficult impact on the condition of the elderly and patients with diagnosed heart and vascular diseases.
During the anticycle, hypertensive patients experience the following symptoms:
- increased heart rate;
- increase in intracranial pressure;
- facial redness (hyperemia);
- stuffy ears;
- feeling of blurred vision;
- pain in the heart;
- throbbing headache.
Increased atmospheric pressure is dangerous because it increases the risk of developing hypertensive crises and their complications: heart attacks, strokes.
People with chronically low blood pressure also feel unwell in anticyclone conditions. This is explained by the individual ability of a particular person to adapt. The bottom line is that for a hypotensive person, his chronically low blood pressure is the optimal state, and even a slight increase in his usual indicators has a very negative impact on his health. A sharp change in barometric pressure can cause fainting and migraines.
The influence of a cyclone can cause the following types of illness in hypertensive patients:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- malfunction of the digestive system.
In hypotensive patients, the cyclone causes dilation of blood vessels and a decrease in their tone. Blood flow slows down, which threatens internal organs with a lack of oxygen.
This is manifested by the following symptoms:
- paroxysmal headache;
- exhaustion;
- nausea;
- difficulty breathing;
- drowsiness.
Low blood pressure and hypertension
Atmospheric pressure and hypertension are related. The level of blood pressure depends on the force with which the heart pumps blood and the degree of vascular resistance. The effect of barometric pressure on a patient depends on what blood pressure is normal for the patient.
When air pressure decreases outside, both a person's upper and lower blood pressure decreases. What is the best blood pressure for hypertensive patients: low. It alleviates the symptoms of the disease and has a positive effect on the general condition of hypertensive patients. In rare cases, low barometric pressure acts differently and leads to a sharp increase in blood pressure. If a person takes medications to lower blood pressure, then surviving a sudden change in weather becomes not so easy. The effect of drugs is doubled or even tripled by the changing mood of nature. With low atmospheric pressure, hypertensive patients are at risk of developing angina pectoris and cerebral hemorrhage if they take strong medications.
A cyclone, or low blood pressure, brings with it high humidity, cloudiness and precipitation. Often accompanied by winds. A natural decrease in blood pressure can be observed in the mountains, where already at an altitude of 5 km it is two times lower than normal and the level of oxygen in the air is significantly reduced. For this reason, hypertensive patients are not recommended to engage in professional mountaineering and choose mountainous areas for recreation. Climbing to great heights can affect health and lead to crisis, fainting and even coma.
How should weather-sensitive people behave?
Weather-sensitive people are physically unable to react to rapidly changing climatic conditions and get used to them. This feature of their body may be a consequence of disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, a malfunction of the immune system, or disorders in the thyroid gland.
But still, such people can take preventive measures in advance to make the weather change as comfortable as possible for them.
To do this, it is important to listen to the weather report daily in order to know in advance about an impending cyclone or anticyclone. Based on the information received, take preventive measures. Recommendations will differ depending on whether a person is hypertensive or hypotensive.
In weather conditions unfavorable for hypotensive patients, they need:
- sleep 8-9 hours a day;
- drink at least 2 liters of still water per day;
- use a contrast shower - alternately stand for two minutes under hot water and two minutes under cold water;
- drink a mug of strong coffee or replace it with a Citramon tablet;
- eat more vegetables and fruits containing large quantities of ascorbic acid and beta-carotene;
- to improve general health, take herbal remedies to improve tone and immunity: ginseng, St. John's wort, eleutherococcus, walnuts or pine nuts;
- massage the head and cervical-collar area to relieve pain;
- reduce physical activity.
Recommendations for hypertensive patients:
- devote time to proper sleep (at least 8 hours);
- limit the consumption of salt, strong coffee and tea drinks;
- include fruits with a high potassium content in your diet;
- minimize or completely eliminate physical training;
- take blood pressure measurements during the day; if the readings rise high, you need to take medications with a hypotensive effect;
- during hot weather, try to stay in a cool, air-conditioned room;
- exclude airplane flights and climbs to heights.
How is air pressure measured?
Depending on what type of device is used to change the pressure of air masses, several measuring units are used:
- Pascals (Pa);
- bars;
- millimeters of mercury.
Liquid barometers use mercury, which, depending on the force of air pressure, either rises or falls along the measuring column. Such devices can often be found in professional meteorologists or at weather stations.
In apartments, mechanical barometers are more common. The principle of operation of which is contained in a metal box with discharged air inside, that is, with a box inside which the pressure is the minimum possible. This means that the metal walls are malleable to atmospheric pressure. The lower the air pressure in the atmosphere, the less it compresses the box, the walls of which begin to move apart under such conditions. Their movement is transmitted to a spring, which pushes the arrow of the device.
The influence of low atmospheric pressure on human well-being
For a person to feel comfortable, the atmospheric pressure should be 750 mmHg. Lower pressure is called a cyclone. It is often accompanied by cloudiness, high humidity, a slight increase in temperature and precipitation. When atmospheric pressure drops, a person's blood pressure also decreases.
People who have problems with the heart and blood vessels, suffering from hypotension and respiratory dysfunction are most susceptible to the influence of the cyclone. With a sharp decrease in atmospheric pressure, even a healthy person feels a slight malaise: drowsiness, decreased performance. Possible deterioration in the function of the gastrointestinal tract - increased gas formation.
During a cyclone, the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere decreases. It becomes more difficult for a person to breathe, and this often leads to a decrease in blood pressure. As a compensatory reaction, breathing and pulse quicken, oxygen starvation of the body may develop, which becomes the cause of fainting and exacerbation of chronic diseases. People with increased intracranial pressure may suffer from migraines.
During a cyclone, people suffering from hypertension feel good if their blood pressure was elevated. However, if a person has brought his condition back to normal with the help of medications, at low atmospheric pressure his health will be poor: a severe headache appears and his temples begin to pound.
Hypotonics tolerate low atmospheric pressure worse than hypertensives. They completely lose strength, experience severe drowsiness, nausea, and dizziness. People with depression also experience a significant deterioration in their health.
Weather dependence is not a disease: scientists explain why headaches occur
Photo from goodtoknow.co.uk
Weakness, malaise, increased or decreased blood pressure, shortness of breath, insomnia, joint pain and, finally, migraines are the symptoms that some of us suffer from due to changes in atmospheric pressure, high humidity, sudden changes in temperature and thunderstorms.
But the influence of weather is not limited to this. There are modern scientific studies that find a correlation between meteorological factors and the number of strokes.
A team of Chinese scientists from Harbin University analyzed data from 735 patients over 2 years and compared it with detailed weather office reports. The researchers found that primary hemorrhagic strokes (bleeds in the brain) with a sharp increase in pressure occurred more often in late spring and early autumn on days when there was a sharp warming or cold snap, and subarachnoid hemorrhages (in the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater) - on days with relatively low temperature.
Does this mean that weather dependence is a real disease that can lead to life-threatening consequences such as a stroke?
This is not entirely true. The modern medical classification of diseases does not include weather dependence as a separate disease. Weather is an external factor that acts on the body and provokes those manifestations that are the result of some diseases and disorders of the body itself.
A healthy person is highly adaptive, that is, external conditions, of course, affect him and may cause some discomfort, for example, it is difficult for any of us to tolerate heat above the temperature of the human body, but generally they do not lead to severe malaise.
Weather dependence is, as a rule, a manifestation of diseases of the cardiovascular or nervous system, asthma, arthritis, which make a person highly sensitive to external triggers, including the weather factor.
Changes in atmospheric pressure cause natural changes in pressure in blood vessels and tissues. When pressure drops, hypoxia develops, that is, a decrease in oxygen levels in tissues, which leads to dizziness, nausea, heart pain and headaches.
With an increase in atmospheric pressure, blood pressure also increases, blood flow increases, which can also lead to illness, sometimes very serious.
Photo from edition.cnn.com
In a healthy person, dilated or spasmodic vessels quickly return to their normal state due to their elasticity, but if they lose elasticity, it is difficult for the body to quickly adapt in accordance with the dynamics of the environment.
There are three degrees of weather dependence.
1st degree – meteosensitivity . With certain weather changes, a person feels only a slight discomfort that does not cause much discomfort.
2nd degree – actual weather dependence . The body reacts to certain weather factors with noticeable deviations from the norm, for example, an increase or decrease in blood pressure and the occurrence of severe headaches. There may be an irregular heart rhythm, and even an increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood.
3rd degree - meteoropathy , when weather phenomena lead to temporary disability.
Statistics on weather dependence are very limited, but there is data on its individual symptoms. Of these, the most common is, of course, a headache.
In the United States, about 45 million people annually consult doctors with complaints of headaches, and half of them report that weather changes are the most important trigger. These very extensive statistics are backed up by medical studies under controlled conditions.
In a 2015 Japanese study, 34 patients with chronic migraines were supervised by doctors and kept diaries of their condition. All of them felt good at 1013 hectopascals (759.8 mmHg), and this atmospheric pressure was taken as the standard.
It was found that study participants suffered from migraines even with relatively small decreases in atmospheric pressure - only 6-10 hectopascals.
But an international group of scientists from Taiwan, the USA and Great Britain, having analyzed a large array of statistical data, found that in different geographical areas, migraine attacks among study participants were correlated with different weather factors: air temperature, low pressure, strong winds, approaching typhoon, approaching cold weather. atmospheric front.
At the same time, some studies do not find any connection between meteorological factors and headaches at all, which may indicate that there are climatic zones that are more or less favorable for a weather-dependent organism.
There is also a theory that the so-called atmospherics (or simply spherics) are responsible for migraines. These are low-frequency electromagnetic waves, the source of which is atmospheric electrical discharges, such as lightning.
Atmospherics have weak attenuation and can propagate over distances of up to several thousand kilometers. That is why their presence in the atmosphere is possible even if there was no thunderstorm directly in the area. Atmospherics affect the cells and membranes of the body and can cause migraine attacks in weather-dependent people.
People suffering from rheumatoid arthritis often complain of weather dependence. They are sure that they feel increased joint pain when rain or stormy weather approaches as a result of fluctuations in atmospheric pressure. However, until recently, most research did not find a correlation between weather changes and arthritis symptoms.
Photo from thedailybeast.com
Maybe this is a kind of “nocebo effect”? So, by analogy with the placebo effect, they call a situation when a certain dummy factor negatively affects the patient’s condition due to the fact that the latter is confident in its real negative impact.
An impressionable person suffering from arthritis may well be influenced by the weather forecast, which reports increased humidity and fluctuations in pressure.
Recently, however, scientific works have appeared demonstrating, albeit weakly, a correlation between meteorological factors and pain and tension in diseased joints.
For example, in this Dutch study, scientists observed patients suffering from arthritis of the hip joints for two years. They compared records of their condition with meteorological data for the same period and found that there was indeed a correlation between them.
The changes in condition were not dramatic, but were clearly visible.
The severity of pain increased by 1 point for every 10% increase in humidity. The functioning of the joints deteriorated by 1 point for every 10 hectopascals increase in atmospheric pressure.
According to experts, changes in barometric pressure can affect the pressure inside the joint, which contains extremely sensitive nerve endings, and this can lead to increased pain.
What can be done to alleviate weather sensitivity?
The main and main advice is to treat the disease that leads to it.
There are, of course, some recommendations regarding lifestyle.
Most weather-related ailments are caused by weak blood vessels, so these are the ones that need to be strengthened. Hardening measures are good for this purpose: contrast showers, dousing with cold water, cold rubdowns.
As always, you can’t do without fresh air and physical exercise: jogging, active walking, hiking in nature, swimming in reservoirs, working out in the gym - all these components of a healthy lifestyle will strengthen the body and reduce weather sensitivity.
Experts recommend that weather-sensitive people select a set of breathing exercises and perform them on unfavorable days to reduce hypoxia.
An important factor in health is proper sleep patterns. With chronic sleep deprivation, your body will be very sensitive to fluctuations in the state of the external environment.
You may need to take restorative medications. These include B vitamins, and Ascorutin, which strengthens blood vessels. The likelihood of a negative effect of vitamin preparations is extremely low, but it is advisable to consult a doctor who will give recommendations regarding the duration of use and compatibility of medications.
Numerous articles on weather dependence on the Internet are replete with the names of general health-improving agents of plant origin. The authors recommend extracts of eleutherococcus and echinacea, infusions of nettle leaves, plantain and corn silk, oregano, St. John's wort, linden blossom, rose hips and hawthorn. You should try them carefully, taking into account allergies and individual reactions, because if something helped your friend, it will not necessarily have the same effect on you.
Photo from globalnews.ca
If the main symptom of your weather dependence is headache, read this article. Perhaps you will find useful information in it.
Sources:
Weather and Headache
Study Finds Evidence of Connection between Arthritis Flare-Ups and Weather Conditions
Headaches in weather-dependent people
Weather dependence - symptoms, treatment, how to get rid of weather dependence?
What to do if you feel unwell during a cyclone
During the cyclone period, it is necessary to control the level of blood pressure in the body. It is recommended to drink more fluids throughout the day. A good restful sleep, a contrast shower, a cup of coffee, as well as tinctures of eleutherococcus, lemongrass or ginseng will help you feel good. It is necessary to provide yourself with fresh air, for this you need to ventilate the room well or just take a walk.
Daytime naps are advisable. Ideally, in winter, quiet time should be from 10 to 12 noon, in summer - from 14 to 16 hours. It is important to wake up at least three hours before dusk. You can improve your health with nutrition. You need to eat something salty, for example a piece of herring. This will have a positive effect on the ion balance and improve the general condition of the body.
A person lives on the surface of the Earth, so his body is constantly under stress due to the pressure of the atmospheric air column. When weather conditions do not change, he does not feel heavy. But during periods of fluctuation, a certain category of people experience real suffering. Low or high atmospheric pressure does not have the best effect on a person, disrupting certain functions of the body.
Although there is no officially registered diagnosis of weather dependence, we are still susceptible to weather fluctuations. Changes in weather cause poor health, and in particularly difficult situations people have to visit doctors and take medicine. It is believed that in 10% of cases, weather dependence is inherited, and in the rest it manifests itself due to health problems.
Atmospheric pressure fluctuations and well-being
These days, sharp changes in atmospheric pressure are observed on the European territory of Russia.
Last weekend, as the North Atlantic cyclone passed through the center of the country, the atmospheric pressure dropped sharply. And at the beginning of this week, the cyclone replaced the anticyclone, the atmospheric pressure on Tuesday will rise sharply and will remain elevated for several days. In the second half of the week, another North Atlantic cyclone will pass through the north of EPR. Sharp rises and falls in atmospheric pressure are again expected with it.
With a noticeable change in atmospheric pressure, both downward and upward, the human body often feels a deterioration in well-being. Here are some generally accepted recommendations from the website for reducing the negative symptoms of high or low atmospheric pressure on our body.
Anticyclone An anticyclone is an increase in atmospheric pressure, which is accompanied by calm, clear weather with no sudden changes in temperature or humidity levels. Increased atmospheric pressure has a very negative effect on human health, especially if he is allergic, asthmatic or suffers from high blood pressure. Such people react quite sharply to various harmful impurities in the air, the number of which increases significantly in dry, windless weather.
In the human body, an anticyclone manifests itself as headaches and heart pain, decreased performance, malaise and general weakness. Increased atmospheric pressure negatively affects the body's protective functions by reducing the number of leukocytes in the blood. All this significantly undermines human health, making him vulnerable to various infectious diseases.
In order to facilitate the effect of the anticyclone, it is recommended to take a contrasting invigorating shower in the morning, do light exercises and introduce more fruits containing potassium into your daily diet. To reduce the load on a person’s immune and nervous systems, it is better to temporarily abandon serious and important matters. If possible, it is necessary to rest more in order to quickly restore the strength lost by the body in the fight against the negative influence of the anticyclone.
Cyclone A cyclone is a decrease in atmospheric pressure, which is usually accompanied by increased temperature, cloudiness, humidity and precipitation. People suffering from low blood pressure, respiratory problems, and cardiovascular problems are most susceptible to the effects of the cyclone. The main manifestations of the negative impact of a cyclone on the human body are: difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, lack of air and general weakness. This is due to a lack of oxygen in the surrounding air. Often during a cyclone, a person’s intracranial pressure increases, resulting in a severe migraine. In addition, there may be disruptions in the functioning of the stomach and intestines, which are associated with intense gas formation. With the arrival of a cyclone, it is necessary to constantly monitor your blood pressure levels. Drinking plenty of fluids, a contrast shower, a restful, sound sleep, and a morning cup of coffee will help you with this. To maintain general health during periods of low atmospheric pressure, it is recommended to drink tincture of lemongrass or ginseng.
Rules for reducing symptoms of weather dependence Atmospheric pressure, or rather its sharp changes, more often take residents of megacities by surprise. It is almost impossible to completely cure this form of weather dependence, but by following some simple rules, you can significantly improve your health in difficult weather conditions. First of all, you need to strictly monitor your daily routine and go to bed earlier if possible. In case of sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, sleep should last at least 9 hours. For a good night's rest, it is recommended to drink a glass of chamomile or mint tea at night, and when you wake up, do a light massage of your legs and feet, and only then get out of bed. In order to cheer up, you should do daily short exercises, which will help tone your blood vessels. It is necessary to exclude bending and squats from the list of gymnastic exercises, as they require balance. After charging, it is recommended to take a contrast shower, which has a positive effect on the health of all internal systems and human organs.
A complex of vitamins, which should be taken during changes in atmospheric pressure, will help to support the nervous system well. You need to eat often, but in small portions, and in no case overload your body with heavy food. While working at the computer for many hours, you need to periodically take a break, during which you can do short exercises, change your position, and also do a massage of the cervical and temporal zones yourself. In order to endure all weather surprises as painlessly as possible, try to avoid severe overexertion and stress. It is also not recommended to carry out strength training and responsible activities at this time. In case of pressure changes, it will be useful to visit the pool, where the calm atmosphere and healing effects of water will help you forget about all the troubles.
Weather-sensitive people are advised to increase their consumption of water and fruit juices. If there are changes in blood pressure, you should rest more in a lying position. Sweet warm tea will help restore tone to the body with low blood pressure. During these difficult days, it is very important to notice in time the alarming signs that may indicate serious illnesses: - unpleasant sensations in the chest, radiating to the shoulder, shoulder blade or umbilical region; - sudden loss of sensation in the lower and upper extremities; - feeling of numbness in half of the face; - difficulty speaking; - unexpected attack of nausea; - blurred vision or flickering of spots before the eyes; - breathing problems.
We wish you vigor and good health, regardless of the level of atmospheric pressure!
Weather dependence of children
Almost always, children’s dependence on weather changes is a consequence of difficult pregnancy or childbirth. Unfortunately, the consequences of such a birth remain with the child for a very long time, sometimes throughout his life. Respiratory diseases, autoimmune diseases, hypertension and hypotension can lead to a person being weather dependent throughout his life. It is very difficult to say exactly how low atmospheric pressure affects people with the same diseases. The manifestation of weather dependence is individual in nature for everyone.
Low atmospheric pressure
When the pressure drops to 748 mmHg, weather-dependent people experience discomfort. Hypotonic people feel especially bad, they lose strength, nausea and dizziness appear. Low atmospheric pressure also affects people with cardiac arrhythmias. Their health leaves much to be desired, at this time it is more advisable to rest at home. But worst of all, such a difference affects those people who are prone to depression and suicide. They experience an increased sense of anxiety and restlessness, which can lead to dire consequences. That is why it is necessary to know this feature of your body in order to be able to control your mood.
What to do?
Understanding how low air pressure affects people is only half the battle. You need to know what measures to take in this case. First of all, you need to take care of free access to fresh air. You can open a window or swing open the balcony door if you can’t take a walk. During such periods, weather-sensitive people will benefit from good, sound sleep. Nutrition also plays an important role. To equalize the ionic balance in the body, you need to eat a piece of salted fish or canned cucumber.
Flying in the air
When traveling on various aircraft or climbing a mountain, a person begins to feel stressed and wonders how low atmospheric pressure affects people. The main factor is that the partial pressure of oxygen decreases. The tension of this gas in arterial blood decreases, which stimulates the receptors of the carotid arteries. The impulse is transmitted to the brain, resulting in increased breathing. Thanks to pulmonary ventilation, the body is able to be supplied with oxygen at altitude.
But rapid and intense breathing alone is unable to fully compensate for all the difficulties that the body experiences. Overall performance is reduced by two factors:
- Increased work of the respiratory muscles, which requires additional oxygen.
- Flushing carbon dioxide from the body.
Most people, being at altitude, experience disruption of certain physiological functions, which leads to oxygen starvation of tissues. Mountain sickness can have various manifestations, but most often it is shortness of breath, nausea, nosebleeds, suffocation, pain, changes in the sense of smell or taste and irregular heartbeat.
Understanding how low air pressure affects people can help reduce discomfort and improve overall health. The manifestation of mountain sickness can occur through dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. A greater amount of oxygen can be transported due to the fact that at altitudes a person experiences increased activity of the hematopoietic organs. To fully assess how atmospheric pressure affects blood pressure, it is necessary to take into account other factors: temperature, humidity, radiation fluxes and wind speed, precipitation, and others.
Sudden changes in temperature also do not have the best effect on people's condition. Those with heart disease, as well as those people who have suffered heart attacks or strokes, are especially sensitive to such changes. During these periods, it is necessary to limit physical activity and adhere to a low-salt diet. Air temperature is perceived by the human body differently, depending on humidity. If it is elevated, the heat is less tolerated. Air humidity is greatly influenced by precipitation. Weather-dependent people may experience weakness and headaches during this period.
Many factors can influence blood pressure indicators, including the difference in atmospheric pressure - the gas shell surrounding the planet, pressing with a certain force on the surface.
The question arises, how does low or high atmospheric pressure affect a person? The most acceptable indicator for people is 760 mmHg. Minor fluctuations in any direction up to 10 mm do not affect DM and DD in any way and do not affect well-being.
University
→ Home → University → University in the media → “Almost every third person reacts to the weather.” Doctors on what to do with weather dependence
You can expect anything from the weather lately. Doctors recommend that weather-sensitive people be on guard. Why weather dependence cannot be considered a universal “excuse” for lazy people, how many Belarusians react painfully to climate vagaries and whether it is realistic to become more resistant to them - GO.TUT.BY was helped to understand by a cardiologist, a psychiatrist and a physiologist.
“Any external changes for the body are stressful, but normally they should not be felt”
Irina Pateyuk, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Let's start with the fact that weather sensitivity and weather dependence are not a disease.
“There is no such diagnosis in the International Classification of Diseases,” states Irina Pateyuk, associate professor of the Department of Cardiology and Internal Medicine of BSMU.
Weather dependence should be regarded as a pathological reaction of the body in response to weather changes. This phenomenon is often encountered by ambulance specialists, hospital emergency departments, therapists and cardiologists.
“The body reacts not only to climate change, but also to any external changes with stress. And this is absolutely normal,” says the specialist. “But the body is designed in such a way that it quickly adapts to external influences, and a person should not normally feel these processes. If your health worsens, it means that adaptation has failed.
Errors in health status can contribute to the development of a pathological reaction to weather changes. As a rule, people who have recently undergone surgery or any infection “respond” to changes in weather conditions. And, of course, those who suffer from chronic diseases. The most vulnerable are heart patients and hypertensive patients, as well as people with diseases of the musculoskeletal system (joint diseases, arthrosis, chronic ailments of the spine). Since the number of chronic illnesses increases with age, older people become “barometers”.
Photo is for illustrative purposes only.
It turns out that increased sensitivity to weather changes is the “prerogative” of people with serious diagnoses?
Irina Pateyuk thinks not. A healthy person who is experiencing psycho-emotional stress or is tired from intense mental work can also react to sudden changes in weather conditions. Hence - drowsiness in the rain and complaints of weakness if it gets colder.
“Hypertensive patients feel changes in atmospheric pressure, people with respiratory pathologies feel changes in humidity”
What kind of disease a person suffers from depends on what parameters he will “respond” to—changes in atmospheric pressure, humidity or temperature.
People with diseases of the cardiovascular system, as a rule, are overly sensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure and changes in geomagnetic fields (magnetic storms).
“The fact is that the nervous and endocrine systems react primarily to changes in atmospheric pressure, and they are both “responsible” for regulating vascular tone,” explains Irina Pateyuk. “Normally, blood vessels quickly restructure in response to changes in external conditions, but when, say, they are affected by atherosclerosis, a malfunction occurs. Blood pressure jumps, shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness appear, and the heart rate may be disrupted.
People with respiratory pathologies tend to react to changes in humidity. Air that is too dry (below 40%), saturated with dust, dries out the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract; it does not retain harmful microorganisms well, allowing them to penetrate the bronchi and lungs, and in response - a defensive reaction - the secretion of mucus begins. Too high humidity (over 80%) in the heat can cause swelling of the airways: their patency decreases, as a result, a person does not receive enough oxygen - shortness of breath occurs.
“Almost every third Belarusian reacts to the vagaries of the weather”
The sharper the fluctuations in night and day temperatures, atmospheric pressure, and humidity, the more people will feel it in their own bodies, Irina Pateyuk is sure. According to international studies, almost every third resident of mid-latitudes, which includes our compatriots, is weather dependent.
Clinical observations in Belarus show: on days when significant changes in the geomagnetic field or significant jumps in atmospheric pressure occur, ambulance calls for heart rhythm disturbances increase by 10-30%. Patients are admitted to the hospital with a hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, or cerebrovascular accident.
Photo is for illustrative purposes only.
The connection between the number of exacerbations and complications of the disease during the vagaries of the weather is confirmed by the clinical practice of Irina Pateyuk:
— It often happens that one day, chronic patients who have been observed for 5-10 years, as if by agreement, begin to call or urgently ask for an appointment: the pressure has “soared”, shortness of breath has increased... As a rule, they all unanimously see the reason as , that “the medicine has stopped working”, “I bought a not very good drug”, and tomorrow it turns out that it has become sharply colder. Before changes in the form of rain, snow or extreme heat become visible, the pressure in the atmosphere changes, and cardiac patients immediately sense this.
A cardiologist warns that for people with cardiovascular diseases, a geomagnetic storm or a jump in atmospheric pressure can be fatal:
— A common mistake made by patients is that, feeling relatively well for a long time, they stop taking medications or arbitrarily reduce the dose, for example, instead of taking a pill, they start taking half a tablet. The drug protection of the cardiovascular system is weakened - and a sharp change in atmospheric pressure or fever below forty during the week acts as a trigger for the occurrence of complications.
To prevent weather changes from becoming a blow to the gut, the specialist advises to monitor the weather forecast and, in unfavorable periods, reduce your load as much as possible, be sure to get a good night's sleep and not miss scheduled visits to a specialist to adjust individual therapy.
“Heat can lead to suicidal thoughts”
Alexey Krot, assistant at the Department of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology, BSMU
Alexey Krot, assistant at the Department of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology of the Belarusian State Medical University, states that changing conditions in weather-dependent people is reflected in the psycho-emotional background.
A natural consequence of high air temperature or changes in atmospheric pressure is depression of the functions of the central nervous system. The person is depressed, lethargic, drowsy, lethargic, gets irritated for any reason, has trouble thinking and works less productively. For those prone to depression, the heat can even provoke thoughts of suicide. The reaction to hot weather may be exacerbated in those who live in conditions that disrupt circadian biorhythms and do not allow proper rest. For example, he works hard on the night shift.
Some weather addicts, feeling unwell, desperately try to cheer themselves up with energy drinks or stimulants. But a fifth cup of coffee, an ice-cold shower or ten push-ups, as a rule, saves you for an hour and a half at best, and then has the opposite effect - lethargy and weakness worsen.
Photo is for illustrative purposes only.
“In a state of depression of the nervous system, it is better to avoid intense physical activity and psychostimulants,” says the specialist. — It’s better to prefer a regular walk in a public garden or park, relaxation exercises, and even better, devote some time to this regularly. Since overstrain of the central nervous system is also caused by intense information load, minimize the use of mobile phones, tablets and computers, watch less TV and do not hang out on social networks.
Alexey Krot points out that not every change in the weather affects your well-being. Either sharp fluctuations or parameters of extreme intensity play a role. We are talking about an increase in atmospheric pressure by 8 or more mmHg. Art., a change in air temperature by 7−10 degrees, wind speed by 5 m per second, an increase in humidity over 80%.
“Weather-sensitive people should forget about any sudden lifestyle changes”
Frantisek Vismont, Physiologist, Corresponding Member of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Anyone looking for effective means of combating weather dependence will most likely be disappointed. Professor František Vismont believes that influencing meteosensitivity is extremely difficult.
“The fact is that meteosensitivity is determined by such an indicator as the reactivity of the body,” he explains. — The more violently it reacts in response to external stimuli, which include temperature changes or a jump in atmospheric pressure, the less stable it is. And reactivity depends on many factors - gender, age, heredity, type of higher nervous activity, constitution, seasonality, functional state of organs and systems, etc. And in order to give recommendations, it is necessary to carefully study all these parameters in a particular person.
Cholerics, for example, are more sensitive to weather changes than phlegmatic people, since the former are characterized by a pronounced reaction to external stimuli. But a young choleric person may be less weather dependent than an elderly phlegmatic person. Tall people with a thin build are more vulnerable to the vagaries of the weather than dense and stocky people. But if an asthenic person is engaged in physical labor, and a hypersthenic person is engaged in mental labor, everything may be the other way around.
Nevertheless, it is possible and necessary to train the body’s resistance to external influences, the professor believes. The methods are not new - hardening, contrast showers, baths and saunas, walks in the fresh air in any weather, morning exercises and other types of moderate physical activity.
“A change of situation, contrasts work as a training of adaptation mechanisms,” says the specialist. - But under one important condition - the loads must be strictly dosed and increased gradually. After all, any adaptation occurs at the expense of the body’s reserve forces, and in weather-dependent people they are already depleted.
So any sudden change in lifestyle for those who are weather sensitive can only be detrimental. Strict diets and travel to countries with exotic climates are contraindicated for them. Otherwise, weather dependence can contribute to the occurrence of diseases.
Photo: Evgeny Erchak, Stanislav Korshunov, Elena Kleshchenok, Dmitry Brushko TUT.BY , May 31, 2018
Share
Clinical picture
What doctors say about hypertension
I have been treating hypertension for many years. According to statistics, in 89% of cases, hypertension results in a heart attack or stroke and death. Currently, approximately two thirds of patients die within the first 5 years of disease progression.
The next fact is that it is possible and necessary to reduce blood pressure, but this does not cure the disease itself. The only medicine that is officially recommended by the Ministry of Health for the treatment of hypertension and is also used by cardiologists in their work is NORMIO. The drug acts on the cause of the disease, making it possible to completely get rid of hypertension. In addition, within the framework of the federal program, every resident of the Russian Federation can receive it for FREE
.
A healthy person’s condition will not worsen if there is a strong drop. However, this statement does not apply to hypertensive and hypotensive people, weather-dependent people. Changes in weather conditions can provoke a sharp decrease or increase in blood pressure.
Fluctuations in the atmosphere negatively affect the functionality of the cardiovascular system and blood vessels, which leads to lability of readings on the tonometer.
Causes and symptoms of weather dependence
Common causes of weather dependence:
- Chronic diseases of blood vessels, liver, heart, brain,
- Reduced immunity,
- Physical inactivity,
- Problems with the activity of the central nervous system,
- Age,
- Reduced elasticity and patency of blood vessels,
- Poor environmental conditions.
A sudden change in weather leads to:
- dizziness,
- drowsiness,
- lethargy,
- Joint pain,
- Severe headaches
- Feelings of anxiety, fear,
- Sudden mood changes
- Nausea,
- Deterioration of the gastrointestinal tract,
- Increased heart rate
- Decreased concentration.
Atmospheric and blood pressure: relationship
The normal pressure in the atmosphere varies from 750 to 760 mm. However, such numbers are rarely observed. With an increase, the weather improves, and the body of hypertensive and weather-dependent people begins to “rebel.”
If the atmospheric load decreases, then the weather is cloudy, and hypotensive patients feel significantly worse. They endure such changes the hardest.
This circumstance is due to the fact that a decrease in numbers in the atmosphere leads to a decrease in “pressure” in the blood vessels. In addition, the oxygen concentration decreases, which complicates the functioning of the respiratory system. The pulse quickens and the rhythm of the heart slows down.
Together, these factors can lead to a sharp decrease in DM and DD in hypotensive patients, resulting in fainting or exacerbation of concomitant pathologies.
Effect of atmospheric pressure on blood pressure:
- In hypotensive patients, when atmospheric parameters decrease, pressure drops sharply; their increase does not affect well-being.
- With a decrease in atmospheric load, hypertensive patients feel good; its growth provokes a number of negative symptoms and can lead to hypertensive crisis, stroke and heart attack.
- If people have diseases of the cardiovascular system, then fluctuations in weather conditions do not go unnoticed. Symptoms appear: severe headache, increased intracranial pressure, shortness of breath, pain in the abdomen.
Atmospheric indicators and air temperature also affect a person’s mental state - aggression, irritability and agitation, and instability of the emotional state appear.
Meteopathy and weather dependence
Hypertensive and hypotensive patients feel changes in blood pressure especially acutely. People suffering from endocrine and vascular diseases also react painfully to the vagaries of the weather.
The body's negative reaction to weather changes is called meteopathy.
It affects about 20% of healthy people, and about 70% of patients with stage 2 and 3 hypertension. Meteopathy attacks can last from several hours to several days. And the degree of reaction to weather changes directly depends on a person’s individual sensitivity.
- The primary degree of meteopathy is characterized by a deterioration in well-being and mood.
- The secondary degree is called weather dependence, and often its symptoms appear even before a change in the weather.
Symptoms:
- Severe headaches
- Weakness,
- Apathy,
- Drowsiness,
- The heart beats faster
- Wet palms
- Chills,
- Sleep disturbance,
- Frequent and sudden mood changes.
Tertiary degree - meteoneurosis. Differs in depressive psychosis. It usually appears in the fall, when daylight hours decrease, and continues until mid-spring.
For people suffering from hypertension, temperature and humidity levels are also important. When the air is dry, heat and cold can be tolerated equally easily. High air humidity is less tolerated by older people, as well as those diagnosed with vascular atherosclerosis, heart and lung diseases. If the humidity level exceeds 80%, then cases of exacerbation of diseases and heart attacks become more frequent.
Effect of cyclones and anticyclones on blood pressure
During cyclones, the air temperature rises, precipitation, high humidity and cloudiness are observed. The oxygen level decreases significantly, while the concentration of carbon dioxide increases.
Such weather conditions negatively affect the well-being of a person with chronically low blood pressure. Due to lack of air, hypotensive patients experience a range of anxiety symptoms.
Blood circulation in the body slows down, the pulse rate per minute decreases, internal organs and tissues suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients. As a result, DM and DD are further reduced.
Upon the arrival of the anticyclone, dry weather without wind sets in. Harmful impurities accumulate in the air, and gas pollution increases several times. How does high atmospheric pressure affect a person?
A healthy person will not notice a change in his condition. In hypertensive patients, there is a sharp jump in blood pressure, symptoms are revealed:
- The heartbeat increases.
- Skin hyperemia.
- General weakness.
- Pulsation in the head region.
- Blurred vision.
- Noise and ringing in the ears.
Elderly people with a history of vascular and cardiovascular diseases are especially susceptible to changes. The likelihood of a hypertensive attack with neurovegetative disorders increases.
Hypertensive patients are strictly prohibited from climbing to altitude, especially when there are changes in the atmosphere. It is recommended to avoid tiring and long flights, mountain hikes, etc.
High blood pressure and hypertension
Due to the specific movement of air, people with high and low blood pressure are susceptible to the influence of the anticyclone. An anticyclone brings with it cloudless weather, decreased humidity and stabilization of temperature. In large cities, calm and clear weather leads to an increase in air pollution with a simultaneous decrease in oxygen levels. All this affects the reduction of leukocytes in the blood.
Such changes in weather conditions negatively affect the body of a hypertensive patient:
- There is noise in the ears,
- Photopsia occurs
- Shortness of breath appears
- Blood appears from the nose. With pressure it can be difficult to stop on your own,
- There are malfunctions in the functioning of the cardiac system, the pulse increases,
- There is a feeling of unreasonable fear,
- Sleep is disturbed.
A sharp increase in blood pressure when the weather changes can result in fainting, thrombosis or hypertensive crisis.
Our readers write
Hello! My name is Lyudmila Petrovna, I want to express my gratitude to you and your site.
Finally, I was able to overcome hypertension. I lead an active lifestyle, live and enjoy every moment!
At the age of 45, pressure surges began, I suddenly became ill, with constant apathy and weakness. When I turned 63, I already understood that I didn’t have long to live, everything was very bad. An ambulance was called almost every week, I always thought that this time would be the last.
Everything changed when my daughter gave me an article to read on the Internet. You can’t imagine how grateful I am to her for this. This article literally pulled me out of the other world. Over the last 2 years I have started to move more, in the spring and summer I go to the dacha every day, my husband and I lead an active lifestyle and travel a lot.
Who wants to live a long and energetic life without strokes, heart attacks and blood pressure surges, take 5 minutes and read this article.
The drink helps increase blood pressure in hypertensive patients, but not for long. After a few hours, the numbers normalize on their own. If you drink the drink on a regular basis, each time the blood pressure will decrease more slowly, and then remain elevated. Coffee can be replaced with chicory.
With stage 2 or 3 hypertension, a cup of strong coffee can provoke a sharp jump and lead to an attack. Therefore, it is recommended to abstain from such a drink.
Foods and drinks that increase blood values:
- Abuse of table salt for hypertension – risk of stroke and heart attack. The powder retains fluid in the body, which further increases the load on the heart, systolic and diastolic numbers.
- One bottle of beer lowers blood pressure for about 5 hours. However, drink lovers cannot always stop at a small dose; in this case, the situation is the opposite - the decrease is replaced by a sharp rise to critical numbers.
- When cognac enters the bloodstream, it causes the heart to beat faster, and the fusel oils in it have a negative effect on the central nervous system, kidneys and liver. Taken together, this leads to disruption of the functioning of internal organs, an increase in DM and DD. Moonshine has a similar effect.
- Sweet red wine “forces” the heart muscle to contract rapidly, causing blood counts to instantly increase. Hypertensive patients are allowed to drink a dry red drink; it has vasodilating and antispasmodic properties.
One of the symptoms of arterial hypertension is headache, which is difficult to relieve with medications. And the Citramon tablet definitely won’t help.
Citramon contains caffeine, which contributes to a rapid increase in blood pressure.
What helps lower blood pressure?
Lemon, a natural antioxidant that has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, is used as a folk remedy for the treatment of arterial hypertension. It can be added to tea, refreshing drinks, and also combined with other ingredients.
Recipe: grind a large lemon using a meat grinder, add granulated sugar or natural honey. The ratio of components to taste. Take one teaspoon every day before meals (10 minutes).
Persons suffering from hypertension should periodically arrange fasting days - once every 10 days. The benefits of this method are undeniable - body weight is reduced, excess fluid and toxic substances are removed, metabolic processes are improved, and diabetes and DD are normalized.
Menu for fasting day:
- Option No. 1 – milk unloading. Throughout the day, six “meals” of 100 ml of milk are allowed. Immediately before bed, drink 200 ml of any fruit juice. If hypertension is complicated by atherosclerosis, then the dosage per day is 1.5 liters of milk, divided into 8 doses.
- Option No. 2 – potato unloading. Boil 800 grams of potatoes with skins or bake in the oven, divide into 5 portions. Reduce your consumption of regular water to a liter.
- Option number 3 – unloading on juices. It is permissible to drink 600 ml of vegetable or fruit juice and 800 ml of rosehip decoction per day. All liquid is divided into 5 doses.
Tea with the addition of lemon balm slightly lowers the levels, the hypotensive effect is weakly expressed. Drinking the drink helps normalize the activity of the central nervous system, eliminate headaches and dizziness that accompany hypertension.
How does chocolate affect blood pressure? The effect depends on the quality of the chocolate. If the bar contains over 70% cocoa and does not contain flavorings or vegetable fats, then the delicacy has a hypotensive property.
Garlic normalizes blood pressure thanks to the substance allicin. The component relaxes blood vessels, dilates arteries, and improves blood circulation. Effective with long-term use - at least a month, one clove per day. Ginger has a similar effect - add a piece to tea.