During these stressful holidays for our body, which follow one after another, you need to be especially careful about your health, especially if you are over 30 or older. Today we’ll talk about such an important indicator as blood pressure.
Sudden changes in a person’s blood pressure can cause harm to the body: both high and low blood pressure are dangerous for humans. But the number of patients with hypertension is higher than with hypotension - and it is growing steadily. If previously these diseases were found only in older people, now they are also observed in young people.
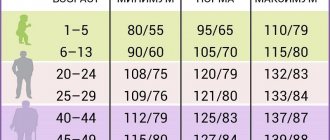
Safe pressure
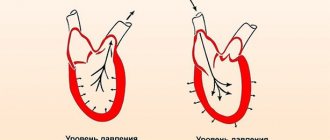
Blood pressure is the force with which blood pushes against blood vessels. The phrase “blood pressure” is used to mean pressure in all vessels of the body, although pressure can be venous, capillary and cardiac. Indicators of 120/80 mm Hg are considered safe for human life. Art. The maximum permissible limit pressure is up to 140/90 mm Hg. Art. If the indicators rise even higher, this indicates a tendency towards hypertension. The largest number, the first, is the systolic blood pressure indicator, this is the critical pressure when the heart is at its peak degree of compression. The second number is the diastolic indicator - at the moment of relaxation of the heart. They are called “upper” and “lower” respectively.
But you shouldn’t constantly check the standards, because each organism is individual. For one, the norm is 80/40, and for others, 140/90. But even if a person does not have any unpleasant symptoms with non-standard blood pressure readings, this is not a reason to be careless about health and not pay attention to it. Consultation with a doctor is necessary even in this case.
How do coffee and tea affect blood pressure?
Photo from tolowerbloodpressure.com
Contrary to popular belief that coffee increases blood pressure, there is no convincing evidence for this. In 2012, American medical analysts collected and summarized the results of all studies on this subject and came to the conclusion that there is no scientific basis for recommending coffee to increase blood pressure or prohibiting it for those suffering from hypertension.
So if you don’t notice a real deterioration in your well-being after a cup of coffee, drink to your health.
But black tea, as it turned out, affects blood pressure if consumed regularly, and in the direction of reducing it, albeit slightly.
Green tea significantly reduces both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, so it should be avoided by hypotensive people. For hypertensive patients, 1-2 cups of green tea per day significantly reduces the risk of developing heart disease.
Critical indicators
Critical norms are considered to be indicators at which the cardiovascular system suffers.
A sharp increase or decrease in tonometer readings is fraught with serious consequences for the cardiovascular system. It is impossible to say an exact figure that will indicate maximum blood pressure for all people. An increase of 20-30 points from the usual, normal level is already dangerous, more than 30 is critical. You can rely on the following numbers:
- below 100/60 mm Hg. st - hypotension;
- above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. - hypertension.
The highest pressure rarely reaches 300 mm Hg. Art., because it guarantees a 100% lethal outcome. During a hypertensive crisis, blood pressure reaches 240-260 per 130-140 mmHg. Critical low blood pressure is 70/40 or even less. High blood pressure threatens the sudden onset of heart failure, sometimes even fatal.
How to lower blood pressure and cure hypertension?
Hypertension is a chronic cardiovascular disease. It cannot be cured completely, but symptoms can only be relieved with medication. Hypertensive patients are dependent on medications, have limited diet and exercise, and are always at risk of developing new diseases.
To maintain quality of life, it is important to minimize risks before the disease actively develops. This can be done using the Atlas genetic test, which includes information about predisposition to the disease, as well as recommendations for prevention.
To treat high blood pressure, you need to consult a specialist. But below you will find tips for preventing and controlling hypertension.
- Reduce salt intake (no more than 1.5 g per day)
- Limit consumption of foods high in saturated fats and trans fats
- Avoid or reduce consumption of sugar, alcohol, coffee and tobacco
- Increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet
- Exercise regularly
- Reduce and control stress conditions
- Measure blood pressure regularly
- Treat high blood pressure and other conditions with the help of a specialist.
In case of a hypertensive crisis, you must call a doctor and not self-medicate. Traditional methods will also not be beneficial. There are many medications available to lower blood pressure. Depending on the symptoms and characteristics of the body, doctors recommend:
- ACE inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Diuretics
- Alpha blockers
- Beta blockers
Most people need to take more than one type of medicine to better control their blood pressure.
Why does the pressure increase?
A person's blood pressure never changes without reason. This is influenced by a complex of certain factors, and they are not always associated with problems in the body. Therefore, if your blood pressure level has increased, then you should reconsider your lifestyle and pay attention to the following factors:
- Dehydration. A person needs to drink about 1.5 liters of fluid per day, but it should only be clean water. If the body does not receive enough water, the blood becomes thicker, which forces the heart to work harder and causes an increase in blood pressure.
- Eating too fatty foods, with a lot of cholesterol - it forms cholesterol plaques in the vessels, interfering with the flow of blood. These foods include animal fats.
- Large amounts of salt consumed.
- Bad habits - alcohol and smoking.
- Heavy physical activity and vice versa, its absence (physical inactivity). Under heavy loads, malfunctions occur in the body, and if there is no load at all, then blood circulation worsens and the strength of the heart muscle weakens.
- Frequent stress.
- The cause may be a hereditary predisposition, age over 50 years, kidney disease or head injury.
Hypertension
Photo from achieveclinical.com
The diagnosis of “hypertension” (also known as arterial hypertension, arterial hypertension and essential hypertension) is given to a patient if his blood pressure is higher than 140/80.
After making a diagnosis, it is very important to get checked by an endocrinologist, and first of all, determine the levels of glucose and insulin in the blood, since their increase is very often the main cause of high blood pressure.
People with type 2 diabetes are often obese, which is another risk factor for cardiovascular disease, so hypertension and insulin resistance are quite closely related.
A patient suffering from both diseases is prescribed a diet that helps lower blood sugar levels and also lose weight. To do this, you should completely eliminate or significantly reduce the consumption of foods containing sugars and starches, that is, baked goods, pasta, rice, cereals, and potatoes. It is also advisable to limit fruits somewhat, but not completely exclude them, since they are an important source of vitamin C, which is necessary for hypertensive patients.
Old and proven advice to all those suffering from cardiovascular diseases is to regularly eat citrus fruits.
It is important to ensure that the level of fructose consumed is no more than 25 grams per day. For reference : one average orange contains 6 g of fructose, banana - 7, peach - 6, apple - 9.5, pear - 12.
The fact is that one of the breakdown products of fructose is uric acid, the accumulation of which leads to several disorders, including hypertension.
Of course, if you have high blood pressure, you should give up alcohol and smoking - however, these two factors are unnecessary for any ill health.
With hypertension, it is very important to pay attention to whether the pressure decreases at night. If it remains elevated early in the morning, you should definitely check your heart as well as your vitamin D levels. The best way to optimize your body's vitamin D levels is to get regular sun exposure, but if you can't avoid taking extra vitamin D, choose a product that contains the active ingredient. its form is vitamin D3 (not D2).
An excellent source of vitamin D is fish oil. By taking it, you simultaneously replenish your body with omega-3 fatty acids, which, as scientific research shows, also have a cardioprotective effect.
Many experts recommend a salt-free diet for hypertensive patients, especially those whose hypertension is associated with kidney disease (and this is a very common combination of diseases). This issue, however, should be approached carefully and individually.
Photo from deccanchronicle.com
On the one hand, salt actually increases blood pressure, on the other hand, a lack of the main source of sodium can lead to an imbalance in the sodium balance in the body, which often causes a decrease in insulin production and leads to cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the decision to limit salt should be made taking into account the patient's comorbidities. If such a decision is nevertheless made, hard cheeses, milk, beef, eggs, and rye bread will help replenish sodium in the body.
It's no secret that high blood pressure is often a consequence of stress, especially in middle-aged and elderly people. Advice to avoid troubles would sound strange, because they happen regardless of our will. It is useful, however, to master one or another technique of emotional control. There are many of them, and anyone who sets such a goal will be able to find something that is right for him to maintain peace of mind.
An important part of the prevention and treatment of arterial hypertension is physical exercise. An exercise program for hypertensive patients should include not only aerobic exercise (with a pulse range of 140-160 beats per minute), but also anaerobic exercise (with a pulse range of 160-180 beats per minute), which largely contribute to improving the functioning of the heart and lungs, and reduce risk of cardiovascular diseases.
This includes fast sprints, jumping rope, weight training, climbing steep hills, and any activity that involves heavy loads.
Under no circumstances should you immediately start intense exercise, as this can lead to the exact opposite result. It is best to start with fast walking, jogging, cycling, swimming.
Why does blood pressure drop?
Causes of low blood pressure.
Causes of low blood pressure:
- The first and main thing is the bad effects of stress and emotional overload.
- Strong mental load.
- Working in harsh conditions is also dangerous. These conditions include working underground, in high humidity or in extreme temperatures.
- A decrease in blood pressure is caused by diseases of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
Hypotension occurs in athletes, even though they do not lead a sedentary lifestyle. It occurs as a defense for the body during frequent physical activity.
Low blood pressure - what is the danger?
Photo from everydayhealth.com
Hypotension is diagnosed when blood pressure is 90/60 or lower. As a rule, stable low blood pressure does not pose a danger to the body and most often does not particularly affect a person’s well-being.
Serious consequences can be caused by a sharp drop in pressure, the causes of which are blood loss, low body temperature, elevated body temperature, sepsis, dehydration as a result of vomiting or diarrhea, a reaction to medication or alcohol, or anaphylactic shock. In all these cases, the patient needs emergency medical care.
There is also a diagnosis such as orthostatic (postural) hypotension. This is a sharp drop in blood pressure when the patient takes an upright position. Fainting, loss and confusion, dizziness, and blurred vision may occur within a few seconds or over a longer period.
This is a manifestation of abnormal regulation of blood pressure, due to various reasons, and not a separate disease.
Orthostatic hypotension occurs in 20% of older people. More often, it can be present in people with concomitant diseases, mainly arterial hypertension, and then the patient complains that the pressure is “jumping.”
In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor, who should adjust medication prescriptions if the patient was taking medications for high blood pressure, diuretics or psychotropic drugs.
If you constantly experience symptoms of low blood pressure, and measurements give readings of 90/60 or lower, then there is a danger that your organs are not receiving enough oxygen, which in turn can lead to dysfunction of the heart and brain.
These are the symptoms:
- Dizziness; – Feeling of lightness in the head; – Loss of body balance; - Weakness; – Fatigue; - Nausea; – Paleness; – Sweat on the skin; - Fainting.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous?
High blood pressure causes severe damage to the body, most of the harmful effects go to the cardiovascular system. Every year, about 1 million people die due to heart problems, the vast majority due to hypertension. High blood pressure is fraught with hypertensive crises - sharp jumps in indicators to critically dangerous levels. In case of a hypertensive crisis, first aid is given as quickly as possible in order to save a person who is still alive. In this condition, the vessels (aneurysms) expand sharply and rupture. In this case, a person immediately begins to have a severe headache and heart pain, suddenly develops a fever, feels sick, and his vision deteriorates for a while. The consequences of high blood pressure are deadly - heart attack and stroke. In the chronic form of hypertension, its target organs are affected. This is the heart, kidneys, eyes.
- During a stroke, there is a sharp deterioration in blood circulation in the brain and this causes paralysis, which sometimes remains for the rest of life.
- Kidney failure is a metabolic disorder in which the kidneys completely lose their main function - producing urine.
- If the eyes are affected, vision becomes worse, and hemorrhages occur in the eyeball.
Genetic factors in the development of hypertension
Many genetic studies have revealed the stability of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). This is the human hormonal system that regulates blood pressure, blood volume, and the balance of fluids and salts in the body. Changes in this system may contribute to the development of hypertension.
But today there is data that shows a predisposition to the development of hypertension much more accurately and up-to-date. For example, genome-wide associations are worth considering. The NOS3 gene synthesizes nitric oxide and relaxes the walls of blood vessels, APOE is a cholesterol transporter, specific polymorphisms in the ADRB1 gene affect resting heart rate and may be associated with heart failure.
Why is low blood pressure dangerous?
Hypotension is dangerous for the entire body, since all organs do not receive the necessary blood circulation.
Low blood pressure is considered dangerous because due to it, a sufficient amount of oxygen does not enter the main vessels, and the blood supply to organs deteriorates. Poor blood supply to the brain is life-threatening due to the risk of ischemic stroke. Hypotension has a bad effect on a person’s general condition: he feels constant malaise, fatigue, and powerlessness. Heart attack, stroke and heart disease are complications of both hypertension and hypotension. Numerous examples confirm that the transition from hypotension to hypertension is possible. This occurs due to pathological changes in the vessels and their restructuring. This type of hypertension is difficult to tolerate by the body, much worse than others.
Hypotension is a common occurrence early in pregnancy. Dehydration requires drinking a lot, but this is bad for the baby.
What to do if a person has dangerous blood pressure?
Both hypertension and hypotension are considered dangerous and require mandatory treatment. The sooner therapy begins, the better it is for the body. Even the highest blood pressure should not be reduced sharply; this is harmful and dangerous for the body. Combination drugs are used for treatment; they help reduce adverse reactions and increase benefits. Recently, drugs have been manufactured that reduce high blood pressure for a day after one dose. It is equally important to review your diet:
- reduce the amount of salt;
- It is advisable to exclude strong coffee, teas and alcohol;
- completely eliminate animal fats and sugar;
- increase consumption of fresh vegetables and fruits;
- eat foods high in potassium and magnesium.
To increase vascular tone, pills are not always used. Coffee is considered the most accessible means for urgently raising blood pressure levels. All antihypertensive drugs contain caffeine: Citramon, Pyramein, Askofen. Cinnamon water will help to quickly increase even the lowest blood pressure: pour a quarter spoon of cinnamon into one glass of boiling water and drink a maximum of 2 teaspoons to increase levels. For hypotension, combination drugs are also successfully taken, most often a combination of an ACE inhibitor and calcium antagonists, or an ACE inhibitor and a diuretic.
What is worse for a person - high or low blood pressure? The danger lies in any violation of indicators. Therefore, if there are systematic jumps in blood pressure (BP), you should consult a doctor who, after a thorough examination, will prescribe optimal therapeutic and preventive measures.
Symptoms of pathologies
High or low blood pressure in a person is manifested by the following symptoms:
| Hypotension | Hypertension |
| Characterized by lethargy, drowsiness, fatigue and decreased performance, aching headache and fainting. These symptoms are especially pronounced when weather conditions change, so hypotensive people are weather-dependent people. With orthostatic hypotension, there is sudden weakness along with spots or darkening before the eyes. | In contrast to low readings, mild and moderate high blood pressure, as a rule, does not manifest itself and is accidentally detected during blood pressure measurement. The patient may also not feel a severe form of hypertension if its development was gradual and without sudden surges in blood pressure. Signs appear when the values increase sharply (minutes, hours or days). In such a situation, one feels compressive pain in the back of the head, tinnitus, stiffness of movement, pain in the chest and a feeling of anxiety. |
Pressure: high and low
Blood pressure problems are common. Moreover, there can be two of these problems: low or high blood pressure, that is, hypotension and hypertension. What is the difference between these states, besides the numbers on the tonometer screen? And which one is more dangerous?
Who does it happen to?
Hypotension
As a rule, hypotension is a manifestation of vegetative-vascular dystonia (more correctly called somatoform dysfunction) - a disease in which the functioning of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) is disrupted. This part of the nervous system regulates the functioning and interaction of other body systems, and, in particular, maintains vascular tone.
In addition to dystonia, hypotension can be caused by various disturbances in the functioning of the heart, a decrease in blood volume (with increased loss or insufficient fluid intake), and the use of certain medications and narcotic drugs.
A typical hypotensive person is thin and pale, but this does not have to be the case. The condition is more common in women and usually appears in adolescence or young adulthood.
Hypertension
In 90% of cases, hypertension is a primary disease (not provoked by other diseases), which occurs due to complex disorders of water-salt metabolism and regulation of the cardiovascular system. In the remaining 10%, it complicates diseases of the kidneys and endocrine system.
A typical hypertensive patient is dense and full-blooded, although, again, this is not necessary. As a rule, primary hypertension begins at the age of 30-35 years and later; in women, its onset may be associated with the onset of menopause.
Pressure level
Hypotension
There is no clear lower limit for blood pressure. If a person feels normal with blood pressure below the average, this is not considered hypotension. Typically, low blood pressure begins to be felt when the pressure is less than 95-90/65-60 mmHg. Art., but this figure is individual.
Hypertension
The upper limit of absolutely normal pressure is 130/85 mm Hg. Art. Blood pressure 130-140/85-90 mmHg. st is called elevated normal and indicates the risk of its further increase.
Anything over 140/90 mm Hg. Art. – this is hypertension.
Manifestations
Hypotension
Hypotension is manifested by lethargy, drowsiness, decreased performance, fatigue, a tendency to faint, aching headache - in general, all the “charms” characteristic of the state of a sleep-deprived person. All of the above manifests itself especially strongly when the weather changes - hypotensive people are weather dependent.
Orthostatic or postural hypotension is also common - severe weakness combined with flickering spots or darkening in the eyes when moving from a horizontal to a vertical position, for example, when getting out of bed. This occurs due to the low tone of the blood vessels, characteristic of hypotension - when standing up, the blood flows away from the head under the influence of gravity, leaving the brain on a starvation diet, and the vessels cannot quickly compensate for this.
At the same time, chronic hypotension is rarely so severe that it leads to serious problems. However, it happens that the pressure regulation mechanisms suffer so much that a person who has been in an upright state for a long time loses consciousness. In some cases, a significant decrease in blood pressure occurs only after eating.
Hypertension
Unlike hypotension, mild and moderate hypertension often does not manifest itself at all and is determined by chance when measuring pressure. Even severe hypertension may not be felt by a person if it developed gradually, gradually, without sudden changes in pressure. Symptoms appear only with a relatively rapid increase in pressure - within minutes, hours or several days. In this case, you will feel a pressing pain in the back of your head, a hum and pulsation in your ears (as if an orchestra is playing in your head), and uncertainty of movements. With concomitant coronary heart disease (CHD), characteristic chest pain may appear. Moreover, as a rule, a hypertensive person tolerates tangible manifestations of his condition more severely than a hypotensive person, although this, of course, is a subjective thing.
Effect on the body
Hypotension
Despite the tiring subjective sensations, hypotension rarely causes serious damage to the body (we are, of course, talking about a chronic condition). Most hypotensive people maintain efficiency and vitality by refreshing themselves with a mug of coffee from time to time. However, due to disturbances in the regulation of vascular tone, low blood pressure often increases with age, and excessively - a hypotensive person becomes hypertensive.
Hypertension
Constant hypertension (even minor), despite the minimum of manifestations, slowly but surely disrupts the functioning of almost all body systems. This occurs because the properties of the vessels that are forced to cope with increased load change, and, consequently, the blood supply to the organs suffers. The most sensitive to this are the brain, retina and kidneys, whose work is the first to be disrupted in hypertension.
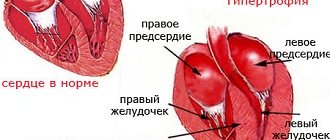
The heart reacts to increased pressure in the same way as any muscle that performs a large amount of work - it begins to grow. However, unlike skeletal muscles, which are permeated with blood vessels, the heart receives oxygen only from the vessels located on its surface. This means that as the heart muscle grows, the load on them increases and “starvation” of the inner layers of the heart begins. This leads to a decrease in performance reserve, and with concomitant atherosclerosis, to the rapid development and progression of coronary heart disease.
Acute condition
Hypotension
A sharp decrease in blood pressure, as a rule, has a specific cause: an allergic reaction, blood loss, a sharp disturbance in cardiac activity, infection and poisoning.
A short-term sharp decrease in pressure goes away on its own when you assume a horizontal position. A longer period poses a threat to life due to impaired blood supply to vital organs, primarily the brain. They require emergency medical attention.
Hypertension
A sharp rise in blood pressure usually develops against the background of existing hypertension and is always dangerous to health and life. It can occur during physical or emotional stress, as a result of the onset or exacerbation of kidney and endocrine system diseases. Often its cause cannot be determined.
With a sharp increase in pressure, the repeatedly increasing load on the walls of blood vessels can lead to their rupture and hemorrhage into any organ. Most often this is a hemorrhage in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke) or in the retina. Under the influence of increased pressure, an atherosclerotic plaque can collapse and clog a vessel, which leads to the death of the area of the corresponding organ - a heart attack. The most common complication of a hypertensive crisis is myocardial infarction and cerebral stroke. Therefore, if your blood pressure suddenly increases, call an ambulance immediately. Better to play it safe.
Conclusion
What is safer – hypotension or hypertension? The answer is simple: it is best to have normal blood pressure. Moreover, in modern conditions this is quite possible with any initial data. Hypotonic patients will benefit from tonic drinks based on caffeine, ginseng and other stimulants; hypertensive patients will benefit from regular use of medications to control blood pressure. But if we ignore treatment issues and compare the health hazard and the risk of complications, the answer is that hypotension as a chronic condition is much less dangerous, although its symptoms are unpleasant.