How long to take Detralex for hemorrhoids
The instructions for the medication say that for acute hemorrhoids, you can take 6 tablets per day during the first 4 days, and in the next 3 days, take 4 tablets per day. The drug should be taken with food. It is better to divide the daily dose into several doses.
For chronic disease, you need to take 4 tablets every day with meals (2 tablets at lunch, 2 tablets in the evening). After a week of taking the dosage can be reduced by 2 times.
The duration of treatment depends on the patient’s condition and the effectiveness of treatment.
Introduction
A woman with chronic pain in the lower abdomen is a frequent, complex and, as a rule, conflict-prone patient encountered by doctors of many specialties. The causes of chronic pelvic pain in women are numerous, and one of the leading places among them is varicose veins of the small pelvis (PVV). The disease occurs in women of all ages and has a progressive course. It should be especially noted that ARVMT is an interdisciplinary problem, since patients often go in circles from a gynecologist to a surgeon, a gastroenterologist, a neurologist, and again to a gynecologist. Thus, doctors of many specialties may encounter the problem of treating ARVMT.
There are two main directions in the treatment of ARVMT. The first of them is represented by surgical methods, among which are ligation of the pelvic veins, their endovascular embolization and sclerosis. It should be noted that surgical methods are effective only for varicose veins of the ovary and have a number of disadvantages - primarily, invasiveness and frequent recurrence [1, 2, 4, 5].
The second direction is conservative methods, in which angioprotectors and microcirculation correctors are widely used. Among the phleboprotective agents in this group, the most effective are drugs based on diosmin, which include Detralex. The advantages of Detralex are good bioavailability, which is ensured by the micronized formula of the drug [6, 7], the absence of contraindications and the possibility of use in all biological periods of a woman’s life - adolescence, reproductive, pregnancy (from the second trimester), pre- and postmenopause [3].
The purpose of the presented study was to study the effectiveness of Detralex in the treatment of ARVMT in women during the main biological periods of life.
Material and methods
The study included 301 patients with URVT. The patients were divided into 4 main groups and 4 comparison groups. The main groups included 50 teenage girls, 30 women of reproductive age, 57 in the postpartum period and 35 in pre- and postmenopause. The comparison groups included, respectively, 50 teenage girls, 20 women of reproductive age, 34 in the postpartum period and 25 in pre- and postmenopause. All women included in the study in the postpartum period were delivered by cesarean section for obstetric indications.
Patients from the main groups received Detralex at a dose of 1000 mg/day (1 tablet 2 times a day) for 2 months. Patients from the comparison groups received placebo.
The effectiveness of Detralex was studied clinically and instrumental methods. The pelvic venous system was examined in all women. Using ultrasound (ultrasound), the diameter of the main venous collectors of the small pelvis was determined: uterine, internal iliac, ovarian and arcuate veins. Adolescents, women of reproductive age, and pre- and postmenopausal women underwent Doppler ultrasound to study peak systolic blood flow velocity (Vps) in the uterine veins. In patients of reproductive age, microcirculation in the pelvic organs was assessed using radioisotope clearance.
Statistical processing of data was carried out using the Statistica 6.0 program. The normality of the distribution of sample means was checked using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. In the case of a normal distribution of means, the hypothesis of their equality was tested using the t-test. In other cases, the Mann–Whitney test was used.
Research results
The leading clinical symptom of ARVMT in women is pain in the lower abdomen, which has varying irradiation and intensity. And if girls are characterized by an asymptomatic course of ARVMT, then with age the frequency of pain increases, and the peak of the pain syndrome occurs during the reproductive period. Detralex relieved pain in women in all biological periods of life, and most effectively during reproductive age. In patients receiving placebo, the frequency of pain did not change significantly (Fig. 1).
It is known that ARVMT in women is characterized by an increase in the diameter of the main venous collectors of the small pelvis, so studying the effect of Detralex on the tone of the pelvic veins is of particular interest (Fig. 2).
The results of ultrasound before and after treatment with Detralex show that a course of taking the drug leads to a significant decrease in the diameter of the uterine, internal iliac, ovarian and arcuate veins in all main groups of patients (Table 1).
Dilatation of the venous wall during URVMT leads to chronic venous congestion in the pelvic organs, which is manifested by a significant decrease in Vps in the uterine veins, detected by Doppler examination (Fig. 3).
Detralex improved the drainage function of the pelvic venous system, which was manifested by an increase in Vps in the uterine veins in patients of three main groups (Table 2), determined using Doppler sonography. Reducing the diameter of the pelvic veins and eliminating chronic venous stagnation is the result of the multifactorial action of Detralex. This has a venotonic effect, normalization of the drainage function of the pelvic venous system, and improvement of microcirculation. While taking Detralex, microcirculation indicators, determined in women of reproductive age using radioisotope clearance, significantly improve (Table 3): the time for establishing equilibrium of radioactivity over the common iliac veins is reduced, the angle of elevation of radioactivity over the iliac veins is increased, and the time for establishing general equilibrium is reduced.
Conclusion
ARVMT is a chronic relapsing disease that cannot be completely cured at the present stage of medical development. The main goals of treatment are to slow down the progression of ARVMT, prevent its relapses and improve the quality of life of patients. Detralex, the therapeutic effect of which is aimed at the main links in the pathogenesis of ARVMT - dilatation of veins, reduction in the speed of venous blood flow and microcirculation in the pelvic organs, allows you to successfully solve this problem. The undoubted advantage of Detralex is its effectiveness in all biological periods of a woman’s life, which makes it possible to prevent ARVMT at puberty, during pregnancy and childbirth, as well as during menopause. It is important to emphasize that treatment of ARVMT in women should not be limited to taking Detralex only, as it must be comprehensive.
Contraindications and adverse reactions
The medicine has practically no contraindications. You should avoid taking it if you are allergic to any of the ingredients.
Negative effects from taking appear in extremely rare cases. They usually present with nausea and stomach upset. Sometimes dizziness, headache, and deterioration in general health may occur. An allergy may appear in the form of a skin rash.
To date, there have been no cases of drug overdose. In the chronic stage of the disease, experts usually advise taking the medicine in courses of 2-3 months. In case of acute form, take in weekly courses.
If after this time the symptoms have not disappeared, the patient should schedule an examination with a specialist.
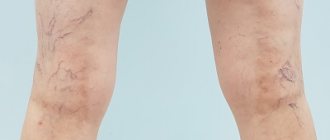
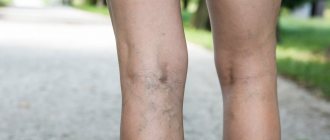
Drug therapy for varicose veins of the lower extremities
Today, a phlebologist has a wide range of different drugs in his arsenal that are used for varicose veins. The main indication for drug therapy is the presence of chronic venous insufficiency or prevention in risk groups.
Phleboprotectors are the main group of drugs that affect venous tone and protect its wall and valves from destruction. The main phleboprotector recommended by world associations of phlebologists is micronized diosmin (Detralex), which improves microcirculation, reduces vascular permeability and protects the venous wall and vein valves from destruction. In addition to the main drug in the treatment of varicose veins, phlebologists prescribe auxiliary drugs that help fight the symptoms of venous insufficiency in the legs (anti-inflammatory drugs, disaggregants, anticoagulants, antihistamines, glucocorticoids, including in the form of ointments and gels). Drug therapy is prescribed in courses. A course of medications is also recommended before and after surgical treatment (EVLT, sclerotherapy, miniphlebectomy) to prevent relapse.
Modern classification of drugs for the treatment of varicose veins:
1. Venotonic drugs:
- Detralex;
- Rutoside (Venoruton, Rutin);
- Tribenoside (Glivenol);
- Troxerutin (Troxevasin);
- Cyclo-tri-forte;
- Endothelon;
- Escin (Aescin, Venen, Venitan, Venoplant, Concentrin, Reparil, Aescusan);
- Ginkor-forte.
2. Drugs that improve blood flow in blood vessels:
- Pentoxifylline (Agapurin, Arbiflex, Vazonit, Darte-lin, Mellinorm, Pentilin, Pentohexal, Radomin, Ra-lofect, Trenpental, Trental, Flexital, Quinotal)
3. Anticoagulants:
- Heparin-containing ointments, gels (Troxevasin, Lyoton 1000 mg, Detragel)
Venotonic drugs
Detralex
Detralex is a venoprotector and venotonic. Effective in the treatment of all types of chronic venous insufficiency. Reduces the severity of symptoms of CVI of the lower extremities (feeling of heaviness, pain in the legs, night cramps, impaired trophic tissue of the legs). Detralex is also used to relieve acute hemorrhoidal attacks (acute attacks of hemorrhoids).
- improves vein tone;
- improves lymphatic drainage;
- normalizes microcirculation;
- fast-acting and lasting effect.
"Detralex" affects the venous vascular system: it reduces the distensibility of veins, increases their tone and reduces venous stagnation. At the microcirculation level, Detralex reduces capillary permeability and increases their resistance. Detralex improves lymphatic drainage.
Rutoside
(Venoruton, Rutin)
"Rutoside" belongs to the group of bioflavonoids (flavonols). Contained in the leaves of mint (Ruta graveolens L.) and other plants.
Has P-vitamin activity. Normalizes capillary permeability, strengthens the vascular wall, and has an anti-inflammatory effect. In patients with CVI, it leads to a reduction in swelling and pain, the disappearance of numbness and cramps.
Troxerutin
Troxerutin: Flavonoid (semi-synthetic derivative of rutin) - venotonic, angioprotective, anti-inflammatory, decongestant, antioxidant effect.
Normalizes the permeability of capillary walls, increases their tone. Increases the density of the vascular wall. Reduces inflammation in the vascular wall.
It is also used for CVI. It is recommended to use both in the initial and late stages of the disease. As a result of treatment, the feeling of heaviness in the legs disappears, swelling of the lower extremities decreases, and trophism improves.
Escin
Triterpene glycoside (saponin) from the fruits (seeds) of horse chestnut.
Synonyms: Aescin, Venastat, Venitan, Concentrin, Reparil, Cycloven forte, Aescin, Concentrin, Cycloven forte, Reparil, Venastat, Venitan.
Herbal preparations from horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum L.): infusions and decoctions of bark, leaves, fruits have long been used in folk medicine as astringents, choleretic, hemostatic (for uterine and hemorrhoidal bleeding) agents. A particularly important pharmacologically active substance is escin - it largely determines the effectiveness of drugs obtained from horse chestnut (escusan, esflazide, etc.).
Escin has a pronounced capillary protective activity and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Be healthy!
Make an appointment with a phlebologist
Surgeon-phlebologist - Andrey Aleksandrovich Nisin
You can make an appointment by calling (391) 218−35−13 or through your personal account