The International Clinic Medica24 does NOT accept or hospitalize patients with transient (transient) and acute cerebrovascular accidents (stroke)
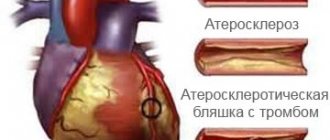
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease of the arteries with the formation of a dense plaque on the inner surface of the vessel, narrowing its lumen. It is clear that such a deformation of the vessel is not able to provide the tissues with an adequate volume of blood; the nutrition of the tissues is disrupted - their ischemia occurs. The most common lesions of the heart vessels are manifested by coronary heart disease, the worst manifestation of which is myocardial infarction. Damage to the blood vessels of the neck and brain in the worst case is manifested by ischemic stroke. Damage to the arteries of the lower extremities leads to the development of ischemic manifestations of varying severity, up to critical ischemia. But veins are not affected by atherosclerosis; they have their own misfortunes: varicose veins and blood clots.
Our expert in this field:
Serebryansky Yuri Evstafievich
Cardiologist, geriatrician, therapist, professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Since the 60s of the twentieth century, a steady increase in the frequency of atherosclerosis and its clinical manifestations in the cardiovascular system has been recorded, which currently hold the lead in morbidity and mortality in developed countries of Europe and America. Gradually, atherosclerosis is taking over the Asian region, where it was practically not noted until the middle of the last century; it comes along with the European way of life. In the structure of mortality from all causes, the share of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) accounts for 55-57%.
Every year, about one million two hundred thousand Russian citizens, mostly men, die from CVDs. Over the last five years, there has been a trend towards a decrease in cardiovascular mortality, however, we are still ahead of European countries: 753 Russians died versus 200 Europeans out of 100 thousand population. How many people actually suffer from atherosclerosis is completely unknown. Atherosclerotic plaques are found in the blood vessels of infants and young men. Thus, almost a third of American soldiers who died in Korea had widespread atherosclerotic vascular disease without any clinical manifestations.
What it is
Atherosclerosis of the aorta is a chronic disease in which cholesterol plaques form on the wall of this vessel.
As a result, the lumen of the aorta narrows and blood flow becomes difficult, and this, in turn, leads to an increase in blood pressure and a deterioration in the blood supply to the body. Since the aorta is the largest blood vessel in the human body, pressure surges in such cases can be life-threatening.
The walls of the vessel lose their elasticity and degenerative changes begin in them, which often lead to life-threatening conditions, which we will discuss later.
Manifestations
Blockage of a vessel by an atherosclerotic plaque can occur at any segment of the vessel. In this case, the symptoms may differ slightly, but the following symptoms remain common:
- weakness;
- heartache;
- headache;
- increased sweating;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- increased heart rate;
- loss of consciousness;
- decreased sensitivity of the limbs;
- dizziness.
Depending on the location of the cholesterol plaque, these manifestations may be accompanied by other symptoms. Thus, when it forms in the ascending aorta, the patient may experience attacks of nausea and vomiting, severe pain in the sternum, unstable blood pressure, shortness of breath, which worsens when lying down, impaired swallowing function, and fainting.
Complications of such localization of aortic atherosclerosis are cardiac ischemia, angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. If the fatty deposit is localized in the area of the aortic arch, the patient may notice severe pain in the chest, which intensifies with physical exertion and emotional stress. It is fraught with complications such as cerebral ischemia and ischemic stroke.
If the atherosclerotic process affects the descending aorta, then the patient experiences a feeling of chest compression, increased blood pressure, and rapid pulsation in the right side of the chest. When the abdominal aorta is blocked by an atherosclerotic plaque, the patient encounters such manifestations as:
- pain in the stomach and intestines;
- loss of appetite;
- numbness of the lower extremities;
- swelling of the legs;
- intermittent claudication;
- decreased potency;
- weight loss;
- bloating and flatulence;
- constipation.
Causes
Experts identify several main causes of AA, although their opinions regarding the priority of one or another factor differ. Simply put, doctors have not yet come to a consensus which of the reasons listed below is most important. However, we can say with confidence that the more risk factors are combined in an individual patient’s history, the higher the risk of developing AA.
The main causes of atherosclerosis of the aorta:
- Stress. At first glance, what could be the relationship between nervous tension and cholesterol deposits in blood vessels? Meanwhile, it exists, and it is the most direct one. According to the neuro-metabolic theory of A.L. Myasnikov, nervous stress leads to disruption of the neuroendocrine regulation of protein-lipid metabolism. The result is hypercholesterolemia - increased cholesterol in the blood. It is these excesses that are deposited on the inner walls of blood vessels.
- Arterial hypertension. With a persistent increase in blood pressure, hemodynamics change, as a result of which acidic mucopolysaccharides gradually accumulate in the walls of the aorta.
- Unbalanced diet. Eating fatty foods in large quantities increases cholesterol levels in the blood. In obese people, the risk of aortic atherosclerosis increases many times over.
- Endocrine factor. In diabetes mellitus, lipid metabolism disorders occur, which lead to hypercholesterolemia. In addition, it has been experimentally proven that estrogens reduce blood cholesterol levels. Probably due to the higher levels of these hormones in women, AA occurs at an older age.
Figure 1. Levels of atherosclerosis.
Source: Betty1994 / Depositphotos 5. Genetic predisposition. This issue causes controversy among experts. However, in people whose close relatives suffered from vascular defects, cases of AA are observed more often. Opponents of this theory insist that additional research must be conducted to confirm it and form an evidence base.
6. Blood clotting disorder. Fibrin and fibrinogen are part of cholesterol plaques, which often form in those places where the blood clot is adjacent to the wall of the vessel.
7. Smoking. Doctors agree that smoking increases the risk of AA, but the reasons for this are explained differently. Some experts believe that the prerequisites for AA in smoking patients develop due to disturbances in regional blood flow, others believe that nicotine causes a deterioration in the condition of the vascular wall.
The process of formation of atherosclerotic plaques
At the first stage, a lipid stain appears in the intima of the vessel - a deposition of cholesterol circulating in the blood, attached to proteins. The complex of cholesterol with a protein transporter is called lipoprotein. Contrary to fears, a very small part of cholesterol comes from junk food, and 80% is created in the body “from improvised substances.” Not all fractions of cholesterol are deposited in the intima, but only low lipoproteins (LDL) - these are “bad cholesterol”. “Good cholesterol” is called high-density lipoprotein (HDL). They do not linger in the vascular intima, and they also take excess cholesterol with them. At the lipid stain stage, there is no need to damage the epithelium; in fact, it forms in a clean place.
At the second stage, the spot’s own immune cells come to the spot and try to pull out “bad cholesterol” from the inner lining. These are macrophages that swallow all “garbage” and carry it out. A direct representative of the macrophage family, xanthoma cells are designed to devour lipoproteins. If less lipids are excreted than are supplied, then the spot turns into a plaque. And the loose masses inside the deposit are created by xanthoma cells that die from gluttony of fats. That’s why atherosclerosis was called “hard porridge” in Greek.
By absorbing lipoproteins, immune cells release biologically active substances, helping to form scar - connective tissue that helps strengthen the defect. Immune defenders - T-lymphocytes, on the contrary, try to suppress cell growth by releasing their biologically active substances. There is a constant struggle inside the choroid, so not all lipid spots grow into plaques.
But if the plaque grows, then over time its own vessels begin to grow into it - the vessels of the blood vessels.
Blood vessels burst, forming microhemorrhages, attracting leukocytes into the plaque, which create the ground for inflammation. Against the background of this active life, the plaque becomes overgrown with calcium, blood clots form and accumulate on the irregularities, which become denser and fuse with the plaque, gradually blocking the lumen of the vessel.
Every year, about one million two hundred thousand Russian citizens, mostly men, die from CVDs. Over the last five years, there has been a trend towards a decrease in cardiovascular mortality, however, we are still ahead of European countries: 753 Russians died versus 200 Europeans out of 100 thousand population. How many people actually suffer from atherosclerosis is completely unknown. Atherosclerotic plaques are found in the blood vessels of infants and young men. Thus, almost a third of American soldiers who died in Korea had widespread atherosclerotic vascular disease without any clinical manifestations.
Risk group
The risk group primarily includes men over 50 years of age who are overweight or obese. This also includes patients:
- with bleeding disorders
- with diseases of the endocrine system;
- with a hereditary predisposition (a history of cases of AA in close relatives);
- with arterial hypertension and other diseases of the cardiovascular system.
A separate group includes people whose work involves nervous tension. If a person tries to deal with stress by smoking or overeating, this significantly increases the risk of developing AA. In other words, the more risk factors identified in an individual patient, the higher the likelihood of cholesterol plaques being deposited on the inner wall of his aorta.
How a vessel is damaged
This is important to know, because without understanding the process of formation of the atherosclerotic beginnings - plaques, it is impossible to tune in to the prevention of atherosclerosis. The creation of a plaque is closely related to our lifestyle; only conscious motivation will allow us to understand what needs to be changed in our personal life so as not to end up in a hospital bed prematurely, or worse. At the moment, there is no single scientific theory of the occurrence of atherosclerosis; about a dozen options are proposed to explain the development of the pathological process.
The creation of atherosclerotic deposits in a separate vessel is carried out in several stages, during which opposite processes simultaneously occur in the vascular intima. Lipoproteins and immune cells penetrate and are simultaneously excreted, entire cell clones multiply and die, intercellular substance is formed and disintegrates, blood vessels grow and calcification occurs. All these processes find their expression in the formation of a dense atheromatous plaque. Atherosclerosis in Greek is a hard paste.
The inside of the vessel is covered with single-celled endothelium, which, together with the underlying connective tissue, forms the inner lining - the intima, which is in direct contact with the blood flow. The middle shell of the vessel is represented by smooth muscle cells immersed in the intercellular substance with elastic membranes. Next comes loose fibrous connective tissue with many elastic and collagen fibers - adventitia or the outer lining of the artery.
Make an appointment with a cardiologist today
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Symptoms
The most common symptom is aortalgia, which is pain in the aorta. It can be both pressing and burning, but its intensity is always high. Such pain is not always associated with physical activity. It can last from several hours to several days. In rare cases, an atypical pain syndrome is observed, when pain first appears in the back or on the sides of the chest.
Figure 2. Aorta in the heart. Source: Blausen.com staff (2014). "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2)
Other symptoms:
- paresthesia (tingling, goosebumps);
- fainting;
- attacks of dizziness;
- xanthoma and xantheplasma - the appearance of yellowish cholesterol plaques on the skin (more often on the skin of the face and eyelids);
- bloating and stool retention;
- blood pressure surges;
- numbness of the limbs;
- weight loss (as a result of digestive disorders);
- difficulty swallowing.
Aortalgia itself should be a reason for an urgent visit to the doctor. If it is combined with any of the symptoms listed above, there is every reason to call an ambulance.
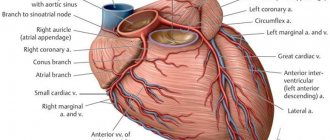
How the heart is supplied with blood
The heart muscle works constantly and needs good blood supply.
To satisfy its needs, two coronary arteries approach it, originating from the aorta. The right vessel is responsible for the blood flow of the posterobasal region, septum and right ventricle. The rest of the myocardium receives oxygen and nutrition from the left artery, which branches into the anterior interventricular branch (LAD) and the circumflex. Venous blood is collected through the coronary veins into the sinus, which is located in the right ventricle. If there are plaques in the lumen of the arteries, then the heart experiences an increased need for oxygen, which increases during physical activity. Without receiving what it needs, the muscle begins to die. Angina pectoris, cardiosclerosis and necrosis develop.
Complications
One of the most common and dangerous complications of AA is the formation of an aortic aneurysm. This is a protrusion in the wall of the vessel, which over time ruptures under the pressure of the blood flow, and as a result of extensive internal hemorrhage, patients in most cases die. The main danger of an aortic aneurysm is its asymptomatic course, which makes diagnosis difficult.
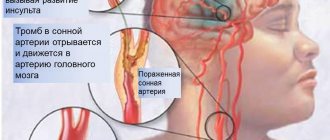
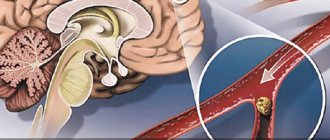
As a result of impaired blood supply to the brain, a stroke (both ischemic and hemorrhagic) can occur, which, in turn, leads to impaired speech function, paresis and paralysis, and death.
Another dangerous complication of AA is thrombosis of the mesenteric arteries, which supply blood to the abdominal organs. Emerging areas of intestinal necrosis due to insufficient blood supply contribute to the rapid development of peritonitis.
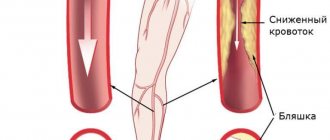
With thrombosis of the abdominal aorta in the area of its branching, the blood supply to the lower extremities is disrupted, which can be fraught with the development of gangrene of the legs.
There is also a risk of myocardial infarction, which can occur as a result of embolism (blockage) of the coronary vessels by a detached atheromatous plaque.
Patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system belong to a high-risk group - complications associated with atherosclerosis occur especially often in them.
Classification of the disease
Experts distinguish 3 stages of the disease:
- Initial. At this stage, a fatty spot appears in the aorta, the vascular wall loosens, and it swells. Special enzymatic substances are capable of providing vascular protection and dissolving lipids, but their resources are depleted over time. Pathology in the lipid spot stage can be detected during diagnosis even in infants.
- Average. At this stage, lipid deposits grow and a plaque is formed, consisting of fats and connective tissue fibers. At this stage, the plaques are still liquid. They can be dissolved. The main danger is the looseness of the plaques. The deposits can rupture and block the artery.
- Heavy. At this stage, the plaque thickens due to calcium salts and can grow and narrow the lumen of the artery. This leads to blockage of the vessel. The development of tissue necrosis, gangrene of an organ or limb cannot be ruled out.
Diagnostics
Source: US Army photo by Jason W. Edwards / DVIDS
If a person experiences symptoms such as sharp pain in the chest, dizziness, difficulty swallowing and numbness of the limbs, he has every reason to suspect the development of atherosclerosis. When contacting a doctor, you should talk in detail about all manifestations of the disease. Based on the patient’s complaints and data obtained during the examination, the specialist can make a preliminary diagnosis, to confirm which a number of diagnostic studies are prescribed.
The emphasis is on hardware diagnostic methods:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- angiography;
- aortography;
- CT or MRI.
Additionally, a blood test is prescribed to determine the level of total cholesterol, lipoproteins and triglycerides. In combination with medical history data, the research results make it possible to make a final diagnosis and begin therapeutic measures.
Treatment of aortic atherosclerosis
Depending on the severity of AA, treatment can be conservative or surgical. It should also be understood that it is very important to follow a special diet, without which the treatment will not be effective.
Medication
To stop the development of atherosclerosis, several groups of drugs are used:
- Statins (mevastatin, fluvastatin, pravastatin). They inhibit cholesterol synthesis, have an anti-inflammatory effect, and improve the condition of the inner wall of blood vessels.
- Fibrates (fenofibrate, gemfibrozil, bezafibrate). Increase the activity of lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme that breaks down lipoproteins. They also accelerate the metabolism of cholesterol in the liver and have an antithrombotic effect.
- Bile acid sequestrants (colestipol, cholestyramine). They slow down the absorption of bile acids in the intestines, as a result of which the level of lipoproteins and total cholesterol in the blood decreases by 10-20%.
- Antiplatelet agents (ticlopidine and clopidogrel). Reduce the tendency to thrombus formation and reduce blood viscosity. Drugs of this group are used in the treatment of AA to prevent parietal thrombus formation.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe symptomatic treatment aimed at normalizing blood pressure and liver function. If necessary, the course of treatment can be supplemented with efferent therapy (enterosorption, hemosorption, LDL-immunosorption).
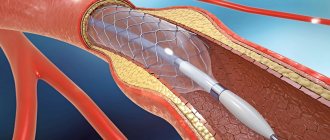
Surgical
In cases where cholesterol plaques grow so large that they damage the inner lining of the aorta and create a noticeable obstacle to normal blood flow, surgical treatment is resorted to. The mechanical obstacle (plaque) is removed along with the affected area of the inner lining of the aorta.
If it is necessary to expand the lumen of the aorta, a stent is installed - an elastic structure made of plastic or inert alloys that follows the shape of the vessel.
Diet
Source: Racool_studio / ru.freepik.com
It is necessary to significantly limit the consumption of foods rich in animal fats. Beef, lamb and pork should be replaced with poultry and sea or freshwater fish. It is also necessary to eat vegetables, herbs and fruits in large quantities - the recommended amount is five pieces a day.
Butter should be replaced with olive oil or any other vegetable oil to taste. It is also necessary to increase the amount of dietary fiber in the diet. For this, flax seeds are suitable (which, among other things, help reduce cholesterol in the blood), as well as granulated food bran, which can be bought in almost any supermarket.
Sclerosis of the aortic arch
Continuing the topic of atherosclerosis, in this article we will talk about the pathology of the aortic arch.
The structure of the aorta is such that each part of it is indispensable for the stable functioning of each organ. Therefore, pay attention to your well-being.
A headache, upset stomach, or even a cough can be a sign of change. The formation of blood clots in the blood vessels disrupts blood pressure, causing chronic symptoms to develop.
The disease and its diagnosis
The arch of the main artery is divided into three branch vessels: the brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid artery, the left subclavian artery.
With atherosclerosis of the aortic arch, the upper part of the body suffers. Impaired blood supply to the brain is fraught with the death of neurons in severe stages.
Symptoms affect the psycho-emotional state of the patient. Chronic headaches, insomnia, confusion, and mood swings are a consequence of high blood pressure and lack of oxygen in the brain.
Atherosclerotic plaques spread in the upper extremities, gradually filling the arteries, and at a severe stage they can completely block blood access. The most common complaints are cold hands, aching pain, and pallor of the skin and a decrease in the amount of hair are visually noticeable.
The structure of the aortic arch has a descending part, which is divided into two sections: thoracic and abdominal. Atherosclerosis of the chest develops gradually, in stages. First, fats and metabolic products accumulate in the vessels, forming a fibrous plaque.
Gradually, the plaques grow, forming smooth muscle tissue that absorbs lipids. On fluorography, the pathology forms a dark spot. Pressure increases, blood vessels are damaged, which provokes coughing, shortness of breath and a burning sensation in the chest.
The abdominal reaction is accompanied by pain and digestive problems. A great danger is aneurysms that arise due to the growth of fibrous tissue. The vessel cannot withstand the load and bursts, and subsequently hemorrhage is inevitable.
Doctors' recommendations and treatment
Most patients with atherosclerosis simultaneously suffer from diabetes and obesity. Doctors strongly recommend monitoring your diet by following a diet.
It is necessary to improve your metabolism by eliminating fatty foods. Avoid daily consumption of fast food cafe products.
Avoid foods high in fat: margarine, homemade milk, sour cream, fatty meat with skin. Use vegetable oils for cooking such as olive, sunflower, flaxseed. Eat more vegetables and fruits.
Oven-baked chicken or turkey will fit perfectly into the menu. Also, do not forget about the benefits of fish. In a strict version of the diet, it is advisable to avoid eating eggs, as they contain fats and cholesterol.
To successfully combat the formation of plaques in blood vessels, drugs are prescribed: statins and fibrates (reduce the level of fats in the blood), fish oil (strengthens the walls of blood vessels and prevents the increase in cholesterol), Niacin or Nicotinic acid (involved in lipid metabolism).
Together with diet, an active lifestyle and modern medications, it is possible to live a full life with atherosclerosis.
Next time we will talk in detail about traditional methods of treating the aortic root.
Forecast
With timely detection of AA, properly selected conservative therapy, as well as adherence to a special diet in combination with lifestyle correction, the prognosis is favorable. In cases where AA is detected at late stages, in which severe complications such as aortic aneurysm or thrombosis of the mesenteric arteries are noted, the prognosis is significantly aggravated.
Prevention involves strict adherence to diet, normalization of body weight and cessation of bad habits (primarily smoking). It is important to avoid a sedentary lifestyle, however, physical activity should also be dosed. To begin with, the patient is recommended to walk for at least 30 minutes a day, then their duration increases as endurance develops. After a few weeks, you can add complexes of therapeutic exercises or swimming in the pool.
It is important to avoid stress and minimize psycho-emotional stress. In addition, it is necessary to carefully monitor the pressure - it should not exceed 130/85 mm Hg. Art.