Numbness is an abnormal sensation that can occur in any part of the body, but is most often felt in the arms and legs. The symptom of numbness is often accompanied by tingling, and can be quite harmless, for example, in the hands when cooling, to a sign of a serious, life-threatening condition. Numbness is a fairly common symptom. Numbness of the limbs is often accompanied by an emotional context with a feeling of detachment and decreased emotional coloring, which is usually a sign of depression. In a physical context, numbness is usually the result of damage, poor circulation, or pathological changes to certain nerves.
In addition, there may be periodic attacks of numbness and tingling due to the presence of certain health problems, such as neuroses or a migraine attack. Also, episodes of numbness can occur during attacks of fear caused by the anticipation of life-threatening events, and in such cases the numbness is caused by shallow breathing and most often affects the fingers and the mouth area.
Numbness of the hands is manifested by a feeling of loss of sensation in the hands; patients often call this condition “asleep” hands. Numbness may be accompanied by a tingling sensation from the needle. Often such numbness occurs after sleeping with your hands under your head. Numbness in the hands is usually caused by carpal tunnel syndrome, which causes compression of the median nerve. Most often, carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by compression of the nerve in the carpal tunnel. In addition, numbness in the hands can be caused by injuries, hypothermia, or systemic diseases such as diabetes. If numbness of the hands is accompanied by shortness of breath, nausea, and palpitations, then this may be a sign of acute, life-threatening conditions and requires emergency medical attention.
Numbness in the legs is a loss of feeling or sensation in the legs, resulting from disruption of communication between the peripheral nerves and the central nervous system. Typically, numbness in the legs is associated with poor circulation in the lower extremities. This numbness most often occurs when sitting cross-legged for a long period of time. In such cases, getting up and walking can relieve the numbness after a while. But numbness in the legs can also be a sign of serious damage to nerve fibers due to mechanical factors (disc herniation, radiculopathy) or nerve damage due to somatic diseases.
Causes of numbness
Both physiological and pathological factors can provoke hand numbness.
Temporal or physiological factors
Physiological (temporary) causes of numbness include:
- Spending a long time in a position where one arm is thrown over the armrest. This leads to pressure on the nerve endings, which causes some discomfort.
- Carrying a heavy bag or backpack. In this case, the pressure will be exerted by its straps. Numbness occurs due to impaired blood supply to the limb.
- Wearing clothes that are too tight.
- Frequently raising your arms above your shoulders.
- Spending a long time in the cold. Numbness occurs due to vascular spasm.
All of these factors do not pose any threat to health. To prevent numbness, you need to change your position more often, massage the limb, do light exercises, and change the position of your backpack or bag. The danger comes from pathological causes that lead to numbness in the hands.
Pathological factors
Fingers may become numb due to pinching of nerve endings and blood vessels in the wrist area. Connective tissue can put pressure on them. If the numbness goes away quickly after a change in position, or after rubbing the tissues, then this symptom can be ignored. If numbness occurs frequently, persists for a long time, and it is not possible to cope with it with massage and changing posture, you need to consult a doctor. Such a symptom may indicate pinched nerve fibers or a disruption in the blood supply to tissues.
The reasons can be very serious. Among them:
- Polyneuropathy. This pathology is accompanied by damage to the nerve trunks of the peripheral nervous system. In addition to numbness, the patient will develop weakness in the hands, and their tissues will begin to atrophy, that is, dry out. The patient suffers from cuts (partial impairment of movement). Sometimes paralysis is observed, that is, the functions of the limb will be completely lost. The cause of polyneuropathy may be diabetes mellitus, alcoholism, diphtheria, hemoblastosis, porphyria, periarteritis nodosa, systemic lupus erythematosus.
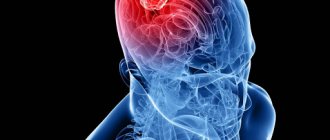
- Stroke. With this pathology, there is a disruption in the nutrition of the brain. Ischemic stroke most often leads to numbness of the extremities. People's hands go numb at rest, and tingling occurs in them.
- Neuroses.
- Shingles.
- Damage to the nerve nodes of various parts of the spine. The cervical, shoulder, and lumbosacral regions may be affected. With such pathologies, in addition to numbness, a person will suffer from pain. It will be localized in those places for the innervation of which the affected nerve plexuses are responsible. The most common pathology is osteochondrosis.
- Median nerve lesion syndrome. This pathology is called pronator syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome, etc. Numbness occurs as a “monkey hand”. The surface of the first finger on the palm side and the entire 2, 3 and 4 fingers of the hand suffer.
- Damage to the ulnar and radial nerves, which can be observed with Turner syndrome and other pathologies.
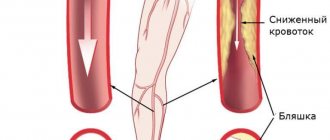
- Vascular damage. Obliterating endarteritis often leads to numbness. With this pathology, microcirculation in small blood vessels is disrupted. This happens against the background of their spasm. Numbness resembles the clinic of osteochondrosis.
- Raynaud's disease. Numbness occurs in the hands and feet. It appears in paroxysms, the cause being a violation of blood circulation in the vessels. Raynaud's disease can be inherited, and severe stress can trigger its manifestation.
- Vitamin deficiency. Numbness develops in people whose bodies lack B vitamins, namely thiamine, folic acid, and cyanocobalamin. Numbness can also develop due to vitamin E deficiency.
- Vibration disease. Numbness is a companion for people who often experience vibrations. In addition to regularly receiving microscopic injuries, such individuals develop pathological reflexes. This causes pain and numbness.
- Injuries received. These could be fractures, bruises, dislocations. All of them contribute to disruption of the integrity of the nerves. This leads to characteristic symptoms.
- Taking certain medications. Numbness appears as a side effect. It is found in antibacterial drugs and chemotherapy agents.
In what areas can numbness occur?
If your arms and legs often feel numb, pay attention to where the loss of sensation occurs. Sometimes this criterion is of value to the doctor during diagnosis.
- Numbness of the hands and feet - observed with a spinal injury, hernia or pinched spinal nerves.
- Loss of sensation in the fingers - occurs with carpal tunnel syndrome, when the nerve is compressed by swollen muscles.
- Numbness in the arm and leg at the same time indicates serious disorders in the body. The causes may be neurological, orthopedic and vascular.
- Numbness combined with dizziness - the most common cause is neuralgia.
- Numbness of the limbs and face - here one should suspect damage to the brain or blood vessels. Consultation with a doctor is required.
- The right arm and leg are numb - a one-sided lesion indicates pinched spinal nerves. Often occurs with curvature of the spine, hernias.
- Reduced sensitivity in the left arm and leg - indicates neurology, the presence of heart and vascular diseases. You should see an orthopedist. Often the cause is a curvature of the spine.
To identify provoking factors, it is necessary to analyze the characteristics of working conditions. Poor posture often contributes to loss of sensation in the limbs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hand numbness largely depend on the exact cause of this disorder.
Common signs of numbness:
- Weakness in limbs.
- Inability to hold an object.
- Tingling sensation in fingers.
- A crawling sensation.
- The appearance of goose bumps.
- Feeling of coldness of the limb.
If after 2-3 minutes the unpleasant symptoms do not go away, then a pathological cause of numbness can be suspected.
When it develops against the background of diabetes mellitus, the patient will experience symptoms such as:
- Numbness in other parts of the body.
- Extreme thirst, dry mouth.
- Frequent urge to empty the bladder.
- Visual impairment.
If a person has diseases of the joints and spine, then in addition to numbness he will be plagued by symptoms such as:
- Pain in the body and limbs.
- Numbness at night. It occurs even if the sleeping position is comfortable.
- Morning stiffness.
- Weak muscle tone.
- Tingling in the palms.
- Numbness of fingers.
Symptoms
Numbness usually occurs due to poor circulation in a particular area or nerve damage. Sensory disturbances (numbness) can also be the result of infection, inflammation, trauma and other pathological processes. In most cases, numbness is due to non-life-threatening illnesses, but it can also be a sign of a stroke or tumor.
Numbness in the extremities is often associated with pain or may be accompanied by other sensory disturbances such as burning or tingling. Strokes also cause motor and speech disorders. Depending on the cause, numbness may disappear quickly, for example, numbness in the arm , which occurs when a person sleeps with their head on their arm, disappears after a few movements of the arm. Chronic numbness in a leg or arm over a long period of time usually indicates some level of nerve damage, such as due to diabetes or multiple sclerosis. Chronic numbness in the fingers may be due to a pinched nerve, as is the case with carpal tunnel syndrome. In any case, numbness that lasts more than a few minutes merits attention and medical attention. And if a person experiences numbness in the groin area and impaired bladder and bowel function, or there are signs of paralysis, confusion, speech impairment, then in such cases it is necessary to seek emergency medical help.
Symptoms that may accompany numbness:
- Anxiety
- Burning feeling
- Frequent urination
- Increased numbness or tingling while walking
- Itching
- Lower back pain
- Muscle spasms
- Pain in the neck
- Pain in other parts of the body
- Pins and needles sensation
- Rash
- Increased sensitivity to touch
A number of symptoms accompanying numbness may be a sign of serious conditions and this must be taken into account by the doctor, since emergency medical care and necessary medical procedures are often required.
These are the following symptoms:
- Lethargy or momentary loss of consciousness
- Labored breathing
- Difficulty walking
- Dizziness
- Loss of control over voluntary urination or bowel movements
- Visual impairment
- Numbness in the head, neck, back
- Paralysis
- Speech disorders (dysarthria)
- Weakness
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
Numbness as a symptom cannot be ignored. Sometimes it becomes the first sign of the development of a serious disease. Numbness often accompanies a stroke. Therefore, you should not hesitate to contact a specialist. If numbness occurs frequently, you should contact a neurologist.
When to visit a doctor:
- There is no way to explain why the numbness occurs.
- Painful sensations appear in the forearm, fingers, and neck.
- The urge to urinate becomes more frequent.
- A rash appears on the body or limb.
- Numbness is accompanied by dizziness, muscle dysfunction and other symptoms.
- Large areas of the body are involved in the pathological process.
- Numbness is bilateral.
A very common manifestation of diseases of the nervous system and musculoskeletal system is numbness . Treatment of this problem can sometimes be very difficult due to the many factors that cause it and the difficulty in treating the underlying pathology.
WHAT IS NUMBITY AND HOW DOES IT OCCUR?
The human brain must constantly receive information from the environment. This is accomplished through receptors, of which there are a large number. These receptors permeate all our tissues, including the skin of the upper and lower extremities. A person’s ability to sense various irritations through receptors is sensitivity, and numbness
- This is a sensory disorder. Receptors with the property of irritability convert this irritation into nerve impulses, which are sent along centripetal fibers to the brain for analysis, bypassing many structures along the way. And a violation in any of these structures leads to sensitivity disorder (numbness).
In medical classifications , numbness
refers to a type of sensitivity disorder such as paresthesia, which includes, in addition to numbness, some other unpleasant sensations. Such unpleasant sensations include: tingling, burning, crawling sensation.
The distal parts of the body, that is, the limbs, are most often affected by numbness. “I have numbness in my hand and fingers,” is such a common complaint, yet people so rarely seek medical help. More often, these symptoms occur at night, when a person wakes up from the fact that his entire hand, or only his fingertips, are numb. This can happen at any time and under any conditions, however, depending on a particular disease, the symptoms will still change. Let's look at some characteristic symptoms that relate to one or another disease.
SYMPTOMS OF NUMBENCY IN VARIOUS DISEASES
Numbness in spinal osteochondrosis and discogenic disorders
With osteochondrosis of the spine, damage to bone structures and intervertebral discs occurs due to degenerative-dystrophic processes. Protrusions and herniations of intervertebral discs will play a key role in impaired sensitivity (numbness). How does this process happen? A hernia or protrusion compresses the spinal roots, or the nerve itself, which exits the intervertebral foramen. As is known, the nerves contain sensory fibers from the corresponding dermatomes. From the dermatomes of the upper extremities - this is the cervical spine, from the lower extremities - the lumbar spine. Nerves compressed by spinal hernias lose their ability to conduct impulses and this is how numbness
. This type of sensitivity disorder is characterized by concomitant vertebrogenic pain syndromes, muscle weakness, stiffness and difficulty moving.
Numbness due to Raynaud's disease
Raynaud's disease is a numbness of the fingertips of both hands, which is often provoked by cold, and they first acquire a pale tint, and then turn blue and become red-purple. All these symptoms relate to Raynaud's disease, which is associated with impaired blood circulation and filling of the smallest vessels (arteries and arterioles) of the distal (end) parts of the fingers. This disease is 5 times more common in women. If the above symptoms of numbness occur, you should contact a neurologist and rheumatologist, who will rule out diseases of the cervical spine or a concomitant autoimmune process and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Numbness due to carpal tunnel syndrome
The following disease is characterized by numbness of the first three fingers of the hand - these are the first, index and middle fingers of the hand. There may also be tingling and soreness that can spread to the entire hand. The condition for the occurrence of numbness in this pathology can be monotonous work of the hands, for example, in a programmer, seamstress, and so on. The pathogenetic cause of this condition is compression of the median nerve in the canal, which is formed by the ligamentous and muscular apparatus. As a result of increased pressure in the wrist, compression of the venules and arterioles supplying the epineurium of the median nerve occurs. Subsequently, intraneural edema forms, myelin fibers are affected and the above symptoms occur (in particular, numbness
). This disease is 2 times more common in women and in obese people. To make a diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome, it is necessary to perform specific test symptoms and exclude radiculopathy of the cervical spine and brachial plexus diseases.
Numbness due to polyneuropathy
Polyneuropathies are characterized by numbness and impaired sensitivity of the distal (end) parts of both the upper and lower extremities. Symptoms such as tingling, itching, swelling, a feeling of “cotton wool” in the legs while walking, and lack of temperature sensations may also occur. Impaired temperature sensations in patients are manifested in the identification of burns on the hands, unsteadiness of gait in the dark, the presence of painless ulcers and peeling of the skin, especially on the dorsum of the lower limb. Major diseases that can lead to polyneuropathy and sensitivity disorders ( numbness
), these are: diabetes mellitus (thirst will also be observed), consequences of operations (laminectomies), drug intoxication, drug addiction, toxic effects of various substances in case of poisoning. Alcohol abuse can be identified as a special group. This is the so-called alcoholic polyneuropathy.
In all these conditions, the nerve sheath is affected, resulting in loss of sensation (numbness).
Numbness due to scalene syndrome
The name of the syndrome indicates the scalene muscle, which is where the pathology is formed. This muscle is attached to the first rib and lower cervical vertebrae, forming an opening through which the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus pass, innervating the upper limb. With cervical osteochondrosis, the scalene muscles are spasmed and cause compression of the subclavian artery and branches of the brachial plexus. As a result, blood flow and innervation of the upper limb decrease, and the hand suffers the most, because it is there that we feel this unpleasant symptom - numbness
. Treatment also occurs after a full examination.
Numbness in ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack
With ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack, there is a disruption of blood circulation in the brain with damage to its structures. Numbness during an ischemic stroke is not difficult to suspect, since it will be characterized by damage to half of the body, for example, the right arm, right leg, or, on the contrary, symptoms such as paresis and paralysis in these or opposite limbs (movements in them are impaired). It all depends on the localization of the pathological process; there may also be visual impairment, speech impairment, memory loss, and so on. In these cases, you should immediately seek medical help for timely provision. The situation is different with a transient ischemic attack, in which symptoms tend to occur unnoticed with low intensity and pass over time. Numbness during a transient ischemic attack persists and the patient, without giving it much importance, usually seeks medical help less often, which can aggravate the condition and then, most likely, a transient ischemic attack will develop into an ischemic stroke, which already directly threatens the patient’s life.
Numbness in demyelinating diseases
Demyelinating diseases are, as a rule, hereditary diseases that affect the nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord, or the nerve trunks themselves. With these types of diseases, symptoms can be very diverse: from local lesions with numbness of one finger or the whole hand, to mosaic lesions with numbness in various areas of the body. This lesion is characterized by persistent symptoms with possible increasing dynamics. As with other pathological conditions, consultation with specialists and a thorough examination are necessary.
CAUSES OF NUMENCE
Considering the symptoms described above, it is worth summarizing the conditions that can provoke its appearance:
- osteocondritis of the spine;
- pinching (compression) of the roots of the spinal nerves, trunk or branches of the corresponding nerves along the course of innervation;
- discogenic disorders;
- Raynaud's disease;
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- demyelinating diseases;
- ischemic stroke;
- transient ischemic attacks (TIA);
- scalene muscle syndrome;
- polyneuropathy (diabetic, alcoholic);
- hypothermia;
- injuries;
- tumor lesions of both the brain and spinal cord, as well as structures adjacent to the trunk or branches of the nerves along the innervation to the site of numbness.
TYPES OF NUMENCE
Numbness of the limbs
The upper and lower extremities become numb quite often. This may indicate temporary compression of the nerve, or the presence of vascular or endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus). It is important to seek help in time and find the cause of the disease.
Numbness of the hand
The hand also becomes numb quite often. The most common cause of this condition is compression of the nerves or blood vessels in the hand area, as well as the median nerve. The consequences of such a pathology can be quite serious.
Numb hand
The most common cause of this pathological condition is pinching of the neurovascular bundle by the muscles and connective tissue. The condition is very unpleasant, as the activity of the entire limb is partially impaired.
Numbness of fingers
Carpal tunnel syndrome is often involved in the occurrence of numbness in the fingers. Damage to the cervical spine may also be the cause. If the fingers of both hands are affected at the same time, we can talk about Raynaud's disease and other causes. Interestingly, at the end of the last century, numbness of the fingers was extremely rare, but now it is one of the fairly common symptoms.
Numbness of the leg
Quite often it occurs in young, working people and this type of numbness is often associated with professional activities. In addition to numbness, there is often a crawling sensation in the legs. Damage to the lumbar and sacral spine is one of the main causes of this symptom.
Numb toes
There are many reasons why the toes go numb: these include spinal diseases, diabetic polyneuropathy, alcohol abuse (alcoholic polyneuropathy), and vascular problems. The pathology is very unpleasant, especially for the female population.
PREVENTION
Prevention will consist of eliminating factors that lead to diseases accompanied by numbness. Loss of sensation ( numbness)
) is already a consequence of a pathological process that has arisen in the body. To avoid these diseases, it is necessary, first of all, to undergo courses of preventive examinations from specialists who will be able to identify diseases hidden about the symptoms of numbness in the early stages. In addition, eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, control your sugar levels and numbness can be avoided.
DIAGNOSTICS
For any type of sensitivity disorder, consultation with a specialist and a thorough examination are necessary. It is quite difficult to determine the cause of numbness on your own without auxiliary methods, especially when this process is caused by a huge number of diseases.
To diagnose numbness, almost all known examination methods are used: survey, visual and manual examination, radiography, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, angiography, myography, as well as laboratory tests (blood tests for inflammation, glucose levels). It is very important to conduct a full diagnosis of numbness; treatment should be appropriate.
Which doctor treats hand numbness?
If numbness occurs, you should contact a neurologist. The doctor will examine the patient, clarify his complaints, and evaluate the presence of other neurological signs.
If the doctor deems it necessary, he will refer the patient to other specialized specialists:
- Patients with vasculitis and Raynaud's disease are referred to a rheumatologist.
- People with suspected cardiovascular disease are referred to a cardiologist.
- Patients with diabetes are referred to an endocrinologist.
- Patients with injuries and tumors are referred to a neurosurgeon.
- Patients with infectious diseases are referred to an infectious disease specialist.
- Patients who have been exposed to harmful substances in the workplace are referred to an occupational pathologist.
Treatment of sensitivity disorders
Therapy depends on the disease that caused the pathology. For example, if the diagnosis reveals osteochondrosis, at the Professor Gorbakov Clinic in Krasnogorsk they prescribe:
- medications - anti-inflammatory drugs, decongestants and angioprotectors;
- manual therapy, massage and other local treatments;
- physiotherapy – “magnets”, UVT, laser;
- exercise therapy;
- acupuncture, vacuum therapy.
If a disorder of skin sensitivity occurs due to a hernia or protrusion, chondroprotectors are prescribed to strengthen the tissues of the intervertebral discs.
The choice of physiotherapeutic methods in the clinic is also carried out depending on the underlying cause. For example, for diabetes mellitus, electrophoresis of nicotinic acid and zinc in the iliac region is indicated, and for multiple sclerosis, magnetic laser irradiation, cryotherapy and massage are indicated. Very often, doctors recommend treating skin sensitivity disorders by supplementing the diet with vitamin B12 and folic acid, the deficiency of which causes the syndrome.
Diagnosis of the problem
The patient's appointment begins with a questioning, which is of no small importance in diagnostic terms. A thorough medical history allows the doctor to suspect the causes of numbness in the hands. After the interview, the doctor begins to examine the patient. During its implementation, it is important to evaluate skin color, its temperature, tendon reflexes, and skin reflexes.
Based on the data received, the doctor refers the patient for further examination, which may include:
- Donating blood for general and biochemical analysis.
- Submission of urine for general analysis.
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- X-ray of the skull and spine. The study is prescribed if there is a suspicion of an intervertebral hernia or other disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
- Vascular angiography using contrast.
- CT. This study provides maximum information about the condition of the organs. It can be used to detect hematomas, aneurysms, blood clots, circulatory disorders, etc.
- MRI. It is prescribed when the doctor suspects vascular compression.
- Electroneuromyography. This study allows us to identify innervation disorders. Diagnostics are carried out using special electrodes.
After the patient has completed the necessary tests, the doctor will be able to give him an opinion on his state of health and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
Based on the medical history, study of symptoms and physical examination, the doctor prescribes an examination plan, which includes both instrumental and laboratory examination methods.
To treat numbness, first of all, it is necessary to find out the cause of this symptom. If numbness is associated with circulatory disorders, diabetes or multiple sclerosis, the underlying disease is treated, both with the help of conservative treatment methods and surgical methods (for example, for vascular diseases). For orthopedic problems, such as disc herniation, osteochondrosis, treatment can also be either conservative or surgical (for example, when it is necessary to decompress the nerve root).
Treatment of hand numbness
To cope with numbness in the hands, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment. Therapeutic measures include therapeutic sets of exercises, as well as certain procedures. They are aimed at improving tissue nutrition and increasing blood circulation in the extremities.
Possible treatment options:
- Physiotherapeutic effects on the body: phonophoresis and electrophoresis. Thanks to these procedures, blood flow is activated, so medications penetrate better into damaged tissues.
- Manual therapy. Working out active points allows you to get rid of excess pressure on nerve endings. Muscle spasms go away, joint blockades are removed.
- Exercise therapy. The development of the complex should be carried out by a professional.
Drug treatment
The doctor will be able to select effective medications only after a diagnosis has been made. Medication correction alone is not enough to cope with the problem. It will be necessary not only to take medications, but also to undergo physiotherapeutic measures, exercise therapy, etc.
Drug correction is based on drugs to relieve inflammation. The treatment regimen also includes chondroprotectors, analgesics, and vasodilators.
To improve the condition of nerve fibers and accelerate metabolic processes in nervous tissue, a course of vitamins is recommended: B1, B6 and B12.
Diet therapy
Patients with hand numbness require a diet enriched with vitamins and proteins. Fresh vegetables must be present on the table: cabbage, carrots, herbs, salads. We must not forget about legumes.
You should give up cocoa and coffee. Preference should be given to green tea, herbal drinks, and mint tea.
Meat and fish should not be too fatty. Minimize the consumption of smoked and fried foods. Chicken eggs are eaten 2-3 times a week. The restrictions include cakes and baked goods.
Video: Dr. Evdokimenko, a rheumatologist and psychophysiologist, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical and Technical Sciences, will tell you why your hands or fingers go numb:
Numbness on the left and right sides of the body: what are the differences?
Numbness of the right arm or leg, simultaneous or sequential, occurs with osteochondrosis, scoliosis, herniated intervertebral discs, when the blood supply to tissues and the conductivity of nerve endings are disrupted. If this syndrome was preceded by a sensitive acute headache or injury, the cause may be much more serious - a stroke or a brain tumor.
When a sensitivity disorder is observed on the left side of the body, a person feels a tingling sensation, and the motor functions of the limbs suffer. If at the same time the facial muscles go numb, blood pressure rises, and dizziness appears, this suggests an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke or serious pathologies of cerebral circulation. Therefore, numbness on the left is considered a more dangerous symptom than on the right.
Prevention of temporary loss of sensation
Treating hand numbness can take a long time, so in order to prevent this problem, you can take preventive measures. In order for the body to be constantly in good shape, one cannot do without physical exercise. Daily moderate physical activity will help prevent the need for treatment for hand numbness. Regarding the choice of training, it is advisable to consult a doctor in this matter. The doctor can sign you up for special health-improving physical education. Remember that some physical activities can only make your situation worse. Treatment for numbness in the hands is often required when the blood vessels and joints are not in order. In order to maintain their health, you need to give up bad habits and try not to eat excessively fatty, spicy and salty foods. Heat is of great importance in the treatment of hand numbness. Try to dress appropriately for the weather and do not let your hands get cold. For clothing, give preference only to natural fabrics. If your work involves constant stress on your arms and spine, then do not forget to give yourself a little rest from time to time by doing a simple warm-up (rotation of your hands, arms, etc.). The main thing to remember is that hand numbness is a symptom, not a disease. In connection with this, it can be caused by a wide variety of diseases. Do not delay your visit to a specialist; sign up for an examination to find out the reasons for your deterioration in health.
Why do our hands sometimes go numb during sleep?
Numbness of the hands at night is a very common phenomenon. All factors that cause numbness in the hands during sleep, the treatment of which is necessary, can be divided into two large classes. The first group of factors is simple and you can get rid of it in a short time. The second group of factors is more complex; it requires an integrated approach to the problem. Numbness of the hands during sleep, the causes and treatment of which are different, can occur due to incorrect body position. The muscles become overstrained, and blood access to the muscles decreases. The result is a feeling of numbness in the hands during sleep, the causes of which are easily eliminated by selecting the right pillow. Numbness of the hands at night may develop if there are problems with the cervical spine. This is a fairly common phenomenon today, which is called osteochondrosis. Along with numbness of the hands during sleep, the causes of which are easily explained, a person may feel a pulling pain below the back of the head, radiating into the hand. Also, hands can go numb due to, as noted above, carpal tunnel syndrome. If numbness in the hands at night, the treatment of which is mandatory, does not go away after taking the correct position for an hour, then you need to call a doctor. Perhaps this is a harbinger of such a serious condition as the formation of a blood clot in an artery.
Numbness of the left hand
Paresthesias are very dangerous, since they can appear due to diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Pre-infarction state
The left arm may go numb if a person has angina. The provoking factors are as follows:
- Smoking.
- Wrong nutrition.
- Stress.
- Fatty and spicy foods.
The symptom begins with the ring finger. Then he moves to the little finger.
There are other symptoms that may indicate a pre-infarction condition:
- Pain in the heart, radiating to the collarbone or jaw.
- Anxiety, cold sweat, fear of death.
- Weakness.
- Insomnia.
- Dizziness.