Updated September 11, 2021 Author: Dmitry Ivanetscu
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. People with a normally functioning circulatory system can be easily distinguished from the general crowd.
It is the coordinated functioning and the necessary balance of all the numerous components that make up the blood that provide a person with an excellent mood, vigor, activity, fullness of strength and energy.
Let's consider the features of platelets, which are one of the three main formed components in the blood - why it needs them and what their imbalance can lead to.
What is P-LCR or large platelet ratio in a blood test and why is the content higher than normal?
Patients are interested in P-lcr in a blood test - what it is, why it is tested. Decoding this analysis allows you to obtain information about platelets that regulate clotting.
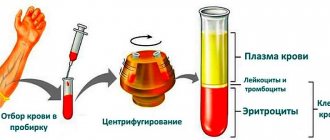
For testing, blood can be taken from a finger or from a vein in the case of an advanced analysis. Blood sampling is almost painless and rarely causes discomfort. When taking blood from a vein, the arm is tied with a flagellum, the skin is treated with a disinfectant solution and pricked with a sterile needle. When taking blood from a finger, it is disinfected with an antiseptic and pierced with a medical blade.
The material is collected in a test tube and transferred for research, which must be carried out immediately in the first hours, because then a precipitate may form and it will be difficult to determine many indices.
For the study to be accurate, you need to prepare for it. You should not eat food 8 hours before the test, so the procedure is scheduled in the morning. Blood is taken from the patient on an empty stomach.
On the eve of the analysis you cannot:
- smoke;
- drink alcohol;
- drink coffee or tea;
- take medications.
Some drugs may distort the results. If the patient has chronic diseases that require constant use of medications, it is necessary to inform the doctor about this. The doctor will explain which medications should not be taken before the procedure.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Signs of thrombocytosis, especially secondary, in the initial phase may not be recognized by the symptoms of the disease that caused it.
But if this disease is treated in a hospital setting, where blood tests are performed regularly, then it is impossible to miss the increase in platelets. However, you should know the main signs of this deviation :
- Subcutaneous hemorrhages. You should pay attention to the appearance of bruises for no reason.
- Increased sensitivity of the fingertips and pain.
- Constantly itchy skin can indicate more than just dermatological diseases. In addition, the skin may take on a bluish tint.
- Intestinal, uterine and nasal bleeding.
- Lethargy, weakness, blurred vision.
It is not necessary that all symptoms will appear at once. But the appearance of 2-3 of them is grounds for a visit to the doctor. To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account all the patient’s current illnesses and those that he suffered previously. Additional tests and studies include:
- general blood analysis;
- bone marrow biopsy;
- molecular research;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs.
Norm
The normal platelet count in the blood of an adult is 13-43%. The indicator may deviate from the norm in some diseases.
Standard values depend on the person’s age:
- The norm for women and men is 180-320x10 9/l.
- In newborns and infants from 180 to 490 × 10 9/l.
- In children under 1 year of age, the indicator is 180-400 × 10 9/l.
- In children from 1 year to 6 years, 160-390 × 10 9/l.
- In children from 7 to 12 years old, 160-380×10 9/l.
- In adolescents from 12 to 18 years old, the indicator is 160-360 × 10 9/l.
If a laboratory test reveals a deviation from the norm, the doctor will prescribe an additional examination in order to establish a diagnosis, because changes in the indicator indicate the presence of pathology.
Different laboratories use different reagents and instruments, so the same person in different laboratories may get different results. The form indicates the patient’s indicators and normal values.
Research methods
Counting the number of blood platelets is part of the general (comprehensive clinical) analysis; the study is not performed separately. The content of PLT, which is abbreviated as platelets, is the main determined blood parameter. There are several ways to find out the platelet concentration and compare the result with the norm in women, and each blood test has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The following methods are used in clinical institutions:
- manual counting;
- automatic platelet detection;
- using a semi-automatic analyzer.
If pathological changes are detected, several tests are performed to confirm the diagnosis and minimize the likelihood of error. First, it is recommended to count manually (under a microscope), then use a specialized apparatus.
Using a Hematology Analyzer
The devices are semi-automatic and fully automatic (used more often). They are designed for quantitative research of blood cells.
Among the indicators characterizing platelets, the following are determined:
- concentration;
- average volume;
- volume share;
- coefficient reflecting the spread of volume values relative to the average value.
The number of cells is calculated automatically. The hematology analyzer provides a quick and accurate result (the coefficient of variation does not exceed 10%), but does not allow examining cells or detecting signs of their atypicality.
Goryaev's counting chamber
It is a simple design that involves visual platelet counting under microscopic magnification with phase contrast. A microscopic grid applied to a glass slide helps determine the number of blood platelets in a removed blood sample; the calculation is carried out using a special formula. The advantages of the technique are the ability to further study the parameters of platelets, their structure, and identify deviations in size, shape, and structure. However, the technique requires certain knowledge and skills from the laboratory doctor. An error in issuing the result of a quantitative assessment cannot be ruled out; the spread of indicators is 25-30%.
According to the Fonio method
This is a microscopic examination method. A stained blood smear is assessed. The smear is fixed with a solution that prevents the formation of a clot. Potassium salt EDTA or magnesium sulfate is used as an anticoagulant reagent. The technique involves simultaneously counting platelets and red blood cells under a microscope and calculating their ratio (in ppm).
The analysis refers to a manual counting method, helps to identify the exact (average range of 10-15%) number of blood cells and platelets, evaluate morphological features, visually determine the characteristics of platelets, including pathological formations.
Increased value
An increased value of the large platelet ratio means that pathological processes are present in the patient’s body.
Causes
High levels mean that the following diseases may develop:
- thrombocytosis;
- circulatory disorders;
- obstructed blood movement through the vessels.
When a person is injured, large platelets stick together and form a blood clot, which clogs the damaged vessel and prevents bleeding. If a person’s index increases, then there is a risk of a blood clot in the vessel.
Treatment
An increase in platelet count threatens the formation of blood clots and possible blockage of blood vessels.
This situation often leads to serious consequences, so thrombocytosis must be treated promptly. You need to seek help from a hematologist (a specialist in blood diseases).
Medicines
Medicines for the treatment of platelets (cytostatics) are prescribed only in case of significant deviations from the norm; most often, therapy is limited to observation and diet. But in some cases, the use of special drugs is necessary .
- Anagrelide.
- Interferon alpha.
- Hydroxyurea.
- Alkylating agents.
- Radioactive phosphorus 32P.
The choice of medications is the prerogative of the attending physician, who takes into account the age and characteristics of the patient’s body.
ethnoscience
It must be remembered that thrombocytosis and thrombocytopenia (low platelet levels) are completely opposite ailments, so when choosing a medicinal herb it is important not to make a mistake and not aggravate the situation. Traditional medicine recipes should be used only with the approval of the attending physician . Here are some of them:
- Take 200 g of mulberry root and pour 3 liters of boiling water. Cook for 15 minutes, then strain and let sit. Take 150 g 3 times a day.
- One teaspoon of sweet clover is poured into a glass of boiling water, after which it is infused for half an hour. Consume within 1 day, in small portions. The recommended course of treatment is no more than 3 weeks. After 3 months the course can be repeated.
Reduced level
The reasons for a decrease in the P-lcr index can be chronic kidney disease, leukemia, and malaria. The index decreases after heavy metal poisoning and after chemotherapy.
A reduced level of the indicator occurs in pregnant women, after heart surgery, with adverse reactions caused by medications, with alcohol abuse, and lack of vitamin B12 and folic acid.
Thrombocytopenia can be caused by congenital bone marrow diseases and hereditary predisposition to this disease. A decrease in the rate is called thrombocytopenia. This diagnosis is made if the number of platelets has decreased by 3 times.
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- skin rashes;
- it is difficult to stop bleeding from the nose;
- gums bleed;
- bleeding increases during menstruation.
The cause of thrombocytopenia must be quickly eliminated, because in this case, a minor injury can cause large blood loss. The attending physician must select individual therapy for this condition for the patient.
What does a low platelet count indicate?
Low concentrations are no less dangerous. Thrombocytopenia may be a sign of:
- inhibition of the hematopoietic function of the bone marrow, damage by metastases;
- leukemia, Marchiafava-Micheli disease;
- autoimmune, aplastic or megaloblastic anemia;
- radiation sickness;
- prolonged viral infection;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- alcoholism;
- uncontrolled use of drugs that inhibit platelet production;
- lack of folic acid, vitamin B12;
- enlarged spleen (splenomegaly);
- liver cirrhosis and its complications – portal hypertension;
- disturbances in the secretory activity of the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of diseases
The large platelet ratio is a test that must be performed to determine the condition of the blood. Deviations from normal indicators can indicate various diseases. In this case, the level can either increase or decrease depending on the reason. A change in the level of cells in the blood indicates the presence of pathological changes in the human body. To understand what p lcr or large platelet ratio is responsible for and how to bring it back to normal, you need to learn more about these blood cells.
How is their level determined?
Let us immediately note that, as such, there is no separate analysis for the determination of platelet plates.
An assessment of their functions and condition is carried out in conjunction with a general analysis of the blood clinic, displaying the result with the abbreviation - PLT (mandatory indicator) and the measurement of thrombocrit - PCT (the level of their concentration in the total volume of blood).
This analysis does not take into account the ratio of age groups and platelet forms (irritation and degeneration).
A more detailed analysis of platelet properties is determined in certain conditions (before surgery, during bleeding, and other critical conditions) by the hemostasiogram (coagulogram) method using screening tests that determine the consistency of the hemostasis process.
What are platelets
Red blood cells produced in the bone marrow are called platelets. They lack a nucleus and are the smallest cells compared to white blood cells and red blood cells. Despite this, their importance in the body is very great.
Thanks to these cells, blood has the ability to clot, which protects a person from blood loss during wounds and injuries:
- An abnormal platelet level often indicates diseases that occur in the human body.
- But the number of cells can also change due to temporary factors, for example, after physical activity.
After production, platelets remain in the blood for 5 to 11 days, after which they are destroyed in organs such as the liver and kidneys.
Based on their origin, platelets are divided into 3 types:
The division into types occurs depending on the reason that caused the generation of cells. Several factors can influence an increase or decrease in the large platelet ratio.
A blood test and further examination of the person will help identify the underlying cause. After which the doctor prescribes treatment adequate to the disease, and the patient may be hospitalized: the sooner the causes are identified, the more effective and easier the course leading to recovery will be.
How to bring the indicators back to normal?
- First, healthy eating. You need to make your menu varied, because there are many diets that are aimed at normalizing the number of platelets in the blood. Of course, food, first of all, must be fresh and healthy. It is recommended to eat more fresh fruits and vegetables and eat less fatty meat. Include whole grains and avoid trans fats, sugars and starches.
- Secondly, maximum nutrients. Depending on the level of platelets in the body, a nutritionist must select an individual diet. Thus, those foods will be selected that can increase or decrease the number of platelets, depending on the situation. For example, vitamin K is responsible for blood clotting and inflammation, and this vitamin can be consumed in the form of vegetables such as spinach, seaweed, cabbage or broccoli. It is best to steam these vegetables or eat them raw if possible. Eggs and liver are very healthy. Folic acid is of great importance in the production of platelets. Therefore, you need to add foods such as asparagus, spinach, low-sugar cereals and oranges to your diet. After consultation with a doctor, vitamins may be prescribed to normalize the condition.
- Thirdly, physical education. Of course, you need to remember that there is moderation in everything and the main thing is not to overdo it. It is recommended to engage in swimming, walking, and light strength training. Such sports make the immune system strong and affect blood circulation. But it is worth remembering that fatigue can come quickly, this is one of the symptoms of thrombocytopenia and excessive exercise can harm the body. Sports activities that entail the risk of injury and the threat of blood loss should be avoided. These sports include: skating, boxing, football, basketball and many others. Just in case, you need to have a special drug with you that will reduce bleeding, if necessary. This drug is prescribed by your doctor.
- Fourthly, you need proper rest. The sleep standard for adults is seven to nine hours, but if we are talking about a person with thrombocytopenia, then sleep and rest should be longer. It is necessary to eliminate overwork and have the opportunity to rest when you feel tired.
Important! Any healthy person needs to drink an average of two liters of water per day. That's about eight glasses
This rule is not difficult to follow, because ordinary water has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the human body.
Lastly, if your platelet levels are abnormal, it is always important to remain calm and positive. The main thing is not to panic and at the first symptoms consult a doctor, listen to his advice and take the prescribed treatment, if prescribed
Remember! It is easier to prevent diseases and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Reasons for changing the coefficient
As already mentioned, various factors can cause a decrease or increase in the level of large platelets.
- inflammatory processes;
- various diseases;
- hematological factors;
- temporary reasons.
Inflammatory processes that provoke a sharp increase in red blood cells in the blood include diseases such as hepatitis, polyarthritis, rheumatoid purpura, inflammatory enteropathy and others.
Having a negative effect on the body, these diseases provoke an increase in interleukins, which are an anti-inflammatory substance. The production of these substances is accompanied by an increase in platelet counts in the blood. And cancer cells can also provoke a change in the coefficient. Oncological diseases often cause thrombocytosis. Lymphomas and hepatoblastoma can also lead to changes. And also the level of cells in the blood changes in patients during the postoperative period. People who are anemic usually have elevated platelet levels in their blood tests.
Reasons that may temporarily affect platelets may include:
- pregnancy;
- injuries;
- physical exercise;
- suffered stress.
The reasons for the change may be temporary (in which case the condition returns to normal without much effort) or such that they will require long-term treatment.
Thrombocytopenia
This is a pathological condition in which there is a decrease in the concentration of blood platelets, which poses a serious threat to human life. A disrupted coagulation mechanism of biological fluid can cause internal hemorrhage and slow down the cessation of bleeding. If the cells are present in a smaller volume, this may mean that thrombocytopenia is developing.
Pathology is considered as an independent disease or as a symptom of certain pathologies of other organs. The disease does not affect the general well-being of the patient.
Causes
There are acquired and hereditary factors of pathology. The former develop throughout life, the latter are transmitted from parents with an affected gene. If the cause of the pathology is not determined, then thrombocytopenia is defined as idiopathic (unidentified).
Scientists identify the main reasons for the decrease in cell number:
- increased production of antibodies that destroy plates;
- changes in the spleen;
- diarrhea and vomiting;
- failure of red bone marrow functions;
- low volume of fluid drunk.
Increased cell destruction is observed in Werlhof's disease and DIC syndrome. It is possible with a transfusion of biological fluid or taking antihistamines.
Volume decreases for other reasons as well.
These include:
- injuries;
- anemia;
- lack of vitamin B12;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking aspirin and heparin;
- radiation therapy;
- overdose of anticancer drugs;
- complicated form of leukemia;
- myocardial diseases;
- surgical operations.
A decrease is observed in infectious diseases. This could be chickenpox, HIV, hepatitis C. In autoimmune diseases (lupus), the body perceives its own cells as foreign and begins to intensively produce antibodies to attack them.
In women, the number of platelets may decrease during heavy menstruation, during pregnancy and in the first time after childbirth.
How to treat
Before choosing a treatment regimen, the cause of the decrease in cell number is determined. This allows you to influence the mechanism of pathology development.
Treatment includes 2 directions:
- a course of hormonal drugs and corticosteroids;
- administration of immunoglobulin and interferon.
In advanced cases, plasmapheresis is required to remove bacterial antibodies and their breakdown products.
To boost immunity, immunomodulators are prescribed:
- Splenin;
- Timalin.
You can raise the level of records naturally.
Doctors recommend:
- include tomatoes, kiwi, oranges, herbs, berries in the diet;
- give up high-calorie foods, coffee, refined sugar;
- eat salmon, tuna, eggs, flaxseed oil weekly;
- drink freshly squeezed juices.
You cannot refuse multivitamin complexes and mineral supplements. To strengthen the immune system and normalize blood pressure, you need to perform moderate cardio exercise.
PLC-R increased
An elevated P-LCR, along with abnormal results of other blood parameters, indicates a pathology occurring in the hematopoietic system and requires a search for the cause. Megakaryocytes with increased ploidy are responsible for the formation of large platelets. The resulting tiles have a longer service life. They exhibit an increased tendency to merge into larger structures and adhere more easily to vessels.
Longer platelet survival and faster platelet production promotes the formation of large or giant platelets. This condition causes an increased percentage of large or giant platelets (P-LCR).
Vorobyova Marina
Neurologist of the highest qualification category (work experience 14 years), doctor of neurofunctional diagnostics (work experience 12 years); author of scientific publications on vertebroneurology; participant of scientific conferences on neurology and functional diagnostics of all-Russian and international significance.