General blood tests
10.27.201825.01.2019 Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova) 1662 Views platelets
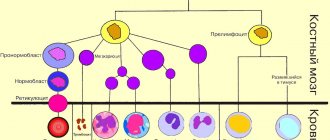
Platelets are produced in the red bone marrow and their main function is to stop bleeding by forming a blood clot. The lifespan of the cells does not exceed 12 days, after which they are destroyed in the spleen or liver.
When visiting a pediatrician with a child, the doctor must prescribe a set of laboratory tests. The set of standard indicators in a general blood test necessarily includes determining the number of platelets. The fundamental importance of the criterion is due to vital functions, and its deviation from normal values indicates a number of serious pathologies.
- 1 Normal platelet counts in children by age in the table
- 2 Deviations 2.1 Exceeding the norm
- 2.2 Platelets below normal
You need to understand how to properly prepare a child for analysis, what indicator norms exist for children of different ages, and also what their deviation from the norm indicates.
What are platelets
Before you begin deciphering the analysis, it is worth understanding what platelets are.
Platelets are blood platelets, the smallest formed elements of blood. The formed elements of blood also include leukocytes and erythrocytes. Together with platelets, they make up the bulk of blood cells.
The functions of platelets are very diverse, but their role in the body is to control the performance of blood vessels by releasing various biological substances. The well-known function of platelets is their participation in the blood clotting process. In this case, platelet levels are associated with the formation of bleeding and blood clots.
General information
Platelets are granulocytic blood cells without a biconvex nucleus, formed from plasma cells of the bone marrow. They are presented in different forms - young, adult and mature. The diameter is directly proportional to age: 2-4 microns. Platelets contain granules that create blood clotting proteins, lytic enzymes, phosphatase and cathepsin, create serotonin, calcium ions and ATP, and contain lysosomal enzymes.
One of the most important functions of blood platelets is participation in blood clotting (primary hemostasis).
Platelets bind clotting factors, making blood clots thicker. As a rule, in an inactive state, when the vessel wall is damaged, platelets are directed to the damaged area. Thanks to the pseudopods located on the surface of the body, they are attached to each other and the vascular wall, forming a blood clot, which is an excellent barrier to bleeding. In the active state, platelets are able to change the shape of the body, due to which they increase their area, and this allows them to completely close the damage.
In addition, platelets are able to protect the body from foreign bodies by catching them with the help of pseudopods, and then digesting them with the help of the enzyme lysocine, which is formed from platelet factors (thrombin, thromboxane), from platelet granules. Thus, platelets are important for the immune response, being “killer” cells for foreign agents entering the body.
Blood plates serve as a storage site for serotonin, providing antitumor and radioprotective effects.
Thus, a violation of the number of platelets leads to inhibition of their functions, this certainly leads to disruption of the body’s activity and entails negative symptoms.
Conditions in which platelets are elevated in a child
An increased number of platelets in the blood is called thrombocytosis.
The reasons for their increased level may be:
- enhanced hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow , which leads to a high concentration of platelets in the blood and other formed elements;
- high platelet consumption , resulting in a compensatory increase in their number;
- infectious process (tuberculosis);
- taking medications and others.
A high level of platelets in the blood is dangerous because it thickens the blood and increases the risk of blood clots. Only a doctor can tell you more accurately whether a child’s platelets are elevated or not.
Thrombocytosis in children
Thrombocytosis is an increase in the number of platelets in the blood to values several times higher than normal. Most often, thrombocytosis is a consequence of a viral or bacterial infection. In particularly severe cases, an increase in blood cells may indicate the development of cancer.
How to determine: symptoms
The symptoms of thrombocytosis are similar to the clinical manifestations of thrombocytopenia, although there are still some differences. If a child has at least one of the listed signs, you should immediately consult a doctor and take a blood test.
Symptoms of thrombocytosis in childhood:
- frequent and severe nosebleeds;
- blue skin;
- the appearance of subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- itching and burning in certain areas of the skin;
- tingling sensation on the skin;
- cold hands and feet at a comfortable ambient temperature;
- dyspnea;
- increased heart rate.
The child may also complain of frequent headaches. In some cases, pressure surges and blood clots may form.
Causes
To correctly determine the cause of the increase in platelets, it is necessary to diagnose what type of thrombocytosis is developing in the child. The treatment regimen and tactics for managing a small patient will depend on this.
- Platelets: normal for women by age (table). What determines the platelet count in the blood?
| Type of thrombocytosis | Causes |
| Clonal | Bone marrow stem cell defects |
| Primary | Pathologies in the functioning of bone marrow cells, the formation of several sites of hematopoiesis |
| Secondary |
|
Recommendations for thrombocytosis
- Consult your doctor about the use of products that contain acetylsalicylic acid (for thinning the blood).
- During the day, offer your child compotes and fruit drinks made from blueberries, lingonberries and cranberries as often as possible.
- Monitor the iodine content in the body, and if there is a deficiency, ensure sufficient consumption of fish and seafood.
- If the child does not have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to add fresh garlic and ginger (in minimal quantities) to food.
- In the morning, you can give your baby cocoa without sugar (a prerequisite is that the drink must be consumed on an empty stomach).
- Olive and flaxseed oils, as well as foods rich in magnesium and B vitamins, should be mandatory products in a child’s diet for thrombocytosis.
- Avoid dehydration (the water norm for a child is 1 liter per day).
- Increase the amount of fruits and vegetables (tomato juice and lemons are especially useful).
Low platelet count
A few words should be said about low platelet levels. Low platelet count in the blood – thrombocytopenia. Due to the fact that platelets take part in blood clotting processes, a lack of them in the blood can lead to bleeding.
The reason for a low platelet count in the blood may be, for example, inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis as a result of radiotherapy or if there are factors leading to their destruction in the blood. The latter may include autoimmune diseases. There are cases when thrombocytopenia is hereditary, for example, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, Bernard-Soulier syndrome .
You can tell that your child has platelet problems by the presence of a rash or bruises that quickly appear when touched.
Classification of pathology
International medicine distinguishes 4 stages of thrombocytopenia in children and adults:
- mild, with a platelet count from 75 to 100X10⁹/l;
- Moderate (from 50 to 74);
- moderate (from 20 to 49);
- heavy (less than 20).
If the indicator is significantly lower than normal, then the symptoms will be understandable. If a patient is diagnosed with an early or moderate stage of the disease, there may be virtually no symptoms. Usually at these stages, pathology is discovered by chance.
Test to determine the level of platelets in the blood
What tests can be prescribed, including counting platelet levels in the blood? One of these tests is a general clinical blood test. This is a study of the level of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets together. Depending on the equipment the laboratory is equipped with, other blood parameters may be determined.
Most often, a hematology analyzer is used for general clinical blood analysis. Therefore, there are a number of factors influencing the reliability of the results.
Sometimes, if the indicators are inadequate or questionable and do not correspond to the clinical picture, a separate study of platelet levels may be prescribed. It is carried out manually, and in this case it is more reliable, as it helps to avoid erroneous readings from the device.
How to prepare properly
One of the important components when preparing for a general blood test is the emotional calm of mother and child.
Drawing blood is stressful and can lead to fluctuations in your readings, so it’s best to be mentally prepared for it. Blood must be donated on an empty stomach. But in infants this is difficult to comply with, so it is allowed to donate the material between feedings.
Also, the child’s hands should not be cold. At low temperatures, the capillaries spasm, blood flow slows down, and the procedure may be delayed.
It is important to sit or lay the child down so that he is comfortable.
Where to get tested for free and for a fee
If you have a compulsory medical insurance (compulsory health insurance) policy, you will be able to test the level of platelets in your blood free of charge. If suddenly, for some reason, you do not have the desire or opportunity to visit your medical institution to which you are attached, then you can contact any medical center that provides paid services.
How much does platelet determination cost in Moscow laboratories?
Determining the number of platelets during a general clinical blood test in laboratories in Moscow will cost you 250-400 rubles; in addition, you may be required to pay money for taking blood. To avoid being deceived, visit the website of a specific medical center. There is almost always a price list there.
You can also additionally request a manual method of platelet counting (according to Fonio). It will cost you somewhere around 200-300 rubles. Some medical centers do not separately conduct manual platelet level testing, only as an additional method. Therefore, you need to be prepared for this.
Decoding indicators
When receiving the research results in person, for example, in a paid center, many parents immediately begin to explore the Internet. They check the level of platelets in the blood using unreliable sources, make their own conclusions, and prescribe treatment.
Parents who care about the health of their child will turn to a specialist, for example, a pediatrician or hematologist, for a transcript of the analysis. If deviations are detected, the patient will be referred to additional research methods to clarify the reasons.
Treatment options
A treatment regimen can be selected after the cause of the disease has been identified. To quickly normalize the blood cell count, it is necessary to act comprehensively.
Medicines
Taking medications from the following pharmacological categories will help increase platelet production:
- Immunoglobulins. Available in the form of a solution for intravenous administration. The positive effect is achieved due to the fact that the active components of the drug interact and destroy antigens, accelerating platelet production. The dosage and duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician.
- Corticosteroids. They regulate the activity of the adrenal glands using hormones. In turn, the adrenal glands normalize the functioning of the bone marrow, and platelet production is activated.
- Platelet transfusion. It is prescribed in the rarest cases, when the disease is in an advanced stage and the patient’s life is at risk.
Medical nutrition
The most important step in fighting disease is changing your diet. Your child should eat a proper and balanced diet to increase their platelet count. Products that worsen the situation should be excluded:
- products with added carcinogens;
- fast food;
- oranges, tangerines, grapefruits and juices;
- fatty food;
- fried and smoked foods;
- a pineapple.
The child’s diet should include lean meat (beef is best), quail eggs, sea and river fish. As a complement to the main dish, it is better to choose buckwheat, rice, beans with a lot of greens. Drink natural vegetable juices or mineral water instead of tea.
Traditional methods
The best folk remedy for thrombocytopenia is drinking nettle juice. The child should be given a medicine made from nettle juice and milk (in a 1:1 ratio). The drug is taken three times a day 30 minutes before meals.
She speaks positively about the use of sesame oil. To avoid complications, consult your doctor before starting therapy.
Specifics of treatment for newborns
The main task of doctors is to prevent the development of complications. For immunological forms of pathology, the infant is prescribed:
- Feeding with donor milk for the first 3 weeks, then breast milk is allowed (under platelet control);
- intravenous administration of immunoglobulins;
- Introduction of ascorbic acid and rutin.
In severe cases, platelet transfusion is indicated.