In many cases, a sharp drop in platelet levels in the blood directly indicates severe infectious diseases. For example, malaria and Dengue fever lead to such consequences. A similar thing happens with diseases of the endocrine system, for example, with diabetes.
What are the dangers of low platelets?
Firstly, when they decrease, the rate of blood clotting also decreases, so even minor bleeding can cause asphyxia (due to blood loss).
Secondly, a low platelet count makes the blood too thin, disrupting the balance of other formed elements. With a long-term condition, the risk of developing chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system increases significantly.
How can you increase your platelet levels? Recent studies confirm that this can be achieved by following a special diet.
What affects platelets?
The first thing you should pay attention to is that the endocrine system regulates the concentration of platelets in the blood. With the help of certain protein compounds-mediators, the production of formed elements in the bone marrow is stimulated or inhibited (red blood cells, leukocytes, hemoglobin are also produced there, and platelets are obtained from plasma).
And nutrition is a secondary factor in this. That is, diet and diet only slightly affect the production of platelets, so it is definitely not possible to normalize a too low level only in this way.
Platelets are synthesized from plasma, which, in turn, consists of a mixture of water, minerals, protein compounds, some groups of vitamins, and iron. That is, in order to speed up platelet production, it is necessary to prevent deficiencies of many micronutrients . And the most “rare” among them is iron.
Iron is absorbed by the body only in the presence of biochemical catalysts, mainly the protein form. Accordingly, it is also necessary to include in the diet those foods that increase the bioavailability of iron.
Beetroot with sugar for platelets. What are platelets, their norm and importance for the body
Platelets are blood elements that are small cells of irregular, flattened spheroid shape that perform the following tasks:
- cover the bleeding site;
- participate in the process of blood clotting;
- stimulate the regeneration of damaged tissues.
In the normal state, these cells are small in size (2-4 microns in diameter). When blood vessels are damaged, when platelets encounter something other than the tissue on the inner surface of blood vessels and the heart, they are activated. Outgrowths (up to 10 pieces) appear from the spherical cells; they greatly increase in size.
With these outgrowths, cells attach to other tissues and cover the site of injury. The appearance of a thick, and then completely dried, blood crust on skinned knees is the result of the work of platelets. The same mechanism operates during blood clotting - only active platelets in this case cling to each other.
After forming a plug that closes the damage, platelets begin to secrete growth factors that promote regeneration - accelerating the division and growth of new cells. The life cycle of a platelet is on average 10 days, after which the liver or lungs destroy it.
- in a baby within 2 weeks after birth – 100-420 thousand/µl;
- in an infant up to one year old – 150-350 thousand/µl;
- in a child under 12 years old – 180-390 thousand/µl;
- in women – 150-380 thousand/µl;
- in men – 180-400 thousand/µl.
During pregnancy or menstruation, the norm decreases to 130-400 thousand/µl and 75-220 thousand/µl, respectively.
Products that increase their level
The following products will help to quickly raise platelets in the blood:
- Kiwi. Helps quickly increase the balance of B vitamins, as well as ascorbic acid. It also contains iron in small quantities (but not all varieties). It is recommended to eat 2 ripe fruits daily.
- Pomegranate. In principle, this is the most beneficial fruit for the circulatory system. Its use also increases the level of red blood cells, speeds up the response of the immune system (white blood cells are one of its most important parts).
- Egg yolks. Doctors recommend eating quail eggs, and fresh ones. Every day - at least 5 pieces. This will help not only raise platelet levels, but also keep them at the current level.
- Sea fish. Fatty fish are ideal because they contain huge amounts of omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids (as well as omega-6 and omega-9). These components are necessary for the normal absorption of iron, as well as its composition with certain amino acids.
Causes
Why this disease occurs is unknown. Doctors talk about hereditary predisposition and the negative effects of the following factors:
- bacterial and viral infections;
- vaccinations;
- excessive exposure to solar radiation (insolation);
- general hypothermia of the body;
- some medications (Indomethacin, Furosemide).
On the surface of platelets there are molecular complexes called antigens. If a foreign antigen enters the body, the immune system immediately begins to produce specific antibodies. By interacting with antigens, they destroy the cells on whose surface they are located.
In essential thrombocytopenia, the spleen produces antibodies to its platelet antigens. They are fixed on platelet membranes and, as it were, mark them. As they pass through the spleen, blood cells are captured and destroyed.
Due to a decrease in the number of platelets, the liver begins to produce them more. The rate of maturation of megakaryocytes and the formation of platelets from them in the red bone marrow increases significantly. But gradually the compensatory capabilities of the bone marrow become thinner, and the disease makes itself felt.
If autoimmune thrombocytopenia is diagnosed during pregnancy, this means that antibodies to one’s own platelets cross the placental barrier and destroy normal fetal platelets. As a result, the child may be born sick.
Thrombocytopenia consumption
Platelets are activated in the vascular bed, and the blood clotting mechanism is activated. Due to the increased consumption of platelets, the red bone marrow begins to actively produce them, and if the cause of the pathology is not eliminated in time, their level in the blood will decrease to a critical level.
The activation of formed elements is caused by:
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Caused by an insufficient amount of prostacyclin in the blood. This anticoagulant factor is produced by the endothelium and prevents platelets from sticking to each other. When its release is disrupted, local platelet activation occurs and microthrombi form. Vessels are damaged and intravascular hemolysis develops.
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. Appears as a result of severe damage to internal organs or tissues (infections, burns, injuries, surgeries, etc.), due to which the blood coagulation system is depleted. Numerous blood clots form in the vascular bed. They clog small vessels, preventing normal blood supply to the kidneys, brain and other organs. In response, the anticoagulant system is activated, aimed at restoring blood flow by breaking up blood clots. Over time, the blood completely loses its ability to clot. Severe internal bleeding may occur, which can be fatal.
- Hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Associated with intestinal infections, hereditary predisposition, systemic diseases and the use of certain medications. Bacterial toxins are released into the blood. They damage the vascular endothelium and activate platelets by attaching them to damaged areas. As a result, microthrombi are formed and microcirculation of internal organs is disrupted.
Thrombocytopenia redistribution
Normally, about 30% of all platelets are deposited in the spleen. In some diseases, the organ greatly increases in size, which is why up to 90% of the formed elements of blood are deposited in it. The disease can be caused by cirrhosis of the liver, systemic lupus erythematosus, infections, tumors, and alcoholism.
Thrombocytopenia dilution
Develops in patients who are transfused with large volumes of plasma, fluids, red blood cells, plasma substitutes, without replacing platelets. As a result, the concentration of the latter decreases to such a level that even their release from the depot is not able to maintain the normal functioning of the coagulation system.
Products that reduce their level
If the goal is to increase platelets in the blood, then it is strongly recommended to avoid or minimize their consumption of the following foods:
- Dairy products. Cottage cheese is especially “dangerous”, as are some varieties of cheeses based on goat’s milk. Their main feature is their high calcium content, which tends to reduce the bioavailability of iron. If it is impossible to give up dairy products, then it is better to give preference to low-fat kefir, yogurt, and sweet desserts.
- Ginseng. Increases red blood cells, but inhibits platelet production. Moreover, in men the platelet concentration decreases faster than in women, which is explained by some physiological characteristics of their bodies.
- Red wine. It acts similarly to ginseng - it increases the rate of red blood cells in the blood, but reduces platelets. Concentrated grape juice is less effective in this regard. That is, it should also be abandoned.
- Coffee. Although it increases blood pressure, it slightly reduces the platelet rate. That is why, in case of diseases of the cardiovascular system, coffee (and tea, since it also contains caffeine) must be avoided.
Useful foods for thrombocytopenia
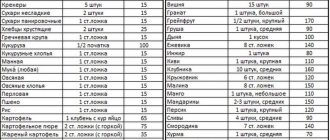
For thrombocytopenia, no specific diets have been developed. You need to eat right, that is, the body must receive the right amount of proteins, carbohydrates, fats and all macro- and microelements, vitamins. For anemia, it is useful to eat foods containing iron (buckwheat, nuts, corn, beef liver, barley porridge, oatmeal, peas, dogwood, sprouted wheat).
If there is a risk of hemorrhages in the stomach or intestines, you need to follow a gentle diet and do not eat or drink excessively hot and spicy foods.
It is useful to drink freshly squeezed juice from raspberries, strawberries, wild strawberries, apples, beets, cabbage leaves and black radish.
If you suffer from bleeding gums, then you need to eat currants, drink teas from the branches and leaves of currants and blackberries.
Traditional medicine for thrombocytopenia:
- To improve the condition of the blood with increased bleeding, you should drink decoctions of nettle, yarrow, rowan fruits (especially chokeberry), chicory, rue, rose hips, strawberries, medicinal verbena, water pepper.
- Sesame oil has excellent properties of regulating the number of platelets and increasing blood clotting. For treatment, you just need to add 10 milliliters of this oil to your food several times a day.
- To increase hemoglobin levels, you need to eat three walnuts a day with a teaspoon of honey.
- For the purposes of prevention and safety, you need to avoid dangerous sports and outdoor activities. Children should only be allowed outside under adult supervision and must wear knee pads, elbow pads and a helmet. Such a child should be told about the characteristics of his body.
Dangerous and harmful products for thrombocytopenia
- fatty, salty, spicy foods;
- products with all kinds of dyes, additives, impurities;
- smoked meats, sauces, seasonings;
- fast food restaurant dishes;
- semi-finished products;
- pickled vegetables and fruits;
- brine and all dishes containing vinegar;
- alcohol;
- all products that can cause allergies.
Also, vegetarianism is strictly prohibited.
You should also stop taking blood thinning medications. These include “aspirin”, “ibuprofen”, “noshpa”, “voltaren”, “acetylsalicylic acid”. This entire list disrupts the functioning of platelets. Attention! The information is for informational purposes only and is not intended to make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment. Always consult a specialized doctor!
Authors: Anna Shelestun, Tatyana Eliseeva Ask a question
Rating:
10
/10
Votes: 3
Usefulness of material 10
Reliability of information 10
Formatting of Article 10
Other methods
In addition to specialized nutrition, the following tips will help increase platelet levels in the blood:
- Rosehip and strawberry tea. Provides the body with a huge portion of ascorbic acid, as well as phytoncides, which indirectly take part in the production of platelets. To prepare this tea you will need about 3 grams of dried rosehip leaves and 1 teaspoon of dried strawberries. All this is brewed in a kettle and left to cool completely. This makes a brew for 2 servings of tea. You can drink it with sugar, at least 2 times a day.
- Multivitamin complexes. Moreover, those vitamins that doctors prescribe for pregnant women to take are suitable specifically for increasing platelet levels - they contain a “therapeutic” dose of B vitamins, including folic acid. Yes, such multivitamin complexes can also be taken by men.
Symptoms of thrombocytopenia
The mechanism for the development of thrombocytopenia symptoms is always the same. Due to a decrease in platelet concentration, the nutrition of the walls of blood vessels is disrupted, and capillary fragility increases. At a certain moment, due to a minor physical factor or spontaneously, the integrity of the capillaries is disrupted, and severe bleeding occurs (this is usually depicted in the photo as thrombocypenia). The lack of platelets prevents the formation of a platelet plug in the burst vessels, so blood flows from the circulation into the surrounding tissues.
The main symptoms of thrombocytopenia:
- Purpura (bleeding into mucous membranes, skin). Small red spots form on the body. They do not disappear when pressed, do not hurt and do not rise above the surface of the skin. Their size can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. At the same time, bruises may appear.
- Bleeding gums. It forms on a large surface and does not stop for a long time.
- Frequent nosebleeds. Can be caused by sneezing, microtrauma, colds. The blood that comes out is bright red. Sometimes the bleeding cannot be stopped for an hour.
- Hematuria (blood in the urine). Occurs due to hemorrhage in the mucous membranes of the bladder or urinary tract.
- Gastric and intestinal bleeding. They are a consequence of increased fragility of the vessels of the gastrointestinal mucosa, traumatizing it with rough food. The stool becomes red and bloody vomiting may occur.
- Heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding.
If you experience similar symptoms,
consult your doctor . It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.