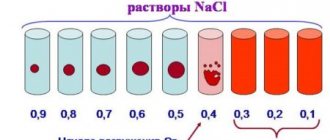
The value of normal hematocrit in humans
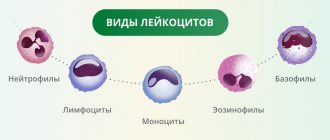
The body of a healthy adult contains approximately 4.5-5 liters of blood. It contains formed elements and cells - red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes, as well as a liquid part called plasma.
Some blood components, for example, red blood cells, do not have all the necessary components of a human cell, losing them during the maturation process. Therefore, red blood cells and platelets are called blood cells, not cells.
In different categories of patients, the normal values of various parameters of the blood tested will differ. So, for most men, the hematocrit will be higher: 40-41%, and in some cases it can reach up to 51%, which is due to its slower renewal.
In healthy women, the hematocrit usually ranges from 36 to 42%. This is due to physiological features - due to regular menstrual bleeding, blood is renewed more often to replenish its volume. During pregnancy, from the 20th week, the indicator begins to decrease, which is also not considered a deviation.
In children, hematocrit differs at different age periods:
- 44-62% for newborns;
- 32-43% for babies up to three months;
- 36-43% for children under one year of age;
- 35-47% (up to 52% for boys) - in the first ten years.
In subsequent years, the hematocrit norm depends on gender and practically corresponds to the values of an adult.
Traditional methods will come to the rescue
Elevated red blood cells in human blood can be stabilized with more than just drug therapy. It will be complemented by herbal tinctures. A ready-made collection of meadowsweet or nettle is sold at the pharmacy. You can make a healthy drink yourself. Take 150 g of each of the following components:
- hawthorn fruits;
- narrow-leaved fireweed;
- Melissa;
- valerian rhizomes;
- meadow grass;
- clover;
- yellow sweet clover.
The herbs are placed in a deep container and poured with boiling water. The collection is infused for 12 hours. Take a decoction of 2 tablespoons three times a day. A person should not ignore repeat visits to the doctor's office. A general blood test allows you to measure hemoglobin, platelets and red blood cells.
Hematocrit is a complex indicator that reflects the ratio of leukocytes, platelets, and erythrocytes in the blood. Deviation from the norm to a greater or lesser extent indicates an inflammatory process, chronic fatigue, and exhaustion. A doctor can distinguish dangerous conditions from those that do not require treatment. To a greater extent, hematocrit reflects the level of red blood cells - the formed elements of blood responsible for the transport of oxygen. If a patient is diagnosed with a deviation from the norm, extensive examination is required.
Methods for determining hematocrit
The indicator is determined as a percentage by calculating the amount of formed elements in whole blood. It is calculated using special instruments or manually.
Centrifugation using the Wintrobe method
The blood is exposed to centrifugal force for 10-30 minutes. The formed elements are heavier than plasma, so they settle to the bottom of the test tube. The hematocrit is determined by the ratio of sediment to the total volume of biomaterial.
Calculation of the indicator using the formula
The ratio of the number of red blood cells to the total blood volume can be calculated mathematically. To do this, the following indicators are required:
- total hemoglobin concentration (ctHB);
- red blood cell count (RBC);
- mean erythrocyte volume (MCV);
- mean erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (MCHC).
The hematocrit number (HCT) is determined by one of the formulas:
- HCT (%)=(ctHB (mmol/l)*0.0485+0.0083)*100
- HCT (%)=0.1*MCV*RBC
- HCT (%)=ctHB/MCHC*100
Direct blood cell counting method
In a given volume of biomaterial, visible blood elements are counted manually or using hematological analyzers. The method is highly accurate, and the measurement process does not take much time - no more than five minutes, but the equipment required is very expensive.
Manual counting method
Blood collected using an anticoagulant is placed in a dry, clean tube and allowed to settle. In this case, the formed elements that have greater weight settle to the bottom of the container, and the light plasma rises to the top, forming two fractions of red and yellow colors, respectively. The hematocrit indicator can be determined by the divisions on the test tube. This method is the least accurate, its error is up to 20%, so it is currently not used in laboratories.
Diagnostic course and treatment
A general blood test is taken every six months for preventive purposes. Its results make it possible to determine the hematocrit level even in a situation where symptoms are not expressed. A coagulogram will help confirm or refute the doctor’s suspicions. The results of blood tests reflect the rate of clotting. The last test is APTT, which reflects the ratio of blood cells. If the information collected does not allow a diagnosis to be made, the patient is referred to specialized medical specialists.
Having dotted all the i's, the doctor proceeds to drug treatment. The patient is prescribed a course of antiplatelet drugs - drugs that stabilize the level of blood viscosity. The dosage is selected by the physician, taking into account possible contraindications. Drug therapy will be complemented by a balanced diet:
- dairy products;
- lean meats;
- seafood;
- kelp;
- olive oil.
People who have high hematocrit, red blood cells and high hemoglobin eat more fresh vegetables, for example, celery, onions, beets. The doctor will prescribe a vitamin and mineral course. The immune system needs additional support. Vitamins C, E and K reduce the negative effects of increased blood viscosity. The following products must be excluded from the diet:
- salt;
- salo;
- mango;
- spices;
- red pepper;
- butter;
- bananas;
- cream;
- brain;
- radish;
- turnip;
- legumes;
- buckwheat and so on.
People who have elevated hematocrit and platelet values monitor their drinking regime. The minimum volume is 2.5 liters of clean liquid per day. The indicated quantity does not include sodas, compotes, teas and other drinks.
On a note! You can independently calculate your daily water consumption using the formula. Take body weight in kg and multiply it by 30 ml.
When is a hematocrit test performed?
Most often, hematocrit is determined as part of a general (clinical) blood test. Therefore, at present this parameter of a clinical blood test is not prescribed separately. The hematocrit level changes when:
- disorder of the blood coagulation system;
- dehydration;
- anemia or polycythemia;
- bleeding.
Assessing the hematocrit level is important when determining indications for the need for blood transfusion or the effectiveness of blood transfusion, during hemodialysis, and some operations. To determine the hematocrit number, venous or capillary blood is taken.
Increased hematocrit
An increase in hematocrit occurs with an increase in the number of blood cells - polycythemia - and a lack of fluid in the body. An increase in the indicator may indicate serious diseases accompanied by blood thickening and thrombotic complications.
Causes
Hematocrit increases due to stress, taking corticosteroid drugs and diuretics, traumatic shock accompanied by intense pain, as well as when climbing to high altitudes, smoking, or playing sports using anabolic steroids to gain muscle mass.
An increase in the indicator may indicate the following diseases:
- dehydration due to vomiting, profuse diarrhea, overheating or heat stroke, excessive sweating, insufficient fluids;
- heavy bleeding in the midst or immediately after it stops;
- pathologies accompanied by a decrease in blood plasma volume, for example, peritonitis, thrombosis, diabetes, burn disease;
- renal dysfunction - hydronephrosis, oncology, polycystic disease;
- vitamin B12 or iron deficiency anemia;
- leukemia;
- erythrocytosis;
- defects and coronary heart disease, heart failure;
- intestinal obstruction;
- bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema, obstructive bronchitis.
Symptoms
An increase in blood viscosity leads to thrombus formation. The latter can manifest itself in the form of tingling or various pains and numbness in the limbs. If the cause of increased blood viscosity is not determined in time, serious complications such as myocardial infarction, stroke, gangrene and even death may develop.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out not for the changed hematocrit level itself, but for the conditions or diseases that caused these changes. In some situations, when serious causes for a slightly changed hematocrit level have been excluded, no treatment is required. But usually such situations are short-lived, in the case of physiological reasons for changes in hematocrit levels.
Causes of high hemoglobin
Increased level of hemoglobin in the blood in women, what is it? If this indicator changes, it means that there is a problem with a specific organ and system. Although sometimes high hemoglobin is the norm - for example, in people who live in the mountains or in elevated areas. The main reasons why high hemoglobin occurs in women are as follows:
- Hemoglobin often increases in those who smoke, as well as in those who have recently been in a fire. The fact is that hemoglobin easily transports air or carbon dioxide, replacing them with each other.
- A high level of water deficiency raises blood counts, resulting in an increase in the amount of circulating plasma.
- Congenital heart disease caused by high pressure in the pulmonary artery blood flow. In this situation, the skin color changes from infancy and has a blue tint. The child coughs frequently and has shortness of breath. Ultrasound of the heart allows you to determine an accurate diagnosis. Treatment of such pathologies with severe symptoms is only surgical.
- Pulmonary diseases.
- Excessive amounts of vitamins B6 and B12 in the human body.
- Cancerous neoplasms.
However, a high level of hemoglobin in the blood can not only indicate various diseases, but also signal that you lead a different lifestyle and live in an unfavorable place.
increased hemoglobin in women
Decreased hematocrit
A decreased hematocrit occurs when the number of red blood cells or their size decreases - erythrocytopenia. The cause may also be the accumulation of water in the body when the blood becomes thinner - hyperhydration, as well as hyperproteinemia or the accumulation of proteins in the plasma, which contributes to fluid retention.
Causes
A decrease in hematocrit is facilitated by prolonged immobility, fasting or a strict diet, taking anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, and intravenous infusions in large volumes; heavy drinking, chronic alcoholism, excessive salt intake, menstruation in women.
Also, a downward change in the indicator may indicate the following pathologies:
- iron-, B12- or folate-deficiency anemia;
- severe bleeding;
- impaired hemoglobin production in sickle cell anemia;
- fibrous degeneration of the liver - cirrhosis;
- disruption of the urinary system;
- hemolysis of erythrocytes - destruction of red blood cells due to hereditary mutation, autoimmune processes or toxic effects on blood cells;
- malaria, typhoid fever;
- oncological diseases of the bone marrow or its metastatic lesions from other organs;
- an increase in the amount of protein in plasma due to vomiting, diarrhea, blood cancer and other conditions.
During pregnancy, a decrease in hematocrit can be observed in the case of toxicosis, a very young age of the mother, multiple pregnancies, a short period of time between pregnancies, and also after the 20th week of gestation due to a physiological increase in fluid in the body.
Symptoms
A decrease in hematocrit in the blood is accompanied by hypoxia of various organs, since it is the red blood cells that normally carry oxygen throughout the body. This condition is manifested by the following symptoms:
- fast fatiguability;
- general weakness;
- drowsiness;
- increased heart rate and breathing;
- feeling of lack of air;
- headache, dizziness;
- decreased memory and concentration;
- hair loss;
- marbling or pallor of the skin.
Treatment
A decrease in hematocrit in an adult to 35-30% requires outpatient medical supervision, exclusion of possible serious diseases, and dietary adjustments with increased consumption of animal products, in particular, red meat and liver, and leafy greens. An indicator below 13% is typical for life-threatening pathologies and is usually detected in patients in serious condition in the hospital. Patient management tactics are determined by the underlying disease that led to a change in hematocrit level.
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician