Published: 04/20/2021 11:00:00 Updated: 04/20/2021
Erythrocytes are red blood cells containing hemoglobin. They carry oxygen and perform many important functions in the bloodstream.
We talked in more detail about red blood cells in the blood earlier.
In urine, red blood cells are contained in extremely small quantities. This is because these red blood cells are large enough that they normally do not pass through the kidney filter. If a lot of blood gets into the urine, it can be seen with the naked eye - the liquid changes color to pinkish or brown. A change in the color of urine is an alarming symptom.
However, a slight increase in red blood cell levels cannot be detected on your own. In this case, laboratory diagnostics will help. Red blood cells in the urine are determined as part of a general urine test.
Interesting Facts
| Options | Indications |
| Time from conception | 37 weeks |
| Period by month | 39 weeks |
| What month | 9 |
| Dimensions and weight of the fetus | 507 mm, 3230 g |
| Uterus dimensions | VDM - 36-38 cm |
| Pregnant weight | Gain from the beginning of pregnancy is 10-15 kg; over the last week 200-300 g |
Your baby is the size of
Watermelon
507 mm Size
3230 g Weight
Surely now you are impatient and counting the days, and maybe even thinking about how to give birth faster at 39 weeks of pregnancy. But don’t rush time; the baby normally has at least a couple more weeks to finally prepare for birth. It is too early to talk about additional medical stimulation, only if there are indications for it. Let's find out what happens to the fetus and mother at 39 weeks of gestation.
What is considered normal
Doctors do not always perceive normal blood pressure in pregnant women as the usual 120/80, since changes in hormonal levels directly affect a woman’s well-being and physiological indicators. Until about the twentieth week of gestation, the pressure level is often reduced. This is due to the active production of the hormone progesterone.
This substance controls the tone of the uterus and relaxes muscle tissue to prevent premature birth. For this reason, even a pressure of 100 over 60 is considered normal if the expectant mother feels well. Measuring blood pressure is a standard procedure that is performed on pregnant women at every appointment with a gynecologist, starting from the 12th week.
The tonometer readings that the doctor receives indicate the general condition of the body, in particular, the functioning of the cardiovascular system. If blood pressure is within the normal range, and the woman does not complain about her health, the gynecologist has no reason to perceive even the numbers 130/90 as a pathology.
Below is a visual table showing the permissible pressure limits for women carrying a child. It is advisable to take measurements daily, especially if before conception the expectant mother had problems with the heart and blood vessels.
| Systolic reading (mmHg) | Diastolic reading (mmHg) | |
| Optimal pressure level | Up to 120 | Up to 70 |
| Normal pressure | Below 130 | Below 80 |
| Blood pressure is higher than normal | 130–139 | 80–90 |
| Not expressed arterial hypertension | 140–159 | 90–100 |
| Moderate arterial hypertension | 160–179 | 100–110 |
| Severe arterial hypertension | More than 180 | More than 110 |
Normal blood pressure is different for each person, with which he feels comfortable, works and performs household duties. As for pregnant women, their normal range varies quite widely and this is not considered a pathology. Features of tonometer indicators in expectant mothers:
Psychosomatics of high blood pressure
- pressure may increase in the third trimester, since after 13–14 weeks of gestation the load on the circulatory system doubles;
- An increase in tonometer readings can be observed under stress, fear of future childbirth, lack of awareness about the upcoming process, etc. In this case, the adrenal cortex produces an excessive amount of stress hormones;
- in the early stages of pregnancy, the pressure drops 5–10 units below normal due to the activity of the hormone progesterone, and in the second or third trimester it increases.
It is difficult to single out specific numbers that a tonometer should show in a pregnant woman - they are individual for each expectant mother. If the indicators go beyond the acceptable limits in one direction or another, the number of measurements needs to be increased. And if dangerous symptoms occur, immediately consult your doctor.
Feelings of the expectant mother
The size of the uterus is impressive - about 40 cm from the cervix to the bottom, but it is no longer growing. The fetus grows, and the amount of amniotic fluid gradually decreases, so sometimes it may seem to you that the baby is moving very much.
At 39 weeks of pregnancy, false contractions periodically continue to bother the woman. They differ from true ones in less pain, irregularity and in that over time the discomfort does not increase and the pain goes away on its own.
The fetus drops lower, and you may feel pressure in the perineum, even cutting pain. If the discomfort does not subside for a long time, it is likely that the cervix is dilated - you should go to the hospital. If at 39 weeks you find mucus on your underwear, it is possible that the plug that is closing the cervical canal is gradually coming off. The discharge may be thick and streaked with blood.
Training contractions, drooping of the abdomen and the passage of the mucus plug are called harbingers of labor. They are the same for primiparous and multiparous women, but they can occur at different weeks of gestation, and some do not experience these sensations until the very beginning of labor.
Symptoms
The woman feels well, leads a normal lifestyle and does not even suspect that there is a problem. If high blood pressure is not detected in time and therapeutic measures are not taken, the consequences can be dire - this is harm to the health of the woman herself and the developing fetus.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the symptoms of hypertension are practically absent, and the consequences develop much later
You can recognize the onset of hypertension by the following signs:
- squeezing pain in the head;
- feeling as if there is pressure on the eyeballs, discomfort and pain when moving the eyes in any direction;
- blurry images in the eyes, flashing “spots” or black dots;
- dizziness, ringing in the ears;
- urge to nausea and vomiting;
- redness of the skin in the neck and décolleté, which can be diffuse or appear in the form of red spots.
The woman’s well-being sharply deteriorates, and headaches bring maximum discomfort, since taking medications during pregnancy is not allowed, and it is difficult to relieve them with other means. Also, many expectant mothers complain of pain in the chest on the right and in the abdominal area.
Bruises may appear on the body, swelling of the limbs may occur, which subsides overnight, but increases again during the day. If such symptoms are detected, the problem cannot be left without a solution. If the pressure rises to 140 and beyond, this condition is dangerous not only for the woman, but also for the child. You need to urgently contact a specialist to take emergency antihypertensive measures.
Fetal development
At week 39, the child’s weight is 3.2 kg, height is 50.7 cm. The exact figures depend on heredity, the sex of the fetus and the number of pregnancies: the second and subsequent children are much larger than the first, and boys are usually larger than girls.
Despite the fact that the baby receives all the nutrients and oxygen through the placenta, his digestive system is already developed, and the original feces - meconium - has formed in the intestines, which is expelled in the first few days of the baby's life. Don't be intimidated by its appearance; normally it is almost black and oily.
The child is highly dependent on the psycho-emotional state of the mother: he experiences all the same feelings as you. Hormones of stress or pleasure enter his blood, and his movements will be more active during your experiences. Therefore, we wish you peace of mind and more positive emotions.
Treatment of headaches in the 3rd trimester
In the last trimester of pregnancy, you should spend more time preventing headaches. Adequate nutrition, taking into account the increasing need for vitamins and microelements, physical activity and positive emotions are the most important components. For headaches that do not go away after rest, you can take certain groups of medications. They will not harm the child, but the correct dosages must be observed:
- valerian extract, glycine - light sedatives that help cope with stress and nervous tension;
- non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen) - relieve inflammation and pain, but are not suitable for long-term use during pregnancy;
- painkillers (Analgin) - can be taken at home during attacks of acute headache;
- other drugs are prescribed only by a doctor.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers a program for diagnosing and treating headaches during pregnancy in the third trimester. The regimen is developed individually, taking into account test results and other characteristics of the body. At the center it is possible to undergo consultation with specialized specialists and undergo treatment on an outpatient or inpatient basis.
Tests and ultrasound
By the 39th week of pregnancy, all necessary studies have already been completed. Your routine visit to the gynecologist includes the usual measurement of blood pressure, abdominal circumference and weight. Don't forget to take a urine test in advance.
Ultrasound is prescribed only for additional diagnostics if the gynecologist suspects or has previously identified:
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- low location or inappropriate degree of aging of the placenta;
- oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios;
- complex entanglement of the umbilical cord.
The results largely influence the choice of delivery method. If necessary, resort to emergency caesarean section.
What to discuss with your doctor
- If you have entered into a contract for childbirth, undergo a consultation and examination with the selected doctor at the maternity hospital, and provide your exchange card for review.
- If you need the presence of a partner in the maternity hospital, hurry up to write the appropriate application and get tested. Usually the list for the accompanying person is small - fluorography, tests for HIV, AIDS and hepatitis. Sometimes they require a test for antibodies to measles or vaccination data.
- If you are prone to varicose veins or already have problematic veins, consult your gynecologist about the need for compression stockings during childbirth. Special stockings will prevent the development of thrombophlebitis, varicose veins and reduce postpartum swelling. They are especially necessary for women preparing for a caesarean section.
Possible complications
The following conditions are considered dangerous and require emergency delivery.
Uterine tone at 39 weeks of pregnancy
You can feel it by the nagging pain in the lower abdomen. Normally, this condition is associated with training or true contractions. But if the pain is unbearable, has no frequency and is accompanied by bloody discharge, fever or rapid heartbeat, urgent medical intervention will be required. With increased tone, the baby suffers from hypoxia. To save him, doctors induce labor or perform a caesarean section.
Preeclampsia in pregnant women
Its signs are severe swelling, which is especially noticeable at week 39, when normally it should disappear. A woman may feel nauseous, dizzy and weak. A urine test will show a high protein concentration. Another important symptom is high blood pressure.
The insidiousness of gestosis is that it is often asymptomatic, so visit your gynecologist regularly, even in the last weeks of pregnancy, so as not to miss the development of complications and be able to seek medical help in a timely manner.
Diagnostic methods
Headache during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester requires examination if it occurs frequently. At the Clinical Institute of the Brain, it is possible to conduct a full diagnosis, consult with a neurologist, therapist, ophthalmologist and other specialists. In addition, additional examinations may be required:
- general and biochemical blood tests will indicate the presence of inflammatory processes, changes in the cellular composition of the blood, disruption of the kidneys, heart, liver and other organs;
- specific blood tests to determine gas composition and hormone concentrations;
- Ultrasound is the main technique that allows you to assess the condition of internal organs and blood vessels;
- MRI is a more accurate diagnostic method and can be used to examine the brain, but if possible it is postponed to the postpartum period.
Timely diagnosis is the key to correct diagnosis and prescription of a competent treatment regimen. It is important to consult a doctor if you have any ailments that are accompanied by a headache.
Lifestyle
We understand how you want something special and tasty, especially since at 39 weeks your digestive problems have most likely disappeared. However, we recommend that you do not indulge in unhealthy junk food: there is no need for additional stress on the liver now.
Intimate relationships are possible only if there is no prohibition from the gynecologist, and the pregnancy proceeds calmly. Be careful during sex. You probably feel especially sleepy right now. This is normal, this is how the body prepares for childbirth. Try to put everything aside and get more rest.
We do not advise you to lift heavy things. Bags of groceries, and even more so the rearrangement of furniture for arranging a nursery, should be entrusted to your relatives. Overexertion can lead to uterine bleeding and provoke rapid labor.
Increased red blood cells in urine
Elevated red blood cells as a result of a general urine test should alert you.
However, an elevated level of red blood cells in urine is not always associated with disease. For example, strenuous exercise, intense exercise, running, or a blow to the groin area can cause blood to leak into the urine. In this case, the indicator returns to normal within 24 hours. Blood in the urine after exercise (especially after long-distance running) is quite common. This phenomenon even has a name – “marching hematuria”. This phenomenon was first discovered in soldiers who made long walks - marches. The cause of the phenomenon is still not fully understood, but if blood appears in the urine after intense exercise, it is necessary to make sure that the genitourinary system is healthy and there are no chronic diseases or infections. If there is no pathology, blood itself in urine after active sports does not pose a threat.
Another safe cause of increased red blood cells in the urine is incorrect collection of biomaterial. This applies to women. A false overestimated result can be obtained when the analysis is carried out during menstruation and without observing hygienic conditions.
Also, in women with cervical erosion or uterine bleeding, blood from the vagina can get into the urine during the collection of biomaterial, which will also lead to a false result.
There are other physiological reasons why the level of red blood cells in urine increases: severe stress, alcohol, overheating of the body (for example, after a bath). All these factors weaken the walls of blood vessels, making them more fragile, which can lead to minor hemorrhages.
All of the above causes of high red blood cell levels do not pose a health threat. But more common is true hematuria (blood in urine), associated mainly with diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
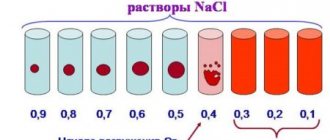
There are two types of hematuria, depending on the amount of blood. Mild hematuria - microhematuria - no more than 20 red blood cells in the field of view. Moderate – up to 200 pieces. Gross hematuria – severe – more than 200 red blood cells in the field of view of the microscope.
An increase in red blood cells in urine can also be caused by the following reasons:
- Urinary tract infections. Bacteria can enter the bladder through the urethra, begin active reproduction and cause inflammation. Symptoms include increased urination, pain and burning, and foul-smelling discharge.
- Kidney infections (pyelonephritis). The disease develops when bacteria rise from the ureters to the kidneys. Symptoms are often similar to bladder infections, although kidney infections more often cause fever and flank pain.
- Stones in the kidneys or bladder. Minerals in urine sometimes accumulate on the walls of the kidneys or bladder, leading to urolithiasis.
- Enlarged prostate. The prostate gland, which lies just below the bladder and surrounds the top of the urethra, often increases in size as men approach middle age. It then compresses the urethra, partially blocking the flow of urine. Signs and symptoms of an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) include difficulty urinating and the need to urinate frequently. A prostate infection causes the same symptoms.
- Kidney diseases. Microhematuria is a common symptom of glomerulonephritis, inflammation of the filtering system of the kidneys. The glomeruli are predominantly affected.
- Oncological diseases. Visible blood when urinating may be a sign of advanced kidney, bladder, or prostate cancer.
- Hereditary disorders. For example, sickle cell anemia (a hereditary defect of hemoglobin in red blood cells) or Alport syndrome (a rare hereditary kidney pathology characterized by changes in the production of type IV collagen fibers, which affect the filtering membranes in the glomeruli of the kidneys).
- Kidney injury. Kidney damage due to an accident, a blow, a fall, or during contact sports.
- Medications. Anticoagulants (such as aspirin or heparin) may cause bleeding in the urinary tract. Penicillin antibiotics have the same property.
The main thing when detecting red blood cells in the urine is to determine the source of bleeding. Three groups of reasons can be distinguished depending on location:
- Prerenal (somatic) – not related to the urinary system.
- Renal – directly related to renal pathologies.
- Postrenal – caused by urinary tract disease.
To determine the localization of the problem, additional diagnostic studies are required - laboratory or instrumental.
Checklist for 39 weeks of pregnancy
- Check all documents and bags for the maternity hospital. Carry your exchange card and passport with you everywhere, and let the signed packages be in a visible place.
- Don't forget about walks in the fresh air. This is both the prevention of hypoxia in the fetus and good preparation of the muscles for childbirth.
- If your stomach becomes hard and pulls your lower back during training contractions, try swinging on a fitball, breathing, lengthening your exhalation, or as if you were blowing out a candle.
- Install the contraction counter app on your phone. It will help you distinguish false from true and go to the maternity hospital on time.
- Try to stay calm and worry less. You can handle everything!