Hematocrit - what is it, what does it depend on
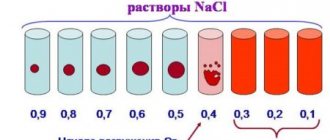
Hematocrit analysis provides data on the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood; sometimes this indicator refers to the ratio of the volume of all formed elements to the total volume. There is no particular difference between the interpretations; 99% of the blood cell volume is made up of red cells. More often, hematocrit is recorded as a percentage of the total volume, less often as a ratio of cell volume to total blood volume.
This indicator is determined as part of a general blood test complex. It is classified as secondary and is calculated based on data on the number of red blood cells. Occasionally, direct measurement of hematocrit is performed by centrifuging the sample. This procedure allows you to separate plasma from formed elements and directly measure this indicator.
What examinations are needed
To identify the cause of the pathological process, a group of techniques is prescribed. Among the events:
- Consultation with a specialist. Specialized doctor. An oral survey for complaints and anamnesis collection are indicated.
- Electrocardiography.
- Ultrasound of the heart. To identify the nature of the pathological process, possible defects and anatomical disorders.
- Ultrasound examination of the digestive tract. First of all, specialists are interested in the condition of the liver.
- General, biochemical blood test. It is used as one of the main techniques.
A decrease in hematocrit occurs against the background of pathological processes and natural phenomena. It makes sense to carefully study the situation. After which, think about how to proceed. This is the task of doctors.
Indications and preparation for analysis
Indications for hematocrit analysis are symptoms indicating the development of anemia or other diseases of the blood or hematopoietic system. These include:
- Pale or jaundiced skin
- Enlarged spleen, liver
- Changes in the size of lymph nodes
- Digestive disorders
- Skin and hair problems (rashes, ulcers on mucous membranes, hair loss or brittleness)
In addition to identifying anemia, the analysis allows us to identify other diseases, for example, polycythemia (a chronic disease in which the bone marrow produces an excess amount of red blood cells) of various origins. This study is also used when it is necessary to assess the need for blood transfusion and calculate the required volume of transfusion.
No special preparation is required for the hematocrit test. It is necessary to follow the standard rules for conducting a general blood test:
- Blood is drawn early in the morning.
- You should not eat food 6-10 hours before the test.
- Avoid alcohol 2-3 days before the procedure.
Patients who smoke are advised to abstain from smoking for at least 2-3 hours before blood collection. If these recommendations are not followed, the analysis may give unreliable results. This is due to the fact that the composition of the blood is subject to strong fluctuations depending on the action of various environmental factors.
Treatment of crises and complications
The main goal of treatment is to prevent crises and reduce the risk of complications, such as kidney and liver pathologies, stroke, heart attack, visual impairment and prolonged depression. Doctors, as a rule, recommend the drug Hydroxycarbamide for any type of disease: it reduces the risk of developing anemia and speeds up recovery.
Advertising:
The patient’s well-being is also positively affected by:
- minimizing stress and overexertion;
- moderate exercise;
- proper consumption of drinking water.
Quite often, cases of false hematocrit are observed, for example, due to incorrect general analysis, long clamping of the vein with a tourniquet, taking the analysis in an inappropriate position, etc.
Critical hematocrit values require immediate blood transfusion to save the patient’s life.
Blood test for hematocrit
The manipulation is performed in the morning, blood is taken from a vein or from a finger. At the Medart clinic, the most modern equipment is used for analysis, so the sampling is most often done from a vein.
To obtain the material, special vacuum containers (vacutainers) are used. This is a modern syringe replacement that provides a number of benefits for the patient:
- Virtually painless procedure.
- Minimum time to obtain the required amount of blood.
- Accurate calculation of the amount of reagent and blood.
- Minimum time for conducting the study and issuing results to the patient.
Modern technologies allow the procedure to be carried out as quickly as possible, without consequences for health.
Reducing factors in children
In young patients, the development of a pathological process is possible as a result of the influence of several other factors.
Children's pediatric diseases
Scarlet fever, chicken pox and many other disorders. Everything goes in line with the infectious inflammatory phenomena described above.
Once the condition returns to normal, the hematocrit will also stabilize. It is the underlying disease that is subject to treatment, not the altered indicator.
Chromosomal abnormalities
They occur quite often. The exact statistics are not known. A low hematocrit level in a child’s blood may indicate the development of a genetic disorder.
A classic of the genre is aplastic anemia, which most often has a congenital origin.
Do not forget about the phenomena described above.
Norms
The normal hematocrit level depends on the age and gender of the person. For a mature woman it is 37-50%, for a man 34-45%. For newborns, this figure may be higher and ranges from 35 to 65%. As people grow older, the hematocrit decreases, reaching minimal levels in the elderly. This is the result of decreased bone marrow activity and decreased production of blood cellular elements.
A decrease in normal hematocrit in women is associated with regular blood loss during menstruation. High values in children are a manifestation of active processes in the development of red bone marrow and other hematopoietic organs.
It is important to consider that after massive blood losses and blood transfusions, determining the hematocrit level will give results with a large error. To reliably assess this indicator in such cases, it is necessary to wait a certain time.
It may take up to 3 months for complete physiological restoration of red blood cell levels to normal levels. This period is the life cycle of red blood cells, during which the cellular composition of the blood is renewed.
Danger during pregnancy
During pregnancy, NCT levels should be constantly monitored: to avoid the development of anemia, doctors prescribe systematic testing. In this case, there are several reasons for low HCT levels:
Advertising:
- pregnancy a short time after a previous birth;
- early age of the expectant mother;
- pregnancy with multiple fetuses;
- severe toxicosis;
- insufficient consumption of foods containing iron;
- anemia was diagnosed before pregnancy.
If left untreated, the following consequences are possible:
- premature birth;
- postpartum depression;
- underweight baby;
- anemia of the newborn;
- blood loss during childbirth;
- the birth of a baby with behavioral problems;
- delayed physical development of the child.
Hematocrit increased
An increase in the level of red blood cells detected in a hematocrit analysis may indicate various pathological conditions. The most common:
- Primary erythrocytosis. It occurs as a result of overactive production of red blood cells, including immature forms. May indicate the development of tumors in the bone marrow.
- Secondary erythrocytosis. Develops as a consequence of pathologies of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems (heart defects, respiratory failure).
- Reduced plasma volume. May indicate the development of peritonitis, leukemia, kidney disease. Often occurs with extensive burns, when blood plasma sweats through the damaged dermis.
- Dehydration. Observed in uncompensated diabetes mellitus, it can result from diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating and lack of fluid in the diet.
Erythrocytosis can develop in heavy smokers, especially if smoking has led to secondary damage to the respiratory system and heart. In this case, the body turns on mechanisms to compensate for insufficient oxygenation due to a significant increase in the number of red cells.
An increase in hematocrit is not always a consequence of disease. An increase in the number of red blood cells is considered normal for residents of mountainous areas and professional climbers. When exposed to high altitude conditions for a sufficiently long time, the body compensates for the lack of oxygen and atmospheric pressure by increasing the production of red blood cells.
Erythrocytosis is often asymptomatic and is discovered by chance during a blood test for other reasons. Only with a significant increase in hematocrit are the following observed:
- Pain in joints, muscles.
- Dyspnea.
- High blood pressure.
- Ringing in the ears and dizziness.
- Increased sweating, sleep disturbances.
These symptoms are not specific, so if such ailments occur, you should consult a doctor for further diagnosis.
To restore the physiological level of hematocrit, it is necessary to find out the reason that led to an increase in the amount of blood cells and eliminate it. For example, if erythrocytosis was caused by dehydration (lack of water in the body - dehydration), it is enough to restore the normal amount of fluid to normalize this indicator.
There is no need to self-medicate; only a specialist can accurately determine the cause of the increase in hematocrit and prescribe the correct diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, if there are any changes in the blood test, you should consult a specialist and strictly follow the recommendations received.
Methods for treating low hematocrit
Advertising:
If the hematocrit is below normal, this means that the patient needs to reconsider his diet and replenish the lack of iron in the body. In addition, you need to increase your intake of vitamin C, which helps to better absorb iron.
Useful products are listed in the table.
| Iron-rich foods | Vegetables and fruits containing vitamin C |
| Greenery | Tomatoes |
| Beef liver | Strawberry |
| Fish | Oranges |
| Legumes | Limes |
| Red fish meat | Tangerines |
| Eggs | Bergamot |
| Dried fruits | Lemons |
| Chicken | Grapefruits |
If consumption of such food is impossible due to allergic reactions, then the patient is given special supplements containing iron. An iron course can be recommended in the form of injections or in tablet form. If the main reason for the indicators is below normal is medications, then they are canceled, and the doctor selects others that do not affect the hematocrit. Iron deficiency can also be replenished with vitamin complexes that are specially designed to increase iron levels and contain all the necessary components for better absorption.
One of the most serious causes of a hematocrit below normal is sickle cell disease. Red blood cells are disc-shaped flexible cells. In the case of sickle cell anemia, they become more rigid and sickle-shaped (contain defective hemoglobin). Such red blood cells cannot move freely and can block blood vessels, leading to damage to organs and tissues. In this case, a special treatment regimen is required, as well as consultation with several specialists: a hematologist, cardiologist, therapist and neurologist.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
The etiology of hematocrit disorders is numerous and varied. A decrease or increase in this specific blood parameter is caused by both natural causes, which resolve themselves over time, and pathologies that require immediate medical intervention.
Type 1 etiological factors include:
- heavy blood loss due to trauma or surgery;
- a debilitating diet and an unbalanced vegetarian diet low in iron;
- sedentary life (physical inactivity);
- dehydration of the body;
- taking diuretic medications and a course of treatment with loading doses of corticosteroid drugs;
- oxygen starvation, which the body tries to compensate for by increased synthesis of hemoglobin.
The latter reason may be caused by the region of residence (mountainous areas located high above sea level) or abuse of nicotine, which constricts blood vessels.
Pathological factors for hematocrit disturbances and deviations from the norm given in the table in women by age include:
- leukemia and other blood diseases;
- erythremia - proliferation of red blood cells;
- secondary erythrocytosis;
- tumor neoplasms in the renal organ, causing increased synthesis of erythropoietin;
- hydronephrosis and polycystic pathologies;
- Congenital heart defect;
- hemoglobinopathy;
- dysfunction of the lungs and other respiratory organs;
- sickle anemia.
Hodgkin's lymphoma, a malignant destruction associated with the proliferation of lymphoid tissue cells, leads to a violation of the hematocrit number. Red blood cells destroy some pathogenic agents and inhibit intoxication of the body with synthetic or organic poisons.
Possible complications
Imbalance of the blood formula leads to acid-base imbalance in the body, dysfunction of internal organs, and creates favorable conditions for the invasion of pathogenic pathogens. This is fraught with numerous complications and the formation of severe pathologies.
With increased blood viscosity, it is difficult to remove waste and toxins from the body, and the protective abilities of the immune system are suppressed.
Life-threatening pathologies resulting from hematocrit disorders:
- myocardial infarction;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- airway spasm;
- gangrene of the limbs requiring surgical amputation.
A change in the rheological properties of blood in a pregnant woman’s body leads to highly complicated labor and fetal hypoxia. A child may be born with severe disorders of the central nervous system, destruction of bones and muscle fibers.
In such a responsible physiological state, a woman needs to carefully ensure that the hematocrit is normal. By age, such a deviation is more typical for pregnant women after 35 years of age than for young girls. If the Ht value is very high, the risk of developing thrombosis and vein blockage increases sharply.
Indications
The appointment of an OAC, which includes a hematocrit study, is included in the standard patient examination plan and is mandatory:
- when undergoing a medical examination and/or medical examination;
- if any disease is detected or suspected by a clinic doctor;
- in preparation for planned surgery;
- during hospitalization (on the day of admission and on the eve of discharge).
Calculation of the hematocrit number is required for certain indications;
- blood clotting disorder;
- dehydration (dehydration);
- assessment of the degree of anemia (anemia), polycythemia (increase in blood cells);
- bleeding.
Why is it dangerous?
What does it mean if the hematocrit is increased? How dangerous is this?
- The cause of an increased hematocrit may indicate a serious disease (for example, erythremia or kidney cancer).
- Hematocrit is a synonym for blood viscosity. The higher the viscosity, the slower the blood flows through the vessels, the higher the risk of stasis and blood clots. And thrombosis in small and medium-sized vessels means strokes, heart attacks, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism. These are the most serious complications that most often lead to sudden death.
How and under what conditions is it produced?
Red blood cells, called red blood cells, are special cells that deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues. This laboratory indicator determines their content relative to other formed elements.
Red blood cells consist of hemoglobin, a specific protein that captures oxygen atoms and transports them into cells, simultaneously removing carbon dioxide. The standard blood formula of a healthy person consists of 60% plasma (liquid) fraction and 40% formed elements.
Hematocrit (the norm in women varies by age under certain physiological conditions) characterizes their ratio with leukocytes and platelets, the total content of which does not exceed 1%. Indirectly, this laboratory parameter acts as an indicator of cell respiration.
The hematocrit value is used for:
- diagnosing anemia and assessing the effectiveness of its treatment;
- determining the level of tissue dehydration;
- making a decision on the advisability of hemosorption;
- obtaining data on the results of transfusion.
This specific laboratory sign is a component of a biochemical blood test and is not assessed separately. The hematocrit number is always directly related to the volume of red blood cells, provided that the latter are of standard size.
There is no relationship between the factors influencing the synthesis of intracellular hemoglobin and the level of their content in the blood plasma. The deviation of this laboratory indicator from the standard value does not necessarily indicate the presence of pathology, but serves as a basis for additional examination.