Important
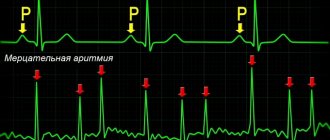
Atrial fibrillation is the most dangerous type of heart rhythm disorder.
It is fraught not only with the unpleasant sensations of heart failure, shortness of breath and pain in the chest, but also with dangerous stagnation of blood, as a result of which clots - thrombi - form in the vessels of the heart. By attaching to the vascular wall, they clog the bloodstream, preventing normal blood flow. But the worst thing happens when this clot breaks away from the walls of the blood vessels and, together with the blood flow through the ventricles of the heart, enters the aorta, and then into the brain. A cardioembolic stroke occurs, the devastating consequences of which cause large-scale brain damage.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation)
There are several ways to treat atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation) and restore sinus rhythm. These are oral administration of antiarrhythmic drugs, intravenous administration of antiarrhythmic drugs, and cardioversion (electrical pulse therapy, EIT). If the doctor restores the rhythm in a clinic or at the patient’s home, they most often start with intravenous medications, then take pills. The procedure is carried out under ECG control, the doctor observes the patient for 1-2 hours. If restoration of sinus rhythm does not occur, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital. In the hospital, drugs can also be administered intravenously, but if time is limited (the duration of the attack is approaching the end of the second day) or the patient does not tolerate the paroxysm well (a decrease in blood pressure is observed, etc.), EIT is more often used.
Cardioversion is performed under intravenous anesthesia, so the electrical shock is painless for the patient. The success of rhythm restoration depends on many factors: the duration of the attack, the size of the heart cavities (in particular, the left atrium), sufficient saturation of the body with an antiarrhythmic drug), etc. The efficiency of EIT is close to 90-95%.
If paroxysm of atrial fibrillation lasts more than two days, restoring the rhythm is possible only after special preparation. The main steps are taking blood thinning medications under the control of a special analysis (INR) and conducting transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) before EIT to exclude blood clots in the cavities of the heart.
Patient Reminder
The following rhythm disturbances are distinguished::
- with an increase in heart rate (tachycardia), in which the heart rate at rest exceeds 100 beats/min. It is observed with increased body temperature, myocarditis, heart failure, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, anemia, and diseases of the nervous system. In this condition, the patient experiences increased heartbeat with unpleasant sensations in the heart area.
- with a decrease in heart rate less than 60 beats/min. (bradycardia). It can be a manifestation of neurocirculatory dystonia, and also occur with myocardial infarction, sick sinus syndrome, with increased intracranial pressure, decreased thyroid function (hypothyroidism), with certain viral diseases, under the influence of a number of medications. It is also found in neuroses and pathologies of the digestive system.
- with extraordinary contractions of the heart (extrasystole). The most common causes of such contractions are myocardial diseases, damage to the valvular apparatus of the heart, coronary disease, reflex effects from other organs (peptic ulcers, cholelithiasis, diaphragmatic hernia, etc.).
Paroxysm of atrial fibrillation - what to do?
If you experience an attack of uneven rapid heartbeat for the first time, you should immediately consult a doctor or call an ambulance. Even if you feel good. Remember - it is very important to record the attack on the ECG. The attack may end on its own after some time, but it is necessary to restore the correct rhythm within the first two days. The more time passes from the onset of paroxysm, the more difficult it is for the heart to restore normal function and the higher the risk of blood clots forming in the chambers of the heart. If more than two days have passed since the onset of the attack or you do not know exactly the time of its occurrence, it is necessary to restore the heart rhythm only under the supervision of a doctor after examining the heart chambers with echocardiography, echocardiography (to exclude already formed blood clots) and special preparation with blood thinning drugs (to prevent thrombosis).
If paroxysms of atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation) occur frequently, you need to work with your doctor to develop a plan for your actions during an attack. If the arrhythmia is well tolerated and during short (no more than 24 hours) attacks of arrhythmia, which often end on their own, no special actions can be taken. It is necessary to continue taking the medications recommended by your doctor without changing the dose. If an attack occurs, your doctor may recommend a one-time dose of an antiarrhythmic drug in addition to basic therapy or a temporary increase in the dose of medications you are already taking. If during a paroxysm of atrial fibrillation your health worsens significantly, or the arrhythmia continues for more than a day, you must consult a doctor.
What is “better” – attacks or constant atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation)?
For a long time, doctors believed that the only optimal result of treatment was the restoration of correct, sinus rhythm. And now, in most cases, the doctor will advise you by all means to restore and maintain sinus rhythm. However, not in all cases. Studies have shown that if it is impossible to effectively maintain restored sinus rhythm (when the heart constantly “breaks down” into atrial fibrillation), permanent atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation) with drug control of the heart rate of about 60 beats per minute is safer than frequent paroxysms of atrial fibrillation (especially prolonged ones, requiring the administration of high doses of antiarrhythmic drugs or electrical impulse therapy).
The decision on the advisability of restoring sinus rhythm or maintaining a permanent form of atrial fibrillation is made by the doctor. In each case, such a decision is individual and depends on the cause of the arrhythmia, the disease against which it arose, its tolerability and the effectiveness of the treatment for atrial fibrillation carried out to maintain the correct rhythm.
An attack that lasts more than two days must be treated only under the supervision of a doctor, after special preparation. If sinus rhythm is successfully restored, the doctor will adjust ongoing antiarrhythmic therapy and recommend taking blood thinners for at least a month after cardioversion.
Treatment methods for arrhythmia
When choosing a treatment method, the type of arrhythmia and the reason that triggered its development are taken into account. 1. In some cases, to normalize the heart rate, it is enough to relieve the symptoms of the underlying disease (thyrotoxicosis, electrolyte imbalance). 2. Treatment of rhythm disturbances associated with degenerative processes in the myocardium is carried out with medication and is complex. Along with antiarrhythmic drugs, drugs are prescribed that improve the supply of oxygen to the myocardium, as well as drugs that facilitate the work of the heart. , drug therapy is also carried out : blood thinning drugs (anticoagulants) are prescribed. The heart muscle is supported with metabolic drugs. 4. If conservative therapy is ineffective, cardiologists recommend low-traumatic surgical techniques that can radically solve the problem of cardiac arrhythmia. The pathological pacemaker is eliminated using radiofrequency ablation, defibrillation is performed, a pacemaker is installed, etc.
Symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia
The severity of symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia does not always correspond to the severity of the condition. Deadly rhythm disturbances often occur asymptomatically, and relatively harmless sinus arrhythmia sometimes causes a painful sensation of cardiac arrest. An accurate diagnosis can be made by a doctor after conducting diagnostic tests. You should seek help from a cardiologist if you have any alarming signs: • a feeling of palpitations, interruptions in heart function; • pain behind the sternum or in the area of cardiac impulse; • attacks of dizziness; • episodes of loss of consciousness; • fast, slow or uneven pulse. In severe cases, pathologies of the rhythm of myocardial contractions lead to circulatory disorders. Swelling appears on the legs, increasing in the evening and subsiding in the morning. Shortness of breath occurs with minor physical or nervous stress. Increasing signs of heart failure hide the symptoms of arrhythmia.
Cost of services of an arrhythmologist
| Payment code | Nomenclature of the Ministry of Health and Social Development | Name | Price, rub.* |
| 1089 | B01.043.003 | Appointment (examination, consultation) with a doctor for X-ray endovascular treatment of cardiac arrhythmias | 4 300 |
| 1090 | B01.043.004 | Appointment (examination, consultation) with a doctor for X-ray endovascular treatment of cardiac arrhythmias with checking the operation of the pacemaker | 6 100 |
| 9004 | A05.10.006 | Electrocardiogram registration | 1 600 |
| 9006 | A05.10.008 | Holter heart rate monitoring (HM-ECG) | 4 800 |
| 15023 | A16.10.014.003 | Implantation of a two-chamber pacemaker (pacemaker), without the cost of the electrode and pacemaker | 125 000 |
Make an appointment for a fee
Find out more about the direction “Arrhythmology”
Causes
Pathology occurs against the background of cardiac (heart) or extracardiac (non-cardiac) diseases, as a result of previously performed surgical operations.
Atrial fibrillation can be caused by:
- arterial hypertension;
- ischemia;
- mitral stenosis;
- mitral valve insufficiency;
- cardiomyopathy;
- pericarditis;
- neoplasms in the heart;
- heart defects;
Extracardiac factors that influence the development of atrial fibrillation:
- lung diseases (pneumonia, malignant tumors, pulmonary embolism, sarcoidosis);
- obstructive sleep apnea (accompanied by snoring and partial cessation of breathing);
- obesity;
- thyroid diseases.
Arrhythmia attack: how to relieve it, symptoms of heart pathology
Acute coronary death: causes, emergency care and prognosis
Unstable heart function can be caused by a variety of reasons, both physiological and pathological. An attack of arrhythmia is often associated with impaired functionality of the cardiovascular system, concomitant diseases and excessive physical stress for the body.
The main signs of an arrhythmia attack
A pathological deviation can manifest itself with many symptomatic manifestations, not always associated with impaired activity of the heart muscle. The main signs of the disease include:
- sudden feeling of pressure and compression in the chest area;
- painful sensations in the retrosternal region, with irradiation towards the scapular area, upper limb or back;
- insufficient oxygen supply, causing shortness of breath;
- bursts of pain in the epigastric region, accompanied by nausea;
- rapidly increasing fatigue and exhaustion;
- panic attacks, with the release of cold sweat and periodic dizziness.
At the time of the attack, changes in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle are recorded in patients - from slowing down to the maximum number of beats per minute. Experts say that the effects of extrasystole and tachycardia pose a greater danger than the symptoms of bradycardia.
Correct identification of the reasons for the deterioration of the condition will allow the deviation to be stopped in an accelerated time, and will prevent the development of serious complications.
How to relieve an attack of arrhythmia at home
Emergency first aid can be provided by any third party who knows the principles of therapy. Attacks of arrhythmia can catch a patient anywhere - at home, on the street or on public transport. To suppress negative symptoms, you must perform the following algorithm of actions:
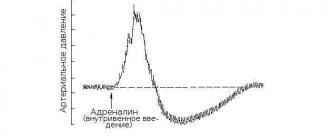
- reassure the victim - any third-party interference worsens the situation, and excess panic causes the body to release new portions of adrenaline, which accelerates the heartbeat;
- free access of oxygen - open all windows in the room, remove the patient from public transport, ask onlookers to disperse;
- unbutton or remove all constrictive clothing - sweaters, ties, collars;
- try to put the victim down or sit down - when in a “sitting” position, the head should look down;
- remove any factors that provoke an attack - stop working, give up cigarettes, coffee and alcoholic drinks;
- if possible, measure blood pressure;
- count your pulse on your wrist.
The main actions in case of sudden changes in condition are explained by the attending physician, for patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular department. In the case of a primary abnormal condition, without a diagnostic examination it is impossible to understand the root cause of the formation of the arrhythmic phenomenon.
During the first outbreak of the disease, doctors recommend using:
- swallow, without chewing, a small crust of bread;
- wash your face with ice water or immerse your face in it for a few seconds;
- take a deep breath, exhale forcefully (covering your mouth and nose with your palms);
- do not breathe for several minutes - to suppress the accompanying panic attack;
- induce a gag reflex by pressing on the root of the tongue;
- try to clear your throat;
- gently press on the eyeballs, after closing the eyes;
- perform a small massage in the cervical area.
Therapy methods
If arrhythmia occurs, every person should know what to do at home. Rhythm disturbances can occur at any time, even in a healthy patient.
Basically, the causes of such failures are hidden in hypertension, chronic diseases, and self-treatment with medications. There are several methods of therapy.
Medicines
The main drugs for arrhythmia: diuretics, statins, cardiovascular drugs. They have a beneficial effect in the development of various emerging pathological processes.
But it is important to consider that the effect lasts only with long-term use. Antiarrhythmic drugs include: Cordarone, Sotalex, Propanorm
They have a good effect on the heart muscle. Often prescribed for prevention
Antiarrhythmic drugs include: Cordarone, Sotalex, Propanorm. They have a good effect on the heart muscle. Often prescribed for prevention.
It is important to remember that medications are taken only after a doctor’s prescription.
First aid
It is important to know how to eliminate heart arrhythmia at home. Useful procedures:
Correct breathing. To do this, the patient must take a deep breath through his mouth. Then you need to hold your breath and strain. Stay in this state for up to 10 seconds. The air should be exhaled gradually, pursing your lips into a tube. It is recommended to carry out such procedures several times. Gentle pressure on the eyes
Using several fingers of each hand, apply gentle pressure on the eyes. Do it within a minute
You can carry out manipulations several times. Often such methods can stop attacks of tachycardia. It also helps reduce your heart rate. Massage. Every person has a carotid artery in the neck. Blood pressure can be monitored at this point. Massage movements are made with the thumb, gently pressing on the artery for 5 minutes. This should be done on both sides of the neck, in turn. Pulse check. If the dysfunction of the organ is associated with emotional tension, stress, then counting the pulse out loud will be useful. The person must take a sitting position. You need to close your eyes and feel the pulse on your left hand. Then you need to count your pulse loudly for 5 minutes. Self-hypnosis of calm. The person takes a position that is comfortable for him, closes his eyes and tries to relax as much as possible. You should place your right hand on the heart area and begin to speak soothing words. This must be done within 10 minutes. Gradually you can see your heart rate return to normal.
Traditional methods
It is useful to know what to take for arrhythmia at home. Especially if there are no medications. Effective means:
- Valerian and calendula. Each product will need 1 tbsp. l. The mixture must be poured with boiling water - 1 cup. It is necessary to insist for several hours, and then take throughout the day, dividing the entire amount. The course of therapy is 14 days, and then take a break for a week.
- Hawthorn. A decoction of this plant is recommended to be taken before meals. In addition to the decoction, take a tincture that helps strengthen the myocardium.
- Motherwort. It is recommended to drink the infusion before bed. If desired, you can add a small amount of honey.
- Tincture of elecampane. Half a glass of the roots of this plant is poured with vodka. They infuse for two weeks. After this time, you can take 1 tsp every day.
Manipulation
If a patient has been diagnosed with cardiac arrhythmia, treatment is carried out using modern methods. One of them is radiofrequency ablation.
The operation is performed by a surgeon using a special catheter equipped with an electrode. It allows you to get a drawing in 3D format. The computer highlights areas that have been affected.
The patient himself is under the influence of an electromagnetic field. Using a catheter, you can determine areas of pinpoint action. Then the affected area is determined.
This intervention is carried out without x-rays. The operation lasts a maximum of 3 hours. The patient is under local anesthesia. Since the catheter is passed through the femoral vein, recovery after surgery lasts no more than 2 days.
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia in City Clinical Hospital No. 31
Treatment of arrhythmia in City Clinical Hospital No. 31 is carried out in accordance with international protocols. The clinic has modern equipment that ensures accurate diagnosis and successful minimally invasive interventions. In the field of arrhythmology, we provide a full range of medical services: • primary diagnostics; • consulting on research results; • conservative therapy; • dispensary observation; • consultations of patients who were treated in another outpatient clinic or hospital; • checking and adjusting a previously installed pacemaker; • implantation of a pacemaker. After the pacemaker operation, patients are provided with comfortable rooms in the cardiology department of the hospital.
The clinic has a compulsory medical insurance policy, and the conditions for the provision of paid services can be found here
Seizure: how rhythm disturbance manifests itself
Most often, arrhythmia is one of the complications or consequences of heart disease, worsening the course of the pathological process
An acute situation or chronic illness may manifest itself with typical cardiac symptoms, of which the following signs should be paid attention to:
- pressing and squeezing sensations in the chest;
- radiating pain in the back, arm or under the shoulder blade;
- shortness of breath with a feeling of lack of air;
- pain in the epigastric region with nausea;
- fatigue and rapidly increasing fatigue;
- feeling of panic and fear with cold sweat and dizziness.
Attacks of cardiac arrhythmia are accompanied by a change in heart rate: extrasystole and tachycardia are more dangerous options than bradycardia.
Variants of rhythm disturbance
It is especially important to recognize the first episode of cardiac arrhythmia in time. For frequently recurring arrhythmic conditions, it is best to prevent an attack using simple procedures and medications recommended by your doctor.
Attacks of atrial fibrillation - how to prevent?
To prevent paroxysms of atrial fibrillation from reoccurring, the patient must constantly take an antiarrhythmic drug. For the purpose of prevention. Today there are many antiarrhythmics; the choice of drug must be made by the doctor. A patient with atrial fibrillation requires observation by a cardiologist, during which regular examination is carried out (for example, echocardiography once a year, or 24-hour Holter monitoring, if necessary, to assess the effectiveness of treatment), and treatment correction. The selection of drug therapy is always, for any disease, a very painstaking task that requires literacy and perseverance on the part of the doctor and understanding and diligence on the part of the patient. Not only the effectiveness, but also the tolerability of treatment can vary from person to person.
The ineffectiveness of drug therapy for atrial fibrillation may be an indication for surgical treatment. In the left atrium (near the confluence of the pulmonary veins) there are zones in which electrical impulses are generated that can trigger atrial fibrillation. Increased electrical activity in these areas can be detected using a special electrophysiological examination (EPI). A special catheter is inserted into the heart cavity, the information obtained allows you to create an electrical “map” and determine trigger (“trigger”) areas. The examination is carried out under local anesthesia and is quite safe for the patient. After identifying the “trigger” areas, an operation is performed - radiofrequency ablation of trigger zones (RFA). The catheter uses high-frequency current to destroy these areas and disrupt the initiation of the arrhythmia. In four out of five cases, atrial fibrillation does not return.