OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE LUMBAR-SACRAL SPINE
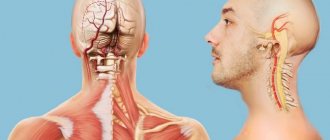
Damage to this part of the spine (Fig. 1) occurs most often, which is due to both the anatomical features of the structure of the spine and the characteristics of human life, because The lumbar region bears the greatest load. The most common pathologies found in this part of the spine are osteochondrosis and complicated forms of osteochondrosis, compression-radicular syndromes, and dysfunction of the nerve root in the form of neuropathies.
The most common syndromes of the lumbar spine are sciatica, lumbago, lumbar radiculitis (lumbar osteochondrosis) and intercostal neuralgia. Each of these syndromes consists not only of pain in the spine, but also secondary inflammatory changes in the muscles near the affected part of the spinal column, as well as symptoms of poor circulation and swelling of internal organs.
Clinic. Manifestations of the disease can be very diverse, depending on the stage of the process. Long-term pain syndrome, foot paresis (“slap foot”), compensatory scoliosis in the lumbar region, tension of the rectus muscles of the back, pain on superficial palpation, hyporeflexia of tendon reflexes, hypotonia of the lower leg muscles with impaired walking function, etc.
The results of clinical observations indicate a pronounced therapeutic effect of laser therapy in patients with osteochondrosis. After the first RT session, the absence of pain was observed in 60-65% of patients, improvement in motor activity was noted in 20-25%, and normalization of sleep in 50% of patients. After the first course of treatment, a positive effect was observed in almost 100% of patients with an early stage of the disease. When the process is started, it is achieved after 2-3 courses of treatment.
OSTEOCHONDROSIS
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic process that develops in the cartilage and bone tissue of the spine. This is the most common spinal disease, affecting more than 70% of the population. The resulting pain syndrome is explained by the fact that the intervertebral disc cannot withstand the load and its protrusion forms.
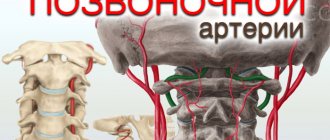
Nerve processes, blood vessels and the spinal cord are located around the intervertebral disc. A disc herniation, affecting any of the nerve processes, causes its inflammation, which leads to pain. The second cause of the pain symptom may be pinching of the spinal nerve at the site where its root exits the lumbar spine, and compression of the root can be caused by bone growths (reactive growth of marginal osteophytes).
Osteochondrosis most often affects older people, as well as overweight people. The disease is a serious medical and social problem, because has a chronic course and often leads to temporary or permanent disability.
Clinical trials conducted in a number of clinics in Russia and the CIS countries have proven the high effectiveness of laser therapy for osteochondrosis.
Considering the fact that with this therapy, the paravertebral vessels running along the sides of the spine enter the treatment zone, i.e. Simultaneously with the local effect, the effect on the blood is also carried out; laser hemotherapy (LHT) is not carried out separately.
The concept of extrasystole
Extrasystole is an untimely contraction of any part of the heart, a subtype of arrhythmia. This violation does not pose a direct threat to life. Moreover, a mild degree of extrasystole is considered physiologically normal. An example of a healthy “failure” in the functioning of the heart muscle is the heart “fading” from happiness, “stopping” it from strong emotions, or a rhythm disturbance as a result of severe fatigue or lack of sleep.
There are 3 types of heart rhythm disturbances based on the frequency of extraordinary contractions:
- Rare – up to 100 per day;
- Medium frequency - extraordinary strikes number in the hundreds;
- Frequent – more than 700 per day.
Up to 70% of people experience symptoms of untimely contraction of the heart muscle. In most cases this is ventricular arrhythmia.
ARTHROPATHIC PSORIASIS
Arthropathic psoriasis. The most severe form and less manageable in terms of treatment in patients with psoriasis is arthropathic. According to established tradition, psoriasis still refers to skin diseases, although the systemic nature of this process and the ability of psoriasis to affect not only the skin, but also internal organs, the nervous system and joints have been established.
Psoriatic arthritis is characterized as a systemic process in which the most pronounced changes appear in the structure of connective tissue. Psoriatic arthropathy can occur benignly as monoarthritis or in the form of polyarthritis, and in some patients it takes on the character of severe destructive polyarthritis. Psoriatic arthritis often occurs in parallel with skin lesions or slightly later, and in some cases, articular syndrome may precede skin manifestations.
Joint involvement usually begins in the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands and feet. Gradually, medium and large joints are involved in the process, including the spine, with the development of ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis). Swelling, pain, and limited joint mobility are noted as a result of infiltration and compaction of the periarticular tissues. In the further course of the process, dislocations, subluxations, and ankylosis can form, leading to joint deformities, and the patient becomes completely disabled.
In addition, a progressive asthenic state sets in, up to cachexia, myalgia, atrophy of the muscles of the hands, forearms, and legs (12-15%). As with ordinary psoriasis, in patients with psoriatic arthropathy, insufficiency of liver and kidney function, immunodeficiency states, and cardiovascular pathology are determined.
Treatment. As with rheumatoid arthritis, treatment is comprehensive and is aimed at eliminating the manifestations of the disease, restoring metabolism in the articular cartilage and preserving the function of the affected joints. Drug therapy is aimed at achieving a desensitizing, detoxifying and anti-inflammatory effect.
We have already mentioned earlier that laser therapy has all these properties, and, in addition, it also has an immunocorrective effect - it must be included in the treatment process. Laser therapy is carried out both by affecting the blood (LHT) and locally on the area of the affected joints.
What is characteristic of vegetative-vascular dystonia
It is important for a VSD patient to understand that his arrhythmia is of a functional nature. And no matter where exactly and in what quantity it occurs, one thing is clear: the heart is healthy, and the reason lies in something completely different.
Extrasystole in such patients manifests itself when a large amount of adrenaline enters the blood. But as soon as it decreases to normal, all sensations subside. That is, the problem is temporary and reversible. But patients tolerate it very hard. For them, this is like death: heart failures catch them suddenly, they can be repeated for several months and even years, until the cause is eliminated.
At this moment, a person is seized by a feeling of fear. He begins to choke, his legs give way, and he may lose consciousness. The patient becomes pale, begins to rush about, and scream. The sensation in the chest resembles a blow to the rib cage.
An even greater fear is the compensatory break after an extraordinary compression. The patient fears that his heart will stop. It seems to him that he will die, and this cannot be avoided.
If the excitement intensifies, then the symptoms worsen. Atrial fibrillation occurs. It seems that the heart works outside the regime, chaotically, as it pleases. Fortunately, this condition rarely occurs.
HEEL SPUR"
It is a bone outgrowth at the site of tendon attachment, which is characterized by painful sensations in the area of the sole.
Clinic. At the beginning of the disease, pain occurs when walking. It is especially difficult to start walking when acute pain occurs during exercise. Then, during the day, the pain when walking subsides somewhat, and by the end of the day it intensifies again. Over time, the pain becomes persistent.
People with excess weight, diseases of the spine and large joints of the lower extremities, flat feet, as well as athletes with prolonged local overload in this area are predisposed to the development of heel spurs. Currently, the treatment of heel “spurs” consists of providing relief with the use of various types of insoles and heels, complex physiotherapeutic treatment, and if there is no effect, surgical treatment - surgical removal of the bone outgrowth and excision of the altered tissue.
Laser therapy. Highly effective for this pathology. As a rule, the full effect is achieved after 2-3 courses.
The high efficiency and safety of modern laser therapy allows the population to use it as a home doctor. The manual included with the device allows you to correctly carry out the appropriate treatment of various diseases of the joints and spine. A prerequisite for purchasing a device for treatment at home is to carefully study the attached manual.
Why do extrasystoles occur during VSD?
Cardiac “dancing” in vegetative-vascular dystonia can occur when both parts of the autonomic nervous system are disrupted.
If the sympathetic department fails, extrasystoles appear after physical exertion. They are poorly controlled by sedatives, and may even intensify after taking them.
If the functioning of the parasympathetic system is disrupted, in addition to cardiac symptoms, digestive disorders are of concern: epigastric pain, diarrhea, bloating. A cup of coffee or sweet tea or a brisk walk will help relieve such an attack.
If the cause is psychological, treatment measures are directed in the other direction.
Most often, dystonics are bothered by two types of extrasystole:
- Ventricular. Usually makes itself felt in the first half of the day. It is caused by disturbances in mental balance, for example, great joy or grief. It also appears when the weather changes or when drinking strong drinks. Other provoking factors include magnesium and calcium deficiency, osteochondrosis. It all starts with an intense beat in the heart area, followed by a pause. The patient becomes covered in cold, sticky sweat and develops a feeling of fear. Despair sets in, he cannot choose a comfortable position for himself, becomes numb or begins to fuss. The violence of his heart leads him into an uncontrollable state, causing him a lot of suffering.
- Supraventricular. The most common type of arrhythmia in VSD. The causes of this condition coincide with those of the ventricular form. In addition, dystonics who are addicted to antiarrhythmic and diuretic drugs are at risk. Patients claim that the condition worsens when lying down. It is this sign that indicates that the cardiac failure is functional in nature.
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Belongs to the group of systemic autoimmune diseases. Its characteristic feature is the formation of autoantibodies to various types of collagen. One of the components in the mechanism of development of autoimmune diseases is inflammation. With the development of inflammation under the influence of infectious factors (streptococcus-A - in rheumatism, intestinal microbes - in reactive arthritis), its main signs are revealed in tissues and organs - pain, swelling, dysfunction. Impaired microcirculation is one of the early mechanisms of rheumatic inflammation. It is caused by an increase in the permeability of the capillary wall due to cross-hemocirculatory disorders, leading to the development of edema and hyperemia. The role of hypercoagulation factors especially increases (chronic DIC syndrome in chronic rheumatoid inflammation).
It is necessary to note the systemic, progressive, self-sustaining nature of chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Pathological metabolic disorders are diverse. Often, a complex metabolic disorder leads to inhibition of osteogenesis processes. Disruption of metabolic processes in articular cartilage leads to depletion of its main substance in proteoglycans, which causes the destruction of cartilage and the development of deforming osteoarthritis.
Arthrosis and metabolic arthropathy, as a rule, are generalized in relation to damage not only to many joints, but sometimes to internal organs. The central and peripheral nervous systems, especially the autonomic part, are involved in the pathogenesis of functional changes. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis experience symmetrical joint damage, muscle atrophy, osteoporosis, and various trophic disorders.
Treatment. It should be carried out taking into account all links of its pathogenesis. For this purpose, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulating, and painkillers are used. Modern complex therapy also includes physical factors. The use of physical factors has the following goal: to reduce or eliminate pain, reduce signs of general and local inflammatory activity. Due to the effect on the neuroendocrine and vascular components of trophism, it normalizes metabolism in the affected tissues. Influence the violation of immunoregulatory processes. Considering the fact that laser therapy has all of the above properties, it must certainly be part of the complex treatment being carried out. RT is prescribed both as a local effect on the joints and as laser hemotherapy.
DYSTROPHIC CHANGES IN THE THORACIC SPINE
Apart from osteochondrosis, these are the most common lesions of the spine.
Clinic. Manifestations of the disease in the form of thoracalgia (chest pain) are associated with reflex syndromes and are often accompanied by cardiovisceral, hyperventilation and other syndromes. Clinically, this usually manifests itself as long-term non-healing gastric ulcers, erosive gastritis, cardialgia of unknown origin with ECG changes in the form of ischemia of various parts of the left ventricle, prolonged bronchitis, and disturbances in emotional stability.
GOUT
Gout. It is considered as a metabolic disease and is characterized by paroxysmal joint pain. Along with acute attacks of pain, gout is characterized by the deposition of salts (sodium urate) in the tissues, resulting in the formation of gouty nodules. In addition to uric acid, they contain a small amount of lime.
Favorite places for salt deposition are the auricles, cartilaginous covers of articular surfaces, especially the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe, wrist, and knee joints. This does not exclude the possibility of salt deposits in other joints. In addition to cartilage, the process affects the synovial membrane, periosteum, and tendons.
The joints thus change noticeably. They become swollen, red and painful to the touch. With a long course of the disease, persistent changes in the joints may occur: the ligaments thicken, effusion appears in the joint, and it becomes painful. When moving, a slight crunching sound is heard. Gouty nodes can enlarge over time and change the shape of the joint. In addition to the joints, gout affects blood vessels, usually the vessels of the kidneys and heart; Sclerotic changes occur in the vessels.
Treatment. Patients with gout need dietary, medication and physiotherapeutic treatment. Laser therapy is performed both on the blood (in the absence of contraindications) and locally on the area of the affected joints.