Causes
Pinching of cervical vessels can occur for a number of reasons, including the following:
- hernias,
- injuries,
- spondyloarthrosis,
- tumors.
But most often the cause of infringement is osteochondrosis. This pathology is so common that doctors call it a kind of payment for a person for walking on two legs, and not on four legs. That is, the human muscular corset is forced to constantly maintain the spine in a straight, anatomically correct position, and if the muscles are poorly developed, osteochondrosis will certainly make itself felt. At the same time, the muscles in the cervical spine are naturally weakly developed, and they bear a large load.
The psycho-emotional state of a person also has an impact: with chronic stress, the tone of the neck muscles increases, which significantly increases the risk of pinched blood vessels, the formation of a local inflammatory process and swelling that impedes blood circulation.
The most common cause of pinched vertebral artery is degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the cervical spine
Risk factors
Factors that affect arteries and increase the risk of damage, plaque formation, and disease include:
- High blood pressure.
High blood pressure is the most important factor in the development of atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries. Exposing the artery wall to high pressure weakens it and makes it more susceptible to damage. - Smoking.
Nicotine irritates the inner lining of blood vessels, and also increases heart rate and increases blood pressure. - Age.
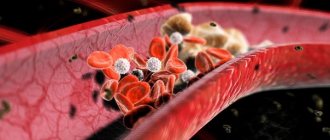
With age, the arterial wall loses elasticity and becomes more susceptible to damage. - Violation of the blood lipid ratio.
Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ("bad cholesterol") and high levels of triglycerides contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. - Diabetes.
Diabetes not only affects the ability to control blood sugar levels, but also lipid metabolism, increasing the risk of hypertension and the development of atherosclerosis. - Obesity.
Excess body weight increases the risk of arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis and diabetes. - Heredity.
The presence of atherosclerosis or coronary heart disease in relatives significantly increases the risk of developing atherosclerotic lesions. - Sedentary lifestyle.
Lack of physical activity contributes to the development of hypertension, obesity and diabetes.
Often, the listed risk factors are present in combination, thereby increasing the degree of risk.
Symptoms
Clinical symptoms may vary depending on whether the process is acute or chronic.
In case of acute pinching, the main symptom is severe pain in the neck. It may intensify when turning the head, or the person will complain of a feeling of numbness when it is physically impossible to turn the head. This happens when a person has suffered a minor injury (strained neck muscles) or slept in an uncomfortable position.
Arteries pass through the cervical vertebrae, feeding brain tissue and carrying out venous drainage. When pinched, this process is disrupted. As a rule, this process develops gradually; the body is able to compensate for a long time for the lack of oxygen and other substances entering the brain with the bloodstream. Therefore, the clinical picture increases progressively.
Symptoms of chronic pinching of the vertebral artery from the side of the brain are expressed as follows:
Cervical gymnastics
- headache;
- fast fatiguability;
- memory loss;
- deterioration of attention;
- visual disturbances (floaters or spots before the eyes);
- hearing loss, ringing in the ears;
- fainting or dizziness.
When such symptoms are constantly present, a person’s quality of life decreases: sleep is disturbed, depression develops, and motivation for any activity disappears. Therefore, if you notice any of the described signs, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Headache and dizziness are the most common symptoms of pinched vessels in the cervical spine
If the pinching is caused not by osteochondrosis, but by another disease (problems with the skeletal system of the body, pathologies of vascular origin, tumor) or injury, the clinical picture may differ. Its intensity will depend on how quickly the underlying disease develops.
Symptoms
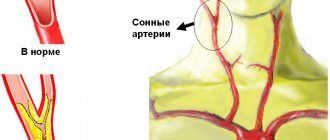
Since atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries develop slowly and are often asymptomatic, the first clinical manifestations of this disease may be a stroke (acute cerebrovascular accident - stroke) or transient ischemic attack (TIA), sometimes called a microstroke.
Treatment of atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries usually includes a set of measures, such as lifestyle changes, drug therapy and, in some cases, surgical treatment (open surgery or stenting).
In the early stages, atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries are usually asymptomatic. You and your doctor may not be aware that you have a narrowing of the carotid artery until an acute disruption of cerebral blood supply develops as the first and very serious manifestation of the disease.
Clinical manifestations of stroke or transient ischemic attack may include:
- a sudden feeling of numbness or weakness in the face or limbs, usually on one side.
- Impaired speech or understanding
- sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- dizziness or loss of balance
- sudden, causeless severe headache
If you have risk factors for developing atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries, you should consult your doctor. Your doctor may order an examination to determine the condition of these vessels. Even if you do not have clinical manifestations of the disease, your doctor may recommend a number of measures aimed at reducing the severity of risk factors and reducing the likelihood of developing a stroke.
Seek immediate medical attention when you experience symptoms of a transient ischemic attack or stroke.
Even if the duration of symptoms is short, usually less than an hour, but possibly longer, tell your doctor right away. The appearance of these symptoms indicates that you have suffered a transient ischemic attack - a short-term decrease in blood flow to the brain. The presence of transient ischemic attacks is the most important sign that you are at high risk of developing a stroke if preventive measures are not taken in time. A timely visit to the doctor increases your chances that atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries will be identified and eliminated before an acute cerebrovascular accident develops.
A transient ischemic attack may also indicate a decrease in blood flow through other blood vessels in the brain. To clarify the diagnosis, your attending physician will prescribe the necessary examination.
Make sure your family and close friends are aware of the clinical manifestations of a stroke and that it is important to act quickly if they occur.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms appear, you can contact a therapist, who will refer you to a neurologist or vertebrologist.
The doctor will take a medical history, conduct a visual examination and tests, and then send the patient for tests, including:
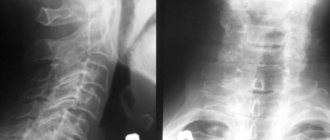
- functional x-ray diagnostics in different head positions;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- Ultrasound of neck vessels;
- angiography.
Based on the results, you can identify the cause of the pinching and the severity of the problem. This information will allow you to choose the most accurate treatment.
Forecast
With atherosclerosis of the vertebral artery, it is quite difficult to give a prognosis for the life and health of the patient. With large narrowings, blood flow is compensated by the second vertebral artery; in addition, there is collateral blood flow. There have not yet been large studies assessing the risk of stroke with damage to the vertebral arteries. However, the fact remains that strokes in the vertebrobasilar system account for at least 25% of all strokes and are much more severe than strokes associated with the carotid artery. Therefore, the identification of significant narrowing of the vertebral artery should be a reason to eliminate this risky condition.
Without identifying and eliminating the causes of the development of vertebral artery syndrome, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable. Most often, the patient's condition gradually worsens, which negatively affects the quality of life.
The most difficult thing is to identify the exact cause. Knowing the cause will allow it to be eliminated surgically or endovascularly and relieve the patient from painful symptoms.
Treatment
Therapy for pinching consists of a whole range of measures that are aimed at restoring blood circulation to the brain, relieving symptoms and normalizing well-being, as well as eliminating the cause of the pinching.
Drug therapy
If there is inflammation and swelling in the neck muscles, which usually results in the inability to turn the head, the doctor will prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are used both internally and externally, in the form of ointments.
Muscle relaxants help relieve muscle tension, but their effect will be temporary if you do not deal with the cause of increased muscle tone, for example, chronic stress.
Help eliminate brain symptoms:
- B vitamins;
- nootropics;
- neuroprotectors;
- vasodilators.
Each medicine has its own contraindications, so only the attending physician can prescribe them.
If the pinching was caused by a disorder in the tissues of the spine, chondroprotectors can be used. If necessary, painkillers may be prescribed.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic techniques are based on heating the soft tissues of the neck. This helps speed up the process of relieving inflammation from the muscles and reducing their tone.
The following treatment methods are used:
- electrophoresis,
- UHF therapy,
- laser,
- magnetic therapy,
- phonophoresis.
Treatment is carried out in a course, the duration of which is determined by the doctor.
Massage
A properly performed massage helps relieve neck tension and pain, as well as improve blood circulation. But only a qualified specialist can perform a massage, otherwise more damage can be caused to the body. For example, there is a risk of developing thromboembolism and stroke.
It is important that massage of the cervical-collar area is performed by a specialist with medical education
Physiotherapy
During the acute phase of the disease, doing any exercises on the neck is strictly contraindicated. On the contrary, at this time the neck should be immobilized as much as possible, which can be conveniently done using the Shants collar.
During the period of remission, it is useful to do exercises to strengthen the muscular corset of the neck. You can press your hand on the side of your head while simultaneously applying resistance with your neck muscles. Gradually and extremely carefully, you can turn your head and bend.
Swimming has great benefits.
Surgical intervention
The help of a surgeon is usually required if the pathological process is caused by a vertebral hernia or injury, after which bone fragments need to be removed. Surgeries may also be indicated for tumors.
After the operations, the patient recovers during the rehabilitation period, the duration of which can reach 8–10 weeks.
Surgical treatment of vertebral artery syndrome
Unfortunately, conservative therapy methods do not always produce positive results. If the patient's condition continues to deteriorate or there is a risk of developing serious complications, surgical treatment may be recommended.
The goals of the operation are to restore blood circulation in the affected vessels. This can be achieved through:
- Decompression of the vertebral artery is carried out using a wide variety of methods, which are selected based on MRI results: removal of intervertebral disc protrusions using cold plasma, laser or radio wave nucleoplasty;
- removal of herniated intervertebral discs using microdiscectomy, endoscopic operations, etc.;
- removal of osteophytes, uncovertebral growths;
- surgical treatment of scoliosis through the installation of special metal structures.
The choice of a specific technique is made by the surgeon based on the nature of the existing disorders. Sometimes their combination is required to ensure high effectiveness of surgical intervention.
Prevention
Preventing pinched vessels of the cervical spine is much easier than treating it. To do this, it is enough to follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- regularly receive moderate physical activity;
- avoid carrying heavy objects, and if necessary, distribute the load evenly in both hands;
- sleep on an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- avoid stress and learn to cope with it correctly;
- sleep at least 7 hours a day.
With a sedentary lifestyle, you need to accustom yourself to do light exercises. This is relevant for office workers and transport drivers. It is very useful for them to wear a Shants collar for a few minutes a day to relieve stress on the cervical vertebrae.
Pinched blood vessels in the cervical spine are a common and unpleasant situation that can be avoided. And if necessary, quickly cure using modern medicine methods.
Types of cervical stenosis
This pathology is represented by the following groups.
- Congenital (primary) stenosis, when the disease develops as a result of congenital abnormalities in the structure of the spine.
- Degenerative , acquired or secondary stenosis of neck vessels is a consequence of destructive-degenerative acquired changes.
- Combined or mixed stenosis is determined in the presence of various causative development factors.
Based on the area of the lesion, a distinction is made between relative and absolute stenosis (area less than 75 mm² or more than 75 mm², respectively).
Lateral stenosis is defined as a narrowing of the intervertebral foramen to 0.4 cm or less.
The term sagittal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the canal in the same plane.
Anatomically, the following types of cervical spinal canal stenosis are distinguished:
- lateral or lateral , when the exit site of the roots (radicular canal) of the spinal cord decreases in volume;
- central , when on the arch of the cervical vertebra (at the point where the roots exit) the distance from the posterior surface to the lateral surface decreases.
How is cervical artery stenosis treated?
Stenosis of the cervical arteries is treated using conservative methods (physiotherapeutic procedures and medications) and surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
The course of treatment is selected for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of his condition:
- painkillers (NSAIDs) with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- injections of hormonal agents into the spine to reduce swelling, tissue compression and pain;
- diuretics to reduce cerebrospinal fluid pressure and relieve swelling;
- electrophoresis with novocaine to relieve pain in the affected area;
- magnetic therapy to reduce swelling and relieve pain;
- when the muscle frame is tense, massage is used;
- physical therapy – special exercises for stenosis help strengthen the cardiovascular system, arm and neck muscles;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- spinal traction.
Surgical treatment
Surgical methods are used if a conservative approach does not provide a lasting effect or the development of the disease calls into question the patient’s life and ability to work. Today there are many methods of surgical treatment, but three operations provide maximum effectiveness:
- decompressive laminectomy - an operation to remove a structure that causes a narrowing of the canal (hernial protrusions, tumors, intervertebral discs and arches, osteophytes;
- installation of stabilizing systems;
- installation of an implant after removal of the affected fragment.