If, as a result of a pathological process, deformation of the valve tissue occurs and the hole through which blood enters the next part of the heart narrows, then such a defect is called stenosis. Deformation can lead to the heart valves not closing due to changes in shape, shortening them as a result of scarring of the affected tissues; this defect is called insufficiency. Valve insufficiency can be functional, resulting from stretching of the chambers of the heart; the area of the unchanged valve is not enough to close the enlarged hole - the leaflets sag (prolapse).
The work of the heart is restructured depending on the changes that have occurred and the needs of blood flow in the body.
Causes of acquired heart defects
In most cases, the defects are caused by rheumatic diseases, in particular rheumatic endocarditis (about 75% of cases). The cause may also be the development of atherosclerosis, systemic connective tissue diseases, trauma, sepsis, infections, overload, and autoimmune reactions. These pathological conditions cause disturbances in the structure of the heart valves.
Classification of acquired heart defects
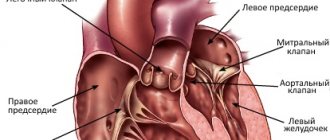
The human heart has four chambers: the left and right atria and ventricles, between which are the heart valves. The aorta emerges from the left ventricle, and the pulmonary artery emerges from the right ventricle.
Between the left heart chambers is a bicuspid valve, the mitral valve. And between the right sections there is a tricuspid valve, another name is tricuspid. In front of the aorta there is the aortic valve, in front of the pulmonary artery there is another valve, the pulmonary valve.
The performance of the heart muscle depends on the functioning of the valves, which, when the heart muscle contracts, allow blood to flow into the next section without obstruction, and when the heart muscle relaxes, do not allow blood to flow back. If the function of the valves is impaired, the function of the heart is also impaired.
Based on the reasons for their formation, defects are classified as follows:
- degenerative, or atherosclerotic, they occur in 5.7% of cases; More often, these processes develop after forty to fifty years, calcium is deposited on the leaflets of the damaged valves, which leads to the progression of the defect;
- rheumatic, formed against the background of rheumatic diseases (in 80% of cases);
- defects that arise as a result of inflammation of the inner lining of the heart (endocarditis);
- syphilitic (in 5% of cases).
Based on the type of functional pathology, defects are divided into the following types:
- simple – valve insufficiency or stenosis;
- combined – insufficiency or narrowing of two or more valves;
- combined - both pathologies on one valve (stenosis and insufficiency).
Depending on the location, the following pathologies are distinguished:
- mitral valve disease;
- tricuspid defect;
- aortic defect.
Hemodynamics can be impaired to varying degrees:
- insignificant;
- moderately;
- expressed.
The mitral valve is affected more often than the aortic valve. Pathologies of the tricuspid valve and pulmonary valve are less common.
Waist Heart
The cardiac waist is the junction of the vascular bundle (arteries and veins entering and exiting the heart) into the left ventricle. Its apex is the left atrium, so when it enlarges, the waist disappears. With the expansion of the left ventricle, the waist will be well defined, “emphasized”.
Diameter of the heart
To measure the diameter of the heart, the midline of the body is visually determined, and from it the distances to the right and left edges of the relative dullness of the heart are measured. In a healthy person of average build, the right size does not exceed 4 cm, and the left - 9 cm; for thin people, a decrease of 1 cm is allowed.
The right diameter is larger than normal when:
- expansion of the right chambers (atrium and/or ventricle);
- accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac (exudative pericarditis);
- displacement of the heart shadow to the right due to the large left ventricle.
The left size increases with diseases of the left chambers of the heart, less often it is shifted by the dilated right ventricle.
Normal dimensions of the vascular bundle
The vascular bundle is formed by the aorta or superior vena cava on the right and the pulmonary artery on the left; its size normally does not exceed 5-6 cm. It is covered by the sternum and does not protrude beyond its edges. If its width is greater, then this may be a sign of an aortic aneurysm or atherosclerosis.
Right heart contour
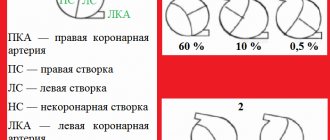
The right contour of the heart includes only 2 arches. The first is the superior vena cava or the ascending aorta (they are very close), and the second is always represented by the right atrium. Between these arches there is an angle called the right atriovasal.
Its location determines the configuration of the heart:
- normally it is approximately in the middle (between equal arcs);
- with mitral it is displaced upward;
- with aortic it moves down;
- with trapezoidal, triangular, spherical it disappears.
Left outline
The left contour includes the arcs:
- the first is part of the descending aorta;
- the second is the pulmonary artery;
- third - left atrium;
- the fourth is the left ventricle.
With a mitral configuration, they are all present, but shifted to the left. With aortic, the first and second arches, as well as the third and fourth, merge, the angle (left atriovasal) between the second and third is sharply expressed. If the patient has a trapezoid or a ball, then there is only the first arch, the angle, and the other three are connected into one large line .
Symptoms of acquired heart defects
Mitral stenosis
It manifests itself as compaction or fusion of the leaflets, a decrease in the area of the mitral valve opening. As a result, the flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle is obstructed, and the left atrium begins to work with increased load. This leads to enlargement of the left atrium. The left ventricle receives less blood.
Due to the decrease in the area of the mitral orifice, the pressure in the left atrium increases, and then in the pulmonary veins, through which oxygenated blood flows from the lungs to the heart. Typically, the pressure in the pulmonary arteries begins to increase when the diameter of the opening becomes less than 1 cm, compared to the normal 4-6 cm, and a spasm occurs in the arterioles of the lungs, which aggravates the process. Thus, so-called pulmonary hypertension is formed, the long-term existence of which leads to sclerosis of arterioles with their obliteration, which cannot be eliminated even after eliminating the stenosis.
With this defect, first of all, the left atrium hypertrophies and expands, and then the right parts of the heart.
At the beginning of the formation of this defect, the symptoms are little noticeable. Subsequently, shortness of breath, cough during physical activity, and then at rest come first. Hemoptysis, persistent pain in the heart, and rhythm disturbances (tachycardia, atrial fibrillation) may occur. If the process goes far, then pulmonary edema may develop during physical activity.
There are physical signs of mitral stenosis: diastolic murmur in the heart, a trembling of the chest corresponding to this noise is felt (“cat purring”), and the boundaries of the heart change. An experienced specialist can often make a diagnosis after a careful examination of the patient.
Mitral regurgitation
Valve insufficiency is expressed in the ability of blood to return back into the atrium during contraction of the left ventricle, since a message remains between the left atrium and the ventricle, which is not closed by the valve leaflets at the time of contraction. Such insufficiency is caused either by deformation of the valve as a result of a tissue-changing process, or by its sagging (prolapse), due to stretching of the chambers of the heart when they are overloaded.
Compensated mitral regurgitation usually lasts for several years; in the affected heart, the work of the left atrium and left ventricle increases, first hypertrophy of the muscles of these parts develops, and then the cavities begin to expand (dilatation). Then, due to a decrease in stroke volume, the minute ejection of blood from the heart begins to decrease, and the amount of blood returning (regurgitation) to the left atrium increases. Blood stagnation begins in the pulmonary circulation (pulmonary), the pressure in it increases, the load on the right ventricle increases, it hypertrophies and expands. This leads to rapid decompensation of cardiac activity and the development of right ventricular failure.
If compensatory mechanisms do not have time to develop in acute mitral valve insufficiency, the disease can begin with pulmonary edema and lead to death.
Clinical manifestations of mitral regurgitation in the compensated stage are minimal and may not be noticed by the patient. Beginning decompensation is characterized by shortness of breath, poor tolerance to physical activity, then, when stagnation in the pulmonary circulation increases, attacks of cardiac asthma appear. In addition, pain in the heart area, palpitations, and interruptions in heart function may bother you.
Right ventricular heart failure leads to stagnation of blood in the systemic circulation. The liver becomes enlarged, cyanosis of the lips and limbs appears, swelling in the legs, fluid in the abdomen, heart rhythm disturbances (50% of patients have atrial fibrillation).
It is not difficult to make a diagnosis of mitral regurgitation at present with the available instrumental research methods: ECG, ECHO-CG, radiation diagnostic methods, ventriculography and others. However, an examination by an attentive cardiologist based on anamnesis, auscultation, percussion, and palpation will allow you to draw up the correct examination algorithm and timely take measures to prevent further development of the process of formation of the defect.
Aortic stenosis
This defect among PPS is detected quite often, in 80-85% of cases it is formed as a result of rheumatism, in 10-15% of cases it is acquired against the background of an atherosclerotic process, with subsequent deposition of calcium in atherosclerotic plaques (calcinosis). There is a narrowing of the aortic orifice at the site of the semilunar valve of the aorta. For many years, the left ventricle works with increasing tension, however, when the reserves are depleted, the left atrium, the pulmonary circle, and then the right parts of the heart begin to suffer. The pressure gradient between the left ventricle and the aorta increases, which is directly related to the degree of narrowing of the opening. The ejection of blood from the left ventricle becomes less, the blood supply to the heart deteriorates, which is manifested by angina pectoris, low blood pressure and weak pulse, cerebrovascular insufficiency with neurological symptoms, including dizziness, headache, loss of consciousness.
The appearance of complaints in patients begins when the area of the aortic mouth decreases by more than half. When complaints appear, this indicates an advanced process, a high degree of stenosis and a high pressure gradient between the left ventricle and the aorta. In this case, treatment should be discussed taking into account surgical correction of the defect.
Aortic insufficiency
- this is a valve pathology in which the outlet from the aorta is not completely blocked; blood has the ability to flow back into the left ventricle during its relaxation phase. The walls of the ventricle thicken (hypertrophy) as more blood has to be pumped. With ventricular hypertrophy, insufficiency of its nutrition gradually manifests itself. More muscle mass requires more blood flow and oxygen supply. At the same time, due to the fact that part of the blood in diastole returns to the left ventricle, the aortic-left ventricular gradient decreases (it is what determines the coronary blood flow) and, as a result, less blood enters the arteries of the heart. Angina occurs. There are sensations of pulsation in the head and neck. Neurological manifestations are characteristic, such as: lightheadedness, dizziness, sudden fainting, especially during physical exertion, when changing body position. The hemodynamics of the systemic circulation with this defect are characterized by: high systolic pressure, low diastolic pressure, compensatory tachycardia, increased pulsation of the croup
ny arteries, including the aorta. During the decompensation stage, dilatation (expansion) of the left ventricle develops, the efficiency of systole decreases, the pressure in it increases, then in the left atrium and pulmonary circulation. Clinical signs of stagnation in the pulmonary circulation appear: shortness of breath, cardiac asthma.
A thorough examination by a cardiologist may allow the doctor to suspect or even diagnose aortic insufficiency. Well-known symptoms such as “carotid dance” - increased pulsation of the carotid arteries, “capillary pulse”, which is detected by pressing on the nail phalanx, de Musset’s symptom - when the patient’s head sways in time with the phases of the cardiac cycle, pulsation of the pupils and others are detected already at the stage a far advanced process. But palpation, percussion, auscultation and careful history taking will help identify the disease at earlier stages and prevent the progression of the disease.
Tricuspid stenosis
This defect rarely occurs as an isolated pathology. It is expressed in the narrowing of the existing opening between the right ventricle and the right atrium, which are separated by the tricuspid valve. Most often it occurs with rheumatism, infective endocarditis and other systemic connective tissue diseases; sometimes there is a narrowing of the opening as a result of the formation of a myxoma-tumor formed in the right atrium, less often there are other reasons. Gamodynamics are disrupted as a result of the fact that not all the blood from the atrium can enter the right ventricle, which normally should occur after atrial systole. The atrium becomes overloaded, stretched, blood stagnates in the systemic circulation, the liver enlarges, swelling of the lower extremities and fluid appear in the abdominal cavity. Less blood flows from the right ventricle to the lungs, which causes shortness of breath. In the initial stage, there may be no symptoms; these hemodynamic disorders arise later - heart failure, atrial fibrillation, thrombosis, cyanosis of the nails, lips, yellowness of the skin.
Tricuspid insufficiency. This pathology most often accompanies other defects and manifests itself in the form of tricuspid valve insufficiency. Due to venous stagnation, ascites gradually develops, the liver and spleen increase in size, high venous pressure is noted, liver fibrosis develops and a decrease in its function.
What is the configuration of the heart, its indicators are normal
The configuration of the heart is the shape, contours, showing the expansion or contraction of the atria, ventricles, and vascular bundle. It includes the borders (upper, left and right), waist (narrowing at the junction of the bundle of blood vessels to the left ventricle), angles between the diaphragm (reflecting the inclination of the axis) and the arcs of the chambers of the heart. If the configuration is normal, this means that they correspond to the parameters (see table) of healthy people:
- relative dullness of the heart (its actual size) in the chest and absolute (the part that is not covered by the lungs and is directly adjacent to the ribs);
- length (length) and width (diameter);
- waist (retraction of the contour, narrowing of the diameter);
- there are angles between arcs.
| Contour type and main parameters | How was she educated? | Upper | Left | Right |
| Relative Dullness | Real contours | Bottom of 3rd ribs on the left edge of the sternum | The fifth intercostal space is 1.5 cm to the right from the conditional line drawn from the middle of the left clavicle | The fourth intercostal space is 1 cm to the right from the edge of the sternum |
| Absolute | Right ventricle | Bottom of 4th ribs on the left edge of the sternum | 2.5-3.2 cm to the right of the line from the middle of the left clavicle | Fourth intercostal space along the left edge of the sternum |
| Width of the bundle of large vessels (vascular) | Aorta, pulmonary artery, veins | The space between the 2nd and 3rd ribs does not extend beyond the borders of the sternum (approximately 4.5-5.5 cm) | ||
| Right contour (arcs) | Superior vena cava, right atrium | The edge of the sternum to the 3rd rib and the third or fourth space between the ribs 1 cm to the right | ||
| Right atriovasal angle | Between the superior vena cava and the atrium | 3-4 intercostal space | ||
| Cardio-phrenic angle right | Diaphragm, right atrium | 5th intercostal space | ||
| Left contour (arches) near the left edge of the sternum | Aorta | 1st intercostal space | ||
| Pulmonary artery | 2nd intercostal space | |||
| Left atrium | Level 3 ribs | |||
| Left ventricle | Inferior to the 3rd rib, just behind the left atrial appendage | |||
| Waist | Bundle of blood vessels, left ventricle (left), right atrium (right) | Level 3 ribs | ||
| Length | Heart length | From the apex to the right cardiophrenic angle the length should be between 11.5-12.7 cm | ||
| Diameter | Width of relative cardiac dullness | From the right border to the midline and from the left (the most protruding part) to the middle, normally 11-13 cm | ||
If the patient has diseases of the heart and/or large vessels, especially valve defects, then the load on its parts changes. Then the atria and ventricles enlarge, which is manifested by a shift in the boundaries of relative and absolute dullness, changes in size, smoothing of angles, and disappearance of the waist.
Determination of heart configuration by percussion
To determine the configuration of the heart, you first need to find the boundaries of dullness. They are so named because they can be examined during a medical examination. To do this, use the percussion (tapping) method. Above the lungs, the sound is clear, since they are filled with air, and as soon as the finger reaches the contour of the heart, dullness appears (relative dullness), and then a completely dull sound (absolute).
First, the true border of the heart is found in the chest. To do this, the finger of the left hand moves from the outside to the center. Since the organ’s entire surface is not adjacent to the chest, part of it is covered by the lungs, and a small area remains open, when tapping it can be identified by a dull (dull) sound. This zone (absolute dullness) reflects the size of the right ventricle. It is found by moving from the center to the edges.
When the boundaries of cardiac dullness change
An increase in the relative dullness of the heart is a ghost of expansion of its cavities (ventricles and atria). Occurs with valve defects, high blood pressure, weakening of the heart muscle or its hypertension (thickening). The absolute dullness of the heart can also change normally - for example, with bloating or pregnancy, the diaphragm rises upward and brings the heart closer to the ribs.
Expansion may be affected by:
- compaction of lung tissue (pneumosclerosis);
- adhesions in the chest;
- dilatation of the right ventricle.
Emphysema (increased airiness), an asthma attack, a low position of the diaphragm with weakness of the respiratory muscles can reduce the area.
X-ray configuration
If the boundaries of dullness (relative and absolute) can be found only by tapping, then measurements of length, width, finding the waist, angles and arcs of the configuration occur only on a chest x-ray. In the conclusion, the radiologist indicates the conformity of the configuration to a certain type and measures the angles, length and diameter.
It is important to understand that X-ray diagnostics will only show an expansion of the heart shadow or its displacement, an unusual shape, but to determine the cause, an ultrasound (echocardiography) will often be required. Only the latter method will help to study the movement of blood through the valves, the contractility of the heart muscle and its thickness.
Expert opinion
Alena Ariko
Expert in Cardiology
An atypical configuration of the heart is not always a sign of illness. For example, young women may have a cardiac shadow shape that is close to the mitral shadow, while older overweight patients may have an aortic shadow shape. Therefore, a diagnosis is never made based on X-ray findings alone.
Types of heart configuration
The following types of heart configurations have been identified:
- normal - the right angle between the vascular bundle is approximately in the middle, the second and third arches are almost equal (2 cm each);
- aortic – the waist is rarely emphasized;
- mitral - expansion mainly to the left, partially to the right, no waist;
- close to geometric figures: trapezoid, ball, triangle;
- “bullish” with a significant increase in all cameras.
Methods for diagnosing heart defects
In order to establish a diagnosis of heart disease, an anamnesis is collected, the presence of diseases that could lead to deformation of the heart valve is revealed: rheumatic diseases, infectious, inflammatory processes, autoimmune diseases, injuries.
- The patient must be examined to identify the presence of shortness of breath, cyanosis, edema, and pulsation of peripheral veins. Using percussion, the boundaries of the heart are identified and sounds and murmurs in the heart are listened to. The size of the liver and spleen is determined.
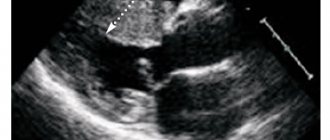
- The main method for diagnosing valve pathology is echocardiography
, which allows you to identify the defect, determine the area of the opening between the atrium and the ventricle, the size of the valves, cardiac fraction, pressure in the pulmonary artery.
More accurate information about the condition of the valves can be obtained by performing transesophageal echocardiography. - Electrocardiography is also used in diagnostics, which allows one to assess the presence of atrial and ventricular hypertrophy and identify signs of overload of the heart. Daily Holter ECG monitoring allows you to identify rhythm and conduction disturbances.
- Highly informative methods for diagnosing heart defects are cardiac MRI or cardiac MSCT. Computed tomography scans provide precise and numerous sections, which can be used to accurately diagnose the defect and its type.
- Laboratory tests play an important role in diagnosis, including urine and blood tests, determination of blood sugar, cholesterol levels, and rheumatoid tests. Laboratory tests allow us to identify the cause of the disease, which plays an important role in subsequent treatment and patient behavior.
Contraindications
Such a study cannot be called completely safe. In this regard, there are a number of situations in which such diagnostics are not performed, but a more gentle method is selected. Often, an ultrasound
or MRI, as well as other studies.
Pregnant women
Before finding out what a heart x-ray is and what this procedure shows, a woman should be absolutely sure that there is no pregnancy. This situation is an absolute contraindication to the procedure, since there is a risk that X-ray radiation will have an adverse effect on the body of both the expectant mother and the baby. It is also not recommended for breastfeeding mothers to undergo diagnostics. However, in some situations, a doctor may prescribe such a procedure if its benefits are significantly higher than the likely risks. Therefore, it is best to trust the doctor.
Prevention and prognosis for PPS
There are no preventive measures that would protect one hundred percent from acquired heart disease. But there are a number of measures that will reduce the risk of developing heart defects. This means the following:
- timely treatment of infections caused by streptococcus (in particular tonsillitis);
- bicillin prophylaxis in the event of a rheumatic attack;
- taking antibiotics before surgical and dental procedures if there is a risk of infective endocarditis;
- prevention of syphilis, sepsis, rheumatism: sanitation of infectious foci, proper nutrition, work and rest schedule;
- rejection of bad habits;
- presence of moderate physical activity, accessible physical exercises;
- hardening.
The prognosis for the life and ability to work of people with heart defects depends on the general condition, fitness of the person, and physical endurance. If there are no symptoms of decompensation, a person can live and work as usual. If circulatory failure develops, work should either be lightened or stopped; sanatorium treatment at specialized resorts is indicated.
It is necessary to be observed by a cardiologist in order to monitor the dynamics of the process and, as the disease progresses, to promptly determine the indications for cardiac surgical treatment of heart disease.
How to prepare for a chest x-ray
A chest x-ray does not require much preparation on the part of the patient. The person will need to remove any jewelry, glasses, piercings or other metal objects on the body before the procedure itself. Because this may make it difficult to make a correct diagnosis and obscure the image. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have a surgically implanted device, such as a heart valve or pacemaker. This determines which diagnostic method can be used in a particular case. Chest X-rays may be performed when the patient has metal implants. But other scans, such as MRIs, can be risky for people who have a metal device inside. Women with long hair are recommended to pin it up, since foreign bodies are prohibited from entering the diagnostic area. If hit, the quality and information content of the x-ray image drops significantly.
You will also need to undress to the waist before the x-ray and follow the instructions of the laboratory assistant. X-rays of the heart can be performed in three types of projections. During the procedure, the laboratory assistant will ask you to hold your breath for literally 10 seconds to get clear contours of the image.
How does the research procedure work?
The X-ray image looks like a black and white photograph. Areas that are translucent and transmit X-rays are shown in black, and areas that cannot transmit ionizing radiation are highlighted in white. That is why the bones and heart muscle in the image are white.
The X-ray machine is located in a special large room with a movable X-ray camera attached to a large metal arm called an arm. The patient should stand next to the “plate”. This plate contains X-ray film or a special sensor that records the images on a computer. The laboratory assistant will tell you how to stand correctly - raise your arms and bend them at the elbows, and record in the front and side projections. Usually the manipulation is carried out in two projections, but for a more accurate and specific diagnosis it can be carried out in three or four - anterior, lateral left, oblique left and right, at an angle of forty-five degrees. It is the images in the oblique projection that help to view the walls of the aortic arch and the walls of the myocardium, which are not examined in the lateral view. For example, oblique right imaging makes it possible to examine all parts of the heart.
While the images are being taken, you will need to take a deep breath and hold your breath as requested by the technician, and to keep your body completely still. If you move, the pictures may turn out blurry. This procedure takes about ten minutes, after which you need to get dressed and go about your business.
This diagnostic method is one of the cheapest and most painless, non-invasive studies of the heart muscle. Only with an X-ray with contrast, the patient can taste the lime barium solution.
Treatment of acquired heart defects can be conservative or surgical
Conservative treatment is effective only in the early stages of the development of heart disease and requires mandatory follow-up by a cardiologist.
PPS should be treated surgically when:
- Heart failure progresses.
- Pathological changes in the valve significantly affect hemodynamics.
- The ongoing conservative therapy does not have the desired effect.
- And there are fears of serious complications.
Types of operations for heart defects
Open heart surgery is performed under artificial circulation through a median sternotomy. Median sternotomy creates optimal conditions for the cardiac surgeon to perform the necessary surgical interventions for various pathologies and to connect the heart-lung machine. The soft tissue incision is approximately equal in length to the length of the sternum (about 20 cm), and the sternum is dissected along its entire length.
The main two types of operations that are currently used for PPS are reconstruction of the affected valves (plastic) or their prosthetics.
Valve-sparing surgery
Performed to eliminate the cause of valve dysfunction.
If the valves do not close (valve insufficiency), then the cardiac surgeon during the operation achieves normalization of the closure of the valve leaflets, performing resection of the valve leaflets, annuloplasty, commissural plastic surgery, and chord replacement. If there is valve stenosis, then the sections of the valves that have fused due to a pathological process are separated and an open commissurotomy is performed.
Valve replacement surgery
If it is impossible to perform plastic surgery, when there are no conditions for this, valve replacement operations for prosthetic heart valves are performed. In case of intervention on the mitral valve, replacement is performed with full or partial preservation of the anterior or posterior valve leaflets, and if impossible, without their preservation.
In valve replacement surgeries, prostheses are used.
- Prosthetics can be made from animal or human tissue. Such prostheses are called biological. Its main advantage is that the patient does not need to take anticoagulant drugs during subsequent years of life, and their main disadvantage is their limited service life (10-15 years).
- Prostheses consisting entirely of mechanical elements (titanium and pyrolytic carbon) are called mechanical. They are very reliable and can serve without failure for many years, without replacement, but after such an operation the patient must always take anticoagulants for life, this is a negative aspect of using a mechanical prosthesis.
Minimally invasive surgeries
Modern surgery, thanks to the creation of new instruments, has the opportunity to modify surgical approaches to the heart, which leads to operations becoming minimally traumatic for the patient.
The point of such operations is that access to the heart is carried out through small incisions in the skin. During minimally invasive operations on the mitral valve, a right-sided lateral minithoracotomy is performed, with a skin incision of no more than 5 cm, this allows one to completely avoid dissecting the sternum and provides convenient access to the heart. To improve visualization, endoscopic video support with multiple magnification is used. With minimally invasive access to the aortic valve, the skin incision is approximately half as large (incision length 8 cm), and the sternum is incised lengthwise in its upper part. The advantage of this method is that the uncut portion of the sternum provides greater stability after surgery, as well as a better cosmetic effect by reducing the size of the suture.
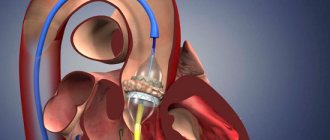
Endovascular operations - transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVI).
Methods of transcatheter aortic valve implantation:
- The entire operation is carried out through a blood vessel (femoral or subclavian artery). The meaning of the procedure is to puncture the femoral or subclavian artery with a guide catheter and deliver the stent valve against the blood flow to the site of its implantation (aortic root).
- Through the aorta. The essence of the method is to dissect the sternum over a short distance (ministernotomy) and puncture the aortic wall in the ascending section and implantation of a stent valve into the aortic root. The method is used when it is impossible to deliver the valve through the femoral and subclavian arteries, as well as when there is a pronounced bend in the arterial arch.
- Through the apex of the heart. The meaning of the procedure is to make a small incision in the fifth intercostal space on the left (minithoracotomy), puncture the apex of the heart with a guide catheter and install a stent valve. Once the new valve is implanted, the catheter is removed. The new valve starts working immediately.
There are two types of stent valves:
- Self-expanding stent-valve expands to the desired size after removing the restrictive sleeve sleeve from it.
- A balloon-dilatable stent valve that expands to the desired size when the balloon is inflated; After final installation of the stent valve, the balloon is deflated and removed.
To determine whether TAVI surgery is appropriate, the patient must undergo a series of tests, including an ECG, echocardiography, computed tomography (CT) scan, and angiography.
Currently, the TAVI procedure is increasingly used not only for aortic stenosis, but also for aortic insufficiency, as well as their combination. In addition, TAVI surgery is used for dysfunction of the biological prosthetic aortic valve.
TAVI surgery is performed under general anesthesia and requires a multidisciplinary approach. The procedure is performed by a specialized team, which includes an interventional cardiologist, cardiac surgeon, anesthesiologist, and radiologist.
The presence of a stent valve is not an indication for the patient to take the indirect anticoagulant Warfarin (in the absence of other indications).
Features of the procedure in children
Sometimes heart x-rays may be performed in children. This type of study is very rarely prescribed to children, since the procedure is contraindicated under 15 years of age. However, it may be required to identify heart defects, as well as when planning surgical interventions or to evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen treatment method. X-rays may also be needed to identify tumor processes.
If we are talking about a very young child, an X-ray of the heart will be taken using a special device. It is a stand on which the child is placed and his torso, head and limbs are secured with belts. This will ensure that the patient remains completely still while the doctor takes the image. The procedure will take no more than a couple of seconds, and discomfort is possible only from the belts with which the fixation is carried out. If we are talking about older children, they can undergo the procedure even without adults.