Roza Ismailovna Yagudina , Ph.D. Sc., prof., head. Department of Organization of Drug Supply and Pharmacoeconomics and Head. laboratory of pharmacoeconomic research of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenov.
Evgenia Evgenievna Arinina , Ph.D., leading researcher at the laboratory of pharmacoeconomic studies of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova
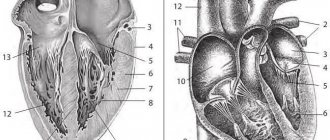
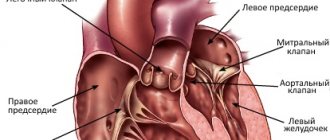
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death worldwide. WHO estimates that 17.3 million people died from CVDs in 2008, accounting for 30% of all deaths worldwide. Of this number, 7.3 million died from coronary heart disease. According to WHO forecasts, by 2030, approximately 23.3 million people will die from CVDs annually.
The group of cardiovascular diseases includes several nosological units:
- coronary heart disease - a disease of the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle;
- disease of the blood vessels in the brain that supply it with blood;
- disease of the peripheral arteries that supply blood to the arms and legs;
- rheumatic carditis - damage to the heart muscle and heart valves as a result of a rheumatic attack caused by streptococcal bacteria;
- congenital heart disease - deformations of the structure of the heart existing from birth;
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism - the formation of blood clots in the leg veins that can dislodge and move towards the heart and lungs.
One of the most common pathologies in the structure of CVD is coronary heart disease (CHD), to which we will devote a number of articles. IHD, as defined by WHO, is acute or chronic cardiac dysfunction resulting from an absolute or relative decrease in the supply of arterial blood to the myocardium.
In more than 90% of cases, the anatomical basis for the development of coronary artery disease is damage to the coronary arteries of the heart, leading to a decrease in coronary blood flow and an imbalance between the need of the heart muscle for oxygen and nutrients and the blood supply capabilities of the heart. Often this effect is caused by dyslipidemias, leading to the development of atherosclerosis, therefore, in the first article devoted to the problem of pharmacotherapy of IHD, we will dwell in detail on dyslipidemias (hyperlipidemias).
Currently, the following forms of IHD are distinguished:
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Angina pectoris
- Silent cardiac ischemia
- Syndrome X (microvascular angina)
- Myocardial infarction
- Cardiosclerosis (atherosclerosis)
- Heart failure
- Heart rhythm disturbances
Causes
- Heredity.
- Hypothyroidism is a dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Diabetes.
- Obstructive liver diseases.
- Taking diuretics, immunosuppressants and other medications.
- Increased content of animal fats in food.
Provoking factors include a sedentary lifestyle, cholesterol abuse, alcohol intake, smoking, and a stressful personality type. The sooner a patient at risk contacts a lipidologist, the higher his chances of avoiding complications.
Risk group
People at risk for developing hyperlipidemia include:
- suffering from abnormalities of the endocrine system (diabetes or obesity);
- who have a history of close relatives with the development of atherosclerosis;
- abusing alcohol and tobacco products;
- those who do not follow proper nutrition (the predominance of fatty and fried foods in the diet);
- over the age of 50;
- leading a sedentary lifestyle.
Principles of treatment of secondary dyslipidemia
If the disease develops against the background of another disease, it is very important to determine the original source and eliminate it. Complex therapy includes non-drug and drug methods.
Non-drug treatment
It is important for the patient to normalize body weight. For this purpose, he is prescribed dosed physical activity and a diet with limited animal fats. The diet must be enriched with vitamins and dietary fiber, and preference should be given to vegetables and fruits. It is mandatory to give up alcohol and smoking, otherwise other actions will be meaningless.
Drug treatment includes the following drugs:
- statins - to reduce cholesterol synthesis in the liver, to relieve inflammation;
- inhibitors of cholesterol absorption in the intestine;
- bile acid sequestrants;
- fibrates – to reduce triglyceride levels and increase high-density lipoprotein levels;
- Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Progressive lipidology specialists also practice extracorporeal methods indicated for severe forms of the disease. Genetic engineering methods have been developed for patients with a hereditary form.
Diagnosis of pathology
At the initial stage, dyslipidemia can be detected by taking a blood test to measure the level of plasma lipids, lipoproteins and fat-like substances. In addition, there is an indicator (atherogenicity index), which is calculated in accordance with the content of total cholesterol and high-density lipoproteins in the blood. To establish an accurate diagnosis, they resort to careful diagnostic methods (in particular, laboratory and instrumental). Among them:
- careful history taking. During the initial examination, the doctor asks the patient in detail about all the symptoms that bother him, finds out who he works for, whether he has suffered from infectious diseases, and whether he has any relatives in his family who suffer from cardiovascular pathologies. The history may indicate vascular atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction or stroke not only in the patient himself, but also in his immediate family;
- physical examination. The pathology is accompanied by characteristic signs that can be seen visually. These include emerging xanthomas, xanthelasmas and lipoid arch of the cornea. During the examination, blood pressure is measured (it may be elevated). When listening to the heart, as a rule, there are no abnormalities with hyperlipidemia;
- general blood and urine analysis. Standard laboratory diagnostics are necessary in order to determine a possible inflammatory process and the presence of concomitant pathologies;
- blood chemistry. Unlike a general blood test, this diagnosis is more informative. It is used to determine the level of blood sugar and protein, as well as uric acid. This is necessary to identify concomitant damage to internal organs;
- immunological blood test. Through this study, the content of antibodies (proteins that can destroy not only foreign substances, but also cells of one’s own body) to pathogens (for example, chlamydia) is determined. In addition, the analysis allows you to determine the level of C-reactive protein - a protein whose level increases significantly due to the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- lipid profile (blood test for lipids). This is the main way to detect dyslipidemia. The resulting lipid profile will clearly show the value of triglycerides (esters of triglycerol with fatty acids), lipoproteins (high, low and very low density), and atherogenicity coefficient. These parameters will allow not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to identify other pathologies. For example, elevated triglyceride levels are diagnosed in patients with diabetes.
Prevention
If left untreated, dyslipidemia leads to atherosclerosis with chronic and acute complications. In the first case, chronic ischemia develops in the area of the blood supply where an atherosclerotic plaque has formed. In the second - acute vascular insufficiency due to the closure of the lumen of blood vessels, and then infarction of various organs.
The prognosis depends on the localization of atherosclerosis, the rate of development of changes and provoking factors that can be influenced. It is very important to normalize body weight and adjust your diet, give up bad habits and emotional overload, and switch to a physical activity program on an individual schedule.
Specialists from Professor Gorbakov’s Clinic will talk about these and other preventive methods with which you can maintain your health and prevent serious consequences.
Procedures and operations
Patients in whom drug treatment is ineffective undergo extracorporeal removal of low-density lipids. Most often, this method is used for familial hypercholesterolemia (homozygous and heterozygous). These are hardware methods based on plasma filtration and plasma sorption. Other types of techniques are also used: immunosorption, heparin precipitation, plasmapheresis. During the procedure, lipoproteins are precipitated and removed by membrane filtration, and the plasma is returned to the patient. There are diseases for which plasmapheresis is used as the first line of treatment, while for others it is used as the second line or in combination with other treatments.
Forecast
The prognosis for type I lipid metabolism disorders is relatively favorable, but there is a predisposition to pancreatitis . In type II, the prognosis depends on the severity of vascular damage. If early atherosclerosis develops and lipid metabolism disorders are not treated, complications are possible (coronary artery disease, stroke). Rational and timely treatment of hyperlipidemia can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve the prognosis. For primary hyperlipidemia, lifelong therapy is carried out.
List of sources
- ESC/EAS 2021 recommendations for the treatment of dyslipidemia: modification of lipids to reduce cardiovascular risk/Russian Journal of Cardiology 2020; 25 (5), pp. 121-193.
- Ershova A.I., Al Rashi D.O., Ivanova A.A., Aksenova Yu.O., Meshkov A.N. Secondary hyperlipidemia: etiology and pathogenesis. Russian Journal of Cardiology. 2019; (5): 74-81.
- Diagnosis and correction of lipid metabolism disorders for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis. Russian recommendations VI revision. Atherosclerosis and dyslipidemia. 2017; 3 (28): 5-22.
- Cronenberg G. M. et al. Obesity and lipid metabolism disorders / Trans. from English edited by I. I. Dedova, G. F. Melnichenko. M.: Read Elsiver LLC, 2010. 264 p.
- Vizir V.A., Berezin A.E. Modern approaches to the treatment of hyperlipidemia/Zaporozhye Medical Journal. - 2011. - volume 13, no. 1, pp. 108-117.
Fully or partially limited products
The diet for dyslipidemia includes the following exceptions:
- Concentrated broths on meat/fish, fish roe, canned fish, cod liver, fried food, shrimp, crayfish, crabs.
- Fatty types of red meat, sausages, offal, smoked meats, waterfowl meat (duck, goose), animal/cooking fats.
- Full-fat cottage cheese, chicken egg yolks, sour cream and cream, cheese, products with palm/coconut oil.
- Products made from puff pastry, cakes, cream pies, pastries.
- White rice, semolina, pasta.
- Products containing quickly digestible carbohydrates - jam, jam, honey, sweets, sugar, confiture.
- Strong black tea/coffee, ice cream, chocolate, cocoa.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bagels | 16,0 | 1,0 | 70,0 | 336 |
| bagels | 16,0 | 1,0 | 70,0 | 336 |
| crackers | 11,2 | 1,4 | 72,2 | 331 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 30% | 2,4 | 30,0 | 3,1 | 294 |
| sour cream 40% (fat) | 2,4 | 40,0 | 2,6 | 381 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
| mutton | 15,6 | 16,3 | 0,0 | 209 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| shrimps | 22,0 | 1,0 | 0,0 | 97 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| sturgeon | 16,4 | 10,9 | 0,0 | 163 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| semi-finished fish products | 12,5 | 6,7 | 14,7 | 209 |
| sardine | 20,6 | 9,6 | — | 169 |
| mackerel | 18,0 | 13,2 | 0,0 | 191 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
| boiled oysters | 14,0 | 3,0 | — | 95 |
| fresh oysters | 14,0 | 6,0 | 0,3 | 95 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| coconut oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| palm oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| rendered beef fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| rendered pork fat | 0,0 | 99,6 | 0,0 | 896 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| lemonade | 0,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 26 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Authorized Products
The basis of the diet for dyslipidemia is:
- Lean sea/river fish (cod, hake, pike, tuna, trout, salmon, mackerel, flounder, salmon) and seafood (excluding squid), seaweed in the form of salads.
- Vegetable soups without frying with a small addition of cereals, vegetables and garden herbs.
- Low-fat red meat (1-2 times a week) boiled/baked, and poultry (turkey, chicken), rabbit.
- Dried grain bread, baked goods with flax/sesame seeds, bran, whole grain bread, dry unsweetened cookies.
- Brown rice, well-cooked oatmeal/buckwheat porridge, wholemeal pasta.
- Milk/fermented milk products of low fat content - cottage cheese, cheeses with a fat content of 20-30%. Chicken eggs (1-2 whole per week, egg whites - unlimited).
- Fresh and cooked fruits/vegetables (400-500 g/day) and legumes in the form of side dishes, salads, seasoned with vegetable oil. Fruits/berries (excluding bananas/grapes) in raw form, decoctions, compotes, jellies. In addition to vegetables/fruits, you should take flax seeds, fenugreek, and bran ground in a coffee grinder.
- Cold-pressed vegetable oils (linseed, olive, sesame corn), mainly for dressing salads.
- Freshly squeezed juices from vegetables/fruits/berries (grapefruit, apple, orange, beet/carrot juices, berry juices), oatmeal jelly/decoction, which effectively removes cholesterol.
- Pumpkin/sunflower seeds, walnuts (at least 30 g/day).
- Rosehip infusion, green/herbal tea with lemon, still mineral water.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| cauliflower | 2,5 | 0,3 | 5,4 | 30 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| squash | 0,6 | 0,1 | 4,3 | 19 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| basil | 2,5 | 0,6 | 4,3 | 27 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 0% | 3,0 | 0,1 | 3,8 | 30 |
| kefir 1% | 2,8 | 1,0 | 4,0 | 40 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| grape seed oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| instant chicory | 0,1 | 0,0 | 2,8 | 11 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||