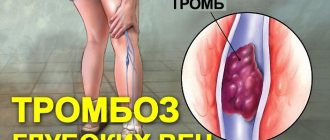
According to the World Health Organization, in most developed countries, deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism have become one of the leading causes of mortality. Millions of people around the world die every year from acute blockage (embolism) of a blood vessel by a thrombus. The danger of thrombosis is that a clot can reach a size comparable to the diameter of a venous vessel and completely block the blood flow in it. Or, if it ruptures, the clot can travel with the blood into the vessels of the lungs and lead to pulmonary thromboembolism. Often with fatal outcome.
Related article Catch it if you can. How to detect and destroy a blood clot
“A blood clot has broken off,” they sometimes say in this case about the cause of death. Even fairly young people often die from detached blood clots. According to specialists from the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A. I. Evdokimov, more than 90% of deaths from pulmonary embolism occur in patients who were not diagnosed with embolism and who did not receive treatment.
How does a blood clot form?
Blood is necessary for a person to live. It circulates through the vessels, delivering nutrients and protective elements to the organs, which help in the fight against viruses and bacteria. If a person is injured, the blood clots, thereby blocking their access to the body. The ability of blood to form clots and clog the lumen of a vessel with them can sometimes play a cruel “joke” on a person, which will lead to disability or even death.
Blood has fluidity so that it can clot at the right moment; the mechanisms of the coagulation system are activated. It triggers the formation of protein fibrin threads, which clog the vessel, preventing excess blood from leaking out.
The human body also has an anticoagulant system that fights the formation of blood clots in those tissues that have not lost their integrity. If at some point there is a malfunction in the functioning of these two systems, then blood clots begin to form in the vessels.
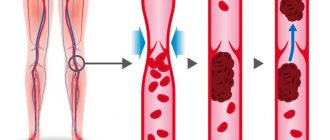
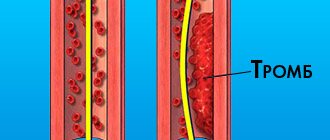
They are located near the inner wall of the vein, going through several stages:
- A blood clot begins to grow in the place where the vessel is damaged and inflamed. Most often this happens against the background of thrombophlebitis. The body reacts to an inflamed vessel by activating the blood coagulation system. It triggers the production of fibrin fibers, which are concentrated near the site of inflammation.
- Red blood cells and platelets begin to become entangled in fibrin fibers.
- New blood cells that are brought in with the bloodstream continue to “stick” to the clot, making it larger and larger. It increases in size, becomes denser and can come off at any moment.
Blood clots can also form in arteries when the vessel narrows. Cholesterol plaques that have grown on the arterial walls are an obstacle to normal blood flow, as a result of which a clot of fibrin threads and platelets begins to grow.
Risk factors for blood clots:
- Belonging to the male gender, over 40 years of age.
- Belonging to the female gender, over 50 years of age. An increased risk of thrombosis is caused by menopausal changes in the body.
- Dehydration of the body.
- A cancerous tumor of a malignant nature.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Serious errors in nutrition.
- Taking certain medications. Hormonal contraceptives pose a particular danger in terms of blood clot formation.
- Postponed surgery.
- Disruption of the normal flow of blood through a vessel as a result of its compression.
- Pregnancy.
- Vein injuries in the legs.
- Heart failure.
- Infections.
Blood clots that form in large vessels pose a danger to human life. Their separation will lead to the rapid death of the patient.
When blood clots do not cure, but cripple
A lack of platelets leads to blood clotting disorders and improper wound healing. If there are too many of these blood cells and they stick together unnecessarily, there is a risk of thrombosis - blockage of blood vessels. In this case, blood circulation is disrupted, causing some organs and tissues of the body to receive less oxygen and nutrients. The World Health Organization has estimated that approximately a quarter of the world's population has a tendency to form blood clots in blood vessels. And this can happen for various reasons.
One of the most common causes leading to the development of thrombosis is vessels with damaged walls. They are perceived by the body as a possible source of danger, so platelets are grouped and sent to “patch” the walls of blood vessels, which ultimately does more harm than good. Vascular walls are damaged, as a rule, due to inflammatory processes - phlebitis (in the veins) or arteritis (in the arteries). Therefore, it is important for people with such disorders to regularly check the condition of blood vessels and blood density.
Another common cause of blood clots is impaired blood flow. With this pathology, in places where the vessel expands or narrows, peculiar “turbulences” can form, where blood clots accumulate.
There is another factor contributing to the development of thrombosis – genetic. Some hereditary diseases affect blood viscosity, making the substance in the vessels thicker. In addition, the thickness of the blood can be affected by taking certain medications, as well as smoking. During pregnancy, if the blood vessels of the placenta are blocked by clots, there is a serious risk to the fetus.
Causes of blood clot separation
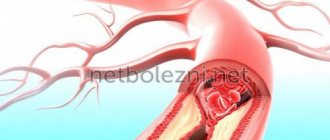
The thrombus can be parietal, or it can be floating. If a blood clot is located near a cholesterol plaque, it is less likely to come off than a floating blood clot. The latter “sits” on a thin leg, which has a weak attachment to the vascular wall. It is floating blood clots that most often lead to the development of pulmonary embolism and strokes.
Also, wandering blood clots may be present in the body, which pose a serious threat to life.
A blood clot can break off as a result of the following influences:
- The blood flow accelerates greatly.
- A thrombus has formed in a wide vessel.
- The stem of the thrombus is weak.
After breaking off, the thrombus begins traveling with the bloodstream along the vascular bed. At this time, it often breaks up into small fractions. Once in a vessel that does not exceed its size, the thrombus clogs it. This entails stopping blood flow and disrupting the nutrition of the limb or organ. This pathological condition is called occlusion.
Symptoms of the disease
It is quite difficult to diagnose yourself. And if a blood clot comes off, it’s even more difficult.
A blood clot that breaks off in the heart, lungs, or brain usually results in death.
But experts call a number of symptoms that signal serious danger:
Advertising:
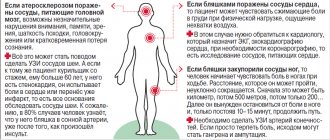
- if the pathogen has formed in the leg, then it begins to hurt, heat up, turn red and swell;
- if it reaches the brain, then speech and coordination are impaired, paralysis appears, the face becomes distorted - all signs of a stroke;
- if in the vein that carries blood from the brain, then vision deteriorates and the head hurts;
- if in the pulmonary arteries, then the person begins to choke and turn blue;
- if in the digestive organs, then vomiting and pain in the stomach appear, which radiates to the shoulder;
- if in the heart, then sharp pain, tachycardia, loss of consciousness;
- if in the portal vein, then abdominal pain appears and liver cirrhosis gradually develops.
Usually everything happens suddenly. Few people can understand in practice what it means that a blood clot breaks off and a person dies.
Signs of blood clot rupture
If you recognize in a timely manner that a person has lost a blood clot, it can save his life.
The consequences of the disaster may be as follows:
- Blockage of a blood vessel in the brain by a blood clot is called a stroke. Its main signs are: speech disorders, facial asymmetry, disturbances in coordination of movements, paralysis of the limbs. If a blood clot enters a vein in the brain, the person will suffer from dizziness, headaches, blurred vision, etc.
- If a blood clot enters the coronary arteries, the patient develops a myocardial infarction. A person experiences severe pain in the heart area, in the neck, stomach, between the shoulder blades.
- Mesenteric thrombus leads to intestinal embolism. In this case, the person experiences severe abdominal pain, which occurs unexpectedly, against the background of absolute well-being. This is a reason to immediately call an ambulance. If a person is not provided with emergency assistance, this will lead to death of intestinal tissue, infection of the peritoneal cavity and death.
- When a blood clot clogs a vessel supplying a limb, it can lead to gangrene. Symptoms of embolism of the veins of the arms or legs are severe pain and blue discoloration of the tissue in the corresponding place.
- Blockage of the pulmonary artery by a thrombus is the most serious condition, which often ends in the death of the patient. A thrombus can enter the pulmonary artery from the veins of the lower extremities. Most often this happens against the background of thrombophlebitis. With pulmonary embolism, a person can die within minutes from heart or lung failure.
If a person experiences one or more of the above symptoms, he should not hesitate to consult a doctor. When there is a suspicion of thrombosis, you need to tell the doctor about it, which will facilitate the diagnosis. If a person knows that he suffers from atherosclerosis, thrombophlebitis, ischemic heart disease and other diseases that carry the risk of a blood clot, he should inform the doctor about this.
It is worth noting that about 50% of people who suffered thrombosis did not experience any pathological symptoms until an acute circulatory disorder occurred.
The following signs can help you detect a blood clot:
- Most often, blood clots are localized in the veins of the lower extremities. A developed system of veins that appear under the skin can lead one to think about thrombosis. The vessels can be compacted, sometimes they become inflamed, which can be seen by redness of the skin and pain that occurs when touching them. If you touch this area, you can feel the heat.
- A blood clot that has formed in the deep veins can make itself felt by swelling in a characteristic location, general malaise and unexplained changes in body temperature.
How to diagnose thrombosis at an early stage?
Thrombosis at an early stage can be detected with timely diagnosis of the veins of the lower extremities. To confirm or refute the diagnosis, phlebologists often recommend laboratory and ultrasound duplex scanning (USD) of the veins. This diagnostic method allows you to see the walls and lumen of the veins, the presence of a blood clot in them, its size, and even roughly judge how long ago the process is. You can also do angiography: a contrast study of blood vessels. And the predisposition to the appearance of blood clots can be identified using a coagulogram: a comprehensive analysis of blood clotting indicators.
If a blood clot comes off, what should you do?
If a person has a blood clot, then you cannot hesitate to call an ambulance. Moreover, even a doctor will not be able to make an accurate diagnosis without special equipment. Therefore, the victim must be urgently hospitalized.
There can be two treatment regimens for thrombosis: either the patient is prescribed medication correction or he is referred for surgery.
Drug therapy includes:
- Prescription of anticoagulants. These drugs help thin the blood (Heparin, Warfarin).
- Course treatment with statins.
- Prescription of fibrinolytics.
- Prescribing thrombolytics, which are necessary to dissolve the blood clot.
If the problem cannot be solved with the help of medications, or the person develops complications of thrombosis, he is indicated for an operation called thrombectomy. It is also possible to install special vena cava filters that will “catch” blood clots, preventing them from clogging vital vessels.
Possible consequences
They depend on where the blood clot clogged the vessel:
- if in the brain, then a stroke occurs;
- if in the coronary arteries - myocardial infarction;
- if in the intestines, then - necrosis, peritonitis of this organ;
- if in the legs, then gangrene is possible.
Advertising:
Stagnant blood is a favorable environment for microorganisms. An infected embolus can cause sepsis.
How to prevent a blood clot from breaking off
People whose blood relatives suffered from thrombosis will have a high risk of developing a similar disease. Therefore, you should be regularly examined by a doctor to detect dangerous vascular growths. Modern medicine has all the necessary tools to detect a blood clot and prevent its rupture.
If a person’s blood has increased clotting, he will be prescribed medications (antiplatelet agents). Sometimes they need to be taken for life. It should be noted that only a doctor can recommend them, otherwise you can cause serious harm to your own health.
If the doctor diagnoses a blood clot that is highly likely to break off, the patient is urgently hospitalized and prepared for surgery.
People with thrombosis should strictly follow their doctor's instructions. They are not recommended to take a hot bath, visit saunas and steam baths, as all these procedures increase blood flow through the vessels. A ban is also imposed on visiting massage rooms and using warm compresses.
To prevent blood from stagnating in the veins, it is necessary to move as much as possible, engage in physical exercise, and walk a lot.
If the patient is at risk of blood clot rupture, then strict bed rest is indicated. Self-treatment of thrombosis or wait-and-see tactics in this case is unacceptable.
A menu containing foods that lower blood cholesterol should be a priority. This will prevent the formation of atherosclerotic deposits on the vessels, and therefore reduce the risk of thrombosis. For this purpose, you can include sea fish, seafood, broccoli, spinach, new potatoes, and dairy products in your diet.
When do blood clots break off more often?
There are many conditions in which the risk of blood clot formation and rupture increases several times. One of them is atherosclerosis.
People suffering from this disease are at increased risk of heart attack, stroke and thrombosis of the lower extremities, which is complicated by gangrene. The main factor leading to such complications is atherosclerotic plaques that accumulate on the walls of blood vessels.
Sometimes it happens that atherosclerotic plaques rupture, releasing the lipids it contains. Platelets perceive these particles as something similar to a wound and stick to them. This is how large blood clots form, which, if they break off, pose a serious danger to life. To prevent disastrous consequences, patients with atherosclerosis are usually prescribed aspirin, which prevents platelets from sticking together and, consequently, the formation of blood clots.
Atrial fibrillation is a fairly common cardiovascular disease, which also increases the risk of becoming a victim of a broken blood clot. With atrial fibrillation, an irregular contraction of the ventricles of the heart is observed, which is why blood can stagnate in the atrium and blood clots form over time. Statistics indicate that the presence of atrial fibrillation increases the risk of heart attack by almost 6 times. Therefore, people with such cardiac disorders are prescribed anticoagulant drugs (slow down blood clotting). Taking anticoagulants prevents the formation of protein threads (fibrin), which, in fact, bind platelets into huge blood clots.
People who lead a sedentary lifestyle may also be at risk of blood clots.
The fact is that due to low physical activity, during sedentary work or when you have to stand in one place for a long time every day, stagnation of blood occurs in the veins. A similar effect is caused by varicose veins. In both cases, the risk of blood clot formation increases. If a clot breaks away from a vein, it will be carried directly into the lungs by the bloodstream, which, as already mentioned, causes a pulmonary embolism. Undesirable consequences can also be prevented by taking anticoagulants.
Diagnosis of pathology
Timely diagnosis will help you avoid surgical intervention and save your life. People who are at risk should undergo the examination.
It is worth systematically diagnosing both young men and women, because the disease is noticeably younger.
The following methods help to identify the presence of a detached blood clot:
| Method name | What is its essence |
| Thrombin generation test | Shows the state of the blood coagulation system |
| Thrombodynamics | Allows you to identify disorders and a tendency to thrombosis in the early stages |
| Thromboelastography | The process of blood clotting and fibrinolysis is determined graphically |
| Prothrombin time test. | Includes indicators for external assessment of blood clotting |
To reduce the risk of a pathological process, it is important to engage in prevention.