Tells Candidate of Medical Sciences, general practitioner, cardiologist at the Atlas biomedical holding Maria Kirillova.
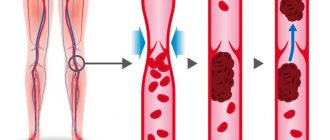
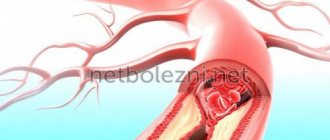
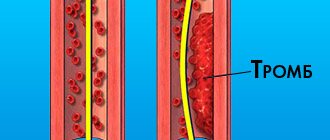
Thrombosis is a condition in which blood clots (thrombi) form in blood vessels (veins and arteries). Most often, blood clots form in the veins or venous thrombosis occurs (in which a blood clot forms in a section of the venous vascular bed, mainly in the legs). Any blood clot interferes with normal blood flow, but a disaster occurs at the moment when the clot reaches a size comparable to the size of the vessel and completely blocks the blood flow, or when the clot (or a small part of it) breaks off and, along with the blood flow, enters the vessels of the lungs (this condition called pulmonary embolism.
Then you will find out...
2/3 of venous thrombosis are asymptomatic or with mild symptoms. A person is bothered by moderate pain in the leg and slight swelling, but not so severe as to force him to see a doctor. Of the three cases of thrombosis, one progresses, and two resolve spontaneously.
However, this does not always mean that resolved thrombosis has passed without a trace. Even in this case, irreversible changes occur on the wall and valve of the affected vein, which lead to the development of chronic venous insufficiency. With duplex scanning of blood vessels, doctors often see post-thrombotic changes in the deep veins of the leg in patients who have never been diagnosed with venous thrombosis.
Blood control and nutrition without “greens”. A doctor on how to live with thrombosis Read more
What thins the blood?
After 30–35 years, even in a healthy person, blood density increases. The following factors lead to this:
- Unbalanced diet, smoking, alcohol, lack of vitamins.
- Violation of the water regime, insufficient drinking or consumption of low-quality tap water.
- Taking certain medications, primarily diuretics.
Some diseases of the kidneys, liver, even viral infections are accompanied by changes in blood density.
What in the functioning of the body should alert and arouse suspicion that not everything is fine with the blood? Pay attention to the following phenomena:
Wait, who's coming?
How to detect thrombosis at an early stage? More often it “starts” in the veins of the leg and is accompanied by quite tolerable local pain and swelling. In an unfavorable scenario, the blood clot increases in size, involving the veins of the thigh and pelvis. Gradually, massive swelling, redness of the skin, bursting pain, and swelling of the saphenous veins appear. From the moment the first symptoms appear until you see a doctor, it usually takes 5-10 days. The exception is iliofemoral thrombosis, which makes itself felt immediately - with pronounced swelling and noticeable pain.
“Silent” thrombosis (with a complete absence of symptoms) can occur in bedridden patients (after surgery or paralysis) or if a blood clot forms in the pelvic veins (usually this occurs during pregnancy and childbirth, in the postpartum period, when taking oral contraceptives). In such situations, the first sign of disease may be pulmonary thromboembolism “without a clear source.”
Article on the topic
There is a cork in the vessel. Where did the child get thrombosis?
Size matters
Which blood clot is the most dangerous? The larger the vein and the larger the size of the clot, the higher the chance of thromboembolism. The most dangerous are proximal (located close to the center of the body) blood clots - in the veins of the thigh, pelvis and retroperitoneum. The incidence of embolism in this location is above 50%.
A small peripheral blood clot (for example, in the lower leg) can also become hypothetically dangerous. It also migrates to the pulmonary arteries and disrupts blood flow. Minor embolisms are asymptomatic in 75% of cases, but they still pose a threat to life, albeit a delayed one. Sooner or later, if left untreated, they can lead to circulatory problems and, in some cases, death. Therefore, any identified blood clot in the veins requires active treatment.
Who to look for?
Venous thrombosis is a multifactorial disease that occurs under unfavorable circumstances. Today it is impossible to say for certain who is at risk of thrombosis and who is not (only in some cases a predisposition to thrombosis can be identified using a coagulogram - a comprehensive analysis of blood clotting indicators).
Article on the topic
Life without traffic jams. Russian scientists against thromboembolism Classic factors that provoke the appearance of blood clots include obesity, air travel, dehydration, long stays in a forced position, pregnancy, varicose veins (deep veins) and taking oral contraceptives.
This is only partly true. These circumstances can indeed lead to the formation of blood clots, but only with a complex effect. For example, if you sit motionless in an uncomfortable position for 9 hours on a plane and refuse drinks for the entire flight, while you suffer from obesity, varicose veins and take contraceptives, the chance of getting off the plane with a blood clot is really quite high. But if the matter is limited to one thing (for example, varicose veins or taking contraceptives), you risk no more than other people.
Surgeries and injuries (especially in combination) are considered truly dangerous factors. Such blood clots are considered clinically induced, so all herbal and post-operative patients are screened for the presence of blood clots.
In 10-20% of patients, thrombosis can serve as the first sign of malignancy. In patients over 50 years of age, when clinically unprovoked thrombosis is detected, an in-depth search for cancer is recommended.
Dissolve the clot. What foods improve blood quality Read more
Causes of blood clots
Several factors play a role in the mechanism of thrombosis, consideration of which is necessary to understand the essence of the process and determine the principles of treatment of thrombosis. These factors are:
- increased blood clotting;
- slowing down the speed of venous blood flow;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels.
High blood clotting can be caused by hereditary and age-related factors, and can also be a companion to certain diseases (autoimmune processes, thrombophilia, acute respiratory infections) and physiological conditions of the body (pregnancy). Increased clotting is also caused by low physical activity, taking oral contraceptives and diuretics.
Disruption of venous blood flow is observed with varicose veins, narrowing of their lumen due to the development of inflammatory processes, as well as with various types of cardiac pathology (heart failure, arrhythmias). A sedentary lifestyle and sedentary work also contribute to a decrease in venous outflow.
Violation of the integrity of the inner lining of blood vessels occurs due to mechanical injuries, including surgical, infectious and inflammatory lesions. Damage to the vascular intima is not a prerequisite for the formation of a blood clot. The first two reasons are often sufficient for this. However, it significantly accelerates the process of thrombus formation.
So, what is next?
At the first suspicion of thrombosis, you should consult a doctor. In acute cases, the patient is immediately sent to the operating table for vein ligation, installation of a vena cava filter, or surgical removal of a blood clot. But more often thrombosis is treated on an outpatient basis. The doctor will conduct an initial diagnosis, confirm the conclusion with an ultrasound examination (duplex scanning of veins) and prescribe anticoagulants - blood thinners, the task of which is to clear the lumen of the vessel. Be patient! The duration of taking anticoagulants can range from 3 months to conditionally lifelong use. And all this time you will need to visit the clinic so that the doctor evaluates the effectiveness (lack of relapse), safety (lack of bleeding) of therapy and determines the required duration of treatment.
Advantages of thrombosis treatment at the Swiss University Hospital
- In our Center for Cardiovascular Surgery, treatment of deep venous thrombosis is carried out not only by conservative methods. We have widely introduced our own minimally invasive surgical interventions into clinical practice, thanks to which we were able to reduce not only the trauma of surgical intervention, but also save the patient from complications, which leads to rapid healing and a reduction in the duration of the rehabilitation period, improving the quality of life.
- To prevent venous thromboembolic complications, our clinic widely uses complex methods of preoperative, intraoperative, postoperative prevention of venous thromboembolic complications in accordance with the degree of risk of their occurrence.
- Vascular surgeons (phlebologists) at our clinic have many years of experience in performing surgical interventions, each of our specialists is fluent in all the techniques used in our clinic. Each surgeon has performed more than 2,500 successful operations for varicose veins, including those complicated by varicothrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis, with analysis of long-term results.
- Ultrasound diagnosis of thrombosis of the main veins of the lower extremities, its nature and the exclusion of local contraindications before surgery is carried out by vascular surgeons (phlebologists) using expert-class equipment at the highest professional level. Doctors of the Center for Vascular Surgery are certified specialists of the highest qualification category with an academic degree.
- We have developed and put into practice a protocol for ultrasound duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities, which allows not only to map in detail varicose veins and their sizes, but also to accurately determine the variants of pathological reflux with the location of sources of reflux, routes of spread of reflux, channels of blood return to the deep vein system, variant of thrombotic lesions of various venous segments of the limb. This protocol allows you to adequately select the method and scope of minimally invasive surgical intervention. Thus, in our practice, the number of tactical errors associated with the choice of method and volume of surgical intervention for venous thrombosis has significantly decreased, which has a qualitative impact on the results.
- The Vascular Surgery Center is equipped with expert-class equipment from world-famous manufacturers (such as Karl Storz, Covidien, ACUSON-Siemens, Valleylab, etc.). Cooperation with leaders in equipment production makes it possible to be several years ahead of other clinics and be one of the first to apply innovative technologies, scientific and medical developments in practice. To perform surgical intervention for deep venous veins, we use, in addition to proprietary low-traumatic surgical instruments, certified disposable surgical instruments.
- We provide treatment in accordance with international standards, the quality of the services provided is assessed by international organizations that regularly visit our clinic to verify compliance with international standards.
- For each patient, we select a set of surgical intervention techniques, based on the individual characteristics of the course and severity of varicose veins, the presence and severity of concomitant pathology, physical and social activity, attitude towards one’s disease, and motivation for a good long-term result.
- We strictly and unswervingly adhere to the principles of continuity of treatment and family medicine, the principle of “open doors”, when the patient has the right to contact the operating surgeon if necessary at any time.
- In addition to vascular surgeons (phlebologists), patients in our clinic, if necessary, can count on the help of other specialists, which makes it possible to undergo a comprehensive examination and treatment.
- Considering the chronic nature of the course of chronic venous diseases, the tendency to relapse, and thrombotic complications, we have moved away from the impersonal “operate and forget” system to a lifelong monitoring system, including annual ultrasound examination.
- We will determine the frequency of further follow-up examinations and examinations for the prevention and timely detection of relapse of venous thrombosis, correction of conservative treatment.
- When determining whether a patient is suitable for surgical intervention for venous thrombosis, we do not follow his wishes, observing, first of all, the principle of “do no harm.”
- Together with you, we will try not only to save you from severe manifestations of chronic venous diseases and possible relapse of varicose veins, but also to significantly improve the quality of your life in the future.