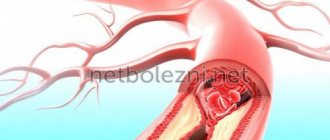
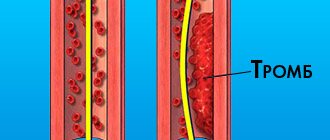
General information about thrombosis
Thrombosis
ー the process of intravital blood coagulation in the cavities of blood vessels and the heart. This process is also dangerous because part of the blood clot can break off and be carried by the bloodstream to other organs. For example, with thrombosis of the deep veins of the lower extremities, thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery or cerebral vessels often develops.
Clinic depending on the location of thrombosis
| Damaged artery | Symptoms |
| Middle cerebral | Speech impairment, paralysis of the upper or lower limbs. Impaired sensitivity. Decreased vision. |
| Forebrain | Paralysis of an arm or leg on the right or left, paresis of the facial muscles. Possible mental changes |
| Posterior brain | Loss of visual fields, visual hallucinations |
| Vertebro-basilar | Signs of cranial nerve damage, dizziness, nystagmus |
If the thrombus is localized in the extracranial (extracranial) part of the carotid artery, then a “flickering” of symptoms is observed, that is, they can disappear on their own and appear with varying severity and frequency.
Classification of thrombosis
Depending on the location of the pathological process:
Arterial:
- arteries of the brain;
- hearts;
- intestines (mesenteric thrombosis);
- liver;
- femoral artery and others.
Venous (phlebothrombosis):
- veins of the lower limb;
- hemorrhoidal plexus;
- femoral and iliac veins;
- cavernous sinus (intracranial collector of venous blood);
- retinal veins.
According to the severity of the disease, acute
ー a sharp blockade of blood flow, and
a chronic
ー thrombus grows gradually, the tissues have time to adapt to this and compensate for pathological changes.
2. Reasons
Considering the critical, priority importance of the brain, evolution took care of its maximum protection: powerful skull bones, upper location, as well as “reserve circuits” of cerebrovascularization (blood supply to the brain). The brain receives nutrition from several main vessels - the carotid and vertebral arteries; the latter, merging, form the unpaired basilar artery, or vertebrobasilar arterial system. If there are disturbances in any of the blood supply channels, other channels compensate for the deficiency in order to preserve the functioning of the brain at any cost. The compensatory capabilities of the brain in this sense are very great (and have not yet been sufficiently studied), however, unfortunately, they also have their limits. With intense sudden ischemia, the cerebrovascular system simply does not have time to react and prevent irreversible necrotic changes.
Spasm of the main cerebrovascular vessels can occur for various reasons: massive bleeding, sudden blow, rapid hypothermia, poisoning with certain substances, etc. However, all these factors occupy only a small proportion compared to the leading cause of ischemic stroke: embolism, i.e. blockage of the arteries by a detached atherosclerotic plaque, a clot of coagulated blood, etc. In general, arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis, lipid metabolism disorders with the accumulation of mushy deposits on the walls of blood vessels, are typical “diseases of civilization”, since they are largely caused by the very lifestyle and destructive habits of modern man: physical inactivity, extremely unhealthy diet and overeating, smoking etc. It is no coincidence that circulatory disorders in various systems of the body (primarily the coronary and cerebral arterial systems) consistently occupy first place in the lists of causes of non-violent mortality.
Visit our Neurology page
Mechanism of development and causes of thrombosis
There are three pathological parts in the process of intravascular thrombus formation:
- Violation of the integrity of the vascular wall. When the internal lining of blood vessels is damaged, enzyme systems are activated, which trigger the process of blood clotting.
- Slowing blood flow. This occurs when the outflow is disrupted (compression of veins, varicose veins), prolonged absence of limb movement, or heart failure.
- Blood thickening. Caused by dehydration, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy, and oral contraceptives.
A blood clot often forms against the background of such diseases:
- atherosclerosis;
- heart failure;
- aneurysms of blood vessels and heart;
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- bone fractures;
- hormonal disorders;
- oncological diseases.
What causes blood clots?
Thrombi, in the form of blood clots, form in blood vessels in response to damage to the vascular wall, slowing of blood flow and changes in blood composition. “Thrombosis does not occur out of nowhere; there must be some prerequisites. This is facilitated by the presence of varicose veins in the lower extremities. If it is, you should pay attention to compactions that may appear in the veins,” says phlebologist, surgeon Fedor Shpachenko .
According to the phlebologist, compactions may indicate that blood clots have already formed in the veins. “Often, these blood clots may not occur in the superficial veins that we see, but in deep veins, and it is impossible to visualize them without special research methods,” warns Shpachenko.
Thrombosis in children
Possible causes of blood clot formation in children:
- thrombophilia - congenital deficiency of anticoagulant blood factors;
- leukemia, other oncological diseases;
- cutaneous fulminant purpura, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (develops with severe intoxication, inflammatory diseases: pancreatitis, peritonitis, etc.);
- the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, lupus anticoagulant, and other autoantibodies (antibodies to one’s own cells).
Episodes of blood clots in a child should prompt a serious examination to determine the cause.
What will they do at the hospital?
- CT (computed tomography) scan of the brain. This is the first thing to do if you suspect a catastrophe in your head. This study allows you to exclude intracerebral hematoma and see the focus of ischemia (but not always, sometimes it will form only after 10-12 hours).
- Examination by a neurologist to assess the severity of the condition.
- Ultrasound scanning of blood vessels.
- In some cases, CT or MRI angiography of cerebral vessels is prescribed.
- Spinal tap.
- ECG.
- General tests, biochemical and coagulogram.
- Consultations with medical specialists (therapist, cardiologist, endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon).
Risk factors for thrombosis
The following factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- age over 50 years;
- obesity;
- smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction;
- poor nutrition;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- injuries;
- the need for frequent intravenous injections and procedures associated with violation of the integrity of blood vessels (blood sampling, hemodialysis, installation of a venous catheter) increases the risk of developing phlebitis and inflammation of the venous wall.
Who is at risk?
Those who are most likely to develop thrombosis are people who are obese and have varicose veins, women who take oral contraceptives, and those who take many long flights. But a high risk of blood clots occurs when all these factors are combined.
“Patients with obesity and varicose veins are at risk. As for medications, in particular oral contraceptives, now most of them are well balanced and we rarely see the development of thrombosis and thromboembolism in women taking these drugs. People with a sedentary lifestyle, impaired hemostasis, namely blood clotting disorders, also fall into this group. If the patient has all these provoking factors, then the risk of developing thrombosis increases. Age also makes it worse. Over the years, the vessels lose elasticity and become brittle, plus a number of concomitant diseases cause swelling of the lower extremities,” says Shpachenko.
Symptoms of thrombosis
The clinical manifestations of this pathology vary depending on the location.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis
When a vein is blocked, the outflow of blood is hampered, so the tissues beyond the blockage swell and turn blue. The waste products of cells accumulate, therefore tissue intoxication develops, this is accompanied by pain, impaired sensitivity (the sensation of “crawling goosebumps”). If you do not intervene in time, the tissues begin to die.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis of the lower extremities:
- swelling of the leg, a sharp increase in size, cyanosis;
- cramps of the calf muscles;
- constant pain in the leg, which intensifies when walking;
- increased venous pattern on the thigh.
Cavernous sinus thrombosis:
The dura mater contains channels into which venous blood from the brain drains. Blockage of one of these sinuses, the cavernous sinus, is dangerous because several cranial nerves and the internal carotid artery pass through it. The most common causes of cavernous sinus thrombus formation are inflammatory diseases of the nose, sinuses, facial skin and scalp. Signs:
- headache;
- decreased visual acuity, double vision;
- confusion;
- heat, fever;
- swelling of the eyelids and periocular area;
- pain in the neck when turning or tilting the head;
- impaired facial skin sensitivity.
Among the consequences of such thrombosis: stroke, loss of vision, coma.
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis
Develops against the background of hemorrhoids. Chronic constipation, physical stress, pregnancy and childbirth, and alcohol abuse contribute to it. Signs:
- pain, burning and itching in the anal sphincter area;
- discharge of blood with feces and regardless of the act of defecation;
- prolapse of hemorrhoids.
Retinal vascular thrombosis
The pathology is a typical complication of diabetes mellitus and hypertension, but can also develop for other reasons. Symptoms:
- deterioration of vision, up to complete loss (usually one-sided);
- the appearance of spots, mesh, veils before the eyes.
Symptoms of arterial thrombosis
Blockage of the artery leads to oxygen and energy starvation of tissues, which quickly leads to their death. Arterial forms of the disease are often acute.
Thrombosis of the cerebral arteries
This process leads to necrosis of the area of the brain that the affected artery supplies blood to - ischemic stroke. Signs:
- hemiparesis ー lack of movement in the right or left half of the body (opposite affected area);
- asymmetry of the smile - one corner of the mouth is lowered, does not take part in conversation and smile;
- unclear speech;
- when the patient sticks out his tongue, it deviates to the side.
Thrombosis of the coronary arteries of the heart
Partial blockage of these vessels leads to attacks of angina pain, complete blockage leads to myocardial infarction. Symptoms:
- pressing, burning pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left shoulder blade, arm, shoulder, half of the face and neck;
- dyspnea;
- with angina pectoris, rest and nitroglycerin help, with a heart attack there is no improvement, urgent medical attention is needed.
Pulmonary artery thrombosis
It is a complication of thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities, endocarditis, myocardial infarction. It develops rapidly and has a high mortality rate. Signs:
- sharp stabbing pain in the chest;
- swelling of the veins of the neck;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- hemoptysis;
- increased heart rate.
Hepatic artery thrombosis
Death (infarction) of liver tissue is a complication of endocarditis, myocardial infarction or liver transplantation and manifests itself as follows:
- severe pain under the right rib;
- nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Femoral artery thrombosis
This form of pathology is manifested by pain when walking, coldness, and paleness of the limb. The pulse in the popliteal fossa and on the foot is palpable weakly or not detected at all.
How to diagnose
First of all, based on the symptoms. Even a non-medic may suspect a stroke. If a person suddenly becomes ill, you need to ask him:
- Smile. A person with a stroke will have a crooked smile, only one corner of the mouth will rise, the other will remain down.
- Raise both arms up. With paresis, one of them will lag behind.
- Ask for your name, age, address, today's date and month. If he has a stroke, he will not be able to answer at all, or his speech will be blurred and incomprehensible.
This test is called FAST (Face Arm Speech Test) - face-hand-speech.
If at least one of the signs is present, you must call an ambulance, and clearly list the symptoms.
Diagnosis and treatment of thrombosis in Medical
Specialists from the Paracelsus Medical Center will help in diagnosing and eliminating this pathology, provide support during the rehabilitation period, and give recommendations for further prevention.
Our center uses expert-class equipment from leading global manufacturers for diagnosis and treatment. The consultation is conducted by practicing phlebologist surgeons.
On the basis of "Operating Room No. 1" phlebological operations are performed for venous disease. The key advantage of the Paracelsus Medical Center network is highly qualified professional surgeons with extensive practical experience.
Drug treatment
The basis of drug therapy is anticoagulants (thin the blood, prevent the growth of a blood clot), fibrinolytics and thrombolytics (dissolve existing clots), antiatherosclerotic drugs (lower cholesterol levels). If necessary, analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, cardiotonic drugs, vitamins, minerals, etc. may be needed as symptomatic therapy.
Surgery
There are such methods of surgical treatment of the disease:
- thrombectomy ー removal of a blood clot;
- stenting (expansion using a frame) and shunting (creating a bypass path for blood flow) for atherosclerotic artery disease;
- arteriovenous shunting.
If the thrombus cannot be removed, a vena cava filter can be installed - the device is placed in the vein above the level of blockage to prevent it from moving and closing the lumen of the vessels of vital organs.
What to do before the ambulance arrives
If a cerebral infarction is suspected, it is advisable to lay the patient down, slightly raising the head end, and calm him down. It is not recommended to sharply reduce blood pressure; it is better not to give any antihypertensive drugs until doctors arrive. It is enough to let a few glycine tablets dissolve.
If a stroke is suspected, the patient is urgently taken to the nearest vascular center or neurological department. If no more than 6 hours have passed since the onset of symptoms, the patient is sent to the neurointensive care unit. Transportation - on a stretcher with a raised head end.
Thrombosis is an emergency condition, and the sooner the patient is taken to a specialized hospital, the greater the chance of a full recovery.
Recovery
What happened happened - the blood clot did its job and turned off part of the brain. It is known that nerve cells do not recover. Does this mean that paralysis or speech impairment will remain forever? Not at all. It all depends on the extent of the lesion. With small foci of necrosis, neighboring areas of the brain gradually “retrain” and take over the function of dead neurons.
This process requires time, effort and attitude of the patient and his loved ones.
Rehabilitation after a stroke includes drug treatment, as well as massage, physical therapy, physiotherapy, classes with a speech therapist and other rehabilitation measures.
The consequences may disappear without a trace, may decrease significantly, or may remain for life.