Symptoms of vasospasm of cerebral vessels
Previously, the disease occurred only in elderly patients. In recent years, pathology has become “younger”. It is facilitated by the unfavorable environmental component that prevails in large cities and industrial zones, and the presence of toxic elements in the air. The latter penetrate the respiratory system and are transported directly to the brain, having a negative effect on the blood vessels.
Angiospasm is a fairly powerful and long-term compression of blood vessels. Spasm occurs due to incorrect blood circulation and supply of nutrients. This disease requires immediate treatment, since untimely assistance contributes to the development of complications, such as stroke.
You should consult a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations in the occipital and temporal region;
- Frequent dizziness;
- High pressure;
- Tinnitus that occurs when a person is in a calm or active state;
- Loss of coordination, speech impairment.
Peripheral neurovascular syndromes. Illness of young people
S.A. Klyushnikov Candidate of Medical Sciences, State Research Institute of Neurology, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Peripheral neurovascular syndromes (NVS) are a combined lesion of neurovascular formations of the neck, shoulder girdle, trunk and limbs. These diseases are widespread among the population and can cause permanent disability in young people. The development of symptoms, as a rule, is caused by long-term pathological effects of various external and internal factors on the neurovascular bundles with disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses in the walls of blood vessels and directly in the tissues.
The clinical picture of SVC is characterized by a combination of pain, muscular-spastic and vegetative-vascular disorders, often with the addition of edematous-dystrophic tissue changes. Clinical signs of NWS are conventionally divided into: • local - muscle soreness and tension, pain points in typical places, tissue swelling • neurological - muscle atrophy, contractures, etc. • vascular – changes in temperature and skin color (cyanosis), changes in blood pressure and pulse on one limb
Well-known forms of NVC are, for example, tunnel neuropathies, often also called “trap neuropathies.” This is the infringement of peripheral nerves and vessels by tendons and ligaments in anatomical narrowings (tunnels) through which neurovascular bundles normally pass - in hard bone canals, openings in ligaments, etc. Currently, the role of congenital narrowing of the bone and connective tissue canals in the development of this form of congenital fibrosis has been established. Compression is also possible with a normal diameter of the canals in the case of an increase in the diameter of the nerve due to edema. A classic example is the development of neuropathy (“paralysis”) of the facial nerve, when, under the influence of some external factor (for example, hypothermia), microcirculation in the area of the facial nerve is disrupted, swelling of the nerve trunk develops, and the nerve seems to compress itself in the bone canal . Some of the most common forms of neurovascular syndromes are:
— Vertebral artery and vertebral nerve syndrome (synonyms: posterior cervical sympathetic syndrome, “cervical migraine”, etc.). The reason is irritation of the spinal nerve due to pathology of the cervical segments of the spine, resulting in the development of a reflex spasm of the vertebral artery. Characterized by headaches, dizziness, a combination of vestibular disorders with pain points on the neck in the projection of the entrance of the vertebral artery into the spinal canal, and various autonomic-sensitive disorders in the head area.
— Scalenus syndrome (anterior scalene muscle syndrome). It consists of compression of the subclavian artery and brachial plexus between the anterior and middle scalene muscles in the neck. As a result, a decrease in blood pressure in one arm and a decrease in the filling and tension of the pulse develop, cyanosis and autonomic disturbances appear in the arm below the point of compression, pain and numbness in the shoulder girdle and shoulder girdle, and local tension in the anterior scalene muscle. Most often develops against the background of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, abnormal cervical ribs, and trauma. Scalenus syndrome often occurs in adolescents who are intensely involved in sports (chronic injury to the anterior scalene muscle against the background of intensive skeletal growth and increased physical activity).
- Raynaud's syndrome. It is characterized by the localization of vegetative-vascular and trophic disorders mainly on the fingers and toes (pallor, cyanosis), as well as the suddenness and severity of attacks of vascular spasm, which become more and more protracted as the disease progresses. The leading factor in the development of the disease is compression and irritation of the arterial vessels of the arms and legs and the surrounding autonomic plexuses.
- Piriformis syndrome is a well-known SUD, in which there is compression of the sciatic nerve and inferior gluteal artery by the piriformis muscle in the buttock area. The clinical picture resembles “radiculitis” with pain spreading over the buttock and posterior thigh, limping, vegetative-vascular and neurodystrophic manifestations, as well as signs of local damage to the piriformis muscle, tension and pain of which can often be determined by touch.
— Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common form of tunnel neuropathies. The median nerve is compressed in the carpal tunnel by the hypertrophied transverse ligament of the palm, which is clinically manifested by a sensation of “pins and needles” in the area of the hand and fingers, pain (especially when raising the arm up). With prolonged suffering, weakness of the hand muscles and trophic disorders develop. The prevalence of this syndrome has increased sharply due to total computerization, since computer keyboards turned out to be unsuitable for long-term work of the fingers with poor fixation of the wrists, which caused hypertrophy of the transverse carpal ligament and the occurrence of symptoms. This prompted computer companies to switch to special ergonomic keyboards, resulting in a sharp decline in the number of new cases of this rather unpleasant suffering.
To make an accurate diagnosis of NWS, both clinical studies (neurological examination using special functional tests) and numerous laboratory and instrumental methods are used to determine the state of the microcirculatory bloodstream, coagulation system and blood viscosity. Doppler ultrasound, electroneuromyography, capillaroscopy, computer thermal imaging, duplex scanning of blood vessels, and magnetic resonance imaging are also used. All these methods make it possible to accurately establish the localization and nature of muscular-tonic, vegetative-vascular and neurodystrophic disorders, to distinguish one form of SUD from another, and to select the correct treatment.
Therapy for these sufferings is divided into conservative and surgical. Conservative treatment is used for relatively early and benign current forms and is often very effective. It is aimed, first of all, at sources of neurovascular compression and vasospasm: spinal osteochondrosis, inflammatory and tumor processes of muscles and connective tissue, diseases of internal organs. The success of conservative treatment depends on the patient’s timely contact with a specialist. Self-medication is in any case unacceptable! Painkillers, drugs that improve microcirculation and relieve inflammation, decongestants and venotonic drugs are used.
Antispastic drugs (muscle relaxants) are important for treatment, since muscle spasm is not only a typical symptom, but also a key pathogenetic stage in the formation of almost any form of SUD. According to the experience of the most authoritative clinics in the world, the leading antispastic drug is currently recognized as baclofen (Baklosan), which not only effectively and quickly reduces muscle tone, but also has an undoubted analgesic effect. The latter circumstance is especially important in the treatment of SUD. Thus, the use of Baklosan and its analogues is an integral stage of therapy for NBC.
Blockades, acupuncture and electropuncture, electrical stimulation and other methods of physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage, orthopedic and sanatorium treatment are also used in the treatment of SUD. If the disease has reached a severe stage, as well as if other methods of treatment are ineffective, surgical treatment is used (dissection of pathologically altered spasmodic muscles, removal of scar-fibrous deposits and ligaments, reconstructive operations on blood vessels).
© Magazine “Nerves”, 2006, No. 3
Causes of cerebral vasospasm
In addition to stress and unfavorable ecology, other factors also influence the disease, for example, insomnia and chronic fatigue, overstrain of the nervous system, strong emotions, and lack of headwear during the cold season.
Vascular angiospasm can cause the following pathologies:
- Osteochondrosis;
- Aneurysm;
- Damage to the structure of the arteries;
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Improper functioning of the endocrine system;
- High pressure;
- Oncology.
Angiospasm of leg vessels
Angiospasm can be observed in all kinds of vascular regions and is accompanied by damage to blood vessels and the nervous system. People who are addicted to smoking are most often susceptible to vasospasm in the legs. The disease also occurs as a result of frostbite and hypothermia. The disease is diagnosed based on the dynamics of symptoms, including changes in skin color and a decrease in its temperature.
Diagnosis of retinal vasospasm
Anamnestic data, the results of a visual examination in combination with additional diagnostic methods allow the ophthalmologist to establish vasospasm of the retinal vessels as a diagnosis. The list of studies within the framework of pathology detection includes:
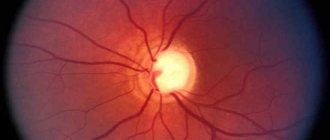
- Ophthalmoscopy. After examining the fundus of the eye, the doctor visually determines a sharp narrowing of the veins in the retina. The vessels are full of blood, but a somewhat swollen, pale pink optic disc is visible. The foveal reflex, like the macular reflex, is not diagnosed during vasospasm.
- OCT. During scanning of the central part of the retina, thickening is visible. In this case, the foveal recess is greatly smoothed, and retinal reactivity is reduced, while the shape of the curve is atypically straight.
- Non-contact tonometry method. During an attack, the specialist observes a slight increase in IOP (intraocular pressure), and after its relief, a normalization of ophthalmotonus.
- Angiography. The ophthalmologist visualizes the changes taking place in the retinal vessels. Diagnosis occurs as part of studying the characteristics of fluorescein circulation. During vasospasm, the internal blood-retinal barrier for contrast remains impenetrable.
Treatment
Mostly conservative methods are used as therapy, which involve strengthening blood vessels and the state of health in general. For the treatment result to be effective, it should begin with a consultation with a doctor, who will collect anamnesis, prescribe additional studies and select the correct treatment method.
Depending on the symptoms, rubbing of the limbs, surgery, novocaine blockade and appropriate medications are prescribed, and a number of other measures are taken to alleviate the patient’s condition.
When does it occur and how long does it last?
It is an officially recognized fact that in some cases a person who has recovered from a coronavirus infection suffers from its consequences for a long time, and the severity of the post-Covid syndrome does not depend on the severity of the disease, age, health status and other factors. It is customary to refer to post-Covid syndrome as symptoms that last more than 12 weeks, are changeable, characterized by a wave-like course, and cannot be explained by any other reasons. The syndrome can occur immediately after suffering from Covid or after some time.