Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Treatment methods
Telangiectasia ( telangiectasia ), also called spider veins in English literature, is a persistent dilation of small-diameter vessels located between the epidermis and hypodermis. On the skin they usually appear in the form of a specific pattern consisting of many dilated microvessels. In some cases, it looks like a thin “spider web”, which is where the English name telangiectasia comes from.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for the treatment of telangiectasia:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
- Fraxel (Solta Medical)
- UltraPulse (Lumenis)
According to statistics, this vascular pathology develops most often in women: the probability of its occurrence after 30 years is 8%, after 50 years - 41%, after 70 years - 72%. As for men, in similar periods of life, telangiectasias occur with a probability of 1%, 24% and 43%, respectively.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of capillary dilatation, but you can reduce the risk of certain forms of telangiectasia:
- balanced diet;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- using UV protective creams;
- excluding sudden temperature changes;
- careful use of hormonal medications.
If the defect does appear and begins to develop, then it is better to consult a doctor; the pathology may be a symptom of dangerous diseases.
Author of the article: Yulia Dmitrieva (Sych) - In 2014, she graduated with honors from Saratov State Medical University named after V. I. Razumovsky. Currently working as a cardiologist at the 8th City Clinical Hospital in the 1st clinic.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The causes of telangiectasias are varied - today there is no single factor that is 100% etiological for this vascular pathology. For example, the formation of arachnid telangiectasia is hereditary. At the same time, there are many other types of telangiectasias that can appear, for example, in people with thin skin and prolonged exposure to the sun. In general, telangiectasia occurs for the following reasons:
- Genetics
- Insolation and/or strong wind
- Taking vasodilators
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Skin injury
- Surgical interventions
- High blood pressure
- Acne
- Pregnancy
- Menopause
- Taking oral contraceptives
- Long-term use of topical or systemic corticosteroids
In addition, the fragility of blood vessels increases with age, which contributes to the relaxation of their walls and the appearance of telangiectasia.
Diagnostics
In order to accurately determine the disease and the degree of its development, you need to make an appointment with a phlebologist. The specialist will conduct an external examination of telangiectasia and palpation of the limbs. As a result, the doctor can draw conclusions about the location of the stars and the nature of the disease.
After this, the specialist will prescribe the necessary studies. They usually include duplex ultrasound scanning, which allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels, determine pathologies and their locations, and assess the direction and speed of blood flow. After this, the phlebologist can draw conclusions about the patient’s condition. For greater accuracy, the doctor may also prescribe tests and studies of other organs, including the heart, thyroid gland, liver, and reproductive system. This will allow us to identify concomitant diseases and establish the cause of the appearance and progression of varicose veins.
Conclusion 3:
You should contact a vascular surgeon immediately after you discover spider veins. Using a series of studies, a specialist will determine the cause of their appearance and prescribe therapy.
Clinical manifestations
Telangiectasias usually appear as red, blue, or purple linear or convoluted tracks on the skin. They can occur in any organ or tissue that has blood vessels (for example, in the brain), but it is the skin manifestations that are available for visual inspection.
Arteriolar telangiectasias are formed from vessels of small diameter, have a bright red color and do not protrude above the surface of the skin. Venular telangiectasias consist of larger vessels with a bluish tint, often rising above the surface of the surrounding skin. These lesions cause concern in patients, not only of an aesthetic nature, but also regarding the possible presence of a more serious vascular pathology.
Based on clinical presentation, telangiectasias are classified into 3 types: tree-like (branching), arachnid (stellate), and linear (simple) ( Figure 1 ). Redisch and Pelser additionally identify a fourth type - macular (pantiform) telangiectasias, which look like a cluster of many small dots on the skin.
Rice. 1. The main types of telangiectasias: a - tree-like, b - arachnid, c - linear (Liapakis EL, et al. Management of facial telangiectasias with hand cautery. World J Plastic Surg 2015; 4(2): 127–133)
Linear and tree-like telangiectasias of a red hue usually form on the face (nose area, middle of the cheeks, chin), while linear and tree-like telangiectasias of a blue hue often appear on the legs.
As for arachnid telangiectasias, they are of hereditary origin and often occur in childhood.
Causes of telangiectasia
Most often, dilated blood vessels appear in people who have thin, dry skin that is sensitive to various irritating factors. Although owners of oily, denser skin may also have single vessels, especially on the wings of the nose.
Poor nutrition, unhealthy lifestyle, bad habits lead to changes in internal organs, manifesting themselves in this cosmetic problem. Dilated blood vessels signal problems with the body. Endocrine diseases, disorders of the stomach, intestines and liver lead to disruption of the absorption and synthesis of vitamins “PP”, “K”, ascorbic acid and some enzymes involved in blood clotting; hypertension.
Acquired vascular skin abnormalities in women are associated with changes in estrogen levels. The hormone has a relaxing effect on the smooth muscle wall of blood vessels. During pregnancy or taking hormonal medications, women are more at risk of dilating blood vessels in the skin.
Active tanning in the sun and in a solarium stimulates the synthesis of growth factor of endothelial cells (cells of the inner lining of blood vessels), the entry into the blood of the mediators histamine, which causes prolonged vasodilatation, and bradykinin, which damages the walls of capillaries. A large number of free radical groups are formed. All this leads to the occurrence of telangiectasias.
Fans of baths and saunas, as well as chefs of restaurants and canteens, workers of “hot shops” after some time may notice a network of blood vessels appearing on the face, resulting from excessive exposure to high temperatures.
Exposure to cold, wind, frost also provokes the expansion of capillaries on the face. Many sellers and anyone who spends a lot of time outdoors in cold air suffer from this. We must not forget about genetic predisposition. If your parents have pronounced rosacea, the likelihood of inheriting this feature increases to 90%.
It is important for everyone who is interested in various and particularly aggressive cosmetic procedures to understand that their skin can become dehydrated, thin, blood vessels can be injured, and the sensitivity of the skin and capillaries to environmental influences increases.
There are several other reasons for the appearance of rosacea: nervous overload, which results in the release of catecholamines into the blood, narrowing under their influence of large vessels and increased blood pressure in peripheral small vessels, spicy and too hot food, as well as silicon deficiency.
Silicon is a mineral that gives the “command” to blood vessels to expand and contract. It helps maintain the elasticity of blood vessels, has a beneficial effect on capillary permeability, and activates metabolic processes in the walls of blood vessels. If the body does not receive enough silicon, calcium takes its place, which blocks the “command”, and the vessels become fragile, brittle and less elastic.
Couperosis can become not only an aesthetic and psychological problem, but also provoke the manifestation of other health problems. You should not wait for the spider veins to spread; it is important to contact specialists in the early stages of development.
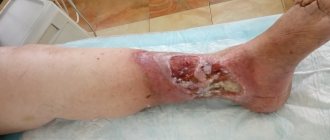
Due to the spread, the blood vessels constantly undergo changes, and the skin suffers serious damage. Due to blood stagnation, the required amount of fluid does not enter the skin cells. The skin becomes dry, thin and sensitive. In addition to fluid, oxygen and other nutrients do not reach the skin cells. This causes dehydration of the skin: it becomes pale in appearance, and even a gray tint may appear. These processes provoke rapid aging of the skin.
Couperous skin reacts sharply to any external influences, constantly itching and inflaming.
The clinical course is divided into 3 stages:
Stage I - redness in the cheeks, chin, wings of the nose and sometimes dry skin in these areas. The first stage is usually called erythrosis. It occurs after exposure to external provoking factors (cold, spicy or salty foods, washing with hard, cold or hot water, after a bath, etc.). Sometimes redness appears for no apparent reason. It causes increased sensitivity of the skin, a feeling of hot flashes, tingling, itching. Such sensations can last from several minutes to hours and spread to the neck and décolleté area.
Stage II is characterized by persistent redness of these areas of the face, the appearance of telangiectasia and a “mesh” of blood vessels, pigmentation.
Stage III is the stage of congestive dermatosis, in which the skin takes on a senile appearance. Pallor with a grayish tint, rosacea with areas of inflammation and infiltration (thickness), and a pustular rash develop. This stage can occur 20-30 years after the initial manifestations of the disease and requires more serious treatment.
Treatment methods
Sclerotherapy is a method in which a sclerosing agent is injected into the vessel, causing it to become sclerotic. It is effective for large veins, but it is difficult to use on microvessels. Sclerotherapy removes the entire dilated vessel, but results vary greatly depending on the skill and experience of the surgeon.
The combination of sclerotherapy and laser exposure is implemented as follows: first, a sclerosing agent is used, which blocks the vessels feeding the area of telangiectasia and/or the blood vessels with a diameter of more than 4 mm that drain from it, and then coagulation of small branches is performed using laser radiation.
Electrosurgery can be used as a treatment method. During this procedure, the tip of the device is guided along the entire length of the vessel, allowing electric current to coagulate the desired area. This method requires special training and is labor intensive if many telangiectasias need to be treated. Electrosurgery is contraindicated in patients with pacemakers.
Intense pulsed light ( IPL ) is used for non-invasive removal of thin superficial telangiectasias, Nd : YAG laser for removal of deep ones. In this case, it is important to take into account the patient’s skin phototype: the work of lasers and IPL is based on the absorption of light radiation by the blood of blood vessels, but this radiation is also indirectly absorbed by the melanin of the epidermis. Modern IPL devices have the ability to select the desired spectral range for any skin phototype.
There is data on the use of 800 nm and 980 nm diode lasers for the removal of telangiectasia on the face, with no undesirable effects recorded.
Questions from our users:
- treatment of telangiectasia on the face
- telangiectasia on the legs treatment
- telangiectasia symptoms
- treatment of telangiectasia with laser
Radio wave apparatus "Surgitron"
Elimination of vascular defects using the Surgitron apparatus is another method used by our specialists, non-contactly, using radio waves, to block blood flow in an enlarged vessel and allow the removal of medium and large venous spider veins on the face and body, eliminating the risk of scar tissue formation.
A wide selection of the most modern equipment allows medical doctors to choose a method for removing telangiectasias in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient, taking into account contraindications. Many years of experience of specialists allows us to eliminate telangiectasia, rosacea, port-wine stains, hemangiomas, and rosacea in more than 90% of cases without complications and restrictions in the usual lifestyle.
It must be remembered that rosacea and other vascular changes can be signs of a systemic disease of the body and progress with age. If you limit treatment to only removing a cosmetic defect, the vascular pattern may appear in another area. The sooner the patient turns to a specialist for comprehensive treatment of vascular pathology, the greater the chance of complete elimination of telangiectasia. Skin with fragile capillaries requires regular and careful care, selection of special cosmetic preparations (must contain vitamins, peptides, flavonoids and venotonics that restore connective tissue structures and improve microcirculation processes), supportive procedures, regular examination and correction of body conditions. Medical doctors provide all the necessary information at training seminars for our patients, as well as conduct facial skin diagnostics and share invaluable advice.
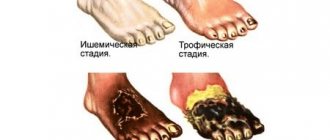
Telangiectasia (spider veins) of the lower extremities.
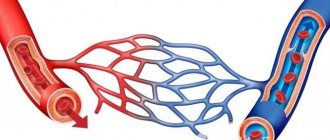
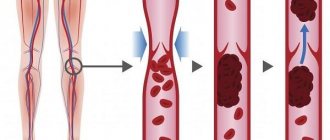
Telangiectasias of the lower extremities are dilated intradermal veins with a diameter of no more than 1 mm. Their formation, as a rule, indicates a chronic venous disease, the development of which is based on inflammatory processes and changes in venous outflow. The process of blood movement through the veins is ensured by cardiac and muscle contractions, and respiratory processes. At the same time, circulation to the lower extremities is easier than to the heart, so the help of valves is required. Venous valves open during heart contractions, blood flow moves to the heart area, and then close until the next contraction. This prevents backflow of blood in the veins. With chronic venous disease, the valves cannot cope with the load, cannot close tightly, and the blood flow is blocked, forming stagnation. Together with an increase in pressure inside the vessel, these processes lead to stretching of the thin walls of the venous vessels and deformation of the valve leaflets. Dilated vessels form a visible network, can be purple or blue, usually have a tree-like shape.
The main causes of the formation of venous telangiectasia are damage to the venous wall of the capillaries and valvular insufficiency. Additional factors leading to impaired venous outflow: excess weight, heart failure, professional activities associated with the body being in one position for a long time. For example, in people who, due to their profession, are forced to stand, the pressure in the veins of the lower extremities increases, the vessels are stretched and the risk of disease progression is inevitable. Provoking factors include a sedentary lifestyle and high-instep shoes that compress the foot. Muscle contractions during physical activity accelerate blood flow, the volume of blood in the veins decreases and pressure decreases, the outflow of lymph through the lymphatic system increases - these are necessary processes for the prevention and treatment of all disorders of the venous system.
A consultation with a phlebologist includes a clinical examination (detailed history taking, analysis of patient complaints, examination) and, if necessary, instrumental diagnostics. At the same time, the clinical class of the disease and the exact diagnosis are determined, methods of treatment of a certain type of chronic venous disease are discussed. To accurately assess the degree of pathology of the veins and arteries of the lower extremities, accurate diagnosis is necessary. Most often in his practice, a phlebologist uses duplex scanning (visualization of blood vessels, determination of blood flow) and Dopplerography as an additional method (determines the direction of blood flow in the vessels, its presence or absence in the main veins, assesses the condition of peripheral veins). More complex diagnostics are indicated for patients with trophic tissue changes and before surgery. Only after consultation and diagnosis does the doctor choose a method for removing venous telangiectasias. To achieve a high aesthetic result, several techniques are sometimes combined: laser technologies and sclerotherapy. The treatment regimen is supplemented by the prescription of pharmacotherapy and the mandatory selection of compression stockings.
Laser photocoagulation is indicated for the treatment of small-caliber vessels (up to 0.5 mm), and for the elimination of venous telangiectasias with a diameter of 1 mm, sclerostherapy shows a good cosmetic effect and elimination of the symptoms of the disease - the introduction under local anesthesia into the lumen of the vessel of a sclerosant in liquid or foam form, which leads to to gluing of its walls (vein fibrosis).
An arsenal of modern medications, sclerotherapy, laser and radio wave coagulation allow the phlebologist to treat vascular pathologies of the first and second clinical classes without resorting to radical methods.