Surgery to remove hemorrhoids is a radical treatment method for an unpleasant and difficult pathology.
Surgical intervention is intended for patients with chronic forms of dilatation of the rectal veins, as well as during their acute course.
Modern experts always recommend conservative treatment methods to patients, but if after this the patient does not experience improvement, then surgical removal of the nodes is urgently prescribed. When acute hemorrhoids develop, patients are always prescribed surgery.
The operation is prescribed as a last resort. First, doctors carry out all possible therapeutic measures - eliminate inflammatory processes and stabilize the patient’s condition. Only after this can a decision be made about the operation.
Briefly about the main thing
Excision of hemorrhoids is a traditional surgical operation, which is performed at such stages of the development of the disease when low-traumatic techniques are no longer indicated.
Traditional surgery is a serious procedure, which is characterized by a record low percentage of pathological recurrences. Doctors recommend removing pathological elements in a timely manner - this will completely restore health and prevent the development of numerous complications of hemorrhoids.
Surgical removal of nodes in City Clinical Hospital No. 31 is performed under anesthesia in a hospital setting. To guarantee the success of the operation, you should first cleanse the intestines and follow all the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period.
Postoperative period
The complexity of the rehabilitation period depends on the technique that was chosen to remove hemorrhoids, and, of course, on the general well-being of the patient. Almost all patients need to follow a special diet. It is strictly forbidden to consume foods that can burden the intestines. You should refrain from bowel movements for the first 24 hours.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
It is worth following all the recommendations of the proctologist. As a rule, after surgery, he prescribes thorough treatment of the wound with special preparations. To reduce pain, doctors prescribe nitroglycerin ointment and analgesics in the form of ointments, which are applied to the affected areas.
Unfortunately, patients may experience serious complications after surgery, so you should adhere to absolutely all recommendations.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids is necessary to establish the number and location of pathological elements, the presence of complications and concomitant diseases of the rectum.
Enlarged hemorrhoids are quite often combined with other pathologies: • anal fissure • proctitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the terminal intestine); • rectal polyps; • malignant tumor.
The necessary amount of information can be obtained using sigmoidoscopy. If there is a suspicion of damage to the overlying parts of the large intestine, a colonoscopy is performed.
If the proctologist decides on surgical intervention, all standard examinations will be needed: • general urine and blood tests, • coagulogram, • tests for blood-borne infections, • ECG, consultation with a therapist, anesthesiologist and gynecologist (for women).
Information about the disease
- Hemorrhoids are one of the most common human diseases. More than half of the population has symptoms. They usually develop after age 30.
- Most often, a person who discovers symptoms does not seek specialized medical help for a long time and tries to treat himself.
- Pregnant women often experience symptoms of this disease, but they usually go away after pregnancy. However, some women may develop chronic hemorrhoids. In case of exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids, specialized medical care is required.
- For any bleeding from the anus, it is very important to consult a specialist, since it can be caused not only by hemorrhoids, but also by other serious diseases.
- About half of the patients who visit a specialized medical facility to treat hemorrhoids have other diseases of the anorectal area, such as anal fissure, anal fimbria, or irritation of the perianal skin.
- Outpatient treatments are usually relatively painless.
- Only a small number of patients require surgical treatment of hemorrhoids; drug therapy and minimally invasive techniques are sufficient.
Types of surgical interventions
All types of surgical interventions for hemorrhoids can be divided into two large groups: minimally invasive (non-surgical) techniques and traditional operations to remove hemorrhoids.
Low-traumatic interventions are performed without the use of a surgical scalpel. The main mechanism of action of such techniques is the cessation of blood supply to the node. As a result, the pathological element decreases in size.
Low-traumatic methods include: • sclerotherapy (bonding of vessel surfaces under the influence of intravenously administered sclerotant); • ligation of the node with latex rings; • radio wave coagulation.
These methods are characterized by a short recovery period with minimal side effects. However, they are not suitable for everyone. In cases where minimally invasive techniques cannot be used, proctologists turn to surgical excision of hemorrhoids .
Prices for surgical removal of hemorrhoids
| Name of service | Price in rubles |
| Sclerotherapy of internal hemorrhoids (1 node) | 4500,00 |
| Separate ligation of internal hemorrhoids (1 node) | 4900,00 |
| Excision of external hemorrhoids or perianal fimbria 1 st. up to 0.5 cm | 1550,00 |
| Excision of external hemorrhoids or perianal fimbria 2 tbsp. up to 1 cm | 2750,00 |
| Excision of external hemorrhoids or perianal fimbria 3rd stage. over 1 cm | 4100,00 |
| Desarterization of internal hemorrhoids under Doppler control | 24800,00 |
| Desarterization of internal hemorrhoids under Doppler control with lifting | 29750,00 |
| Hemorrhoidectomy with corrugated suture (author's technique) | 34850,00 |
| Hemorrhoidectomy with corrugated suture, internal disarterization. hemorrhoids nodes under Doppler control with lifting (author’s technique) | 36800,00 |
| Sphincterometry | 1300,00 |
| Thrombectomy for acute thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid using the radio wave method up to 1 cm. | 3800,00 |
| Thrombectomy for acute thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid using the radio wave method over 1 cm. | 4800,00 |
| Removal of external thrombosed hemorrhoids up to 1 cm. | 4800,00 |
| Removal of external thrombosed hemorrhoids over 1 cm. | 5500,00 |
| Doppler "Angiodin-PK" (1 vascular bundle) | 1180,00 |
| Desarterization (1 vessel bundle) | 7450,00 |
| Mucopexy (1 node) | 3620,00 |
| Hemorrhoidectomy with corrugated suture (1 node) | 13280,00 |
Indications for traditional surgical methods
Surgical removal of chronically enlarged hemorrhoids is performed when minimally invasive techniques are technically difficult to implement or are doomed to failure due to the increased risk of relapse.
The most popular indications for excision with a scalpel: • Stage IV of the disease (nodes cannot be moved into the rectal cavity); • Stage III with large nodes (hemorrhoids can be reduced by hand in a warm bath); • a significant number of pathological elements; • presence of complications (necrosis, thrombosis, bleeding, etc.).
The decision to perform surgical excision is made on an individual basis. This takes into account the condition of the terminal intestine and adjacent organs, as well as the age and general health of the patient. To clarify all the data, it will be necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination.
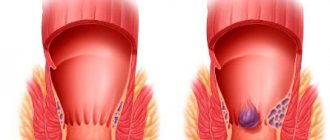
Stages of development of hemorrhoids
The first stage of hemorrhoid development is characterized by the formation of small internal hemorrhoids. They are almost invisible and are detected only during palpation (examination of the anus with fingers) or colonoscopy (examination with a special device). Symptoms include intermittent discomfort and constipation, which cause bleeding from the rectum.
During the second stage of hemorrhoids, the growth of the rectum continues, although the nodes have not yet fallen out. Discomfort during defecation increases; it also appears when sitting for a long time. At the third stage, the nodes increase to even larger sizes (2-3 cm in diameter). The rectum can fall out when lifting weights or simply under stress, but the body still has enough resources to independently return it to its place after exercise.
Finally, at the fourth stage of hemorrhoid development, the nodes no longer return to their original position. Traditional treatment with suppositories or other drugs is no longer effective here, since the tissues are very weakened. Often the last stage of hemorrhoids is accompanied by the formation of blood clots, which further complicates the life of patients. Treatment is carried out using various surgical methods.
Contraindications
• Surgery will have to be postponed for any acute illness or exacerbation of a chronic illness . • Severely obese are first advised to lose weight. • Hemorrhoids during pregnancy are treated conservatively, since there is a high probability of healing after the end of the child's feeding period. • Some relative contraindications may be: ___• blood clotting disorders; ___• colon oncology; ___• diabetes; ___• cirrhosis of the liver; ___• unstable angina; ___• recovery period after injuries, operations, etc.
Surgical intervention can be performed after stabilization of the condition and consultation with a medical specialist (cardiologist, endocrinologist, hematologist, hepatologist, etc.).
It must be remembered that only a doctor can assess the indications and contraindications and decide on the need for surgery. If you have questions about choosing a treatment method, be sure to consult a proctologist!
When is surgery indicated?
Hemorrhoids are a rather unpleasant disease that can haunt a person for years with constant relapses and steadily progressing. At the initial stage, the pathology is treated with conservative methods. These include the use of various gels, ointments and other products. Mandatory prevention of relapses is the establishment of regular soft stools, which is achieved through a diet rich in fiber. Hemorrhoid surgery is prescribed when conservative methods are ineffective and a person experiences characteristic symptoms that require surgical intervention.
If surgery is prescribed to remove hemorrhoids, each situation should be considered individually. This approach is used in the coloproctology department of the Yusupov Hospital. After an examination, the doctor determines whether surgery is necessary and what type of surgery will be most effective under the circumstances.
Surgery to remove hemorrhoids may be used if the following factors are present:
- The presence of external hemorrhoids, or their regular prolapse even at rest;
- There is constant bleeding, which can lead to anemia;
- The patient is predisposed to thrombosis;
- There is obvious progression of the disease, despite the therapy;
- Hemorrhoids cause severe discomfort, which is manifested by pain, itching, decreased performance, etc.;
- Conservative methods turned out to be ineffective.
In case of severe bleeding, it is initially stopped, which can be done with medication. And only after that they begin surgical operations.
Preparing for hemorrhoid excision
Diet
Diet is necessary to fully cleanse the intestines and prevent unwanted inflammatory reactions. Three days before surgery, foods that contribute to the formation of gases in the intestines, as well as dishes that can negatively affect stool are prohibited: • legumes; • cabbage; • fresh vegetables and fruits; • juices, mineral water, alcohol; • sweet dishes; • spices, marinades, pickles; • rice, semolina; • smoked products.
Liquid soups, dietary meat, fish, and mashed potatoes are recommended. The volume of fluid consumed is increased to 2 liters per day.
The last meal should be no later than 12 hours before surgery, and the last drink of water no later than 8 hours.
What to do
If you are going to undergo anesthesia, you need to visit a dentist . Sick and loose teeth should be removed.
During your consultation with the operating surgeon, you should talk about cases of drug intolerance. If you are forced to use any medications, be sure to tell your doctor.
Three days before surgery, you must stop taking any medications that affect blood clotting (ibuprofen, aspirin, birth control pills).
On the eve of the operation, the intestines are cleansed using a saline laxative such as Fortrans, which is taken at about four o’clock in the evening. It will be necessary to prepare a solution in accordance with the weight according to the formula specified in the instructions and drink one glass every fifteen minutes (3-4 hours). Bowel movements will begin a maximum of two hours after drinking the last glass of solution.
The procedure can be replaced by a double cleansing with an enema (in the evening and in the morning three hours before the operation) or a Microlax microenema.
Types of surgery
The option of removing internal and external hemorrhoids is associated with severe symptoms, the location and volume of inflamed lumps, and the nature of the pathology. The operation is performed to excise the affected nodes.
There are traditional and radical methods for surgically removing hemorrhoids:
- traditional: sclerotherapy, cryodestruction, use of laser, radio wave radiation, infrared coagulation, ligation, disarterization;
- radical: hemorrhoidectomy, hemorrhoidopexy.
Traditional methods
Features of the traditional method of removing hemorrhoids are the effect on inflamed nodules without the help of a surgical scalpel. The treatment method is effective in the first stages of development of the pathology, when internal varicose veins and weakness of the rectal vessels are not observed.
Minimally invasive techniques are performed without the use of anesthesia, which promotes rapid recovery of the body after the procedure.
The traditional method of removing hemorrhoids involves excision of the affected lumps with minimal damage to the inner lining of the rectum . Minimally invasive techniques are prescribed to older people, young children, and pregnant women who have restrictions on the administration of anesthesia. The operation time is no more than half an hour.
Sclerotherapy
Sclerosis is a method of surgery to remove affected hemorrhoids, which involves administering medication through an inflamed vein. The injection promotes the soldering of blood vessels, as a result of which new blood flow does not occur, therefore, the cones decrease in size.
- The best and most effective remedies for treating hemorrhoids
This method of minimally invasive treatment is not effective in removing external hemorrhoids.
Cryodestruction
Hemorrhoids can be removed by exposing the inflamed areas to liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which reaches -200°C. Freezing the lump will help it fall off on its own within a week.
The effectiveness of the procedure lies in the effect of cold liquid nitrogen on the epithelium, due to which there is an improvement in blood microcirculation, restoration of the immune system, and metabolic processes.
Laser coagulation
Laser therapy is prescribed to remove internal and external hemorrhoids. The method promotes protein coagulation in venous vessels due to the thermal effect on the problem area.
Traditional treatment allows the arteries to stick together, which prevents blood flow to the hemorrhoids. Loss of nodules along with feces is observed 14 days after the procedure, which lasts about a quarter of an hour.
Infrared coagulation
Removal of external and internal hemorrhoids is possible using infrared rays to coagulate the protein substance in the venous vessels. The number of procedures is prescribed according to the severity of the pathology and the size of the anal cones.
The effectiveness of coagulation is determined by the prolapse of nodes and stopping of anal bleeding during defecation.
Ligation
To remove the internal shape of hemorrhoids, a ligation method is used with the insertion of round latex devices. The peculiarity of the method is bending the base of the cones to interrupt blood circulation in the veins. The fallen internal node leaves the body along with the stool 14 days after the procedure.
Lack of ligation is a temporary sensation of a foreign object in the anus.
Desarterization
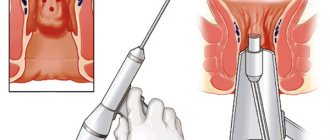
For hemorrhoidal cones to die, it is necessary to block the blood supply to the venous vessels of the rectum. The disarterization method involves inserting an anoscope into the anus to determine the exact location of the artery, which is the source of fluid flow to the nodule. Through the opening of the equipment, blood vessels are cut off with medical threads. Desarterization is effective in the second or third stages of rectal disease.
- Folk remedies for hemorrhoids in women
Minimally invasive methods of removal by excision of the hemorrhoidal node have negative consequences:
- pain;
- discharge of blood from the anus;
- formation of blood clots during removal of external hemorrhoids.
Pain is a recurring consequence of using traditional minimally invasive surgical treatment options for hemorrhoids. The sensitive skin of the anal epithelium becomes inflamed under the influence of latex rings or infrared radiation, causing spasms. Mild anal bleeding is observed with each removal procedure, except for laser coagulation and cryodestruction.
The negative consequence is caused by the passage of a dying hemorrhoidal nodule through the damaged area of the anus. Thrombophlebitis of clots is observed when the cones are incompletely removed when blood accumulates.
The disadvantages of using traditional methods include:
- relapse of the disease;
- cost of removal;
- lack of qualified specialists.
If there are restrictions on the implementation of minimally invasive therapy, there is no positive effect, or complications of the pathology are detected, surgical removal of hemorrhoids is prescribed.
Radical methods
Inflamed lumps should be removed in the last stages of pathology development, when the symptoms pose a threat to health.
Hemorrhoidectomy
Surgical intervention - excision of internal and external hemorrhoids of an open or closed type, which has clear advantages:
- suturing the postoperative wound of the skin after removal of hemorrhoids;
- use of local anesthesia;
- rapid recovery of the patient.
The open type of this surgical intervention involves performing the operation in a hospital ward without additional suturing of the wound, when a catheter is used for emptying. The recovery period takes more than a month for the independent healing of excised, inflamed hemorrhoidal cones and damaged mucous membranes.
There is a submucosal type of removal operation using the Parkes method. This type of intervention involves excision of only the inflamed node without removing the intestinal mucosa.
The hemorrhoidectomy operation is prescribed to remove nodes inside and outside and eliminate the cause of the first symptoms of the disease. The advantages of this type are the absence of possible relapse of the pathology.
- What are hemorrhoids, what does it look like and what treatment is needed?
But there are downsides to surgical removal of hemorrhoids using the Milligan-Morgan method:
- duration of surgical intervention;
- copious bleeding;
- pain during the rehabilitation period;
- use of general anesthesia;
- dangerous complications after hemorrhoidectomy;
- use of potent drugs;
- long-term recovery of the body;
- restrictions on the operation:
- malignant tumors;
- Crohn's syndrome;
- gestation, postpartum period.
Hemorrhoidopexy
Inflamed hemorrhoids of the anus can be removed using the Longo method, which involves transanal resection. It is not the hemorrhoids located inside the rectum that are subject to surgical removal, but the damaged mucous membrane located above the cones.
During surgery, equipment with a visual sensor is used to identify the artery through which the venous vessels are filled with blood. After cutting off the membrane of the anal tumor, it is pulled out and dried with staples, as a result of which it falls off.
The advantages of the method of removing blood clots from hemorrhoids using the Longo method are:
- use of local anesthesia;
- absence of anal blood discharge;
- The procedure takes no more than 20 minutes;
- performing surgery at any stage of hemorrhoid development;
- minimum list of contraindications;
- absence of pain during the recovery stage;
- short rehabilitation time – no more than 7 days;
- minimal risk of possible complications, as after hemorrhoidectomy;
- no stitches or scars on the wound.
The main disadvantages of the hemorrhoid removal method are the possibility of cutting off only internal hemorrhoidal cones, as well as the high cost of the operation.
Before surgery to remove hemorrhoids, additional preparatory measures should be taken:
- visual inspection;
- instrumental diagnostics;
- laboratory tests;
- purgation.
To determine the treatment option, the surgeon examines the patient, identifies disturbing symptoms, and identifies the nature of the course and severity of hemorrhoids. After visual contact, the patient is prescribed a medical examination, including tests and instrumental diagnostics.
Preparation for a dangerous removal operation involves the collection of biological materials to determine coagulability, platelet and red blood cell levels, establish the Rh factor, and identify infectious, colds, and viral diseases. Mandatory methods of instrumental diagnostics are anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy. These methods make it possible to determine the size, location of hemorrhoids, probable complications of the pathology to determine possible risk factors and contraindications to surgical intervention.
You need to prepare for the operation in advance. Before surgery to remove hemorrhoids, you should follow a diet to normalize the functioning of the intestinal tract in order to avoid constipation, diarrhea, and increased gas formation.
If swelling, swelling, or ulcerative tumors have formed in the anal area, they should be localized as much as possible with the help of medications. Before the operation, you should cleanse the intestines with a microenema or rectal suppository, and also refrain from eating and drinking 12 hours before the procedure if general anesthesia is used, and also shave the anal area.
How is hemorrhoidal excision performed?
Open hemorrhoidectomy
Open hemorrhoidectomy is the most “ancient” traditional operation, which was first performed in the 30s of the last century by proctologists Milligan and Morgan.
The Milligan-Morgan operation is performed under general anesthesia, less often under local anesthesia. The patient is positioned on the couch in a supine position, with the legs fixed on supports in an elevated position.
Hemorrhoidectomy is performed using a speculum and anoscope. The surgeon grabs the internal nodules and turns them out along with the surrounding tissue. The node is removed after cutting the skin and suturing the feeding vessel.
A characteristic feature of the method: the surfaces of the wound are not sutured - hence the name “open hemorrhoidectomy”. After the operation is completed, the surgeon installs a tampon with an antiseptic and a wound healing agent.
The patient remains in the hospital for 5-7 days. Stool softeners and healing tablets are prescribed.
Closed hemorrhoidectomy
Closed hemorrhoidectomy is a modified Milligan-Morgan operation, first performed in the middle of the last century by surgeon Ferguson.
Ferguson surgery can be performed under general or local anesthesia. When the anesthetic relaxes the anal sphincter, the surgeon inserts an anal speculum there. Subsequently, closed hemorrhoidectomy in general terms repeats the Milligan-Morgan technique: the vascular base of the hemorrhoid is sutured and bandaged.
Then the knot is removed, and the wound surface is sutured with catgut thread, which subsequently resolves. The average length of hospital stay after a Ferguson hemorrhoidectomy is 5 days.
In the postoperative period, painkillers and mild laxatives are prescribed. There is no need to remove the sutures, since the thread will dissolve on its own.
Parkes' operation
Another modification of the Milligan-Morgan operation was proposed in the middle of the last century by the English proctologist Parks.
Surgery is performed under anesthesia. The patient lies on his back with his limbs apart. The surgeon dissects the mucous membrane located above the nodule, a ligature is applied to the base of the nodule and stitched with thread.
Then the pathological element is removed, the thread is pulled, and the edges of the mucous membrane are sewn together. Thus, Parks' hemorrhoidectomy is a kind of plastic surgery.
Upon completion of the intervention, a tampon with medicinal substances is inserted into the anus. To prevent sphincter spasm, mechanical dilatation of the anus is used.
After a Parkes hemorrhoidectomy, the patient must fast to delay bowel movements, which threaten the sutures. Subsequently, a gentle diet is indicated to ensure timely soft stools.
Advantages and disadvantages of the Milligan-Morgan, Ferguson and Parkes methods
With the Milligan-Morgan, Ferguson and Parkes operations, both internal and external hemorrhoids can be removed.
The advantage of open hemorrhoidectomy is a high percentage of complete healing (relapses occur in only 2% of cases), and the main disadvantage is a very painful and rather long recovery period.
Closed hemorrhoidectomy is characterized by less pain and a shorter recovery period. However, there are also disadvantages: the sutures may come apart during bowel movements, as well as suppuration of the wound.
The Parkes operation is characterized by a short recovery period and minimal risk of complications. However, the technique is considered more difficult for the operating doctor.
It must be remembered that only a doctor can decide on the choice of treatment method.
Rehabilitation period
After the surgeon has performed the operation and the hemorrhoids have been removed, the patient will need to undergo a recovery course. At the Yusupov Hospital, a rehabilitation plan is drawn up for each patient, which will need to be followed both in the hospital and at home.
For the speedy healing of wounds, various creams, ointments and gels are used, and the pain syndrome is relieved with painkillers. The most important action during the recovery period and to prevent relapses is to normalize nutrition. A healthy diet helps regulate bowel movements, preventing constipation (one of the causes of hemorrhoids). The Yusupov Hospital employs professional nutritionists who will draw up a balanced nutrition plan that will help normalize the functioning of the intestines and the whole body.
Possible side effects and complications
Pain syndrome
Pain is an unpleasant side effect of any surgery, so after surgery your doctor will prescribe painkillers. They should be taken in the dose prescribed by the doctor.
It should be remembered that pain is the body’s watchdog, reporting danger. Be sure to tell your doctor if: • pain is not relieved by standard means; • pain changes its character (becomes throbbing, radiating, etc.); • pain syndrome is accompanied by other symptoms of ill health (weakness, headache, increased body temperature).
A change in the nature of the pain syndrome, an increase in pain intensity and the appearance of additional symptoms may indicate the development of complications.
Infectious and inflammatory processes
The most common complication of surgical interventions is wound infection with subsequent suppuration. This development of events is facilitated by both the presence of a wound and a decrease in immunity after surgery (any intervention is stress for the body).
When excision of hemorrhoids, the situation is aggravated by the fact that the wound surface is located in the rectum populated with microbes, through which feces filled with bacteria pass in transit.
The development of an infectious-inflammatory process can lead to the formation of an abscess (ulcer), intoxication due to the entry of microorganism toxins into the blood, or even sepsis (blood poisoning).
To prevent the development of infection, doctors regularly clean the postoperative wound and prescribe antibiotics orally or intramuscularly. If an abscess occurs, it is opened surgically.
Seam divergence
Suture dehiscence most often develops as a result of injury to a postoperative wound by hard feces. Prevention of such complications consists of a special diet.
According to indications, doctors may recommend abstaining from food for some time in order to delay the first bowel movement. Another precaution is stool softening medications.
This complication most often occurs in the early postoperative period. Depending on the specific situation, the problem can be solved with surgical intervention or conservatively.
Dehiscence of sutures is fraught with the addition of an infectious process and/or the development of other rarer complications.
Retention of feces and urine
Postoperative urinary retention, as a rule, is of a reflex nature. This complication develops predominantly in men. In such cases, doctors use a catheter to empty the bladder in a timely manner. Subsequently, urine passage is completely restored.
Habitual fecal retention may result from the patient's fear of pain during bowel movements. Cases of chronic constipation and even “psychological” intestinal obstruction have been described. This complication can be easily treated with “mild” laxatives.
However, it should be borne in mind that fecal retention after surgery is a symptom of many dangerous complications. Therefore, if you are prone to constipation, you should seek help from a doctor.
Other complications
Complications during excision of hemorrhoids are rare. Some pathologies, as a rule, develop against the background of an infectious-inflammatory process, suture dehiscence or other complications.
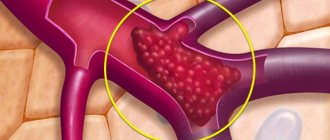
Relatively rarely, after surgery to remove hemorrhoids, the following occur: • rectal fistulas (abnormal communications between the rectum and another organ and/or the surface of the perineum); • thrombotic complications (thrombosis or thrombophlebitis of the inferior vena cava); • bleeding; • thromboemboria (blockage of the main arteries due to a detached blood clot); • narrowing of the anal canal.
All described pathologies are treatable. For fistulas and bleeding, surgery will be necessary, and narrowing of the anal canal is often treated with mechanical stretching.
Be sure to tell your doctor if swelling suddenly appears - this may be a symptom of thrombophlebitis of the inferior vena cava. This complication requires emergency measures.
To protect yourself from complications during surgery, it is enough to follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Where to have the operation?
First of all, you need to know that the appointment for a serious procedure is given by a doctor. The operation is a solution to a long and painful problem.
You can make an appointment with a doctor at our family clinic. We successfully treat hemorrhoids at all stages. Patients note discomfort during the procedure and a difficult postoperative period, but subsequently they get rid of pain in the rectal area. In our clinic, surgery is prescribed only in extreme cases, if previous treatment does not bring the desired result. Preparation is carried out in compliance with all the necessary requirements, and after its completion, patients receive detailed instructions on wound care and recommendations on proper nutrition.
Recovery period
Depending on the surgical method, the patient may remain in the hospital for 3 to 7 days. In some cases of closed hemorrhoidectomy, discharge from the hospital is possible after the doctor makes sure that urine flows freely. Further treatment is carried out at home under the supervision of a doctor until complete recovery.
The rehabilitation period includes a protective regime and an intestinal-friendly diet. In the first days after surgery, you should not be in a sitting position, and heavy physical activity is also prohibited. You should avoid rough, spicy, salty foods and alcohol.
For the speedy healing of a postoperative wound, it is necessary to strictly follow the rules of hygiene (washing after each bowel movement), as well as use all local medications recommended by the doctor (ointments and suppositories).
An important condition for preventing complications is normalizing stool. Bowel movements should be regular, preferably daily. If necessary, use mild laxatives.
Features of surgical removal of hemorrhoids
Traditional “closed” hemorrhoid surgery involves complete resection of the cavernous tissue with a scalpel. The three large blood vessels that supply it are first ligated. Then the surgeon cuts off the inflamed node, after which he performs plastic surgery of the rectal canal shell (applies sutures). This allows you to secure its walls and prevent unwanted relapses. This type of intervention can be used in an outpatient setting.
With an open technique, the doctor, after cutting off the affected area and surrounding mucosa, leaves the wound without suturing. It then heals on its own. To prevent subsequent bleeding, cauterization of the vessels is performed using a biopolar coagulator. The choice of an open method is justified in the presence of severe complications (identification of fissures and paraproctitis).
Submucosal hemorrhoidectomy according to Prax is difficult to perform. The surgeon excises the node itself, but preserves the membrane covering it. Because of this, the recovery period is noticeably shortened.
The choice of classical methods has its positive and negative sides. With the help of them today, thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node is removed and a long-term process of remission is achieved. Complications and relapses are extremely rare.
Traditional surgical methods are used when it is necessary to immediately remove two or three pathological formations. To carry them out, it is necessary to use anesthesia, and then carry out anesthesia and bandages. Rehabilitation is taking longer. It is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, the patient remains in the surgical hospital all the time.
Is it possible to postpone surgery to remove hemorrhoids?
Excision of hemorrhoids is a planned intervention , which is performed at a time convenient for the patient. However, surgical treatment should not be delayed for a long time.
With a long course of chronic hemorrhoids, the following complications may develop: • bleeding with the development of chronic anemia; • thrombosis and/or gangrene of the node; • infectious and inflammatory processes; • exhaustion of the body; • anal fissure; • colon polyps, etc.
The development of complications means longer, more painful and more expensive treatment. Take care of yourself and your loved ones, do not try to “heal” with folk remedies, contact a proctologist in a timely manner.
Preparatory and operational period
Before the operation, the patient must fulfill certain conditions, namely: pass all the necessary tests, undergo a diagnosis of concomitant pathologies, and undergo a consultation with a therapist to determine possible contraindications.
The preparatory stage consists of complete bowel movement. Cleansing is carried out on the eve of the operation and immediately before the procedure itself.
A similar procedure is carried out using an enema and laxative medications. It is also worth paying special attention to nutrition in order to normalize all functions of the intestine and its walls. It is necessary to restore normal stool. This is a mandatory condition, since constipation during removal of hemorrhoids can cause serious complications. Let us remember that constant constipation is the first step to the development of hemorrhoids.
Before surgery, it is very important to relieve the inflammatory process in the anus, if it is present, of course. It is also worth relieving irritation and swelling. This can be done with the help of medications and traditional medicine.
Features of the rehabilitation period
On the first day, a diet is prescribed, including gentle, soft foods and products that thin the stool. This is necessary to minimize damage to unhealed wounds of the anal canal. If necessary, symptomatic treatment is prescribed - decongestants, painkillers.
In the first few days after the intervention, slight sanguineous rectal discharge is observed; this is normal; it goes away on its own as the wound heals. The maximum pain syndrome is observed on the first day, but it is easily relieved with analgesics prescribed by the doctor. During the recovery period it is recommended:
- follow a diet;
- reduce physical activity, but physical inactivity is not recommended;
- do not take blood thinning medications;
- come regularly for examinations with a proctologist.
Full recovery takes 3–6 weeks, depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the scope of the intervention. You can get information about the operation and the rehabilitation period by making an appointment with a coloproctologist online or by phone.
Why surgery is needed
As a rule, surgical intervention is necessary for stage 3 and 4 hemorrhoids if conservative therapy is ineffective. When enlarged dense nodes fall out even with the slightest load, they are poorly adjusted or not adjusted at all, causing severe suffering to the person. Hemorrhoidectomy has a high success rate (98% or more), and relapses are kept to a minimum.
Unfortunately, pathologically enlarged hemorrhoids up to 3–4 cm will not disappear on their own. If in the initial stage the disease can still be stopped with the help of a balanced diet and an active lifestyle, then as the disease worsens, such methods do not provide a therapeutic result. Drug therapy is also temporary - with pronounced internal and external foci of the disease, it can eliminate symptoms, relieve swelling, pain and inflammation, but cannot cope with hemorrhoids. The disease can be completely eliminated only surgically - by eliminating the cause itself. And our surgeons can help with this by performing hemorrhoidectomy quickly and with minimal trauma to the patient.
Advantages of surgery at GMS Hospital
In Moscow, specialists at our clinic use the latest methods of conservative and surgical treatment of the disease. Our department of surgical proctology has a modern operating unit and a comfortable hospital for hemorrhoidectomy and recovery after surgery. Advantages of hemorrhoid removal in our clinic:
- experienced coloproctologist surgeons of the highest category;
- the whole procedure takes 30–40 minutes;
- the use of modern microsurgical technologies reduces the time spent in hospital to 1 day, and sometimes makes it possible to avoid hospitalization;
- minimal trauma to surrounding tissues;
- minimum postoperative complications;
- moderate pain syndrome;
- minimal risk of disease relapse;
- fast recovery.
The use of a low-traumatic hemorrhoidectomy method ensures rapid wound healing and a speedy return to normal life.