Mildronate is a metabolic agent based on meldonium, which has angioprotective, cardioprotective, antianginal and antihypoxic effects. The drug helps activate the compensatory capabilities of the cardiovascular system, significantly increasing its functional readiness. Available in capsules and tablets of 250 mg, 500 mg, as well as in the form of a solution for parenteral (intramuscular, intravenous and parabulbar) administration of 100 mg/ml.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacodynamics
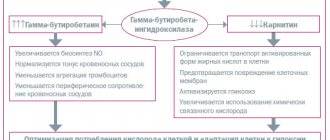
Meldonium in its chemical structure is an analogue of gamma-butyrobetaine, which acts as a precursor for the synthesis of carnitine in the body. It inhibits the action of the enzyme gamma-butyrobetaine hydroxylase, which reduces the synthesis of carnitine molecules and eliminates the active transport of fatty acids into the cell. Thus, it prevents the accumulation of active forms of under-oxidized forms of fatty acids, which are one of the main agents that can damage cell membranes. This is due to the cytoprotective effect of the drug Mildronate.
In conditions of oxygen starvation of cells that develop during physical activity, meldonium maintains the exchange of oxygen in the cell in balance, balancing its delivery and consumption in the cells. It also prevents disruption of the transport of the main energy molecule ATP to target organs and activates anaerobic glycolysis.
Thus, by influencing the basic components of the metabolism of oxygen, fatty acids and ATP, Mildronate provides vasodilation, angioprotection, and a cardioprotective effect. In conditions of ischemic infarction, the drug significantly slows down the spread of the necrosis zone, and during physical activity it maintains the delivery of a sufficient amount of oxygen, increasing exercise tolerance. Tones the central nervous system, prevents mental exhaustion, and when applied topically, eliminates dystrophic changes in blood vessels.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered orally, Mildronate is effectively absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Capsules allow the drug to bypass the aggressive environment of the stomach and enter the intestines, where absorption is fastest. The bioavailability of the drug reaches 78%, and the maximum concentration in plasma is observed 1.5–2 hours after use.
From the systemic bloodstream, meldonium enters the tissues. It has been established that meldonium metabolites penetrate the blood-placental barrier and are also found in breast milk. The protein binding coefficient is 61.7%. Most of the metabolism of the substance occurs in the liver, and excretion is carried out by the kidneys. The half-life of the drug is 4 hours.
Release form
The drug Mildronate is produced by the manufacturer in the form:
- clear colorless solution for injection;
- hard gelatin capsules No. 1 and No. 2, filled with hygroscopic white crystalline powder. The powder contained in the capsules has a weak characteristic odor and a sweetish taste (the capsule itself has a neutral taste);
- tablets Mildronate Gx 500 mg (tablet taste slightly sour).
The solution is sold in 5 ml ampoules (500 mg/5 ml). One cardboard package contains: 2 blister packs with 5 ampoules of Mildronate in each and instructions for use of the drug.
Capsules are packaged in blisters of 10 pieces each. One cardboard box contains 4 blisters and instructions for use of the drug.
Indications for use of Mildronate
Mildronate is used to maintain cardiac muscle tone in chronic heart failure, cardiomyopathies of any origin, in the treatment of coronary heart disease, heart attack, and angina attacks. It is also used for the treatment of cerebral blood flow disorders, strokes and transient ischemic attacks. In ophthalmological practice it is used for hemophthalmia, dystrophic changes in the blood vessels of the eye, and retinopathy of vascular origin. Reduced performance, chronic fatigue, physical activity in athletes, depletion of the central nervous system due to mental stress are relative indications for the use of Mildronate. Also used to reduce withdrawal symptoms in alcoholism and hangovers.
For the treatment of cardiomyopathy, 500 mg/day orally is prescribed for a course of 12 days.
Chronic heart failure, coronary heart disease, angina attacks and heart attacks, which are accompanied by contractility disorders and bradycardia, suggest the appointment of Mildronate for oral use at 500 mg/day, the dose is divided into two doses. The course of treatment can last 4–6 weeks.
For cerebral circulation disorders, a dose of 500 mg/day is indicated for 4–6 weeks.
To relieve withdrawal symptoms and in case of severe hangover, 4 oral doses of Mildronate are prescribed at a dose of 500 mg/dose. The course of treatment can last up to 7 to 10 days. A loading dose quickly eliminates the symptoms of alcohol intoxication.
In case of a pronounced decrease in performance, physical overstrain and exhaustion of the central nervous system, 500 mg of the drug is prescribed 2 times a day for 1–2 weeks.
To increase energy supply before training and for weight loss, athletes are prescribed 500 mg 1-2 times a day for 14-21 days. However, you should be careful, because meldonium can give a positive result in a doping test.
Injection forms of the drug can be used for intravenous, intramuscular, and parabulbar administration. The injection should be given in the first half of the day, given the stimulating effect of Mildronate.
In case of myocardial infarction, intravenous bolus administration of 0.5–1 g of the substance per day (5–10 ml of the drug, respectively) is recommended. For coronary heart disease, angina attacks, cardiomyopathy and chronic heart failure, 0.5–1 g is prescribed intravenously or 2 injections of 0.5 g intramuscularly. The course of treatment lasts up to 14 days, after which the patient should be transferred to oral forms, the course of which will last 4–6 months.
For hemophthalmia, dystrophic changes in the vessels of the eye, retinopathy of vascular origin, 0.05 g of the substance (which corresponds to 0.5 ml of Mildronate) is administered parabulbarly for a course of 10 days.
Repeated courses for the prevention of the underlying disease can be carried out for any form of the drug 2-3 times a year, but only based on medical indications according to the recommendations of the attending physician. It is not recommended to prescribe the drug independently for heart rhythm disturbances, surges in blood pressure, for the purpose of stimulation or achieving an immunomodulatory effect (for colds, acute respiratory viral infections).
Use by athletes
The widespread use of Mildronate by athletes is due to:
- increased endurance due to the transfer of muscle fibers to more economical ways of using energy;
- improvement of metabolism and uniform formation of the muscle frame (relevant for bodybuilders);
- accelerating recovery after physical activity or injury.
Application regimen: 500-1000 mg/day before training for 21 days of the preparatory period and 10-14 days during competitions.
In 2021, the International Anti-Doping Committee banned the use of Mildronate by athletes.
Contraindications for use
- age under 18 years (based on the lack of data from isolated clinical studies on the tolerability of Mildronate in patients under the age of 18);
- hypersensitivity to meldonium or other components that are part of the drug, episodes of anaphylactic reactions or other allergic reactions (itching, swelling, hyperthermia) in the anamnesis;
- increased intracranial pressure caused by impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, impaired venous outflow (in the presence of an obstructed vessel or intracranial tumor);
- end-stage liver and kidney failure: the drug will not be able to undergo transformation in these organs, so conversion and elimination will be impaired and toxicity will increase;
- pregnancy;
- period of lactation and breastfeeding.
Compound
- One hard gelatin capsule of Mildronate contains 250 or 500 mg of meldonium in the form of dihydrate as an active component and excipients: potato starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, calcium stearate. Gelatin and titanium dioxide are used to make the gelatin shell.
- One Mildronate tablet contains 500 mg of meldonium in the form of phosphate and auxiliary components: mannitol E421, povidone K-29/32, potato starch, silicon dioxide, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate.
- One milliliter of Mildronate injection solution contains 100 mg of meldonium and water for injection as an auxiliary component.
Side effects
Side effects of the drug are classified by frequency of occurrence based on reports of adverse reactions and reviews received in the post-marketing period as follows: very common (1 case in 10), common (1 case in 100); uncommon (1 in 1000), rare (1 in 10,000), very rare (less than 1 in 10,000), unknown (no exact data on the frequency of occurrence). Mildronate is characterized by:
- From the immune system: rarely - allergic reactions, allergic dermatitis, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylactic reactions, shock.
- From the nervous system: often - headache; rarely - changes in sensitivity, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, tremor, tinnitus, dizziness, fainting.
- From the mental side: rarely - psychomotor agitation, unreasonable fear, panic attacks, sleep disturbances.
- From the respiratory system: often - infectious diseases of the respiratory tract, decreased local immunity of the respiratory system; rarely - cryptogenic cough, dyspnea, apnea.
- From the cardiovascular system: rarely - hypertension, hypotension, hypertensive crisis, hyperemia or pallor of the skin, changes in the contractility of the heart, arrhythmia, palpitations, sinus tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, a feeling of discomfort or heaviness in the chest and in the area of the projection of the heart behind sternum, chest pain.
- From the gastrointestinal tract: often - dyspeptic manifestations; rarely - loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dry mouth, hypersalivation.
- From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: rarely - rash, itching, dermatitis, papules.
- From the musculoskeletal system: rarely - myalgia, muscle weakness.
- From the kidneys: rarely - pollakiuria.
- General reactions: rarely - swelling, sensations of heat or cold, weakness, asthenic manifestations.
- Changes in laboratory parameters: often - increased levels of C-reactive peptide, dyslipidemia; rarely - eosinophilia, increased wave voltage on the ECG.
Overdose
Subject to the conditions of use, Mildronate does not exhibit toxic properties to specific organs and systems. There have been no documented cases of meldonium overdose resulting in severe consequences.
If the therapeutic dosage is exceeded for hypotension, the following symptoms can be expected: headache, dizziness, general malaise, severe tachycardia, instability of blood pressure.
There is no specific antidote; in case of overdose, symptomatic treatment is carried out aimed at relieving pathological manifestations. In case of severe overdose, strict control of the function of the kidneys and liver is necessary as the organs that interact with the drug the most.
Hemodialysis is not effective in case of an overdose of Mildronate due to the high binding coefficient to blood proteins.
"Mildronat" for a long term without a doctor's prescription: dangerous or not?
Metabolic drugs are one of the components of complex therapy for neurological and cardiovascular diseases (sometimes during the recovery process in oncology, surgery and traumatology). The peculiarity of the use of drugs in this group is a wide range of dose-dependent effects on various organs of the body, therefore a specific amount is selected for each patient in a short course (maximum 6 weeks).
Uncontrolled use of Mildronate is accompanied by the risk of:
- development of arrhythmias;
- formation of cardiomyopathy (due to restructuring of the heart muscle);
- drop in blood pressure;
- violations of the excretory function of the liver and kidneys.
If it is necessary to take the drug for a long time (according to indications), it is recommended to take 30-day breaks every 2 weeks.
Interaction
Due to its profound effect, meldonium often enhances the effect of drugs that are its agonists in terms of the expected effect and mechanism of action. Thus, by combining drugs, greater progress can be made in the treatment of pathology.
Mildronate enhances the effect of drugs that have angioprotective, antianginal, drugs, cardiotonics, cardiac glycosides. It prolongs the time of their active action, makes the rise and fall of the effect smoother. It is recommended to use Mildronate simultaneously with drugs that improve circulation in the microcapillary bed.
Mildronate significantly enhances the effect of vasodilators, antihypertensive drugs, in particular beta-blockers. With an increase in the therapeutic dosage of the drug meldonium, bradycardia may develop when combined with beta-adrenergic receptor blockers (Concor, Nebivolol).
The simultaneous use of Mildronate and Mexidol leads to mutual potentiation, the membrane protective effect of Mexidol is enhanced, it acquires a pronounced antihypoxic agent, increasing the endurance of the body as a whole and cells in particular under conditions of ischemia. Nonspecific actions of Mexidol are antiepileptic and nootropic effects, which are also enhanced when Mildronate is used.
Actovegin and Mildronate are compatible and are agonists in relation to the antihypoxic effect. These drugs in combination help maintain the integrity of the cell membrane and cell function under conditions of acute oxygen starvation. This action is most relevant in the context of myocardial infarction, to reduce the size of the area of necrosis.
Meldonium promotes better absorption of microelements by the target organ, which is used in cardiology when prescribing Panangin, Asparkam simultaneously with it. This ensures the restoration of electrolyte balance, and therefore the heart rate.
Mildronate, in addition to its effect on striated muscles and energy metabolism, also has the property of improving brain microcirculation, which is why it is used for central nervous system overstrain and chronic fatigue syndrome. Mildronate is compatible with nootropics and enhances their effect, so it can be taken with Glycine, Piracetam, Noopept, and ginkgo biloba preparations. Similar compatibility is observed with drugs that are used to restore cerebral circulation - Phezam, Cytoflavin.
Meldonium can be combined with drugs that have antiplatelet and anticoagulant effects for effective prevention of thrombosis. The medicine is compatible with Cardiomagnyl and acetylsalicylic acid.
Separately, Mildronate’s ability to potentiate the effect of psychotropic substances, in particular antiphobic drugs and anxiolytics, will highlight. The simultaneous use of meldonium with Afobazol, Phenibut, Grandexin is possible.
The use of Mildronate and caffeine is not recommended due to unexpected changes in blood pressure that these drugs together may cause.
conclusions
Mildronate is a widely prescribed drug in the complex treatment of cardiovascular and neurological pathologies. The effectiveness of the drug is explained by its effect on metabolism in cardiomyocytes, rehabilitation after “disasters” and prevention of complications. The use of Mildronate by athletes improves endurance and strength, speed of recovery without the side effects characteristic of anabolic steroids. The drug should be used only after consulting a doctor, according to the instructions and dosage regimen.
Analogues of Mildronate
Analogs of a drug based on meldonium are medicines that also contain meldonium as the main active ingredient and are its derivatives (generics) or have a similar effect. But they are not completely similar to Mildronate. Medicines differ not only in price, but also in indications for use, and in greater or lesser intensity of the effect for individual therapeutic purposes.
Which is better: Mildronate or Cardionate?
Cardionate contains the same active ingredient as Mildronate - meldonium. The dosages and indications for use of this drug are the same, but Mildronate in this case is more affordable, and Cardionate has a more complex composition, and therefore a higher chance of developing allergic reactions and unwanted interactions with other drugs.
Which is better: Mildronate or Idrinol?
This drug continues the list of those developed on the basis of meldonium. It is distinguished by its convenient capsule form, otherwise the doses and indications are similar to Mildronate, and the price is sometimes significantly higher than its price. Idrinol is not the drug of choice for maintenance treatment of cardiac pathology and cerebrovascular accidents.
Which is better: Mildronate or Mexidol?
Mexidol is based on the active ingredient ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate. Unlike meldonium, this substance also has a nootropic and antioxidant effect - it protects membranes from active free radicals that are formed in cells. A wide range of effects includes stabilization and protection of membranes, normalization of microcirculation, and relief of mental stress. However, this drug does not have an evidence base and does not undergo the most serious studies, unlike Mildronate.
Which is better: Mildronate or Meldonium?
It is obvious that Mildronate as a drug that has been patented and put on the market will be as effective as the pure active ingredient - meldonium. The only difference is that meldonium is more accessible.
Which is better: Mildronate or Riboxin?
Riboxin contains inosine, which is an angioprotector, anabolic and antiarrhythmic agent. It significantly affects energy metabolism, in particular the synthesis and use of ATP. Its indications for use are somewhat broader than those of Mildronate: Riboxin is also used for the treatment of myocarditis, liver diseases, for the prevention of leukopenia, and for glaucoma. But it is contraindicated in patients with disorders of purine metabolism, with gout, which precludes its use for a whole group of patients.
Which is better: Mildronate or Trimetazidine?
This medicine is used exclusively in therapy and cardiology, because it acts selectively on the heart and blood vessels. Trimetazidine improves the energy and oxygen supply of the heart muscle, increases resistance to hypoxia, and prevents the death of cells that are in an intermediate state between life and necrosis - in parabiosis. However, for systemic use, relieving mental stress, and treating cerebral blood flow disorders, Mildronate is better suited, and Trimetazidine is better suited for the heart.
Which is better: Mildronate or Preductal?
Preductal is based on the above-described trimetazidine, and all the properties are characteristic of this drug. But there is a feature that concerns Preductal and its use in otorhinolaryngology - the drug helps compensate for dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus: it reduces the severity of dizziness, tinnitus, and hearing impairment. In other areas, the use of Mildronate is more appropriate.
Which is better: Mildronate or Panangin?
Panangin contains a balanced ratio of potassium and magnesium, which are widely used in cardiological practice. This is necessary to normalize electrolyte balance and proper heart function. But Panangin alone cannot provide the therapeutic effect that is expected from taking a real cardioprotector. However, the simultaneous use of Mildronate and Panangin solves the problem and allows one to achieve results in the treatment of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.
Which is better: Mildronate or Elcar?
Elkar contains levocarnitine (L-carnitine), which is one of the main metabolites in the work of skeletal muscles. It is used for a lack of levocarnitine in the body (normally it is synthesized endogenously in sufficient quantities) or for kidney diseases. It is used to restore balance after hemodialysis, for congenital enzymopathies, but has no metabolic effect. Mildronate performs much better in this regard.
Which is better: Mildronate or Actovegin?
Actovegin has pronounced neuroprotective, metabolic and microcirculatory effects. It is used for recovery after acute cerebrovascular accidents and is even more effective for this purpose than Mildronate. The medicine also improves the metabolism of glucose, oxygen, and maintains the energy supply of cells. But due to its composition (it is made from physiological material - calf blood), it may be intolerable to some patients, and the scope of application of the drug outside of neurology and neurosurgery is narrow.
Which is better: Mildronate or Cytoflavin?
Cytoflavin contains inosine and succinic acid. Inosine is very similar to meldonium in its metabolic action, but differs in mechanism. Succinic acid reduces tissue hypoxia and normalizes metabolism and energy metabolism. Mildronate has a much more pronounced and reasonable effect.
special instructions
Due to the fact that the drug can provoke a stimulating effect, it is recommended to use it in the first half of the day.
There are no data regarding the ability of Mildronate to change the reaction rate and influence transport control.
The drug is prescribed with caution to people with liver and/or kidney pathologies.
Experience in treating patients with myocardial infarction and unstable angina shows that the active substance Mildronate is not a first-line drug for ACS.
Alcohol compatibility
It is not recommended to take Mildronate during the acute phase of alcohol intoxication (alcohol intoxication), this can cause unpredictable interactions at the stage of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. The active substance meldonium undergoes all stages of transformation in the liver using enzyme systems and inhibits them during metabolism. This cross-folds the toxicity of both ethanol and meldonium due to its incomplete conversion.
Inhibition of the protective function of the liver in relation to meldonium and alcohol can lead to a pronounced hepatotoxic effect, increasing manifestations of alcoholic encephalopathy, and the accumulation of toxic breakdown products of ethanol.
It is possible to develop allergic reactions due to the simultaneous use of Mildronate and alcohol.
Use of Mildronate during pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy and lactation, as well as the period of breastfeeding, are absolute contraindications to the use of the drug Mildronate. Due to the distribution characteristics and high activity, metabolites perfectly penetrate from the systemic bloodstream into tissues, this ensures the effective effect of the drug on any target organ. But meldonium also penetrates the hematoplacental barrier and accumulates in the fetus.
There is no data on the effect of meldonium on the fetus, but the drug is not recommended for use under 18 years of age due to the development of adverse reactions. No teratogenic effect of meldonium on the embryo was detected, but the concentrations of the drug inside the placenta were higher than permissible. Changes in hemodynamics caused by meldonium can be difficult to tolerate by the body of a pregnant woman.
The drug also passes freely into breast milk in high concentrations and in the form of active forms, which can lead to unforeseen consequences for the baby. If there are vital indications for the use of Mildronate, breastfeeding should be stopped immediately.